Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 6S
Impact of Customer Relationship Management on Services Recipient Satisfaction of the Directorates of Buildings and Land Tax in Jordan
Mohammad Issa Ghafel Alkhawaldeh, Directorates of building and land tax, Ministry of local administration
Citation Information: Alkhawaldeh, M.I.G. (2022). Impact of customer relationship management on services recipient satisfaction of the directorates of buildings and land tax in Jordan. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S6), 1-12.
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effect of customer relationship management on recipient satisfaction in Jordan. The researcher used the descriptive analytical approach. The study population consists of the service recipient of the directorates of buildings and lands in Jordan. A random sample (700) selected who received the services, (400) of them were back valid to analyses; the researcher used statistical methods which are suitable through SPSS program to analyse data. The study results showed that customer relationships management has a statistically significant effect on satisfaction of service recipients of building and land taxpayers, the researcher recommended the need for concern from the directorates of buildings and land tax in Jordan in particular to pay attention to the satisfaction of service recipients, and the need to move away from complex routine procedures that may affect the satisfaction of service recipients.
Keywords
Customer Relationship Management, Services Recipient Satisfaction, Directorates of Buildings and Land Tax, Jordan
Introduction
The world is witnessing at the present time great and continuous changes in the ways of providing service to customers, especially remotely through smart applications, where the world has become a small village despite the distance of its parties, which calls for attention to improve the services provided to customers in all fields (Al-Hawary & Al-Syasneh, 2020; Allahow et al., 2018). The sustainability of the relationship between the organization and customers and the raising of the level of customer satisfaction (AlTaweel & Al-Hawary, 2021), and this is because the satisfaction of service recipients is one of the most important indicators of success in any organization at all, and the importance of its role In the success of the Buildings and Land Tax Directorates in Jordan and providing their services with high efficiency, it was a duty for them to pay primary attention to the satisfaction of the service recipients by studying in depth everything related to this regard and what affects the quality of the service provided that reflects the satisfaction of customers. Buildings and Land Tax Directorates in Jordan, like other governmental organizations, deal with large numbers of customers, which requires them to maintain distinguished relations with them. It was necessary for these directorates to benefit from the development in the application of customer relationship management strategies, and to work on adopting an advanced approach to raise the efficiency of the services provided and increase levels of satisfaction, and seeks to reach the satisfaction of service recipients to the highest possible level and improve it (Alolayyan et al., 2018; Alshurideh et al., 2017). To rehabilitate employees, which is one of the challenges in light of the increase in the number of taxpayers and the increasing population expansion, in addition to the need to provide the necessary services for building and land tax payers within the limited budgets available. Therefore, a single window service system has been introduced to facilitate citizens when making their transactions, as well as facilitating electronic payment services, and the creation of a number of directorates and other government institutions outlets to facilitate the conduct of related transactions. The success of public sector organizations is linked to several criteria, the most important of which is the satisfaction of service recipients, as many countries have monitored awards and rewards for government organizations that excel in providing their services through appreciating their employees, developing their competencies and promoting the concept of justice and equality among them. Their commitment and ability to employ their skills and knowledge to improve the level of services provided to service recipients (King Abdullah II Award, 2015).
The levels of satisfaction of service recipients in the Buildings and Land Tax Directorates rise when customer knowledge management is one of its strategic objectives for dealing with the local community to improve the level of satisfaction with services provided through e-governance, and for a more comprehensive understanding of customer knowledge, which is interested in building a relationship between the customer and the organization. Combining information management and knowledge management with customer relationship management makes it easier for taxpayers to complete their transactions, which includes raising the level of taxpayer satisfaction. The effectiveness of customer relationship management depends on improving the procedures for the flow of transactions, because the quality and ease of use of the information system in the flow of transactions is one of the main dimensions affecting the management of customer relations (AL-Weshah et al., 2018; Al-Hawary & Aldaihani, 2016), in addition to the efficiency of employees because of their important role in customer satisfaction through customer relationship management, especially front-line employees (Hsieh et al., 2012), and the emergence of the strategy of Customer Knowledge Management (CKM) in conjunction with the emergence of globalization and modern technology led to the creation of a new challenge that must be exploited as an opportunity to build a strong relationship with the customer as it affects the It is important to know the effectiveness of applying the "single window system" in the building and land tax directorates and its impact on the satisfaction of service recipients from the building and land tax payers.
Due to the nature of the researcher’s work in the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate, he noticed a discrepancy in the level of taxpayers’ satisfaction due to the different level of service efficiency provided by the Buildings and Land Tax Directorates and lands. The importance of this study lies in its connection with an important aspect related to service recipients, considering that their satisfaction is one of the main goals of the existence of the building and land tax directorates, and one of the strategies on which the directorate’s interest in service recipients in general is based. Moreover, this study helps directorate officials and decision makers to raise the level of customer satisfaction. This study is considered the first of its kind in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, which concerned the satisfaction of the recipients of the services of the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate, according to the researcher's knowledge, as it is applying the customer relationship management model in the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate, to find out the most important variables that affect the degree of satisfaction of the recipients of this public service. Also, this study will contribute to adding the single window system as a new dimension to managing customer relations. This study also presents recommendations and research proposals related to public services in Jordan, which can be used in the public sector in general, and in the directorates of building tax in particular.
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management is defined as the process concerned with building relationships with customers in a way that contributes to creating additional value for the customer, making him more satisfied and loyal to the organization, and making the latter increase its turnover and profitability, by giving a positive image of it and its products (Zahran & Prihadini, 2020; Al-Hawary & Alhajri, 2020). Top managers realize the importance of customer relationship management, which aims to improve organizational performance and develop managerial strategies that focus on customers (service recipients) and their satisfaction. The dimensions of customer relationship management related to the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate can be defined as (transaction procedures, staff efficiency, knowledge of customers and a single window system). Customer relationship management is a strategy that focuses on creating service recipient satisfaction and long-term relationships with him by integrating several functional areas of the organization to achieve a competitive advantage (Nguyen, et al, 2007). The results of research conducted by Ardiyhanto (2011) show that there is a strong relationship of CRM regarding the loyalty of the service recipients and their satisfaction towards the organization providing the service, and this means that the better implementation of CRM in the organization providing the service has a positive impact on the service recipient (the customer), so CRM applications allow organizations to take advantage of information from all points of contact with the customer, whether through transaction flow procedures, customer knowledge management, or through service staff in this field. The single window system is one of the leading applications in providing electronic service.
Procedures for the Conduct of Transactions: The issue of simplifying the procedures for the conduct of transactions, especially the procedures for providing services to customers, has gained increasing attention in all calls for administrative reform, and this interest is due to the fact that comes from any administrative development program, whose results and effects must be reflected on all categories of customers and not on limited areas (large customers) Rather, it is directed to all categories of customers, which necessitates simplification of these procedures, and simplifying work procedures is a mainstay of the comprehensive administrative reform, which would improve the process of activating public sector institutions and enhance its transparency.
The simplification of work procedures may face some legal conditions represented in the powers, and associated sub-procedures that guarantee the rights of the organization or for reasons related to the division of work and the distribution of responsibilities and powers among the employees of the organization and to ensure effective control and supervision. This is due to the nature of the services provided, where services are distinguished from goods - in general - in the procedures for conducting transactions that the services are intangible, and it is difficult to give specifications for them, but they can be realized through a set of constituent dimensions, and opinions differed about a unified classification of the basic dimensions constituent of the transaction flow procedures, so there are many methods that must be included in simplifying the procedures of the transaction flow.
Staff Efficiency: Employees are one of the most important CRM tools, whose efficiency greatly affects the quality of service provided, which is directly related to the level of satisfaction of service recipients. The services provided by directorates and organizations include tangible and intangible components, as indicated by (Al-Hawary & Metabis, 2012). Intangible services provided by employees to the service recipient (the customer) is considered a competitive advantage, as these personal interactions shape the service recipient’s perceptions of the quality of the service provided and their level of satisfaction. The service experience with employees distinguishes a service organization from another as a result of the efficient interaction between the customer and the employee. Frontline service personnel play a pivotal role in shaping the customer’s perceived level of service quality (Prentice, 2019). The behaviour of the efficient employee and the way he performs the service with high efficiency forms positive perceptions of the service recipients in the organization, which leads to customer satisfaction and retention (Birgelen et al., 2013), as well as the perceptions of service recipients of the level of service provided (Delcourt et al., 2013).
Customer Knowledge Management: Customer Relationship Management uses the concepts of Customer Knowledge Management to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of all processes and procedures related to providing services to the customer, influencing their satisfaction and building trust with them. Customer knowledge management also uses customer relationship management to expand its technology-based and data-oriented approach, while customer knowledge management enables customer relationship management through the use of both people and technology elements and its reflection on service recipient satisfaction. The integration of customer relationship management with customer knowledge management is one of the aids for the organization to deal with obstacles and enhance comparative advantages by communicating with customers and constantly learning from them in the management process, and consolidating the relationship with them (Wang & Yu, 2010), and the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate can then use customer knowledge Acquired to achieve the objectives of obtaining maximum benefits from customer relationships and increasing their satisfaction. Customer knowledge has been defined as: “the combination of experience, value, and information, which is created and absorbed during the transaction and exchange between the customer and the organization.” Customer knowledge is defined as: structured information about the customer as a result of systematic processing (Mitussis et al., 2006), and customer knowledge is defined as one of the most complex types of knowledge, where customer knowledge can be obtained from different sources and channels (Nejatianet al., 2011).
Single Window System: The single window system is concerned with processing all administrative transactions and procedures related to building and land tax operations, through one point. Ministries, departments, institutions, and organizations often participate in this system, and this system may be connected to a government system to process data and review documents, before accepting transactions refuse or request more information or documents. It is "a principle based on providing all services to the recipients in one place and providing facilities to them by gathering representatives of the organizations concerned with the service under one roof, in order to ensure the ease and speed of providing services and thus reducing the cost, providing the best services and increasing the satisfaction of service recipients, so that it serves as a central point between all parties concerned with obtaining these approvals and signatures” (Ministry of Public Sector Development, 2012). Therefore, in theory, the single window system can be defined as a system that allows the collection of information with one authority to meet all the regulatory requirements related to service delivery operations to service recipients. In practice, the single window system is a single entry, whether physical or electronic, aimed at providing data, and the documents related to the procedures related to the Directorate of Buildings and Lands through a single window linked with all relevant authorities to provide an integrated service in one port.
Service Recipients' Satisfaction
Service recipient satisfaction is a major measure of the quality of services provided, with which it is difficult to measure this satisfaction (Al-Hawary & Al-Khazaleh, 2020; Mohammad et al., 2020; Al-Hawary et al., 2017), as achieving service quality and service recipient satisfaction are critical factors in influencing the decisions of service recipients and the desire to deal with government organizations in the future (Metabis & Al-Hawary, 2013; Al-Hawary & Metabis, 2012). So improving the quality of services provided it has a positive impact on achieving satisfaction, and many organizations have tended to pay attention to achieving quality in order to ensure the continuity of providing their services (Sharma, 2016), and service quality is one of the important topics in managing customer relationship and has great importance in achieving customer loyalty and strengthening the relationship with them (Rauyruen & Miller, 2007).
Customer satisfaction is defined as the emotional state that expresses reactions that result when an individual purchases or obtains a service, and satisfaction should be dealt with as the main support for the success and continuity of organizations (Al-Hawary & Al-Menhaly, 2016; Al-Hawary & Abu-Laimon, 2013), and Al-Alawna (2019) indicates that the satisfaction of service recipients is a function of Levels of expectations and perceived performance, and there are three levels of satisfaction. If the results are greater than the expectations of the customer, he feels high satisfaction, and if the results are equal to the expectations of the customer, he feels satisfied, but if the results are less than the expectations of the customer, he feels dissatisfied, and thus high levels of quality creates a kind of emotional connection between the customer and the organization, and thus this connection creates loyalty. Through the previous definitions, it can be concluded that there is a strong relationship between the satisfaction of the service recipient and the connection with the organization providing the service. Thus, the degree of his loyalty, and the satisfaction of the service recipient is measured by the degree of his awareness of the effectiveness of the organization in providing services that meet his needs and desires. The satisfaction of the service recipient is also measured by the feeling that suggests satisfaction or dissatisfaction that results when comparing the observed service performance with its expectations. In the event that the performance exceeds what is expected or exceeds expectations positively, in this case the recipient of the service remains linked to the organization providing the service (Akhilesh, 2011).
The term "customer" for government organizations is much more comprehensive than other general terms, and although the main stakeholders in most business organizations are individual customers (considered consumers), suppliers, owners, competitors, employees and shareholders, as for public organizations, public services are defined as what the state provides to its citizens to facilitate and increase their well-being, directly or indirectly, to facilitate their lives, and to give them a kind of economic and social well-being, within the areas the limits of its authority and material capacity, and in accordance with international laws, such as educational, social, economic, health and security services (Masa’dah, 2016). From a marketing point of view, the recipient of the service in the governmental organization is what represents the external customer, and it is the customer for whom this organization was established and services are provided to him. He must be treated as a customer, even if the organization is a non-profit organization, being the focus of the work of this organization.
Customer Relationship Management and Service Recipients' Satisfaction
Effective CRM practices are highly related to customer satisfaction (the recipient of the service) (Feinberg & Kadam, 2002), in addition to that, satisfaction is a major goal of CRM, which also greatly affects the medium-term goals, such as customer retention, loyalty towards the organization, and thus achieving organizational performance (Abdullateef & Salleh, 2013). Kumaretal (2021) studied the relationship between Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) and customer satisfaction through the mediating role of customer experience in the banking industry, and revealed the mediating role of customer experience in the relationship between Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) and customer satisfaction. Sofi, et al., (2020) referred that there is a substantial and positive relationship between the dimensions of CRM, namely customer orientation, knowledge management, and CRM organization with regard to customer satisfaction, although the results also indicate a significant positive impact of CRM-based technology on customer satisfaction, However, the magnitude of this effect is very weak.
Khairawati (2019) in a study of the effect of the customer loyalty program on customer satisfaction and its impact on customer loyalty stresses that the member card has a significant impact on customer satisfaction, while discount promotion does not have a significant impact on customer satisfaction and also does not affect customer loyalty. Customers, member cards and discount promotion are a direct influence on customer loyalty. in general, Santouridis, et al., (2017) researched the correlations between Customer Relationship Management (CRM) practices, relationship quality and customer satisfaction, with a focus on the potential mediation effect of relationship quality on customer relationship management methods and the relationship of satisfaction, and the results revealed two factors in customer relationship management practices. Classify them as customer care and communication. Customer care has been found to have a significant positive impact on customer satisfaction, moreover, dimensions of customer relationship management practices have been found to have a significant positive impact on relationship quality. Based on the above literature, the study hypotheses may be formulated as:
There is a statistically significant effect at the level (α ≤ 0.05) of customer relationship management on the satisfaction of service recipients of building and land tax payers in Jordan.
Research Framework
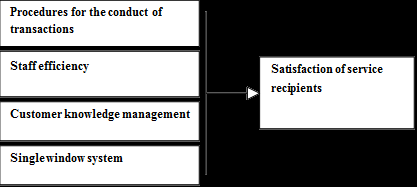
The following theoretical framework is provided in Figure 1 based on the study hypothesis. The study investigates the impact of customer relationship management on satisfaction of service recipients of Jordan's directorates of buildings and land tax, where customer relationship management is the independent variable and satisfaction of service recipients is the dependent variable, as shown in the framework.
Methodology
The present study's methodology section displays the study's sample, measurements, and statistical analysis tools used to investigate the link between the studies constructs (Customer Relationship Management and Services Recipient Satisfaction).
Study Population and Sample
The study population is made up of personnel from Jordan's directorates of buildings and land tax, with the goal of determining the extent of Customer Relationship Management implementation and service receiver satisfaction. A sample of the population was obtained. The study's sample includes 700 people who used the services of Jordan's directorates of buildings and lands, with 400 of them returning valid data for research.
Study Tool
The study's instrument is divided into three components, the first of which is concerned with demographic characteristics. The independent variable is discussed in the second section (Customer relationship management). Customer relationship management has several elements (Procedures for the conduct of transactions, staff efficiency, customer knowledge management, and a single window system). Previous studies Al-Weshah, et al., (2018); Zahran & Prihadin (2020) were used to develop the measurements. The dependent variable is the third section (services recipient satisfaction). These questions were answered on a 5-point Likert scale, with 1 indicating strong disagreement and 5 indicating strong agreement.
Data Gathering
The questionnaire was used to collect data for the study. The questionnaire began with an introduction message that encouraged respondents to administrate their own responses, as well as assurances of secrecy. Following that, a request for demographic information as well as the measurements was made. Random questionnaires were used to obtain data. The 700 employees in the sampling frames were chosen at random. The research was done in Jordan and was based on the development and administration of a self-administered survey.
Reliability of Research Instrument and Measurement Scales
The internal consistency of degree of customer relationship management between various aspects affecting Services Recipient Satisfaction for validity was examined after the survey was completed by determining their coefficient alpha (Cronbach alpha). A higher a value suggested a higher internal consistency within the questionnaire as a whole after examining the complete scale and relevant (Wang, 2005). If the Cronbach Alpha is 0.6, according to Sekaran (2000), it is a low and acceptable norm. A minimal criterion of 0.6 was found to be exceeded by all scales. When the individual variable scores are integrated into a single scale with a Cronbach alpha of 0.892, it suggests convergent validity. Procedures for conducting transactions, staff efficiency, customer knowledge management, and a single window system, as well as Cronbach's alpha, are all examples of customer relationship management strategies. 87. The Cronbach's alpha for service receiver satisfaction was. 89. It was discovered that there was a good correlation between customer relationship management procedures and service receiver satisfaction, and that this correlation was in line with internal characteristics. Tables (1) and (2) show the actual results of the scale reliability analysis.
| Table 1 Scale Reliability of the Customer Relationship Management |
||
|---|---|---|
| Reliability | Item to total correlation | Construct and item |
| 0.87 | Procedures for the conduct of transactions | |
| 0.64 | PCT1 | |
| 0.79 | PCT 2 | |
| 0.84 | PCT 3 | |
| 0.74 | PCT 4 | |
| Staff efficiency | ||
| 0.88 | SE1 | |
| 0.73 | SE 2 | |
| 0.67 | SE 3 | |
| 0.93 | SE4 | |
| 0.74 | SE5 | |
| Customer knowledge management | ||
| 0.74 | CKM1 | |
| 0.89 | CKM2 | |
| 0.64 | CKM3 | |
| 0.78 | CKM4 | |
| 0.79 | CKM5 | |
| 0.82 | CKM6 | |
| 0.75 | CKM7 | |
| single window system | ||
| 086 | SWS1 | |
| 0.67 | SWS2 | |
| 0.77 | SWS3 | |
| 0.69 | SWS4 | |
| Table 2 Scale Reliability of the Services Recipient Satisfaction |
||
|---|---|---|
| Reliability | Item to total correlation | Construct and item |
| 0.91 | services recipient satisfaction | |
| 0.75 | SRS1 | |
| 0.63 | SRS2 | |
| 0.71 | SRS3 | |
| 0.74 | SRS4 | |
| 0.68 | SRS5 | |
| 0.80 | SRS6 | |
| 0.86 | SRS7 | |
| 0.74 | SRS8 | |
Correlation Analysis
The correlation matrix was calculated to identify bivariate links among the variables of the study. The results of these correlations can be viewed in Table (3).
| Table 3 Summary of Correlations |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWS | CKM | SE | PCT | Variables |
| 0.65** | 0.75** | 0.76** | 1 | PCT |
| 0.64** | 0.77** | 1 | SE | |
| 0.72** | 1 | CKM | ||
| 1 | SWS | |||
The correlation coefficients ranged from (0.64) to (0.64) in the correlation matrix shown in Table (3). (0.77). Customer relationship management characteristics (transaction procedures, staff efficiency, customer knowledge management, and a single window system) were positively connected with service receiver satisfaction, according to the table. The greatest correlation coefficient between independent variables was (0.77), and the correlation values did not surpass (0.90), indicating that the study's model is multicollinearity-free (Trippi & Settle, 1976).
Descriptive Statistics Analysis
Table 4 shows the findings of the means and standard deviations of customer relationship management and service recipient satisfaction.
| Table 4 Descriptive Analysis of Customer Relationship Management and Services Recipient Satisfaction |
||
|---|---|---|
| Standard deviation | Mean | Dimension |
| 0.77 | 3.79 | Customer relationship management |
| 0.87 | 3.89 | Procedures for the conduct of transactions |
| 0.86 | 3.85 | staff efficiency |
| 0.90 | 3.66 | customer knowledge management |
| 0.89 | 3.83 | single window system |
| 0.89 | 3.77 | services recipient satisfaction |
Table (4) shows that procedures for the conduct of transactions is the most common practice of customer relationship management (M=3.89, SD=0.87), followed by staff efficiency (M=3.85, SD=0.86), single window system (M=3.83, SD=0.89), and customer knowledge management (M=3.66, SD=0.90). Regarding satisfaction with services (M=3.77, SD=0.89).
Multiple Regression Analysis
Multiple regression analysis was used to examine the impact of customer relationship management on service receiver satisfaction. Simultaneous regression analysis was used, which meant that all study constructs were entered at the same time. Table 5 shows the regression results. The tolerance values exceeded 0.10, while the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) values were below ten. As a result, the model has no severe multicollinearity issues (Trippi & Settle, 1976). Based on the findings, it can be stated that the multiple regression model utilized in this study met the assumptions required to assure the significance test's validity. As a result, there was a strong association between customer relationship management and customer satisfaction with services.
| Table 5 Regression Summary of Customer Relationship Management and Services Recipient Satisfaction (N=400) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | Collinearity Statistics | ||
| ß | Tolerance | VIF | ||||
| Procedures for the conduct of transactions | 0.034 | 1.142 | .419 0 | 0.344 | 2.910 | |
| staff efficiency | 0.308 | 5.950 | .000 | 0.326 | 3.070 | |
| customer knowledge management | 0.442 | 9.992 | .000 | 0.295 | 3.391 | |
| single window system | 0.178 | 4.625 | .000 | 0.445 | 2.247 | |
Table 5 shows the regression analysis for customer relationship management and services recipient satisfaction. About 76.2% of the variance in services recipient satisfaction can be explained by the four customer relationship management. The proposed model was adequate as the F-statistic=315.464 were significant (p<0.05). This indicates that the overall model was reasonable fit and there was a significant correlation between customer relationship management and services recipient satisfaction. The individual model variables revealed that staff efficiency, (ß=0.308, t =5.950, p<0.01), customer knowledge management (ß=0.442, t =9.992, p<0.01), and single window system (ß= 0.178, t=4.625, p< 0.01) were revealed to have a positive relationship with services recipient satisfaction. So that customer knowledge management has the highest impact in the research model.
Discussion
The results of the study revealed that customer knowledge management explains (69.5%) of the changes in service recipients’ satisfaction, while the second model added the employee efficiency variable to become the size of the interpretation of changes in the dependent variable (74.7%), while the third model added the single window system variable to become the size of the interpretation of the change in the dependent variable (76.1%), and the transaction flow procedures variable was excluded, as the program considered it to have a lower explanation on the dependent variable. This variable becomes weak in the presence of other independent variables. The results of the study concluded that there is an effect of customer relationship management on the satisfaction of service recipients, the results of the current study agree with what was indicated by (Feinberg & Kadam, 2002) that the practices of effective customer relationship management are significantly related to customer satisfaction. The results of this study are also consistent with what was indicated by (Nguyuen et al., 2007) that customer relationship management is a strategy that focuses on creating service recipient satisfaction and building long-term relationships with him by integrating many functional areas of the organization to achieve a competitive advantage. The results also showed that employees are considered one of the most important CRM tools, whose efficiency greatly affects the quality of service provided, which is related to the level of service recipients' satisfaction in the Buildings and Land Tax Directorates. The services provided by the directorates and organizations include tangible and intangible components. The results show that there is a statistically significant effect of the transaction procedures on the satisfaction of service recipients, and these results are consistent with the results of previous studies that indicated that service quality is a very important concept in customer relationship management and has great importance in achieving customer loyalty and strengthening the relationship with him (Rauyruen & Miller, 2007), and the empirical results of previous studies in service organizations indicate that customer satisfaction with the services and products provided can affect the loyalty of customers and their decision to continue the relationship with the organization (Ndubisi & Wah, 2005). The results also show that there is a statistically significant impact of the efficiency of the employees on the satisfaction of the service recipients, as these results are consistent with the findings of previous studies that the efficiency of the employees plays an important role in influencing the perceptions of the service recipients for any type of services provided and thus increasing the level of satisfaction. The service experience with employees distinguishes one service organization from another as a result of efficient interaction between the customer and the employee (Prentice, 2019).
The results of the study also found a statistically significant impact of customer knowledge management on service recipient satisfaction, which confirms the importance of communicating with customers and constantly learning from them for administrative processes and consolidating the relationship with them for the Buildings and Land Tax Directorate, so that the acquired customer knowledge is used to achieve the directorate’s objectives in achieving maximum benefits. It is possible from its relations with customers and raise the degree of their satisfaction and thus their level of loyalty (Wan & Yu, 2010), and the development of customer knowledge affects the relationship between customer relationship management and customer satisfaction (Netjatian et al., 2011). The results also show that there is a statistically significant effect of the single window on service recipient satisfaction, and this reflects what was stated in the report of the United Nations experts on paperless trade in Asia, and the quest for the success of the single window system in influencing the speed of service provided to the customer (service recipients), and improving their satisfaction with the services provided.
Recommendations
The researcher recommends managers and decision-makers that the building and land tax directorates in Jordan should pay attention to the satisfaction of service recipients, and the need to stay away from complex routine procedures that may affect the satisfaction of service recipients. Developing the efficiency of employees and refining their knowledge, especially direct service providers, through holding courses and workshops in the field of communication skills and public relations. The study also stresses the need for the building and land tax directorates in Jordan to adopt the concepts of customer satisfaction applicable in the private sector by activating all the tools of the single window system and conducting standard comparisons to reach the specifications for providing work in an optimal form, especially business procedures and facilitation. And the application of knowledge management concepts Customers in all its dimensions to reach the highest levels of satisfaction for service recipients.
References
Abdullatif, A.O., & Salleh, S.M. (2013). Does customer relationship management influence call centre quality performance? An empirical industry analysis. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 24(9-10).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Akhilesh, B. (2011). Impact of supply agility on customer satisfaction. International conference on e-business management, 3(2). Oxford university press: Oxford, London.
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Abu-Laimon, A.A. (2013). The impact of TQM practices on service quality in cellular communication companies in Jordan. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 11(4), 446–474.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Aldaihani, F.M. (2016). Customer relationship management and innovation capabilities of Kuwait Airways. International Journal of Academic Research in Economics and Management Sciences, 5(4), 201–226.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Al-Khazaleh A.M. (2020). The mediating role of corporate image on the relationship between corporate social responsibility and customer retention. Test Engineering and Management, 83(5l6), 29976-29993.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Al-Menhaly, S. (2016). The quality of e-government services and its role on achieving beneficiary’s satisfaction. Global Journal of Management and Business Research: A Administration and Management, 16(11), 1-11.
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Metabis, A. (2012). Service quality at Jordanian commercial banks: What do their customers say? International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 10(3), 307-334.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Hawary, S.I., Batayneh, A.M., Mohammad, A.A., & Alsarahni, A.H. (2017). Supply chain flexibility aspects and their impact on customers satisfaction of pharmaceutical industry in Jordan. International Journal of Business Performance and Supply Chain Modelling, 9(4), 326–343.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Hawary, S.I.S., & Alhajri, T.M.S. (2020). Effect of electronic customer relationship management on customers' electronic satisfaction of communication companies in Kuwait. Calitatea, 21(175), 97-102.
Al-Hawary, S.I., & Al-Syasneh, M.S. (2020). Impact of dynamic strategic capabilities on strategic entrepreneurship in presence of outsourcing of five stars hotels in Jordan. Business: Theory and Practice, 21(2), 578-587.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Allahow, T.J.A.A., Al-Hawary, S.I.S., & Aldaihani, F.M.F. (2018). Information technology and administrative innovation of the central agency for information technology in Kuwait. Global Journal of Management and Business, 18(11-A), 1-16.
Alolayyan, M., Al-Hawary, S.I., Mohammad, A.A., & Al-Nady, B.A. (2018). Banking service quality provided by commercial banks and customer satisfaction. A structural equation modelling approaches. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 24(4), 543–565.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Alshurideh, M., Al-Hawary, S.I., Batayneh, A.M., Mohammad, A., & Al-Kurdi, B. (2017). The impact of Islamic banks’ service quality perception on Jordanian customers loyalty. Journal of Management Research, 9(2), 139-159.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
AlTaweel, I.R., & Al-Hawary, S.I. (2021). The mediating role of innovation capability on the relationship between strategic agility and organizational performance. Sustainability, 13(14), 7564.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Al-Weshah, G.A., Al-Manasrah, E., & Al-Qatawneh, M. (2018). Customer relationship management systems and organizational performance: Quantitative evidence from the Jordanian telecommunication industry. Journal of Marketing Communications, 1-21.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Ardiyhanto, D., (2011). Analisis Pengaruh Customer Relationship terhadap Loyalitas Pelanggandalam Pembelian Sepeda Motor Yamaha pada PT. Megatama Motor di Makasar.
Delcourt, C., Gremler, D., van Riel, A., & van Birgelen, M. (2013). Effects of perceived employee emotional competence on customer satisfaction and loyalty. Journal of Service Management, 24(1).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Feinberg, R., & Kadam, R. (2002). E-CRM web service attributes as determinants of customer satisfaction with retail web sites. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 13(5).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Hsieh, R., & Petter, Z. (2012). Impact of user satisfaction with mandated CRM use on employee service quality. MIS Quarterly, 36(4).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Khairawati, S. (2020). Effect of customer loyalty program on customer satisfaction and its impact on customer loyalty. International Journal of Research in Business & Social Science, 9(1), 15-23.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Kumar, P., Mokha, A.K., & Pattnaik, S.C. (2021). Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM), customer experience and customer satisfaction: Evidence from the banking industry. Benchmarking: An International Journal.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Metabis, A., & Al-Hawary, S.I. (2013). The impact of internal marketing practices on services quality of commercial banks in Jordan. International Journal of Services and Operations Management, 15(3), 313-337.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Mitussis, D., O'Malley, L., & Patterson, M. (2006). Mapping the reengagement of CRM with relationship marketing. European journal of Marketing, 40(5/6).
Mohammad, A.A., Alshura, M.S., Al-Hawary, S.I.S., Al-Syasneh, M.S., & Alhajri, T.M. (2020). The influence of Internal Marketing Practices on the employees’ intention to leave: A study of the private hospitals in Jordan. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(5), 1174-1189.
Ndubisi, O.N., &Wah, C.K. (2005). Factorial and discriminant analyses of the underpinnings of relationship marketing and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 23(7).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Nejatian, H., Sentosa, I., Piaralal, S.K., & Bohari, A.M. (2011). The influence of customer knowledge on CRM performance of Malaysian ICT companies: A structural equation modelling approach. International Journal of Business and Management, 6(7).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Nguyen, T.U.H., Sherif, J.S., & Newby, M. (2007). Strategies for successful CRM implementation. Information Management & Computer Security, 15(2).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Prentice, C. (2019). Emotional intelligence and marketing. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte, Ltd.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Prentice, C., Lopes, S.D., & Wang, X. (2019). Emotional intelligence or artificial intelligence–An employee perspective. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 1(27).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Rauyruen, P., & Miller, K.E. (2007). Relationship quality as a predictor of B2B customer loyalty. Journal of Business Research, 60(1).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Santouridis, I., & Veraki, A. (2017). Customer relationship management and customer satisfaction: the mediating role of relationship quality. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 12(1).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Sekaran, U. (2010). Research methods for business: A skill-building approach, (4th Edition). John Wiley & Sons, UK.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Sharma, S. (2016). Using SERVQUAL to assess the customer satisfaction level: A study of an urban cooperative bank. Journal of Economics and Public Finance, 2(1).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Sofi, M.R., Bashir, I., Parry, M.A., & Dar, A. (2020). The effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) dimensions on hotel customer's satisfaction in Kashmir. International Journal of Tourism Cities.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed at
Wang, H., & Yu, Z. (2010). The research of customer knowledge management in CRM. paper presented at the Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA). 2010 International Conference, 901-904.
Zahran, P. (2020). The importance of training and development to improve the quality of public service: A phenomenological approach of human resources performance at district offices in Jakarta. Technium Social Sciences Journal, Technium Science, 14(1).
Received: 06-Jan-2021, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-10868; Editor assigned: 08-Jan-2021, PreQC No. ASMJ-22-10868 (PQ); Reviewed: 19-Jan-2021, QC No. ASMJ-22-10868; Revised: 27-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-10868 (R); Published: 08-Feb-2022