Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 1S
Impacting Training Service Quality on Students Satisfaction at Universities in Dong Nai Province
Huynh Thuc Hieu, Lac Hong University
Ngo Quang Huan, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City
Vo Tan Phong, Lac Hong University
Keywords
Student, Satisfaction, Training, Service, Quality, UEH, LHU.
Abstract
In the past, education was seen merely as a non-profit human training career activity. Today, it is under the influence of external factors and especially the impact of the market economy. Education has been seen as an “Educational service” where the customer (students, investors) chooses a service provider to join the university to study with the best fit. Therefore, the paper aims to determine the factors affecting students’ satisfaction based on the training service quality at universities in Dong Nai province. The results showed five factors affecting the training service quality, including the quality of Human Resources (HR), Training Program (TP), Facilities (FA), Support Services (SUS), and Extracurricular Activities (EA). Besides, the training service quality affecting the students’ satisfaction with 1% significance. Finally, the authors proposed some recommendations to enhance the training service quality and the students’ satisfaction at universities in Dong Nai.
Introduction
The modern world has affirmed the significant role of education, in which the quality of training is considered the key to a better world. The part of education is to develop human potential. Education is the most powerful lever to move into the future. Education is also the essential condition for realizing human rights, cooperation, democracy, equality, and mutual respect by Abdullah (2006). In Vietnam, education is based on the realization of the goal of improving people’s knowledge. Education also focuses on training human resources - this is a core team with scientific qualifications, mastery of modern production technology, necessary qualities of workers in a civilized society in all economic fields, socio-culture to meet the requirements of integration and development.
According to Higher Education statistics of the Ministry of Education and Training, from 2018 to 2019, Vietnam has 236 universities, of which 172 are public, and 65 are private universities. This report has exceeded the number of targets set by the Government in Decision No. 37/2013/QD-TTg dated June 26, 2013, on adjusting the network planning of universities and colleges in the 2006-2020 periods. Specifically, the country that has college training by 2020 will have 224 universities and 236 colleges. In today’s highly competitive and globalized university, student satisfaction plays a significant role in the success of an educational institution. In modern society, along with the competition of large and small universities, student satisfaction is one of the most accurate university measures. Therefore, the authors studied the factors affecting students’ satisfaction based on the training service quality at universities in Dong Nai province.
Literature Review
Quality of Training Services (QTS)
In essence, the quality of training service is a relative concept and is understood in many different ways, depending on the problem approach. In each position, people perceive the quality of training services in various aspects. Students, admissions centers, faculty and staff, governments and sponsors, accreditation agencies, and professionals all have their definition of the quality of training services. Each different point of view gives other concepts about service quality by DeShields, et al., (2005).
DeShields, et al., (2005) emphasized that higher education must create high service quality and student satisfaction to ensure sustainability in a competitive service environment. Students are the main customers of a university and directly receive the services provided. The quality of service assessed from the student’s perspective becomes a critical issue by managing universities by Gronroos (1984). Higher education is seen as a business market. That is only successful when we identify customers such as students.
Abdullah (2006) asserts that excellent service quality will become an important goal for most higher education institutions. Therefore, assessing the level of service quality to understand the various factors will enable higher education institutions to design their services.
Student Satisfaction (SS)
Student satisfaction results from a comparison between the effectiveness of the service and what they expected earlier, their response to the perceived difference between experience and expectations they wait. Panagiotis Lykogiannis (2014) said that satisfaction could be associated with feelings of acceptance, happiness, help, excitement, and joy. According to Nino (2019) showed that customer satisfaction is their overall attitude towards a service provider, or an emotional response to the difference between what a customer foresaw and what they receive, for the fulfillment of some need, goal, or desire by Parasuraman Zeithaml & Berry (1985).
According to Kotler & Keller (2010), satisfaction is the degree of a person’s sensory state derived from comparing the results obtained from comparing perceptions of a product with one’s expectations. The expectation is seen here as human expectations. It comes from personal needs, previous experience, and the impact of outside information. Thus, customer perception includes three levels: (1) If the result received is lower than expected, the customer feels dissatisfied; (2) If the results received are equivalent to expectations, the customers feel satisfied; (3) If the results received exceed customers’ expectations, they feel satisfied and excited by Zeithaml, Berry & Parasuraman (2000).
Quality of Human Resources (HR)
Houston & Shelley (2013) assessed the quality of human resources. On the one hand, HR evaluated the employees’ ability to work in physical strength, mental strength, and mental strength compared with specific job requirements to achieve the unit’s overall goals. On the other hand, it evaluates the organization’s activities in the human resource structure to improve the quality of human resources. Nino Tandilashvili (2019) showed that the faculty of academic expression includes elements that describe faculty responsibilities to students such as having a positive attitude, good skills, adequate counseling, and yes Can provide regular feedback to students, faculty for highly specialized, experienced.
Besides, Abdullah (2006) studied the aspect of staff mentioned: the service style and duties of the office staff by paying attention to students. He found out the needs demand of students while creating a sense of peace of mind and safety for students, helping students fulfill their academic obligations. And employees show respect, provide fair treatment and protect confidential information for students by Teerapat & Athapol (2015). The better the quality of the human resource, the higher the quality of training service. Based on the concept mentioned above and studies, the authors proposed hypothesis H1 following:
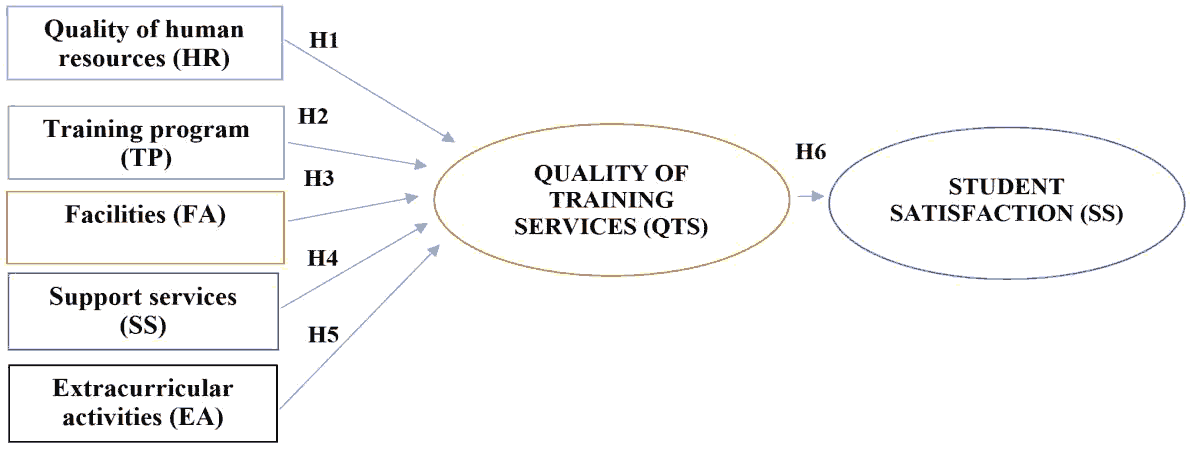
Hypothesis H1 The quality of human resources positively impacts universities’ quality of training services in Dong Nai province.
Training Program (TP)
Luo Siming, et al., (2015) showed that the curriculum elements include the diversity and flexibility of the training program and the quality of the training program. Besides, this element emphasizes providing a broad and reputable offer of academic and specialized programs with flexible structures and curriculum-related issues aligned with the university’s training objectives and the student’s learning goals.
Abdullah (2006) built a curriculum scale on the following aspects: a diverse curriculum with many different majors, allowing students to study further or switch disciplines easily. The universities provide high-quality training programs, content to meet the practical requirements of the profession, combining knowledge and professional skills by Taweena & Chenin (2018). The training program emphasizes subject outline issues, timetables, teaching methods, learning process evaluation processes, and systems that have clear objectives and meets the requirements of knowledge standards, skills, and attitudes. The higher the quality of the training program, the higher the quality of training services. Based on the concept as mentioned earlier and studies, the authors proposed hypothesis H2 following:
Hypothesis H2 Training programs positively impact the quality of training services of universities in Dong Nai province.
Facilities (FA)
Facilities (FA) related to the image of the educational institution. Besides, facilities are also understood as the university’s image through the students’ perceptions by Nino (2019); Abdullah (2006). The facilities are the building of the university’s vision through training and research organization. Abdullah (2006) built a scale of facilities on the following aspects: the university creates a professional image; spacious and modern facilities; full and handy teaching and learning aids; class sizes are limited to give individual students good attention; The university has a convenient location; Students have many opportunities to be recruited after graduation. Sufficient facilities for learning, modern teaching, and learning support equipment. The more modern the facilities are, the higher the quality of training services. Based on the concept as mentioned above and studies, the authors proposed hypothesis H3 following:
Hypothesis H3 Facilities positively impact the quality of universities’ quality of training in Dong Nai province.
Support Services (SUS)
Nino (2009) said that this factor demonstrates the accessibility and ease of communication, readiness, and convenience for educational institutions. Support services have also been identified as a significant factor in the research on service quality from Parasuraman, et al., (1985). Abdullah (2006) built a scale of support services in terms of students are treated fairly and with respect, with confidential information when provided to the university. They can communicate with the easy human office, are encouraged to participate in Union activities, Student Union urged feedback by the university to improve services, operation processes of the university are simple and accessible.
The supporting services factor refers to the university’s ability to access services; convenient, timely, complete, and accurate communication between the university and students... these increase the level of access between the university and the student. The better the support service, the higher the training service quality. Based on the concept mentioned above and studies, the authors proposed hypothesis H4 following:
Hypothesis H4 Support services have a positive impact on the quality of training services of universities in Dong Nai.
Extracurricular Activities (EA)
An educational environment is a set of spaces with individual social activities, means, and exchanges coordinated to create favorable conditions for education to achieve the highest results. Gamage, et al., (2008) suggested that universities can provide and support a wide range of student organizations to meet student’s diverse needs and interests, such as clubs, teams, teams, and groups. Encouraging and supporting students to participate in organizations from their earliest days at university helps them bond with friends and university, enhances social activities and helps students become more engaged in liver function.
es such as clubs, social events held at the university helps to detect student talent and helps students have a healthy playground after stressful hours by Taweena & Chenin (2018). When students fully provide extracurricular activities, they will appreciate the quality of training that the university offers and increase training services. Based on the concept mentioned above and studies, the authors proposed hypothesis H5 following:
Hypothesis H5 Extracurricular activities positively impact universities’ quality of training services in Dong Nai province.
Research on the relationship between the training service quality and students’ satisfaction. The authors proposed the hypothesis following:
Figure 1 : A Research Model for Factors Affecting The Training Service Quality and Students’ Satisfaction
Methods of Research
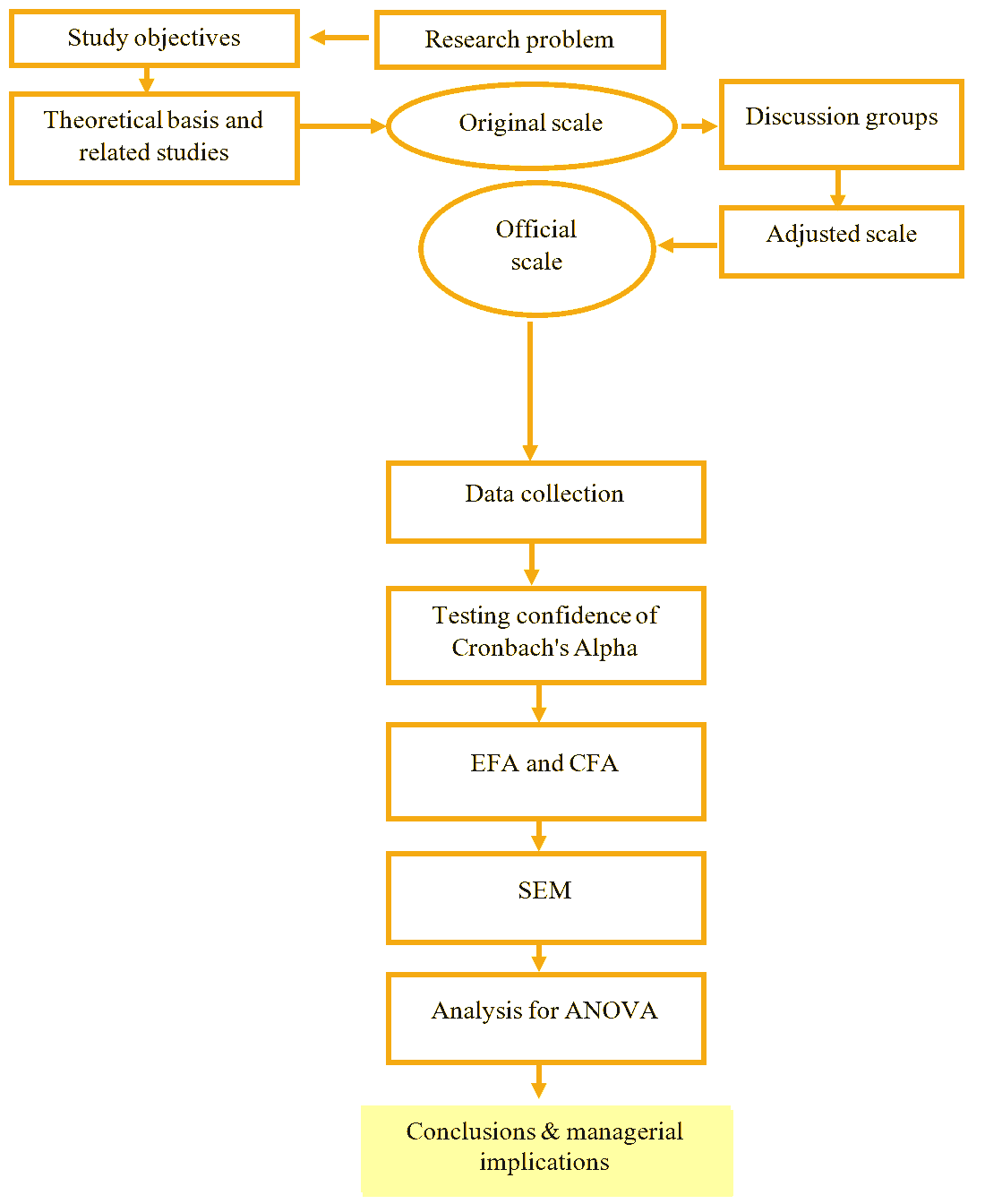
The research methodology of the paper is a combination between qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods.
Qualitative research: the authors had an overview of the theoretical basis and related studies to give a research model and design the initial scale to identify the factors affecting training service quality and satisfaction of students from universities in Dong Nai. Next, focus group discussions were conducted with 30 experts who are educational administrators with extensive experience in education management and final year students by Hair, J., Anderson, Tatham & Black (2010). This method aims to explore the factors affecting the quality of training services and student satisfaction at universities in Dong Nai. Based on the results of qualitative research, the authors adjusted the model and scale to suit the research context.
Quantitative research: the authors had Data for this methodology collected through survey questionnaires. The quantitative study was performed with an expected sample size of n=700 students studying at universities in Dong Nai, selected by the convenient sampling method. Data collection was done through direct interviews with questionnaires designed based on the results of qualitative research by Hair, Anderson, Tatham & Black (2010). The authors used data collected from the survey using SPSS 20.0 and Amos software to test the reliability of the scales with Cronbach’s Alpha’s confidence coefficient, EFA discovery factor analysis, Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and Structural Equation Model (SEM) and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).
With the following steps:
(1) Process survey questionnaires using SPSS 20.0 software;
(2) Descriptive statistics of the variables;
(3) Verify the scale;
(4) Exploratory factor analysis;
(5) Analysis of structural equation model;
(6) Model testing;
(7) The authors proposed the managerial implications.
We can see the research process following:
Figure 2 : A Research Process for Factors Affecting The Training Service Quality and Students’ Satisfaction
Research Results
Table 1 showed that Cronbach’s alpha of the quality of training services (QTS) is 0.941, which meets this technique’s requirements. Specifically, all of Cronbach’s Alpha values are more than 0.6.
| Table 1 Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for Quality of Training Services (QTS) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Items | Cronbach’s alpha | |
| Quality of training services (QTS) | 0.941 | |
| QTS1 | In general, students get jobs as soon as they graduate | 0.928 |
| QTS2 | Students meet the needs of employers and social needs in the stage of international integration | 0.879 |
| QTS3 | Students are equipped with good knowledge, skills, and attitudes when they graduate | 0.933 |
Table 2 showed that Cronbach’s alpha of the student satisfaction (SS) is 0.864 and all of Cronbach’s Alpha values are more than 0.6.
| Table 2 Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for Student Satisfaction (SS) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Items | Cronbach’s alpha | |
| Student satisfaction (SS) | 0.864 | |
| SS1 | Overall, students are satisfied with the quality of training services at the university | 0.842 |
| SS2 | Students will introduce to their friends and relatives about the quality of training services at the university | 0.797 |
| SS3 | Students will continue to use training services at the university in the future | 0.851 |
| SS4 | Students will continue to study higher at the university in the future | 0.812 |
Table 3 showed that Cronbach’s alpha of the support services (SUS) is 0.853, and Cronbach’s alpha of the quality of human resources (HR) is 0.896.
| Table 3 Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for Two Factors Affecting The Quality of Training Services (Qts) |
||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Items | Cronbach’s alpha |
| Support services (SUS) | 0.853 | |
| SUS1 | The staffs and managers care and support students in the learning process | 0.798 |
| SUS2 | Any reasonable requests/responses from students promptly resolved | 0.813 |
| SUS3 | The staffs and managers are willing and able to support students when required actively | 0.844 |
| SUS4 | The university’s service department is courteous, considerate, and responsive to students’ needs | 0.796 |
| Quality of human resources (HR) | 0.896 | |
| HR1 | The lecturers are knowledgeable enough to answer students’ questions related to the major | 0.887 |
| HR2 | The lecturers are considerate and are courteous, and polite to students | 0.865 |
| HR3 | The lecturers are always ready to support and answer students’ questions when facing difficulties | 0.895 |
| HR4 | The lecturers have a positive working attitude towards students | 0.85 |
| HR5 | The lecturers have good pedagogical and teaching skills in their profession | 0.862 |
Table 4 showed that Cronbach’s alpha of the Extracurricular Activities (EA) is 0.962, Cronbach’s alpha of the Facilities (FA) is 0.943, and the Training Program (TP) is 0.862.
| Table 4 Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for Three Factors Affecting The Quality of Training Services (QTS) |
||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Items | Cronbach’s alpha |
| Extracurricular activities (EA) | 0.962 | |
| EA1 | Students have the freedom to study and participate in social activities | 0.935 |
| EA2 | Students treated fairly and with respect by the university when participating in the extracurricular activities | 0.962 |
| EA3 | The university has a psychological counseling department, which introduces extracurricular programs to students | 0.957 |
| EA4 | The university cares and encourages learners to participate in organizations such as Union, Association, and Green Summer | 0.943 |
| Facilities (FA) | 0.943 | |
| FA1 | Classrooms meet the requirements for area, light, and sound | 0.916 |
| FA2 | The university has a sports field, hall to serve the needs of sports and entertainment of students | 0.932 |
| FA3 | The university has a beautiful campus, beautiful landscape, and fully equipped dormitories to meet the requirements | 0.935 |
| FA4 | Modern facilities for study, research and meet the needs of students | 0.918 |
| Training program (TP) | 0.862 | |
| TP1 | The university offers a variety of training programs and training majors | 0.84 |
| TP2 | The training program has clear objectives to meet the requirements of standard knowledge, skills, and attitudes | 0.794 |
| TP3 | The training program is updated every year to meet the needs of human resources in international integration | 0.852 |
| TP4 | The university offers training programs tailored to the needs of the labor market and the career orientation of students | 0.809 |
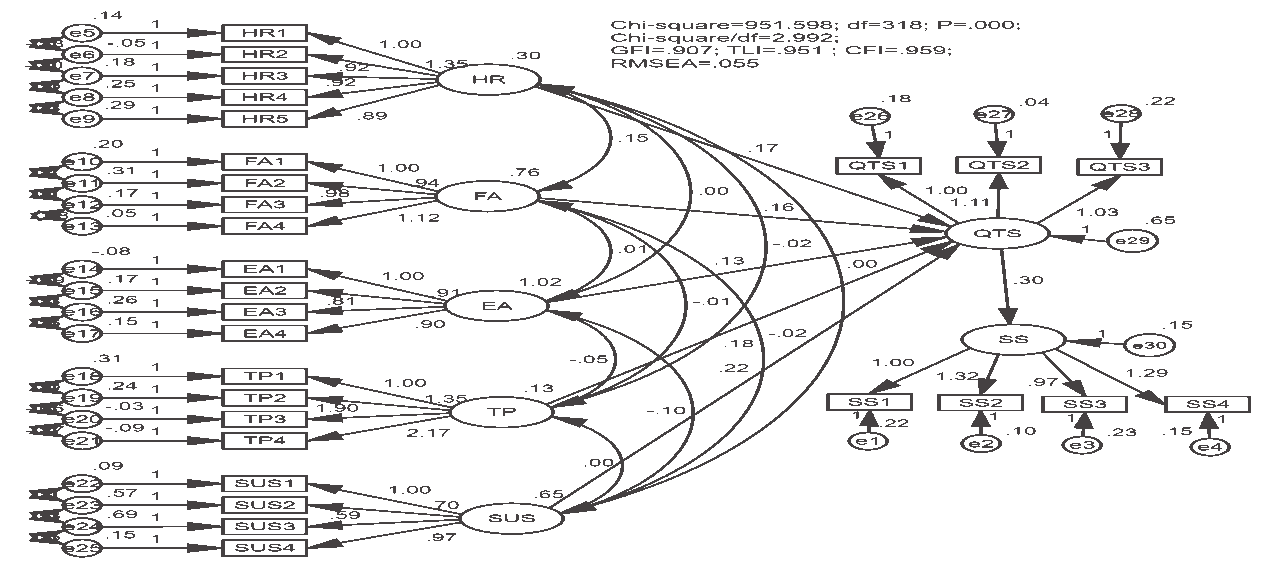
Figure 3 : Testing CFA for Factors Affecting The Quality of Training Services (QTS) and Students’ Satisfaction
Table 5 showed that the assessment of the scale for the quality of training services and students’ satisfaction included: CMIN/DF=2.992 (<5.0), GFI=0.907 (>0.8), TLI=0.951 (>0.9) and CFI=0.959 (>0.9).
| Table 5 Test CMIN/DF for All of The Components |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NPAR | CMIN | DF | P | CMIN/DF | GFI | TLI | CFI |
| Default model | 88 | 951.598 | 318 | 0 | 2.992 | 0.907 | 0.951 | 0.959 |
| Saturated model | 406 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Independence model | 28 | 15880.424 | 378 | 0 | 42.012 | 0.337 | 0 | 0 |
Figure 4 showed that the SEM assessment affected the quality of training services and students’ satisfaction with a significance level of 0.01.
Table 6 showed that five factors affected the quality of training services and the quality of training services affecting the students’ satisfaction with a significance level of 0.01. These results are critical information for managerial implications to enhance the quality of training services and students’ satisfaction at universities in Dong Nai province.
| Table 6 Testing Coefficients for Factors Affecting The Quality of Training Services and Students’ Satisfaction |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relationship | Unstandardized Estimate | Standardized Estimate | SE. | CR. | P | Hypothesis | ||
| QTS | <--- | HR | 0.172 | 0.11 | 0.056 | 3.057 | 0.002 | Accepted |
| QTS | <--- | FA | 0.161 | 0.165 | 0.038 | 4.184 | *** | Accepted |
| QTS | <--- | EA | 0.134 | 0.159 | 0.031 | 4.271 | *** | Accepted |
| QTS | <--- | TP | 0.183 | 0.077 | 0.071 | 2.587 | 0.01 | Accepted |
| QTS | <--- | SUS | 0.219 | 0.207 | 0.044 | 5.02 | *** | Accepted |
| SS | <--- | QTS | 0.301 | 0.552 | 0.024 | 12.756 | *** | Accepted |
Table 7 showed that the bootstrap test results are very good with a sample of 20.000 students. These results indicated that five factors affect the quality of training services, and the quality of training services affecting the students’ satisfaction with a significance level of 0.01.
| Table 7 Testing Bootstrap with 20.000 Students for Factors Affecting The Quality of Training Services and Students’ Satisfaction |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | SE | SE-SE | Mean | Bias | SE-Bias | ||
| QTS | <--- | HR | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.168 | -0.004 | 0.001 |
| QTS | <--- | FA | 0.042 | 0.001 | 0.161 | 0 | 0.001 |
| QTS | <--- | EA | 0.033 | 0.001 | 0.133 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| QTS | <--- | TP | 0.065 | 0.001 | 0.178 | -0.005 | 0.001 |
| QTS | <--- | SUS | 0.043 | 0.001 | 0.215 | -0.004 | 0.001 |
| SS | <--- | QTS | 0.028 | 0 | 0.3 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
Conclusions & Managerial Implications
Conclusions
The authors tested research results based on survey results from 700 students (665 samples processed) studied at universities in Dong Nai province. The results showed that five factors affected the quality of training services and the quality of training services affecting the students’ satisfaction with a significance level of 0.01. The authors evaluated the scale’s reliability through Cronbach’s Alpha coefficients and Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), Confirmation Factor Analysis (CFA), and Structural Equation Model (SEM). Five factors including the quality of Human Resources (HR), Training Program (TP), Facilities (FA), Support Services (SUS), and Extracurricular Activities (EA). Support Services (SUS) have a standardized estimate that is the highest factor in five factors. And, Training Program (TP) has a standardized assessment that is the lowest factor in five elements. Research results are critical and practical information for educational managers to refer to practicum activities to improve the quality of training services and the student’s satisfaction in the future.
Managerial Implications
In the context of international integration and increasing competition in the quality of training services today, student satisfaction is becoming more and more critical and essential. Student satisfaction with the quality of training services is a prerequisite and fundamental in retaining students and building student loyalty. Besides, student satisfaction is simply the universities that create trust and cheerful, positive points in the minds and feelings of students. Besides, student satisfaction is one factor that universities need to follow to shape their training services in the coming time.
(1) The university managers and staffs need to be more polite when communicating with students. Politeness in communication is a crucial factor in maintaining a good relationship between people. So, in contact, there should be a minimum of politeness. Students recognized as educated, aware, and highly educated people; relational object communicates frequently.
Therefore, it requires staff and staff to have primary and essential communication skills to build relationships in university and life, creating a perfect atmosphere, innovative, and polite. Besides, the university managers and staffs need to handle work on schedule with students. They facilitated the quick and straightforward resolution of all students’ questions, avoiding students having to go back and forth repeatedly. The university should have a one-stop-shop under student affairs. The one-stop staff has ethical qualities, professional capacity, dedication to work, a high sense of responsibility, a polite attitude, and an amiable attitude to students.
(2) Classrooms must meet the requirements for area, light, and sound. In addition to factors such as the training program’s content, the curriculum system, reference books, management staff, teachers, area, light, and sound also play a significant role, important, as it helps get the best quality of training. The dormitory should be fully equipped to meet the needs of students. Therefore, the university continues strengthening facilities such as repairing the dormitory. Providing learning facilities such as wifi in the dormitory and modern study rooms in the dormitory will contribute to training the workforce. have quality, well meet the requirements of socio-economic development in the current integration trend. The university managers need to build facilities for adequate learning and meet the requirements of students. Facilities in the university - an essential factor to ensure the requirements of improving the quality of training. There must be multi-purpose classrooms fully equipped with modern machines to meet students and staff’s learning and training requirements. Multi-purpose classrooms practically serve teaching and learning activities.
(3) Students should be treated fairly and with respect by the university. In addition to teaching specialized knowledge, training organizations should focus on soft training skills: Communication skills, teamwork, critical thinking, and problem-solving based on respect for professional ethics and care for students. The university needs to perfect the department of psychological counseling and student job placement. The university needs to build a broad and close relationship with different types of businesses in the province and increase students’ job opportunities. The university should pay attention and encourage learners to participate in activities in organizations of Unions and Associations. Therefore, students need to change their minds: learning is to take knowledge, mature thinking, and life skills are the basis for later going to work, not learning to get a degree.
(4) Lecturers need to care for and treat students more courteously. Each lecturer communicates appropriately, preserving the teacher’s moral character and standards. Absolutely not for profit, a bit of materialism, but do behaviors or have non-cultural behaviors, not for material benefits, but behave erroneously, bias in the classroom. The lecturers should be available to answer students’ questions. Lecturers take learners to the center of the teaching and learning process. Effectively apply advanced and effective teaching methods suitable for each target student such as freshman, a sophomore. Lecturers need to have good pedagogical and teaching skills. Each good lecturer must have a system of highly specialized and profound pedagogical skills and continuously adapt to many different circumstances.
(5) The university should provide various training programs and training majors and enable instructors to continuously update their professional knowledge and technology by participating in training classes and seminars. Professional conferences contribute to increasing the quality of training programs. The university should provide training programs tailored to the needs of the labour market and career orientation for students. Therefore, the university needs to develop training content to help post-graduate students promptly adapt to the digital age and international integration. Training programs need to be updated annually to meet the needs of human resources in global integration. The university needs to build the number of credits, the number of modules for the training disciplines, and the module structure to reduce the time of theory, increasing the time for practice, experiment, and experiment. Students practice and have discussions, self-study on the continuity of modules of branches.
References
- Abdullah F. (2006). HEdPERF versus SERVPERF: The quest for the ideal measuring instrument of service quality in the higher education sector. Quality Assurance in Education, 13(2), 305-328.
- DeShields, O.W., Kara, A., & Kaynak, E. (2005). Determinants of business student satisfaction and retention in higher education: Applying Herzberg’s two-factor theory. International Journal of Educational Management, 19(1), 128-139.
- Gronroos, C. (1984). A service quality model and its marketing implications. European Journal of Marketing, 4(1), 36-44.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (2010). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Houston, D., & Shelley, P. (2013). Knowledge, power and meanings shaping quality assurance in higher education: A systemic critique. Quality in Higher Education, 19(3), 261-282.
- Kotler, P., & Keller, K.L. (2010). Marketing management. Pearson Prentice Hall, USA.
- Lykogiannis, P. (2014). A study of customer satisfaction in greek postal services. International Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities, 1(2), 280-290.
- Ngamkamollert, T., & Ruangkanjanases, A. (2015). Factors influencing foreign students’ satisfaction toward international program in thai universities. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 5(3), 170-178.
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V., & Berry, L. (1985). A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. Journal of Marketing, 49(1), 41-50.
- Siming, L., Niamatullah, Gao, J., Xu, D., & Shafi., K. (2015). Factors leading to students’ satisfaction in the higher learning institutions. Journal of Education and Practice, 31(3), 114-118.
- Songsathaphorn, T., & Chen, C. (2018). Factors influencing students’ satisfaction based on the quality of training service at bangkok university – Thailand. Journal of Economics, Business, and Management, 13(2), 70-78.
- Tandilashvili, N., (2019). Factors influencing student satisfaction in higher education, the case of a georgian state university. Research Association for Interdisciplinary Studies, 1(3), 40-54.