Research Article: 2020 Vol: 19 Issue: 5
Information and Analytical Support for Security Management: Conflicts Monitoring in Corporate Governance
Tetiana Momot, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Galina Shapoval, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Oleksandr Vashchenko, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Ksenia Savenko, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Anna Zubenko, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Inna Kraivska, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Svitlana Plotnytska, O.M. Beketov National University of Urban Economy
Abstract
The paper examines the role of transparent information and analytical support for the conflicts monitoring in the corporate governance system to increase the level of corporate security in the condition of decrease in the investment attractiveness of Ukrainian joint-stock companies. The objectives of the study were to: conduct a scientific and theoretical analysis of modern domestic and international experience of the corporate governance conflicts monitoring in security management; investigate the problems of the information and analytical provision of the corporate governance in Ukraine; and propose the model of the information and analytical support for conflicts monitoring in corporate governance system on the example of Ukrainian joint-stock companies. Methods adopted were: abstract-logical analysis, theoretical generalization, systemic and statistical analysis, graphical method. Results revealed that the implementation of transparent information and analytical support of corporate conflict monitoring is the solution for corporate security management. Also, to prevent and solve corporate governance conflicts the proposed model of the information and analytical support for corporate governance conflicts monitoring includes two subsystems - information and analytical support. Corporate governance conflicts monitoring in the system of security management allows to identify potential conflicts of interests and to prevent corporate governance conflicts occurrence, that will result in the stable and efficient operation of corporate enterprises in the long-term period, raise the level of their corporate security and increase their investment attractiveness.
Keywords
Corporate Security Management, Corporate Governance Conflicts, Corporate Security, Conflicts Monitoring, Corporate Enterprises.
Introduction
In today’s interdependent digital world, marked by unprecedented business opportunities but also with numerous and complex, the theory and practice of corporate security management are fast evolving. In such a challenging business climate, there are significant risk changes in the external and internal environment of the functioning of corporate enterprises, corporate enterprises, which are characterized by the destabilizing factors, namely threats of re-regulation, a decrease in the financial stability of most corporations, a decline in production volumes, an increase in the share of unprofitable enterprises, an increase in the number of bankruptcies, decrease in corporate security and existence of corporate conflicts in the system of corporate governance.
Problems of corporate governance are permanent and typical for Ukrainian enterprises for a long period (Shkurupiy, 2000; Momot et al., 2015a; Nikolaichyk & Grynyshyn, 2019). Thus, researches in the last decade have shown that problems of corporate governance have a negative impact on the investment attractiveness of Ukrainian joint-stock companies (Benedysiuk, 2019). Poor corporate governance, including a low level of corporate security, was one of the main problems which have led to restrictions of investments into the Ukrainian economy according to the opinion of 57% of American investors, who were the respondents in a survey made by Segura (2016). The main problems of corporate governance in Ukraine, which were mentioned by American investors were: 1) absence of shareholder’s protection in case of restricting their rights by companies’ managers or owners; 2) insufficient transparency of information public disclosure (is considered to be the main problem of corporate governance in Ukraine); 3) absence of appropriate legislation and normative standards in the sphere of corporate governance, which results in dishonest behavior of company’s management; 4) complexity of quarrel procedure concerning illegal actions of management and owners of the company (Segura, 2016). The situation has not changed for better for the last five years and such problems of corporate governance as poor protection of minority shareholders’ interests and ignorance of their rights remain in Ukrainian enterprises and lead to a decrease in their competitiveness and investment attractiveness (Redziuk, 2019). According to the data of World Economic Forum (2019), majority of the problems Ukraine had in corporate governance in 2019 are the following: the strength of auditing and accounting standards (118 place among 141 countries), conflict of interest regulation (85 place among 141 countries) and shareholder governance (55 place among 141 countries) (Schwab, 2019). Besides, the “protection of minority shareholders’ interests” is one of the key indicators for assessing corporate governance level and global competitiveness index of Ukraine. According to this indicator, Ukraine is on the 129th place among 137 countries, which also emphasizes the necessity of corporate governance conflicts monitoring in the system of corporate security and proper information and analytical support of this process providing (Schwab, 2018).
Theoretical Background
The provision of corporate security is one of the indicators of a high level of corporate governance, which is an object of study for economists in Ukraine and abroad (). There are several approaches to defining the concept of corporate security. Corporate security management literature reflects the prevailing shift toward a comprehensive view of general principles of security, together with a methodical approach to solving security issues, making logic, creativity, and skills are in the ability to correctly blend and apply the essence of corporate security in new circumstances to meet new challenges (Cabric, 2015; Campbell, 2014). Simultaneously, in the current authors previous research, it was proved that the influence of each group of stakeholders on corporate security in the system of corporate governance should be taken into account (Momot et al., 2015b). Protection of shareholders' rights supposed to be the central issue of corporate governance and the most important one for companies operating in emerging markets (International Finance Corporation, 2010). Problems of corporate governance in Ukraine, including shareholder’s rights protection, are considered to be solved on the legislative level (Povazhnyi & Orlova, 2012), as well as on the level of corporate governance through the integrated corporate reports (Kuzina, 2015).
Corporate governance conflicts are considered to be one of the main threats to corporate security, which is especially topical for Ukraine, taking into account imperfection of legislation, poor corporate governance, and low level of the corporate culture. Thus, corporate governance conflicts are to be monitored to reduce the possibility of their appearance. This might increase the level of corporate security. To reduce the number of corporate governance conflicts, some researches are devoted to the investigation of the types of corporate governance conflicts in the system of economic security, their reasons and the possibilities to minimize them (Kotov & Mozgovaya, 2015).
Measures on reducing agency problems amount are also taken by leading world companies. For example, in Japan, the Financial Services Agency enacted a Stewardship Code in 2014, with a Corporate Governance Code from the Tokyo Stock Exchange entering into force in June 2014. These codes are considered to reduce a number of corporate governance conflicts by “creating a more equal environment among shareholders, ensuring more disclosure and transparency, specifying the responsibilities of company boards, and requiring outside independent directors on company boards” (Marcus, 2015), which will make Japan more attractive to foreign investors. Making amendments in corporate charters is also considered to be one of the ways of reducing corporate governance conflicts (Sasso, 2013). To reduce corporate governance conflicts in the USA, a rule requiring public companies to disclose the pay gap between workers and CEOs was enacted by the Securities and Exchange Commission (Marcus, 2015). Member states of the European Union have enacted boardroom gender quotas to reduce corporate governance conflicts (for example, in Germany new quotas require that from 2016 large companies fill 30% of non-executive board seats with women) (Marcus, 2015). The necessity of potential conflicts of interests between stakeholders monitoring for conflicts minimization is one of the central problems for providing security of financial institutions (Russo et al., 2004). Thus, conflicts in corporate governance is one of the main factors influencing corporate security level, which emphasizes the necessity of their constant monitoring and developing accounting and analytical support for this process.
Research Objectives
The purpose of the paper is to treat the stages of corporate governance conflicts monitoring in the system of corporate security management and to develop the system of information and analytical support for corporate governance conflicts monitoring.
There are three research objectives in this research:
1. to conduct a scientific and theoretical analysis of modern domestic and international experience of the corporate governance conflict monitoring in security management;
2. to investigate the problems of the information and analytical provision of the corporate governance in Ukraine;
3. to propose the model of the information and analytical support for conflicts monitoring in the corporate governance system on the example of Ukrainian joint-stock companies.
Research Method
This study was based on scientific works of domestic and foreign specialists in the field of security management and corporate governance. In the course of processing, studying and analyzing the accumulated materials, a set of general scientific methods abstract-logical analysis, theoretical generalization, systemic and statistical analysis, graphical method combined by a system approach to studying this problem were applied.
Data accumulated from the sources of information published on the official web portal of the World Economic Forum, which contains indicators of the Global Competitiveness Index 2017, 2018, 2019 Rankings.
On the base of the information and data that were compiled and / or collected by the World Economic Forum, International Finance Corporation, State Statistic Service of Ukraine on the base of system approach the model of information and analytical support for conflicts monitoring in corporate governance system is proposed.
Results and Discussion
One of the main problems of corporate security in Ukraine is a violation of minority shareholders’ rights. Outsiders and insiders have different rights regarding shareholding and, consequently, the level of access to confidential information about the performance of the company. To align the capabilities of these categories of shareholders such tools as the general meeting of shareholders and information disclosure have been introduced by legislation. Using these tools outsiders have an ability of corporation activity direct monitoring, as well as an opportunity to participate in decision-making concerning corporate development. However, there is a constant threat of control and management rights redistribution between outsiders and insiders in favor of the latter. This is especially typical for Ukraine, where there is a close relationship between ownership and management and corporate governance is often reduced to the control of the property. Moreover, taking into account the fact that most owners are inclined to authoritarian management style owner is in fact the manager of the corporation (Shkodin, 2012).
International experience shows that there are two basic solutions to corporate governance conflicts. Thus, according to the Anglo-American model of management shareholders may exercise their own right to vote without the presence at the general annual meeting of shareholders. All shareholders who are registered receive a meeting’s agenda with the necessary information, proposals, annual corporate report, and ballots for voting by e-mail. Shareholders may vote by proxy, which means that they fill the ballot and send it back by mail. Sending ballot by mail, the shareholder empowers the Chairman of the Board of Directors to act on his behalf, which is to serve his trustee and to distribute the votes in the way stated in the ballot.
In addition, it is necessary to ensure control over the corporation and corporate governance, which according to the Anglo-American model is made by institutional investors and financial experts and the stock market. Among such professionals are funds (such as index funds and funds that focus on a specific industry); venture capital funds or funds that invest in the new corporation; agencies that assess the creditworthiness of borrowers or the quality of their securities; auditors and funds that focus on bankrupt companies or distressed corporations. This situation is on control of the specific property relations that are based on the multiyear practice of information disclosure.
Ukrainian legislation also gives to the shareholder the right to make decisions on company management at the general annual meeting of shareholders through his representative, but the mechanism of using this right is more complicated, then in the developed countries (Law of Ukraine, 2008). Not all the minorities, who owns a few shares (little amount in comparison with majority shareholders) will be able to visit general annual meeting of shareholders (not because of their reluctance, but because of economic inefficiency, which takes place when the company is situated in another city, for example). So, to ensure the possibility of shareholders using their rights in voting without a personal presence at the general annual meeting of shareholders, it is reasonable to use the example of the Anglo-American model of management concerning the possibility of voting by e-mail. Such change in Ukrainian legislation will enable all shareholders, especially minorities, to affect decisions taken by the general annual meeting of shareholders, which will undoubtedly decrease potential corporate governance conflicts concerning minority shareholders’ rights and will positively influence on corporate security. External control is an important factor for decreasing corporate governance conflicts amount and ensuring a high level of corporate security, but, in contrast to developed countries, the stock market is less developed in Ukraine, besides the information disclosure is also not on a high level of development, which complicate the control procedure. Nevertheless, some steps have been already taken in Ukraine towards information disclosure. Thus, information on the financial activity of corporate companies is in free access and since 2012 financial reports are prepared following international accounting standards. But not all corporate companies prefer to disclose the information on their financial activity. For example, on the 1st of March 2020, only 1388 of Ukrainian corporate companies are public companies (which have to disclose their financial reports) and the quantity of public companies has decreased on 18.3% in comparison with the same period in 2019, and the quantity of private joint-stock companies is 5357 on the 1st of March 2020 (Ukriform, 2020). Besides, problems of information disclosure among shareholders and problems of easy access to information remain unsolved, which raises the possibility of corporate governance conflicts. So it is necessary not only to increase corporate culture level but also to develop mechanisms of information disclosure among all shareholders.
To prevent and solve conflicts in corporate governance it is proposed to conduct their monitoring by the following stages: 1. Planning. At this stage it is necessary to assess the capital structure of the company; to define the parameters which will be evaluated to assess the effectiveness of business management and corporate governance and the owners’ ability to influence the activity outcomes and enterprise policy. 2. Collecting information. At this stage, it is necessary to determine the specific performance indicators that are necessary to evaluate and to create a list of indicators for assessing the quality of corporate governance, complexity and efficiency of decision-making by owners, their possible impact on enterprises; frequency of occurrence and characteristics of corporate governance conflicts. 3. Assessment and analysis. At this stage, it is necessary to assess identified indicators, analyze them, and to make conclusions concerning their potential impact on corporate security. 4. Dissemination. The information is required mainly for investors when deciding on the advisability of buying shares and for the company security service to make decisions on the impact of corporate governance conflicts on enterprise performance and corporate security level. Information can be obtained from financial statements, statutory documents of the company, and for ease of analysis, it should be transformed into appropriate analytical tables depending on the purpose of analysis and required performance. 5. Use of information. Information got during the process of corporate governance conflicts monitoring can be used while developing companies’ strategy and for solving issues of operational business management and managing of corporate security.
To ensure the effectiveness of corporate governance conflicts monitoring it is necessary to provide the proper information and analytical support for this process. Moreover, information support includes both general information about the potential emergence of corporate governance conflicts (corporate code of ethics, compliance policy, and other internal company standards, presence or absence of which and their content shows a potential possibility of corporate governance conflicts occurrence) and accounting information on company’s activity. Analytical information involves the calculation of proper indicators and parameters of corporate security level assessment and creating analytical tables to analyze information and simplify the process of monitoring.
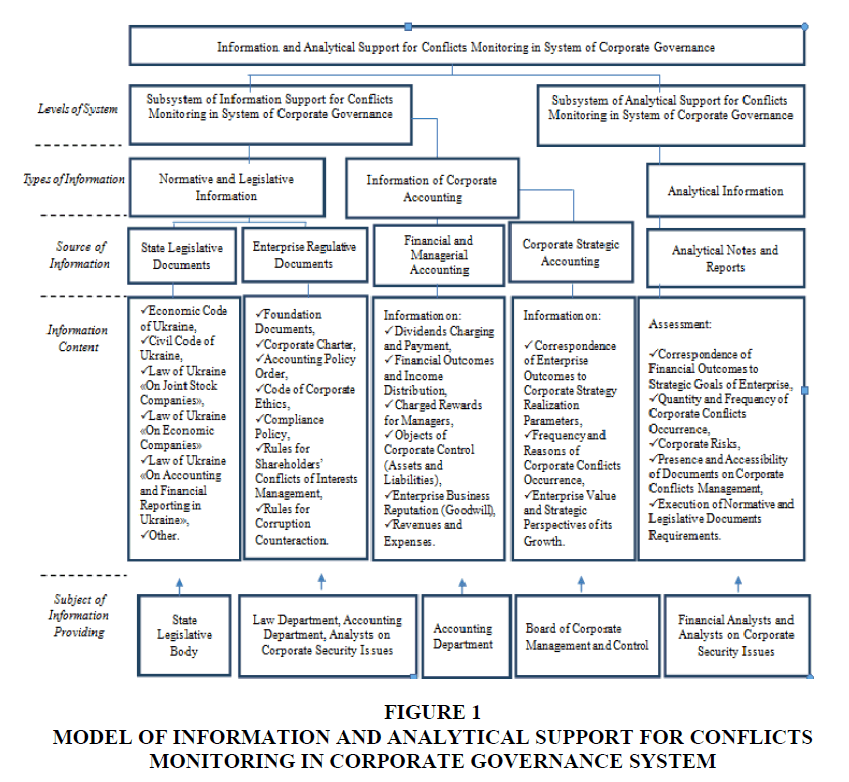
System of information and analytical support for corporate governance conflicts monitoring, proposed by the authors (Figure 1), includes two subsystems – subsystem of information support and subsystem of analytical support. The subsystem of information support includes two types of information – normative and legislative information on levels of the country and on corporation level, and information of corporate accounting, which should include not only financial information from financial and managerial accounting but also information of strategic accounting, which should be prepared by the bodies of corporate management and control and by accounting office concerning strategic aspects of corporate enterprise activity, corporate enterprise value and strategic perspectives of its change and information concerning occurrence and reasons of corporate conflicts, which have already taken place at an enterprise.
Figure 1 Model of Information and Analytical Support for Conflicts Monitoring in Corporate Governance System
Financial analysts and analysts on corporate security issues should prepare analytical reports and calculate parameters for assessment of corporate governance conflicts and their influence on the corporate security level, assess the level of corporate governance conflicts regulation by the enterprise, and evaluate correspondence of achieved economic results to strategic plans of the corporation.
Analytical information should be the basis for making recommendations on corporate governance improving for reducing the number of possible conflicts by taking into account the corporate interests of all stakeholders and strategic perspectives of corporate development.
Conclusions
Competing interests of insiders and outsiders is one of the main problems of corporate governance of joint-stock companies in Ukraine. Conflicts between owners of joint-stock companies between owners and managers not only reduce the effectiveness of the company’s activity but also can lead to serious problems of the company’s functioning, indicating their negative impact on the corporate security level. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor corporate governance conflicts to minimize their negative impact on corporation activity and its security level.
The information and analytical support for the conflicts monitoring in the corporate governance system is defined as the comprehensive system of planning, collection, systematization, analytical processing, dissemination and transmission of sound and reliable information, which allows to monitor corporate governance conflicts and to harmonize the interests of all groups of stakeholders with the interests of the environment, taking into account the peculiarities of the corporate enterprises. Corporate governance conflicts monitoring in the system of corporate security management allows security managers to identify potential conflicts of interests and to prevent corporate governance conflicts occurrence, that will result in the stable and efficient operation of corporate enterprises in the long-term period, raise the level of their corporate security and increase their investment attractiveness. Normative and legislative information, information of corporate accounting, and analytical information is the basis for making recommendations on corporate governance improvements to reduce the number of possible conflicts by taking into account corporate interests of all stakeholders and strategic perspectives of corporate development.
References
- Benedysiuk, S. (2019). Problems of investment attractiveness of Ukraine. Retreived from https://www.mondaq.com/inward-foreign-investment/786710/problems-of-investment-attractiveness-of-ukraine
- Cabric, M. (2015). Corporate security management: Challenges, risks, and strategies. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Campbell, G. (2014). Measures and metrics in corporate security. Elsevier.
- International Finance Corporation (2010). Corporate governance: Manual. Vietnam: BACSON. Retreived from https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/c09ff531-b7a6-405a-bbd6-89780979f271/CG+manual+for+Vietnam-second+edition-Eng.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CVID=jog7Uju
- Kotov, A.M., & Mozhova, L.O. (2015). Corporate conflicts in system of economic safety of enterprise. HeraldofTransportEconomy and Industry), 49, 127-131.
- Kuzina, R.V. (2015) Corporate accounting and reporting in Ukraine: Modern state and perspectives of development. Kherson: Grin.
- Law of Ukraine. (2008). On joint stock companies. https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/514-17#Text
- Marcus, L. (2015).3 Factors driving better corporate governance.. Retreived from https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2015/08/3-factors-driving-better-corporate-governance/
- Momot, T., Filatova, I., & Konoplina O. (2015a). Stakeholder-oriented approach to enterprises financial & economic security provision: theoretical and methodical fundamentals of implementation.
- Actual Problems of Economics, 8(170), 36-45.
- Momot, T., Vashchenko, O., Avanesova, N., & Chudopal, A. (2015b) Corporate governance intelligence: Minority shareholder’s aspects (evidence from Ukraine). Chinese Business Review, 14, 210-218.
- Nikolaichyk, O., & Grynyshyn, M. (2019). Corporate governance in Ukraine. Retreived from https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=9e923894-156f-4a59-8386-b9971aa9d27d
- Povazhnyi, O.S., & Orlova, N.S. (2012). Corporate relations in Ukraine: Modern state and perspectives of development.
- Redziuk, E. (2019) State and corporate governance – the path to European values or nowhere? Retreived from https://zn.ua/ukr/macrolevel/derzhava-i-korporativne-upravlinnya-shlyah-do-yevropeyskih-cinnostey-chi-v-nikudi-303670_.html
- Russo, D., Hart, T.L., Malaguti, M.C., & Papathanassiou, C. (2004). Governance of securities clearing and settlement systems. ECB occasional paper, (21).
- Sasso, L. (2013). Capital structure and corporate governance: The role of hybrid financial instruments. Kluwer Law International BV.
- Schwab, K. (2018). The global competitiveness report 2017-2018. Retreived from http://www3.weforum.org/docs/GCR2017-2018/05FullReport/TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2017%E2%80%932018.pdf
- Schwab, K. (2019). The Global Competitiveness Report 2019. Retreived from http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf
- Segura, D. (2016). Investment Climate of Ukraine – 2016. How is it seen by American Investor? Retreived from https://glavcom.ua/publications/investiciyniy-klimat-v-ukrajini-2016-yakim-yogo-bachit-amerikanskiy-investor-doslidzhennya-374495.html
- Shkodin, Y.V. (2012). Problems of corporate governance in Ukraine. Business Inform, 9, 297-300.
- Shkurupiy, K. (2000). OECD the corporate governance environment in ukraine and its impact on corporate performance and finance. Retreived from https://www.oecd.org/daf/ca/corporategovernanceprinciples/1930649.pdf
- Ukriform. (2020). Quantity of joint stock companies is extremely decreasing in Ukraine. Retreived from https://www.ukrinform.ua/rubric-economy/2894505-kilkist-publicnih-akcionernih-tovaristv-v-ukraini-strimko-zmensuetsa.html