Review Article: 2018 Vol: 17 Issue: 6
Implementing Roadmap Model ahead Indonesian Bureaucratic Reform through Quick Wins Method
Fernandes Simangunsong, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Imelda Hutasoit, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Abstract
This study aims to set forth the Roadmap model on Indonesian bureaucratic reform trough Quick Wins method by which the place was taken in West Java Province as the first model area. The respondents for this study are the regional work unit speaker at West Java Province of 56 people. The data is revealed by interview and focus group discussion. The result of this study indicates that Quick Wins method applied by regional government should meet five parameters: (1) Radically Redesign Public Services to Improve Quality of Service and Cost Efficiency, (2) Restructure The Government’s Approach to Managing Public Finances: Budgeting, Investment and Revenue and Working-Capital Management, (3) Strengthen Functional Leadership and Capabilities Across Government to Support Delivery, (4) Optimize the Government’s Structure, Scale and Operating Model, and (5) Develop the Vision, Accountability and Capabilities Needed to Drive a Large-Scale Transformation.
Keywords
Bureaucratic Reformation, Regional Government, Roadmap Model, Quick Wins Method.
Introduction
By the current globalization era, government including local government can not be the only main actor in national development. There are other actors beside government, for example academics, businessmen, civil society, and diaspora group or migrants overseas who can return to Indonesia any time. Local government needs to understand the changes comprehensively and adjust its way of thinking and acting. In reform era, civil society organizations, political parties and intellectuals (faculties/academics) seem to have a bigger role in creating social changes, especially in the realization of a democratic society. Therefore, it is necessary that bureaucrats change their way of thinking and acting in order to provide well and optimum services to the public (Dwiyanto, 2010).
Lipsky (2010) introduced Street-level bureaucrats term which difined as officials whose duties involve direct interaction with citizens and who have some discretion in carrying out their work. Due to the enforcement of the information disclosure system, information that was exclusively retained by the government in the past can now be disclosed, which grants citizens a means of checking on Government activities (Oh, 2003).
However, some bureaucracies are still unable to completely adjust to changes, either by public demand or competition in globalization era. There are still obstacles to the application of organizational performance and organizational culture properly and efficiently in order to encourage government apparatus to be competent and honest. Other causes are an existing drawback in an information system, inadequate quantity, and quality of government apparatus according to national and international standard, centered-decision making process regarding policy, and not optimal law enforcement. All of those indicate that bureaucratic behavior and culture has not changed significantly, despite the fact that administrative paradigm has changed from centralized to decentralized (Keban, 2004).
Central and local governments define public participation as a mandatory task of public Policy Making Processes (PMPs). Therefore, it is imperative to engage with citizens and take into consideration their opinions throughout any PMPs to ensure the sustainability of public sector policy implementation public participation processes (Leea et al., 2017).
The implementation of regional autonomy for decentralization is a complex and continuous change. In the initial step of decentralization, transfer of various types of authority is conducted from central government to various institutions, especially sub-national government institutions. After the transfer of authority, it is followed by transfer of funding, documents and facilities, and infrastructures. After all those steps above accomplished, it is continued by improvement of the capacity of institutions that receive transfer of authority in order to manage it properly and appropriately. Without appropriate management, transfer of authority from central to local government by which objectives are to develop democracy, to improve effectiveness and efficiency of administration and to distribute social justice, will not be achieved. There will be new sources of inefficiency, ineffectiveness and injustice in regions that can trigger a multidimensional crisis (Silaban & ed, 2012).
Regard with implement regional autonomy according to the Constitution’s mandate, local bureaucracy should be reformed in all aspects, including reform of management in order to be in accordance with dynamics of development of the strategic environment. Management becomes a vital factor in the implementation of bureaucratic reform in order to achieve successful implementation of regional autonomy in Indonesia. This view is in line with opinion by Peter F. Drucker in Savage (1990), the Father of Modern Management, who declined the term “underdeveloped country” for country that lags behind most others. Drucker suggested using term “undermanaged country”, because their lagging behind is mostly caused by poor management. In other words, advancement of a country is very determined by the quality of its management. This mutatis-mutandis also happens in autonomous regions in Indonesia. Moreover, Drucker suggested that the failure of government organization as service institution is caused by three things. First, the managers lack of perception and capacity for business. Second, they need fresh new personnel. And third, its target and output are immeasurable and intangible.
Management reform is Conditio Sine Qua Non for bureaucratic reform in order to realize the successful implementation of regional autonomy. Without reformed management, mistakes did in the past that brought our nation and country to the edge of destruction can repeat itself. Political will to reorganize the management of local government shall return to the stakeholders, especially the sector of local government itself.
Law No. 22 of 1999 and Law No. 32 of 2004 and replaced by Law No. 23 of 2014 on Local Government suggest new paradigms in the administration of local government. This momentum should be used to reorganize bureaucracy at the level of local government, including its management as a system that regulates coordination to achieve its objectives. The condition of bureaucracy in Indonesia in this reform era does not yet show the direction to good development, because of there are still many arrogant bureaucrats acting like an autocrat, and many corruption, collusion and nepotism practices at the level of central, provincial, and Regency/city government. In addition, bureaucrats tend to stay in their comfort zone with more based on seniority instead of competitiveness. A bureaucrat is generally not ready to enter the competitive zone. This is indicated by their refusal on open job-bidding other than simply a formality.
To make bureaucracy reliable and professional, Government has formulated various strategic policies. One of them is Presidential Regulation No. 81 of 2010 on Grand Design of Bureaucratic Reform in Indonesia 2010-2025, followed by Regulation of Minister of Administrative and Bureaucratic Reform No. 37 of 2013 on Guidelines for Preparation of Roadmap of Bureaucratic Reform of Local Government.
To accelerate the achievement of output of change by the bureaucratic reform 9 (nine) Acceleration Programs of Bureaucratic Reform is made. Acceleration program is used by all government institutions, including West Java Province Government, to support the implementation of bureaucratic reform in each institution of Ministry, Agency and Local Government. Those 9 (nine) Acceleration Programs of bureaucratic reform are:
1. Restructuring of Government Organizations.
2. Resetting of Number and Distribution of Civil Servants.
3. Development of Open Selection and Promotion System.
4. Improvement of Professionalism of Civil Servants.
5. Development of integrated Electronic Administrative System.
6. Improvement of Public Service.
7. Improvement of Integrity and Accountability of Performance of Apparatus.
8. Improvement of Welfare of Civil Servants.
9. Increasing of Efficiency in Personnel Expenses.
Based on the overall statement above, this study will focus on how the Roadmap model on Indonesian bureaucratic reform through Quick Wins method and what the parameter, program and activity for Roadmap model on Indonesia bureaucratic reform through Quick Wins method.
Theoretical Background
West Java Bureaucracy Condition
The final objective of bureaucratic reform program is realization government that is free of corruption, collusion and nepotism, accountable and having high performance, and able to provide quality public service. In the implementation of bureaucratic reform in West Java Province Government, it refers to great agenda of bureaucratic reform that covers 9 (nine) areas of change:
Management change
Management Change aims to encourage bureaucratic reform with the systematic and continuous system through well-planned and controlled steps. The target of this program is to trigger commitment of all elements of government to implement bureaucratic reform, to change the mindset and work culture, to reduce the risk of resistance in the implementation of bureaucratic reform.
Management of laws and regulations
One of the programs of bureaucratic reform is expected to increase the effectiveness in the management of laws and regulations issued by Ministries/Agencies/Local Government. The effectiveness can be by reducing the overlapping regulations in all levels of government and increasing effectiveness in the management of preparation and implementation of laws and regulations.
Restructuring and consolidation of organization
Restructuring and consolidation of organization is aimed to resolve problems that frequently occur in the government, especially local government. Main objective of this program is to increase organizational efficiency of ministries/agencies/local government proportionally according to the needs of each organization in order to achieve appropriate functionality and appropriate size.
Redesigning of management
This program aims to increase effectiveness of efficiency of system, process, and work procedure in each institution to be clear, effective, efficient and measurable. Each government organization needs to set machinery of government that connects clearly between structure and process. The target of redesigning of management is to improve the usage of information technology in the administration of government and management of government, to increase efficiency in the process of management of government and to increase performance of government.
Redesigning of human resources management system
One of priority program in bureaucratic reform is redesigning of apparatus human resources management system, which program is expected to create professional and competent human resources with support from transparency and competency-based recruitment and promotion. This program is conducted by improving the recruitment system, job analysis, job evaluation, competency standardization, individual assessment and performance evaluation system.
Consolidation of accountability
This program aims to increase the performance capacity and accountability of government institutions with the final target is to increase the performance and accountability of government. Activities conducted to achieve the target are a consolidation of performance accountability of government institutions, development of performance management system and main performance indicators which begins from the process to make a comprehensive, continuous and transparent plan.
Consolidation of supervision
This program enables the realization of government administration that is clean and free of corruption, collusion and nepotism in all government institutions. The target of this program is improved compliant to national financial management and decreased level of abuse of authority in each ministry/agency/local government. Priority activities are reconsolidation of the role of the internal supervisory system of government by developing an early warning system in case of there is procedure deviation or abuse of authority that potentially lead to criminal corruption.
Improvement of quality of public service
Public Service is one of indicators in the bureaucratic reform of government. Program of improvement of public service quality aims to improve the quality of public service in each government institution according to the public needs and expectation. Activities that support the program are setting of Service Standard, setting of Minimum Service Standard and increasing of public participation to improve quality of public service by Public Satisfaction Survey.
Monitoring, evaluation and reporting
This program aims to ensure that bureaucratic reform is properly implemented according to the rules and target as stated in Roadmap of each ministry, agency and local government.
Materials And Method
This article is using descriptive analytic method as it is used to overview bureaucratic condition in one of Indonesian provinces: Banten. The descriptive analytic will involve the true phenomenon and condition of bureaucracy, and supported by relevant theories. Bureaucratic reform will encourage the achievement of clean government and good governance principles which are universally considered as principles required providing excellent public service. In bureaucratic reform, there are several change areas in which changes will have impacts such as declining practices of corruption, collusion and nepotism, better quality of policy and public service management, the better productivity of apparatus, the increased welfare of civil servants, and real output of development felt by whole society. This condition can be achieved by several attempts such as the application of Quick Wins.
By the application of Quick Wins, or also known as Low Hanging Fruit, it is expected to provide positive initial momentum and self confidence to implement bureaucratic reform consistently and continuously. The output of the implementation of Quick Wins is improved system and work mechanism or better main product of Central and Local Government of province and regency/city according to their own main duties and functions and characteristics.
To watch and guide the implementation of Quick Wins, it is necessary to understand how the implementation should be. The objectives of Quick Wins are: (1) to provide guidelines for Central and Local Government in determining and implementing Quick Wins; and (2) to provide guidelines for Central and Local Government in monitoring and evaluating the implementation of Quick Wins
Besides, Quick Wins should meet criteria as follows:
1. It derives from programs of bureaucratic reform, which is stated in the Roadmap of Bureaucratic Reform 2016-2020.
2. It is part of the core business role, duties, functions, and characteristics of concerned Central and Local Government.
3. It gives the great corrective impact that can be felt by external and internal stakeholders of Central and Local Government.
4. It is real activity by which benefit can be felt by external and internal main stakeholders of Central and Local Government.
There are 9 quick wins programs of bureaucratic reform, are:
1. Campaign of national movement of mental revolution in the sector of state apparatus.
2. Implementation of effective, efficient and accountable organization of working cabinet ministry.
3. Consolidation of transparent, competitive, integrated, and merit-based management of state civil apparatus.
4. Accomplishment of special issues in recruitment of state civil apparatus.
5. Acceleration of operationalization of state civil apparatus commission to accelerate the application of merit system in the appointment of high chief officer.
6. Consolidation of public services in one-stop integrated services.
7. Competition of national public service innovation to accelerate improvement of the quality of public service.
8. Consolidation of performance accountability and integrity of government institution by evaluation on performance accountability level, evaluation on service unit in central and local government that have declared the integrity zone, and also issuance of policy on performance agreement and performance reporting.
9. Improvement of effectiveness and efficiency in government administration by issuance of circular letter of minister of administrative and bureaucratic reform on cost saving of operational activities, usage of facilities and infrastructures, and utilization of domestic products.
By the application of descriptive analysis method on highlighting Banten’s bureaucratic condition in the term of its kind of new method of bureaucratic reform by using Quick Wins method, it is essentially expected to be beneficial for reader to enlarge the insight on government research under the research of descriptive analysis. This style of analysis is coherently matched to the researched topic, because in analyzing the eligibility and space for applying Quick Wins method in bureaucratic reform, the writer(s) uses relevant theories and bases as those are still concerned to the essential discussion of this research.
DISCUSSION
Roadmap Model on Indonesian Bureaucratic Reform through Quick Wins Method
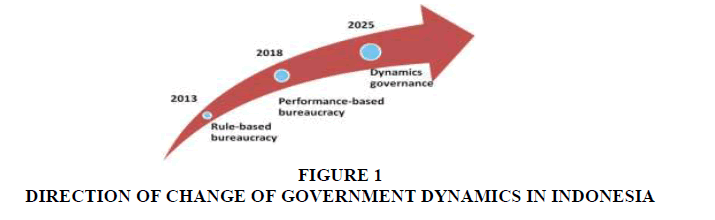
Vision of bureaucratic reform that is stated in the Grand Design of Bureaucratic Reform of Indonesia is “Realization of World Class Government in 2025”. This vision is reference for any level of government, including West Java Province Government. World Class Government is administrative system with basis of information and communication technology and support by professional and high integrity bureaucrats that are able to implement excellent public services and adapt with recent development of administrative management and to develop democratically (Silaban & ed, 2012).
The step for change is from Rule-based Bureaucracy. This view is heavily influenced by Max Weber’s view that was developed in 1800. The next step is Performance-based Bureaucracy, with measurable culture in terms of performance. The next step is towards dynamic governance with characters of “Thinking Again”, “Thinking Across”, and “Thinking Ahead”. The explanation can be simplified in figure as follows (Neo & Geraldine, 2013).
The missions of bureaucratic reform of Indonesia to become dynamic world-class government Indonesia are:
1. To make/complement laws and regulations for realization of good governance that is free of collusion, corruption and nepotism.
2. To reorganize and consolidate organizations into new generation of organizations that have slim structure and rich functionality, management with standard operational procedure, human resources management for competitive and high performance apparatus, professional supervision from the bottom to top level, accountability with check and balance principle, zero complaint quality of public services, mindset that is free from ethnicity, religion, race, and inter-group relations context, and cultural set that make bureaucratic culture into more professional.
3. To develop effective control mechanism from central to regional with transparency and high discipline in its operational system.
4. To manage administrative disputes effectively and efficiently according to development of sources of regulation.
Bureaucratic reform in West Java Province is not detached from Vision and Missions of West Java Governor Period 2013-2018, especially on the third mission that emphasizes on: Improving Administrative Performance, Apparatus Professionalism, and Extension of Public Participation, in which becomes the cornerstone for Local Government Agencies to prepare make strategic programs in order to achieve “West Java with World Class Bureaucracy” inter alia, emphasizing on (Silaban & ed, 2012):
Sector of development planning
Through strategy (1) improvement of control and evaluation on regional development that is integrated, open, up to date and online, (2) improvement of quality of regional planning that refers to accelerate the achievement of nawacita (nine priorities) in whole West Java region, (3) Improvement of quality of study and research for regional development that collaborates with existing universities in West Java Province.
Sector of communication and information
Through strategy to (1) development and application of information technology in administrative management into management networking and quantum organization-based administration that is supported by functional bureaucrats (expert in the science); (2) improvement of Communication Information Technology in public service to be cyber province and most recent level of service, such as stop complain.
Sector of land affairs
Through strategy to Improve effective administrative management with directives to achieve online open, and quick administration order of land affairs to achieve extensiveness in issuance and legalization of land certificate in whole West Java region.
Sector of national integrity and domestic politics
Through strategy to improve public understanding on their political rights and obligation as citizen, with directives (1) improvement of functions of political parties in continuous political education without elements of ethnicity, religion, race, and inter-group relations, (2) Increasing of public participation in political development, (3) Increasing of public participation in general election. Second strategy is to solidify spirit of nationality and statehood, with directive: Improvement of public understanding on national and state ideology.
Sector of Regional Autonomy, General Administration, Regional Financial Administration, Local Agencies, Personnel and Cryptography
The first strategy through Improvement of administrative management is to do: (1) Restructuring of proportional organization, (2) Improvement of organizational administration service, (3) Accomplishment on clarity of administrative borders, (4) Acceleration on Public Treatment and Service, (5) Improvement of transparency of accountability fund through development of integrity zone, (6) Management of regional finance, (7) Improvement of regional financial management and reporting service, (8) Maintenance of Unqualified Opinion Financial Report of West Java Province Government, (9) Increasing of local revenue according to potential, (10) Improvement of control and evaluation of regional development, (11) Improvement of coordination with vertical institutions in resolving problematic local assets, (12) Improvement of Implementation of Government Internal Control System, (13) Improvement of internal supervision to support management and performance of local government administration, (14) Redesigning of management of population affairs and civil registration administration.
The second strategy is to improve facilities and infrastructures to support public service with directive of improvement and maintenance of facilities and infrastructures to support apparatus performance. The third strategy is to improve cooperation in development with several directives: (1) Improvement of strategic cooperation and partnership between provinces, central government, and regencies/cities, (2) Improvement of quality of West Java cooperation management by strategic alliance between domestic and foreign parties. The fourth strategy is to improve human resources quality of local apparatus, with directives: (1) Improvement of competency-based knowledge, skills, and behavior of apparatus, (2) Improvement of performance-based performance of apparatus. The fifth strategy is to re-organize legal system at local level with several directives: (1) Preparation of local legal products to support government administration, (2) Improvement of harmonization of local regulations, (3) Improvement of synergy in handling issues together with other agencies.
The sixth strategy is to improve law-abiding culture, with directive of improvement of public understanding on laws and regulations and Human Rights. The seventh strategy is to increase synergy of the implementation of public security and order with several directives: (1) Improvement of control of public security and order, public security unit, and other trained civil defense units, (2) Improvement of quality and quantity of Civil Service Police Unit and Civil Servant Investigator of West Java. The eight strategy is to improve public understanding on their political rights and obligation as citizen with directive to improve capacity of legislative institution and intensity of communication between local government and Regional People's Representative Assembly.
Sector of public and village empowerment
It is a strategy to improve capacity of village administration and public participation, with directives: (1) Improvement of village administration performance by improvement of financial capacity and facilities and infrastructures of village administration, (2) Improvement of stewardship on village apparatus, (3) Improvement of organizational capacity and public participation in development, (4) Improvement of Village Infrastructures.
Sector of statistics
A strategy to improve effective administrative management directed to improve the management of one data of development.
Sector of archiving
Through strategy to improve effective administrative management, with directive to achieve management of local archiving that support the performance of local government administration..
The Parameter, Program and Activity for Roadmap Model on Indonesia Bureaucratic Reform through Quick Wins Method
Bureaucratic reform is an urgent effort and, considering its extensive implication for public and the state, it needs serious efforts to have well-implemented and continuous bureaucratic reform. For West Java Province, appropriate Quick Wins can be formulated to be implemented by all components of local government with concept of “No Superman but Super Team” with model as follows.
Parameter I: Radically Redesign Public Services to Improve Quality of Service and Cost Efficiency
Based on this Parameter, West Java Province Government decides the spectacular programs and activities of Quick Wins 2016-2020 that reflects the realization of “world class government” as follows:
To inventory various public services in each Local Government Agency those are provided for free (such as making of e-ID card). If there is regulation that inhibits it, the regulation can be amended. And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of the planning of free service.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the implementation of services to be made free.
3. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the implementation of free services.
To simplify requirements and procedures of services in each Local Government Agency for cost-saving (to avoid making local government bankrupt). If there is regulation that inhibits it, the regulation can be amended. And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of planning of simplification of services.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the implementation of services to be simplified.
3. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to implement the simplification of services.
To make ICT-based impersonal public services that prevent direct contact between provided and public, except for types of service that cannot be replaced by devices. And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of the planning of making of ICT-based public service.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the implementation of services to be ICT-based.
3. Initial, technical and final study for preparation of implementation of ICT-based services.
4. Special training for local agencies assigned for implementation of ICT-based services.
5. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the implementation of ICT-based services.
6. Maintenance of ICT-based service system.
7. Publication of implementation of ICT-based services.
Parameter II: Restructure the Government’s Approach to Managing of Public Finances: Budgeting, Investment and Revenue and Working-Capital Management
Based on This Parameter, West Java Province Government decides the spectacular programs and activities of Quick Wins 2016-2020 that reflects the realization of “World Class Government” as follows:
To re-study the expense management for more effective and efficient and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion of implementation of effective and efficient expense management.
2. Inventorying of all types of expense in all local agencies in detail and openly.
3. Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively for the implementation of accountable expense management.
4. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the implementation of open and accountable expense management.
5. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the implementation of open and accountable expense management.
To spend more funds for development of infrastructures and facilities of public service and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion on optimization of spending funds for development of infrastructures and facilities of public service.
2. Inventorying and prioritizing of fund for development of infrastructures and facilities of public service.
3. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the usage of fund for development of infrastructures and facilities of public service.
To expand territorial development by using Triple-Helix/Quad-Helix/Penta-Helix approach on certain possible sectors and territories And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion of implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta- Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
2. Inventorying of all territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
3. Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively in implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
Consolidation and Amendment of regulations to support the implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix approach on certain possible sectors and territories. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail in territorial development by using all Triple-Helix/Quad-Helix/Penta-Helix approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion of implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta- Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
2. Inventorying of all territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
3. Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively in implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
4. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
5. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail in the implementation of territorial development by using Triple-Helix or Quad-Helix or Penta-Helix approach or using all approaches together on certain possible sectors and territories.
Parameter III: Consolidate Functional Leadership and Capabilities across Government to Support Delivery
Based on This Parameter, West Java Province Government decides the spectacular programs and activities of Quick Wins 2016-2020 that reflects the realization of “World Class Government” as follows:
To consolidate administrative leadership training by providing apprenticeship opportunity in private sector of the same area with concerned Local Government Agency to welcome the using of open career system (Public sector must learn from successful private sector). And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of administrative leadership training by providing apprenticeship opportunity in private sector of the same area with concerned Local Government Agency to welcome the using of open career system (Public sector must learn from successful private sector).
2. Consolidation and amendmend of regulations to support the implementation of administrative leadership training by providing apprenticeship opportunity in private sector of the same area with concerned Local Government Agency to welcome the using of open career system (Public sector must learn from successful private sector).
3. Reward and punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver administrative leadership training by providing apprenticeship opportunity in private sector of the same area with concerned Local Government Agency to welcome the using of open career system (Public sector must learn from successful private sector).
To develop competency-based education and training for human resources of apparatus, both nationally and internationally and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of development and implementation of competency-based education and training for human resources of apparatus, both nationally and internationally.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the development and implementation of competency-based education and training for human resources of apparatus, both nationally and internationally.
3. Reward and punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver development and implementation of competency-based education and training for human resources of apparatus, both nationally and internationally.
Parameter IV: Optimize the Government Structure, Scale and Operating Model
Based on This Parameter, West Java Province Government decides the spectacular programs and activities of Quick Wins 2016-2020 that reflects the realization of “World Class Government” as follows:
To re-structure organization to be slim structure and to avoid overlapping functions and activities between Local Government Agency and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of restructuring of organization to be slim structure and to avoid overlapping functions and activities among all Local Government Agency.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support development and implementation of the restructuring of organization to be slim structure and to avoid overlapping functions and activities among all Local Government Agency.
3. Reward and punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail in development and implementation of the restructuring of organization to be slim structure and to avoid overlapping functions and activities between Local Government Agency.
To build Machinery of Government (MoG) that connects structure and process. To dismiss committee system (except for very specific issues) because all functions have been covered by existing units and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of implementation of Machinery of Government (MoG) that connects structure and process. Dismiss committee system (except for very specific issues) because all functions have been covered by existing.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the development and implementation of Machinery of Government (MoG) that connects structure and process. Dismiss committee system (except for very specific issues) because all functions have been covered by existing.
3. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail in the development and implementation of Machinery of Government (Mog) that connects structure and process. Dismiss committee system (except for very specific issues) because all functions have been covered by existing.
To inventory jobs into three groups: a) by self-conduct; b) by cooperation; c) by contracted to third party, which will have impact on quantity and quality of human resources, administrative facilities and infrastructures, in order for cost-saving. To anticipate policy on moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants that will force the system to redesign ICT-based business process. And the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all types, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively of implementation of inventory of jobs in three groups: a) by self-conduct; b) by cooperation; c) by contracted to third party, which will have impact on quantity and quality of human resources, administrative facilities and infrastructures, in order for cost-saving. To anticipate policy on moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants that will force the system to redesign ICT-based business process.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the development and implementation of inventory of jobs in three groups: a) by self-conduct; b) by cooperation; c) by contracted to third party, which will have impact on quantity and quality of human resources, administrative facilities and infrastructures, in order for cost-saving. To anticipate policy on moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants that will force the system to redesign ICT-based business process.
3. Reward and Punishment for local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the development and implementation of inventory of jobs in three groups: a) by self-conduct; b) by cooperation; c) by contracted to third party, which will have impact on quantity and quality of human resources, administrative facilities and infrastructures, in order for cost-saving. To anticipate policy on moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants that will force the system to redesign ICT-based business process.
Parameter V: Develop the Vision, Accountability and Capabilities Needed to Drive a Large-Scale Transformation
Based on This Parameter, West Java Province Government decides the spectacular programs and activities of Quick Wins 2016-2020 that reflects the realization of “World Class Government” as follows:
To re-design vision and mission of local agencies according to political decision made by political officials and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion of planning, Inventorying of all factors, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively to implement the redesigning of vision and mission of local agencies according to political decision made by political officials.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support development and implementation of redesigning of vision and mission of local agencies according to political decision made by political officials.
3. Reward and punishment to local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the development and implementation of redesigning of vision and mission of local agencies according to political decision made by political officials.
To make big leap of change by benchmarking against units of the same type in other countries and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion of planning, Inventorying of all factors, and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively to make big leap of change by benchmarking against units of the same type in other countries.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the making of big leap of change by benchmarking against units of the same type in other countries.
3. Reward and punishment to local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the making of big leap of change by benchmarking against units of the same type in other countries.
To anticipate the change of system and procedure due to policy of moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotion, Inventorying of all factors and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure comprehensively for anticipating the change of system and procedure due to policy of moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the anticipation of change of system and procedure due to policy of moratorium of increasing of a number of civil servants.
3. Reward and punishment to local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the anticipation of change of system and procedure due to policy of moratorium of increasing of number of civil servants.
To build an accountable organizational culture in order to be accustomed to hold responsible and accountable for each duty and the programs and activities are as follows:
1. Promotionn, Inventorying of all factors and Preparing of Standard Operational Procedure of building the accountable organizational culture in order to be accustomed to hold responsible and accountable for each duty.
2. Consolidation and amendment of regulations to support the building of an accountable organizational culture in order to be accustomed to hold responsible and accountable for each duty.
3. Reward and punishment to local agencies that succeed and fail to deliver the building of accountable organizational culture in order to be accustomed to hold responsible and accountable for each duty.
Conclusion
Based on the overall statement above, it can be concluded that the roadmap model on Indonesian bureaucratic reform through Quick Wins method senses to be an effect ive as it should be applied in 8 sectors: (1) Development planning, (2) Communication and information, (3) Land affairs, (4) National Integrity and Domestic Politics, (5) Regional Autonomy, General Administration, Regional Financial Administration, Local Agencies, Personnel and Cryptography, (6) Public and village empowerment, (7) Statistic, (8) Archiving. Besides, the parameters, programs and activities of Indonesia's bureaucracy reform roadmap model Through the Quick Wins Method must pass 5 (five) phase parameters in a sequence and should be supported by steps: (1), straightening orientation, (2), strengthening commitment, (3), Building a new culture, (4), Rationalization, (5), applying legal standing. In essence, to be successful in bureaucratic reform in West Java Province, the five points mentioned above need to be implemented altogether.
References
- Chin, D., Dimson, J., Goodman, A., & Gleeson, I. (2015). World class government-transformating the UK public sector in an era of austerity-five lessons from around the world. UK: World Class Government.
- Dwiyanto, A. (2010). Restoring public trust through bureaucratic reform. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama
- Keban, Y. T. (2004). Main points of mind inprovment of PNS human resource management system in Indonesia. Journal of Public Policy and Administration, 8(1), 3-17.
- Leea, H., Tsohoub, A., & Choic, Y. (2017). Embedding persuasive features into policy issues: Implications to designing. Government Information Quarterly, 34(4), 591-600.
- Lipsky, M. (2010). Street-level bureaucracy: Dilemmas of the individual in public service (expanded ed.). New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Neo, B.S., & Geraldine, C. (2013). Dynamic governance: embedding culture, capabilities, and change in singapore. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing.
- Oh, G.S. (2003). Information opening and decentralization in the e-democracy. Association of Political Science and Communication Journal, 6(1), 113-144.
- Savage, C.M. (1990). 5th generation management: Integrating enterprises through human networking. Digital Press.
- Silaban, T., & ed. (2012). Toward world class public management, for bureaucratic reform in Indonesia. Jakarta: Secretariat of Vice President of The Republic Indonesia: Jakarta.