Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 2S
Human Capital, Social Capital, Financial Strategy Performance, and Financial Sustainability
I Gede Cahyadi Putra, Udayana University
Ni Luh Putu Wiagustini, Udayana University
I Wayan Ramantha, Udayana University
Ida Bagus Panji Sedana, Udayana University
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of human capital and social capital on financial strategy performance and its impact on financial sustainability. The study population was 134 people's credit banks in Bali. The method of determining the sample using purposive sampling with a sample of 127 companies. Data analysis was performed using the SEM-PLS method. The results showed that human capital and social capital had a positive and significant effect on financial strategy performance. Human capital and social capital have no direct influence on financial sustainability, Good management of human capital and social capital within the company is able to create work harmony among employees and support a conducive work climate, which results in an increase in financial performance and ultimately has an impact on increasing financial sustainability.
Keywords
Human Capital, Social Capital, Financial Strategy Performance, Financial Sustainability
Introduction
This study aims to examine and analyze the effect of human capital and social capital on financial strategy performance and its impact on financial sustainability. This research was conducted at a Rural Bank operating in Bali. In accordance with government programs that continue to carry out community empowerment programs, especially through micro, small and medium enterprises. Community empowerment is an important aspect to improve community welfare. Community empowerment contains strategic value in overcoming poverty which is one indicator of the achievement of national development goals. The role of the government is not strong enough in poverty reduction efforts, so it requires strong cooperation and synergy from various forces, one of which is the People's Credit Bank. The role of BPR is very significant in optimizing the achievement of the goals of national development, both directly towards the business sector budget and in supporting activities that are concerned with the interests of the people. The development of the People's Credit Bank is in a dilemma, are at a difficult choice to run their business. If the owners and managers of rural credit banks choose one option to move forward, the bank's ability to compete must be improved. This is because financial intermediary is changing. Four years ago, the speed and flexibility that became the strengths of the people's credit banks could not competence.
Emphasis on human capital research, positions humans as the main component that most dominantly determines business success. Human capital as an intangible resource is a source of creativity, innovation and corporate strategy renewable. Nafziger & Terrel (2006) examined the influence of the human capital characteristics of company founders with indicators (education, business experience, age, area of origin and caste) on the long-term success opportunities of companies in India and found that companies founded by entrepreneurs who are older and coming from higher castes tend to have a greater chance of success. Maar's research (2007) states that human capital is needed for business continuity and success. Improving the quality of human resources by paying attention to the level of education, experience, interests and skills of employees (including managers) will produce professionals that have an impact on business sustainability.
Helmut, et al., (2006) stated that human capital is the knowledge and nature of individuals in carrying out work, such as intelligence, energy, job satisfaction, learning abilities, and creativity, motivation and collaboration skills. In human capital, there are collective strengths of employees including management which can provide a strong mechanism to ensure organizational success (Liebowitz, 2004). Collective wisdom can transform them into intellectual organizations, where the organization can become an agile and adaptive learning institution. The key to realizing intellectual organization can be human or human capital. Human capital is one of the important capitals for companies, because it is the source of dreams for companies.
The sustainability of the company is also inseparable from the social capital that exists in the company. The role of social capital influences the development of business units to achieve success (Chan, 2009). The social capital model developed by (Johnson et al., 2002) stated that functionally social capital is to facilitate the achievement of business objectives in obtaining the necessary information through a network of personal contacts that have been maintained by employers, reducing uncertainty and monitoring of transaction costs based on trust embedded in individuals and within the organization. Efforts and encouraging the creation of collective action between business organizations. Social capital is a force capable of building a civil community that can increase participative development.
Several studies have found different results regarding the effect of social capital on corporate financial performance. Research conducted by (Dar & Mishra, 2020) found that social capital provide a significant impact on the increase in company performance. (Ofori & Sackey, 2010; Liu, 2017; Agyapong et al., 2017) show that social capital can improve organizational performance. Meanwhile, research conducted by (Sulastri, 2005; Meflinda et al., 2018; Akintimehin et al., 2019) concluded that social capital has no influence on company performance.
Literature Review
The Resource Based View Theory
RBV is very appropriate to explain research on human capital, especially in the context of the relationship between human capital and corporate financial performance. Companies have unique knowledge, skills, values and solutions (intangible resources) that can be transformed into value in the market. Management of intangible resources can assist companies in achieving competitive advantage, increasing productivity and market value. Barney (1991) states that RBV is a thought that develops in strategic management and a company's competitive advantage, which believes that a company will achieve excellence if it has superior resources. Thus, based on the RBV theory, companies with rare and valuable assets will have a competitive advantage.
Financial Sustainability
Corporate sustainability is a business approach that creates long-term shareholder value by creating opportunities and managing risks arising from economic, environmental and social developments. Sustainable companies are able to achieve long-term shareholder value with strategy and management; they exploit the market and potential for sustainable products and services. Meanwhile, the company has also succeeded in reducing and avoiding the cost of sustainability and risk. Sustainability means the company's ability to increase its income stably (Adams et al., 2010). Sustainability is a measure of an organization's ability to fulfill its mission and serve stakeholders from time to time. Therefore it is important for a company to pay attention to the continuity of its business. Strong sustainability will enable the company to achieve above average profitability and increase shareholder wealth (Adams et al., 2010).
The Relationship between Human and Social Capital and Financial Strategy Performance
Research by Roca-Puig, et al., (2012); Clarke & Whiting (2011); Gates & Langevin, 2010) found that there is a positive relationship between human capital and company performance. Komnenic & Pokrajcic's (2012) research concluded that human capital increases company productivity and profits. The same result was also obtained by Al Amin (2012) who found that human capital has a positive effect on the company's financial performance. The results of research by Khan & Park (2020); Sheikh & Wepukhulu (2019); Xu et al., 2019; Xu & Li (2019) found that human capital is an important factor and has a positive effect on organizational performance. Based on the description above, the first hypothesis developed in this study is:
H1: Human capital has a positive effect on financial strategy performanc
Ofori & Sackey (2010) examined the effect of social capital on the performance of business organizations. Research by Farida (2016) found that social capital has a positive effect on market ability and marketing performance. Agyapong, et al., (2017) found that social capital has a positive effect on company performance. Lins, et al., (2017) proved empirically that the high level of corporate social capital has a positive effect on company performance. Research conducted by Dar & Mishra (2020) found that social capital has a significant impact on increasing company performance. Liu (2017) provides results that social capital can improve organizational performance. Based on the description above, the second hypothesis developed in this study is:
H2: Social capital has a positive effect on financial strategy performance.
The Relationship between Human Capital and Social Capital and Financial Sustainability
Edvinson & Malone (2007) state elements of creativity and innovation as a reflection of the human capital owned by an individual, the existence of creativity and innovation in the individual, the individual can have several characteristics, namely organizational flexibility, speed in decision making, the ability to read opportunities, dare to take risks and be consistent in dealing with uncertainty. In the context of business continuity, a company that has human resources is a key element in creating competitive advantage and increasing business sustainability. Research conducted by Naz, et al., (2019) which examined cooperatives in Kenya concluded that human capital is positively related to organizational financial sustainability. The same results were also obtained by Sheik & Wepukhulu (2019) which found that human resources had a positive effect on financial sustainability. Based on the description above, the third hypothesis developed in this study is:
H3: Human capital has a positive effect on financial sustainability.
According to Johnson, et al., (2002) it can be done collectively. These activities carried out collectively can have a bigger impact because they are carried out together and are believed to be able to reduce costs because they are also shared. Market access and market information can also be obtained more easily if an individual has a high level of social capital. Research conducted by Simatupang, et al., (2019) found evidence that social capital plays a dominant role in the financial sustainability of the sago processing business in Tambat village, Merauke. Meflinda (2018) found that social capital has a positive and significant relationship to the financial sustainability of industrial and trade SMEs in Riau. Based on the description above, the fourth hypothesis developed in this study is:
H4: Social capital has a positive effect on financial sustainability.
The Relationship between Financial Strategy Performance and Financial Sustainability
A study conducted by Dave, et al., (2013) provides empirical evidence that the company's financial performance has a positive influence on financial sustainability. Marwa & Aziakpono (2015) conducted a study in Tanzania that found that financial performance as measured by ROA is positively related to financial sustainability. Weber (2017) examined banks in China and found that financial performance has a positive effect on financial sustainability. Research by (Nas et al., 2019) concluded that in the operational activities of Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) in Pakistan using assets to create profitability and this has an effect on the financial sustainability of MFIs. Based on the description above, the fifth hypothesis developed in this study is:
H5: Financial strategy performance has a positive effect on financial sustainability
Methodology
This paper is quantitative research. There are 4 variables examined in this study, namely, Human Capital (HC), Social Capital (SC), Financial Strategy Performance (FSF) and Financial Sustainability (FS). Human capital measurement indicators use a questionnaire developed from the research concept of Mayo (2000); Han, et al., (2008); St-Pierre & Audet, (2011). Measuring social capital through a questionnaire was developed from the research results of Ridell (1997); Putnam (1995); Islam (2013). Financial strategy performance is measured using the CAEL ratio, namely Capital, Asset Quality, Earning, and Liquidity US. Financial sustainability measured using Operating Self-Sufficiency (OSS) ratio and Financial Self-Sufficiency (FSS). This research was conducted at all Rural Banks (RB) in Bali Province, as many as 134 RBs. The method of determining the sample using purposive sampling technique, criteria of stipulated are Rural Banks which have assets of more than 10 billion and have a minimum equity participation liability ratio of at least 12 percent. Based on criteria obtained 127 people's credit banks as the research sample. The data analysis technique used SEM-PLS.
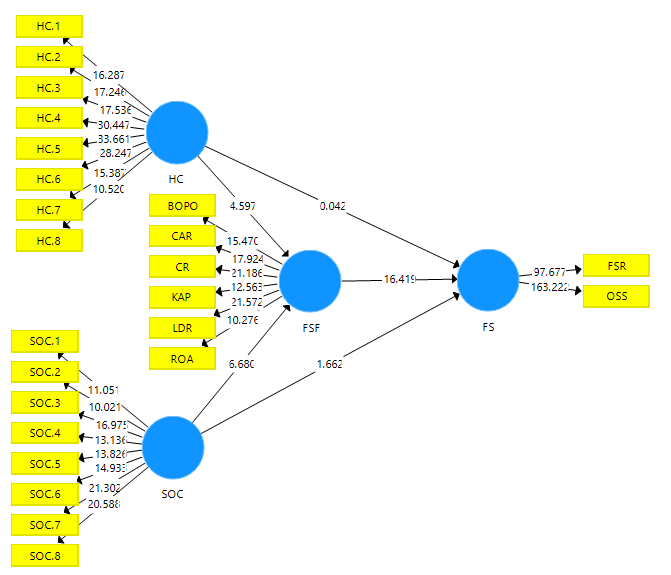
This research examines the effect of human capital and social capital on financial strategy performance and financial sustainability. Acceptance of the hypothesis can be calculated from the results of the path coefficient and the significance of the model based on the t statistic and p value. In the path coefficient, the relationship between two variables can be categorized as significant if the t statistical value is greater than 1.96 and the p value is smaller than 0.05. the results of hypothesis testing are as in Figure 1 below.
Based on the results of the path coefficient In Figure 1, the results of the research hypothesis can be explained as follows.
The Influence of Human Capital on Financial Strategy Performance
Based on the results of the analysis, the coefficient value of human capital on financial strategy performance is 0.363 with a statistical t value of 4.579 (t statistic>1.96) and a p value of 0.000 (p value<0.05). This shows that the first hypothesis is accepted, this means that human capital has a positive and significant effect on financial strategy performance. These findings indicate that the existence of human capital in rural banks in Bali is able to boost the company's financial performance. Human capital is all investment in the knowledge and skills of an individual capable of supporting the achievement of the company's financial strategy. The results of the study support the opinion of Liebowitz (2004) which states that human capital provides a strong mechanism to support the success of a company. Human capital in people's credit banks in Bali is an important factor in improving their financial performance, this is in accordance with the results of research by Khan & Park (2020); Sheikh & Wepukhulu (2019); Xu, et al., (2019); Xu & Li (2019). The results of the study are also in accordance with the results of research by Al Amin (2012) who found that human capital has a positive effect on the company's financial performance.
The Influence of Social Capital on Financial Strategy Performance
Based on the analysis, the social capital coefficient on financial strategy performance was 0.528 with a statistical t value of 6.680 (t statistic>1.96) and a p value of 0.000 (p value<0.05). This shows that the second hypothesis is accepted, this means that social capital has a positive and significant influence on financial performance strategy. There is a sense of togetherness and mutual trust between employees which leads to mutual cooperation for the progress of the company. The value of local wisdom is employee compliance with high leaders and vice versa leaders who are able to nurture subordinates to become high social capital in encouraging work harmony and having a positive impact on the company's financial performance. The results of the study support the results of research conducted by Farida (2016); Agyapong, et al., (2017) which found that social capital has a positive effect on company performance. Lins, et al., (2007) proved empirically that the high level of corporate social capital has a positive effect on company performance. Research conducted by Dar & Mishra (2020) found that social capital has a significant impact on increasing company performance. Liu (2017) provides results that social capital can improve organizational performance.
The Influence of Human Capital on Financial Sustainability
Based on the results of the analysis, the coefficient value of human capital on financial sustainability was 0.002 with a statistical t value of 0.042 (t statistic<1.96) and a p value of 0.966 (p value>0.05). This shows that the third hypothesis is rejected; this means that human capital has no significant effect on financial sustainability. These findings indicate that human capital is unable to provide support for revenue creation by streamlining all company operating costs. The high human capital in people's credit banks in Bali has not been able to provide full support in generating stable income and stable use of fees. The results of this study contradict the results of research conducted by Naz, et al., (2019) found that human capital is positively related to an organization's financial sustainability. The results of the research by Sheik & Wepukhulu (2019) found that human resources have a positive effect on financial sustainability.
The Influence of Social Capital on Financial Sustainability
Based on the results of the analysis, the coefficient value of human capital on financial sustainability was 0.113 with a statistical t value of 1.660 (t statistic<1.96) and a p value of 0.097 (p value> 0.05). This shows that the fourth hypothesis is rejected; this means social capital owned by rural credit banks in Bali is not able to affect the financial sustainability of the company. Financial sustainability in this study is the capacity of an organization to earn income in maintaining its productive processes at a stable level or more to produce results. Social support capital has not been able to promote stability between revenue and the use of fees made by rural credit banks in Bali. The results of the study do not support the research of Simatupang, et al., (2019) which concluded that social capital plays a dominant role in financial sustainability and research. Meflinda (2018) who found that social capital has a positive and significant relationship to financial sustainability.
Effect of Financial Strategy Performance on Financial Sustainability
Based on the results of the analysis, the coefficient value of human capital on financial strategy performance is 0.971 with a statistical t value of 16.419 (t statistic>1.96) and a p value of 0.000 (p value<0.05). This shows that the fifth hypothesis is accepted. The implementation of the people's credit bank financial strategy provides improvements and increases in corporate profits. Management implements the right strategy to improve financial performance. The rapid changes in the business environment as a result of the development of science and information technology as well as regional and global conditions with market liberalization have made the level of competition between companies increasingly tighter. Mand this can be done to improve performance and competitive advantage in the long run (sustained competitive advantage). A study conducted by Dave, et al., (2013) provides empirical evidence that the company's financial performance has a positive influence on financial sustainability. Marwa & Aziakpono (2015) found that financial performance as measured by ROA is positively related to financial sustainability. Weber (2017) states that financial performance has a positive effect on financial sustainability.
Indirect Influence of Human Capital and Social Capital on Financial Sustainability through Financial Strategy Performance
Based on the value of the Specific Indirect Effects coefficient, the human capital variable on financial sustainability through financial strategy performance has a value of 0.352 with a statistical t value of 4.411 (t statistic>1.96) and a p value of 0.000 (p value<0.05). These results indicate that human capital has an effect on financial sustainability through financial strategy performance. Human capital is the main element in intellectual capital, owned by rural banks, which can increase company profits and this has a positive impact on the sustainability of the company. The results of this study indicate that the human capital variable is not directly able to encourage the creation of corporate financial sustainability. However, the human capital owned by the company is positively able to encourage the company to achieve higher financial performance. The results showed that the financial strategies implemented by rural credit institutions were able to optimize human capital to achieve business stability in the long term.
Based on the value of the Specific Indirect Effects coefficient, the social capital variable on financial sustainability through financial strategy performance has a value of 0.352 with a statistical t value of 5,994 (t statistic>1.96) and a p value of 0.000 (p value<0.05). This shows that social capital has an effect on financial sustainability through financial strategy performance. The results showed that directly social capital was not able to realize the financial sustainability of rural credit banks in Bali, but had an indirect effect through financial strategy performance. Based on these results, it shows that the people's credit bank financial strategy with existing social capital, such as having a strong sense of brotherhood between employees, compliance with regulations, Employee compliance with the leadership and the existence of a people's credit bank leader who protects all components of the company creates harmony in the company which causes higher company performance and has an impact on the sustainability of the bank's business. The findings are in accordance with the research of Nas, et al., (2019) concluded that in the operational activities of Microfinance Institutions in Pakistan using assets to create profitability and this has an effect on financial sustainability.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Based on the results of the analysis and discussion, it can be concluded that the variables human capital and social capital affects the financial strategy for the performance of rural credit banks in Bali. Human capital management and the existence of social capital that is able to create harmony in the work environment is able to improve the financial performance of rural credit banks. Human capital variables and social capital does not directly affect financial sustainability, but indirectly human capital and social capital has a significant effect through financial strategy performance. Good human capital management and high social capital in the company are able to create work harmony among employees and support a conducive work climate, which results in an increase in financial performance and ultimately has an impact on increasing the company's financial sustainability. The results of the research prove that the people's credit banks in Bali have good human capital and social high capital. Based on this, people's credit banks must continue to increase their human capital by increasing knowledge and increasing skills training activities for all employees so that they are able to carry out their jobs properly. Social capital owned by rural banks needs to be improved by increasing the network among employees by maintaining togetherness and kinship through activities, such as: company anniversary celebrations, joint healthy walks, tirta yatra, and ngayah.
References
- Adams, M., Thornton, B., & Sepehri, M. (2010). The impact of the pursuit of sustainability on the financial performance of the firm. Journal of Sustainability and Green Business, 1-14.
- Agyapong, F.O., Agyapong, A., & Poku, K. (2017). Nexus between social capital and performance of micro and small firms in an emerging economy: The mediating role of innovation. Cogent Business & Management, 4(1), 1309784.
- Al-Amin, M. (2012). The influence of firm size on intellectual capital relationship with company performance (empirical study of companies listed on the idx 2001-2010). Journal of the Faculty of Economics, 1(2), 1-23.
- Akintimehin, O.O., Eniola, A.A., Alabi, O.J., Eluyela, D.F., Okere, W., & Ozordi, E. (2019). Social capital and its effect on business performance in the Nigeria informal sector. Heliyon, 5(7), 2024.
- Barney, J. (199). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17, 99-120.
- Boekestein, B. (2006). The relationship between intellectual capital and intangible assets of pharmaceutical companies. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 7(2), 242-253.
- Brennan, N., & Connell, B. (2000). Intellectual capital: Current issues and policy implications. Journal of Intellectual capital.
- Chan, K.H. (2009). Impact of intellectual capital on organizational performance an empirical study of companies in the hang seng index (Part 1). The Learning Organization, 16(1), 4-21.
- Chegini, M.G., Alipour, H., & Zamani, A. (2012). The relationship between social capital and inter-organizational entrepreneurship in Rasht Industrial City, Iran. Journal of Basic Applied Scientific Research, 2 (1/2/3): 389 - 401.
- Clarke, M., Dyna, S., & Rosalind, H.W. (2011). Intellectual capital and firm performance in australia. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 12(4), 505-530.
- Dar, I.A., & Mishra, M. (2020). Dimensional impact of social capital on financial performance of SMEs. The Journal of Entrepreneurship, 29(1), 38-52.
- Dave, P., Wadhwa, V., Aggarwal, S., & Seetharaman, A. (2013). The impact and development on the financial sustainability of Information Technology (It) companies listed on the s&p 500 index. Journal of Sustainable Development, 6(11), 122-138.
- Edvinsson, L., & Malone, M.S. (1997). Intellectual Capital: Realizing Your Company's True Value by finding its Hidden Roots. New York: HarperCollins Publishers Inc.
- Farida, N. (2016). Determinants of marketing performance: Innovation, market capabilities and marketing performance. Journal of Management Dynamics, 7(1), 56-65.
- Fukuyama, F. (2002). Trust: The social virtues and the creation of prosperity. London: Hamish Hamilton.
- Gates, S., & Langevin, P. (2010). Human capital measures, strategy and performance: Hr managers' perceptions. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 23(1), 111-132.
- Grant, R.M. (1991). The resource-based theory of competitive advantage: implications for strategy formulation. California Management Review, 33(3), 114-135.
- Han T.S., Lin, C.Y.Y., & Chen, M.Y.Y. (2008). Developing human capital indicators: A three way approach. International Journal Learning and Intellectual Capital, 5(3), 387-403.
- Helmut, K., Manfred, O., & Maximilian, G. (2006). Human capital management. Prozessexzellenz im HR-Management.Schönenberg. Islam, M.R. (2013). Indigenous knowledge as social capital. International Journal of Social Science, 1, 68-79.
- Jardon, C.M.F., & Martos, M.S. (2009). Intellectual capital and performance in wood industries of Argentina. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 10(4), 600-616.
- Johnson, N.L., Suarez, R., & Lundy, M. (2002). The importance of social capital in Colombian rural agro-enterprises (No. 577-2016-39226).
- Khan, M.Z.A., & Park, J.H. (2020). Retraction: The effect of human capital on performance of East African commercial banks. Banks and Bank Systems, 15 (2), 56.
- Komnenic, B., & Pokrajcic, D. (2012). Intellectual capital and corporate performance of MNCs in Serbia. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 13(1), 106-119.
- Lin, C.Y., & Chen, M.Y. (2007). Does innovation lead to performance? An empirical study of sme in taiwan. Management Research News, 32(2), 132.
- Liebowitz, J. (2004). Linking knowledge management with human capital strategy development. Issues in Information Systems, 1, 194-200.
- Lin, C.Y., & Chen, M.Y. (2007). Does innovation lead to performance? An empirical study of SMEs in taiwan. Management Research News, 30(2), 115-132.
- Liu, C.H. (2017). The relationships among intellectual capital, social capital, and performance-The moderating role of business ties and environmental uncertainty. Tourism Management, 61, 553-561.
- Marr, B. (2007). What is intellectual capital? In joia, la (ed) strategies for technology and intellectual capital. Challenges and opportunities. Information Science Reference. London: Idea Group Inc.
- Marwa, N., & Meshach, A. (2015). Financial sustainability of Tanzanian saving and credit cooperatives. International Journal of Social Economics, 42(10), 870-887.
- Mayo, A. (2000). The role of employee development in the growth of intellectual capital. Personal Review, 29(4) 521-533.
- Mayo, A. (2001). The human value of the enterprise - valuing people as assets - monitoring, measuring, managing. London: N. Brealey Publishing.
- Meflinda, A., Mahyarni, M., Indrayani, H., & Wulandari, H. (2018). The effect of social capital and knowledge sharing to the small medium enterprise's performance and sustainability strategies. International Journal of Law and Management.
- Nafziger, E.W., & Terrell, D., (2006). Entrepreneurial human capital and the long - run survival of firms in India. World Development, 46 (2), 223-242
- Naz F., Salim S., Rehman R., Ahmad, M.I., & Ali, R. (2019). Determinants of financial stability of microfinance institutions in Pakistan. Upravlenets - The Manager, 10(4), 51–64.
- Nuryani, N.N.J., Satrawan, D.P.R., Gorda, A.A.N.O.S., & Martini, L.K.B. (2018). Influence of human capital, social capital, economic capital towards financial performance & corporate social responsibility. International journal of social sciences and humanities, 2(2), 65-76.
- Ofori, D., & Sackey, J. (2010). Assessing social capital for organizational performance: Initial exploratory insights from Ghana. Organizations and markets in emerging economies, 1(2), 71-91.
- Prusak, L., & Cohen, D. (2001). How to invest in social capital. Harvard business review, 79(6), 86-97.
- Puntillo, P. (2009). Intellectual capital and business performance: Evidence from Italian banking industry. Journal of Corporate Finance, 5(12), 96-115.
- Putnam, & Robert, D. (1995). Bowling alone: America’s declining social capital. Journal of Democracy, 65 - 78.
- Riddell, S., Baron, S., Stalker, K., & Wilkinson, H. (1997). The concept of the learning society for adults with learning difficulties: human and social capital perspectives. Journal of Education Policy, 12(6), 473-483.
- Roca-Puig, V., Beltran-Martin, I., & Segarra, C.M. (2012). Combined effects of human capital, temporary employment and organizational size on firm performance. Personnel Review, 41(1), 4-22.
- Sheikh, H.I., & Wepukhulu, J.M. (2019). Effect of intellectual capital efficiency on financial sustainability of savings and credit cooperative societies in Nairobi country, Kenya. International Academic Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(4), 16-31.
- Simatupang, D.O., Dawapa, M., Fachrizal, R., & Untari, U. (2019). Social and economic capital on sustainability of sago processing business. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 3(10),
- St-Pierre, J., & Audet, J. (2011). Intangible asset and performance. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 12(2), 202-223.
- Sulastri. (2005). The Influence of intellectual capital and social capital on employee compensation and company performance in manufacturing companies listed on the stock exchange Jakarta, DiPDIM certificate of Postgraduate Faculty of Economics UB. Poor
- Wang, W.Y., & Chang, C. (2005). Intellectual capital and performance in causal models: Evidence from the information technology industry in Taiwan. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 6(2), 222-236.
- Weber, O. (2017). Corporate sustainability and financial performance of Chinese banks. Sustainability Accounting. Management and Policy Journal.
- Xu, J., & Li, J. (2019). The impact of intellectual capital on SMEs' performance in China: Empirical evidence from non-high-tech vs. high-tech SMEs. Journal of Intellectual Capital.
- Xu, J., Haris, M., & Yao, H. (2019). Should listed banks be concerned with intellectual capital in emerging Asian markets? A comparison between China and Pakistan. Sustainability, 11(23), 6582.