Research Article: 2020 Vol: 23 Issue: 3
Internal Quality Assurance Affecting Educational Quality: A Case of Private Universities in Ho Chi Minh City
Thai Dinh Do, Saigon University
Abstract
The internal quality assurance helps private universities identify problems, risks, ethical practices, and opportunities. So, private universities can better serve their students. The information on quality assurance got from a useful review. It is a university's asset, and its value is much higher than the meager cost of training and time the organization has invested. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to explore critical factors that influence the internal quality assurance of the private universities in Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) and educational quality. The authors surveyed 600 persons related to education, such as managers, lecturers, and staff who are working at six private universities in HCMC. Each private university has 100 persons surveyed. The authors applied a random sampling technique and used Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). The study used items on a 5-point Likert scale. Research results showed five factors influencing the internal quality assurance of the private universities and its' impact on educational quality in HCMC with significant at 1.0 percent.
Keywords
Internal, Quality, Assurance, Private Universities and HCMC.
Introduction
Higher education is one of the issues that the Party, the State, and the people pay exclusive attention. This study is reflected in Resolution No. 29-NQ/TW of the Central Executive Committee of the 11th Session on
"Basic and comprehensive innovation of education and training, meeting the requirements of Industrialization-Modernization in the context of a market economy-oriented socialist and international integration"
The Resolution stated that Vietnam's higher education goals are to focus on training highly qualified human resources, fostering talents, developing quality, enhancing self-study capacity, enriching self-knowledge, and creation. According to the Ministry of Education and Training, by the end of 2019, Vietnam has 65 private universities, accounting for 38.2% of the total number of universities nationwide. Vietnam has the growth in the number of universities; the number of students of private universities has also increased accordingly. However, the quality of education for private universities in Vietnam is a controversial issue.
Private universities have during the process of formation and development over 20 years, the quality of higher education in these universities block also showed signs of uncertainty. Specifically, while the scale, the number of student’s increases rapidly, the conditions to ensure the quality of training of some schools are not commensurate. According to a report by the Ministry of Education and Training in 2019, private universities have little initial investment; the primary revenue for serving the university's activities is from the fees. The training capacity of some private universities does not yet meet the number of students the private universities currently have. Specifically, Private universities have the problem with assurances of facilities, laboratory equipment, practices, and libraries, lecturers, workers. Therefore, these facilities do not meet the standards prescribed by the Ministry of Education and Training. The characteristics of faculty members at private universities usually concentrated in two groups. Firstly, the elderly are lecturers with professors and associate professors who have taught at other universities and account for about 5% of the total lecturers of the private universities system. The second is the subject of young lecturers and managers, who have just graduated from universities, so their qualifications are not high and inexperienced.
Regarding facilities, in 2019, there were 12 private universities currently having to rent training institutions, of which 05/12 are training institutions that established over 20 years. Some private universities have too many campuses, the size of a small facility because the managers do not have a long-term vision to create an academic environment. Besides, in some industries in the engineering and technology sector, the conditions of equipment, laboratories, and practice facilities are limited and not updated continuously. The library system of some private universities is weak; the number of learning materials does not meet the research needs of lecturers and students. From the signs of uncertainty about the quality of higher education at the private universities mentioned above, it showed that this is an important issue, affecting the training of high-quality human resources for the country, and reducing public confidence in the quality of education in the country. The above fact also shows the weak management issue in private universities. Therefore, the study finds a relationship as well as measuring the extent of the impact of internal quality assessment on the quality of education at private universities in HCMC to ensure and improve the educational quality. Today, educational quality is an urgent requirement and stemming from this urgency. The motivation of this paper is to help educational managers to improve educational quality in private universities. The authors chose the topic "Internal quality assurance affecting educational quality: a case of private universities in Ho Chi Minh City." This study helps educational managers to improve educational quality in the future.
Literature Review
Internal Quality Assessment (IQA)
Internal quality assessment is a system of policies and procedures set up to achieve four objectives: safeguarding the entity's assets, ensure the reliability of information; ensure the implementation of legal regimes; ensure operational efficiency (Amid, 2016). Quality assurance is to achieve the objective, and it is necessary to develop an internal control system, whereby the system includes specific policies and procedures designed to provide managers with reasonable assurance to fulfill the objectives. Such objectives include: ensuring the reliability of information, property, and bookkeeping, promote operational efficiency, strengthen adherence to proposed policies and procedures. Internal quality assessment is not a phase or a stage of the management process but an inseparable function of management. During the management process, control always exists before, during, and after each orientation or organization activity to implement or adjust each activity (Andreea, 2011). Besides, control understood as the combination of methods to capture and operate the managed object or object. Internal quality assessment is an activity of evaluating and recognizing the extent of the achievement of educational objectives, programs, and contents for schools and other educational institutions. Education quality accreditation includes education institution quality accreditation (referred to as university accreditation) and education program quality (program accreditation). Quality accreditation of educational institutions applies to all educational institutions of all educational levels and training levels (Benneth, 2018). Quality accreditation of educational programs applies to educational programs of the professional, intermediate, college, university, masters, and doctoral levels.
Educational Quality (EQU)
The organization's products and services conform to the stated mission/vision or a set of specifications, requirements, or standards, including accreditation standards and regulatory bodies, and manage. Researchers also said that the quality of higher education is a system of a set of inputs, training processes, and outputs to provide satisfactory education services for employers by meet their requirements and desires (Benneth, 2018). This research continued to assert that in this view, the quality of higher education is a multidimensional concept. These studies all emphasize that the quality of higher education is a multidimensional concept which encompasses all its functions and activities such as academic and teaching programs, research and scholarships, personal students, facilities, equipment, community services, and learning environment (Cenar, 2016). Thus, through the process of studying the concepts of the quality of higher education, the authors found that, although viewed from different angles, the goal of the quality of higher education is still provide human resources to meet the needs of society. So, from the author's perspective, the quality of education understood in the multidimensional concept is a set of inputs, training processes, and outputs to provide educational s (Aquila, 2013). Satisfying employers by equipping learners with knowledge, skills and ethics.
Environment Control (ECO)
According to (Aquila, 2013), the control environment may be the most critical element of the internal control system. The controlling environment is the foundation of the Ethical Culture of Universities and is established at the top level of the organization. Researchers argued that the inclusion of an ethical component in the organization's mission statement is critical, but the effort does not stop there. Senior managers must demonstrate a strong commitment to the development of ethical culture by supporting efforts to improve school integrity and improve the development of ethical reasoning skills in class (Dobre, 2015). Researchers pointed out that a controlled environment is a set of standards, processes, and structures that underpin the organization's internal control. The control environment influenced by a variety of internal and external factors, including the entity's history, market value, competition, and legal situation. Standards, processes define it, and structures that guide employees at all levels in carrying out their responsibilities for internal control and decision making (Ewell, 2010). It creates a principle that helps support the risk assessment of achieving organizational goals, the use of direct information systems, carrying out monitoring activities, and conducting monitoring activities. A well-controlled environment positively impacts the quality of education. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
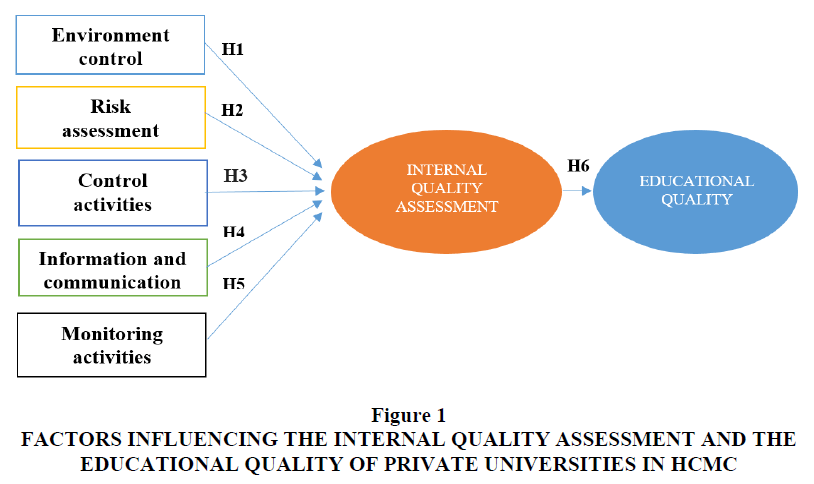
Hypothesis H1: Environment control influencing the internal quality assessment of private universities in HCMC.
Risk Assessment (RAS)
Each unit in the operation process faces many risks from external and internal sources. Researchers had described risk Assessment as identifying potential errors and designing control measures to prevent or detect errors in time. Risk assessment is the process used by an organization to determine how to deal with the risks that threaten its achievement (Fazlic, 2015). According to (Haruti, 2015), risk assessment is a process involving risk identification, risk analysis, and risk management. According to (Kuo, 2014), the risk assessed through the management's awareness of the environment in which it operates and its direct involvement in the day-to-day operations of the organization.
Risk assessment requires identifying organizational goals, identifying risks, and assessing their capabilities and impacts. Therefore, Jones views Risk Assessment as the identification, evaluation, and management of risk. The researcher also further noted that risks might be related to financial reporting fraud or asset misappropriation (Michael, 2016). Risk assessment involves a dynamic and repetitive process for identification. Therefore, it is the basis for determining how the risks managed. The prerequisite for risk assessment is the setting of goals and links at different levels of the entity. A functional risk assessment positively impacts the quality of education. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H2: Risk assessment influencing the internal quality assessment of private universities in HCMC.
Control Activities (CAC)
Control activities are supporting policies and procedures to ensure that management directives successfully implemented. Control provides the means to address the various risks that can hinder the achievement of an organization's goals. In essence, control activities established to deal with identified risks (Savulescu, 2012). Researchers described control activities as policies and procedures that help ensure that management directives implemented.
Control activities carried out at all levels of the unit, at different stages of the business process, and in the technological environment. They may include a range of manual or automatic operations such as licensing and approval, verification, reconciliation, and evaluation of business performance. Task assignments integrated into the selection and development of Control activities (Michael, 2014). When the assignment of duties carried out, the management select and developed alternative control activities. Control activities positively impact the quality of education. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H3: Control activities influencing the internal quality assessment of private universities in HCMC.
Information and Communication (ICO)
In a good organization, an information system is essential to guide the organization's operating process. An information system that creates reports, containing information related to finance, allows the administration and control of an organization (Yusuf, 2018). This factor should include an accounting information system to ensure that the accounting process is valid and reliable. Besides, information required to record and communicated to management and others in the organization who need it and in the space and time allowed for them to conduct audits: internal control and other responsibilities. Effective communication should take place in a broad sense with information up, down, and across organizational divisions. It allows employees to receive a clear message from senior management responsibility control that taken seriously. Relevant and relevant information flows, both internal and external sources, must be identified, captured, processed, and communicated to those who need it in a useful form and time frame (Yusuf, 2018). A piece of great information and communication positively impacts the quality of education. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H4: Information and communication influencing the internal quality assessment of private universities in HCMC.
Monitoring Activities (MAC)
Studies show that Monitoring activities needed to ensure reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of organizational goals; a monitoring process should be in place to evaluate and evaluate internal control systems to ensure that processes consistently applied over a long time. Spencer believes that internal audit is part of the internal control system. Managers should promptly evaluate the findings from the audit and other assessments, including deficiencies and recommendations reported by the auditor and others evaluating the organization's performance. They were thereby identifying appropriate actions to respond to findings and recommendations from auditors and auditors (Savulescu, 2012). The researcher considers they monitored to be a process of assessing system performance over time. On an ongoing basis, employees should evaluate the various internal control systems and update, modify, and upgrade the system as needed. Any deficiencies found are immediately addressed and added to the overall internal control system (Michael, 2014). Monitoring of internal control should include policies and procedures to ensure that the results of audits and other assessments addressed promptly. Monitoring activities positively impact the quality of education. Therefore, the following hypothesis built (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Factors Influencing the Internal Quality Assessment and the Educational Quality of Private Universities in HCMC
Hypothesis H5: Monitoring activities influencing the internal quality assessment of private universities in HCMC.
Hypothesis H6: The internal quality assessment influencing the educational quality of private universities in HCMC
Currently, in scientific research, there are 3 research methods used qualitative research, quantitative research, and mixed research (Hair et al., 1998). In this research, we suggest that mixed research is a methodology based on a pragmatic cognitive system combined with the application of scientific products to solve problems and deals in production and business activities.
Based on previous studies, there is a relationship between internal quality assessment and educational quality. The authors used qualitative research methods by conducting in-depth interviews with experts. The method needed to identify re-determining which internal quality assessment factors the studies mentioned used to measure internal quality assessment in private universities in Vietnam, which factors inconsistent with the Vietnamese context and discovering new factors that have only appeared in private universities in Vietnam but not in previous studies. Factors influencing the internal quality assessment and the educational quality of private universities in HCMC, which had many stages following:
Stage 1
The problem of study: the authors had to identify research issues. The study is a factor that influencing the quality of education at private universities in HCMC.
Stage 2
Goals of the study: the authors find the objectives of the study. The goal is to test factors that influence the quality of education at private universities in HCMC.
Stage 3
Author's research overview and theoretical basis for identifying research objectives and questions. The authors found the study theories and related to internal quality assessment and the quality of education at private universities.
Stage 4
Qualitative method: The authors interviewed 60 experts in educational subjects and internal quality assessment. The authors did preliminary scales based on 60 experts about education and internal quality assessment to improve the scale and design of the surveying of questions. The authors asked 60 experts, and all of them had an agreement that all factors are influencing internal quality assessment and the quality of education at universities in HCMC. This study helps the authors tested the results of qualitative surveys and built a research model.
Stage 5
Quantitative method: Based on the mentioned theories and related to studies as mentioned earlier. The authors built preliminary scales and the preliminary model for factors influencing internal quality assessment and the quality of education at public universities in HCMC after surveying 200 lecturers.
Stage 6
The authors adjusted the study model after testing the preliminary model from 200 samples. This stage helps the model improved.
Stage 7
The authors had an adjustment and refined scale by testing a reliability scale with Cronbach Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. The authors surveyed 400 managers, lecturers, and staff, who are working for six private universities in HCMC. This stage helps preliminary Data, and the study results improved the questionnaire for the quantitative study of 600 persons.
Stage 8
Quantitative study for 600 persons: the authors continued to survey 600 persons, including 100 managers, 400 lecturers, and 100 staffs at six private universities. This sample based on formula n=5*Item (5*29=140). They are working many majors for six private universities by questionnaires. Reliability scale with Cronbach Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis testing. There are 29 items and 588 persons answered, and data collected from July 2019 to April 2020 at six private universities in HCMC.
Stage 9
Cronbach alpha, EFA, SEM: the authors used a random sampling technique and spent 40 minutes for a survey. Reliability scale with Cronbach Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis testing. Next, the authors had continued to confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). CFA showed to clarify: Chi-square testing is P-value > 5 percent; CMIN/df ≤ 2, some cases CMIN/df maybe ≤ 3.0 or < 5.0; GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. Besides, RMSEA ≤ 0.08.
Stage 10
Official model of study: the authors tested the SEM model based on the results of the study (Hair et al., 1998).
Stage 11
Conclusions and Recommendations: the authors analyzed study Data and proposed management recommendations to improve internal quality assessment and the quality of education at public universities in HCMC. This study is to increase the science and objectivity of the research results, the subjects surveyed must ensure the criteria of professional qualifications and seniority in the field of higher education, with many studies and knowledge about internal quality assessment for private universities in HCMC.
Study Results
Study results of the scale reliability testing for factors influencing internal quality assessment and the quality of education at private universities in HCMC.
Table 1 showed that Cronbach's Alpha is more significant than 0.6. After obtaining the survey results, the author used Cronbach's Alpha reliability coefficient method to evaluate the reliability of the scale. 29 variables divided into seven components such as Cronbach's Alpha for internal quality assessment (IQA), educational quality (EQU), environment control (ECO), risk assessment (RAS), control activities (CAC), information and communication (ICO) and Monitoring activities (MAC).
| Table 1 The Scale Reliability Tests for Factors Influencing Internal Quality Assessment and the Quality of Education at Private Universities in HCMC | |||
| Items | Content | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |
| ECO1 | Commitment to the integrity and ethical compliance of the university | 0.884 | |
| ECO2 | Roles and powers of the Board administrators | 0.896 | |
| ECO3 | Establishment of authority structure and responsibility | 0.908 | |
| ECO4 | Use qualified staff and develop resource policies | 0.884 | |
| ECO5 | Personal request for reporting and accountability | 0.900 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Environment Control (ECO) | 0.914 | ||
| RAS1 | Determine suitable goals | 0.910 | |
| RAS2 | Identify and analyze risks | 0.933 | |
| RAS3 | Assess the risk of fraud | 0.917 | |
| RAS4 | Identify and analyze significant changes | 0.898 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Risk Assessment (RAS) | 0.934 | ||
| CAC1 | Control activities are set up on a selective basis to minimize risk and achieve goals | 0.916 | |
| CAC2 | Select and develop standard control measures through the use of information technology in control activities | 0.947 | |
| CAC3 | Develop control activities through procedural policies | 0.941 | |
| CAC4 | The manager has to review the policies and procedures enacted | 0.924 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Control Activities (CAC) | 0.948 | ||
| ICO1 | Collect or create quality appropriate, timely information | 0.811 | |
| ICO2 | The manager applies an intranet system to convey information to all staff | 0.807 | |
| ICO3 | The manager publishes information related to the school's activities | 0.841 | |
| ICO4 | The manager set up a Communication Board to collect and answer information from outside subjects | 0.805 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Information and Communication (ICO) | 0.855 | ||
| MAC1 | Managers conduct regular reviews and periodic reviews | 0.920 | |
| MAC2 | The Board of Directors have a review of the results of regular and periodic assessments | 0.936 | |
| MAC3 | The Board of Directors shall take appropriate disciplinary measures when violations occur | 0.930 | |
| MAC4 | The board of management has remedied the shortcomings of the internal control system | 0.913 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Monitoring Activities (MAC) | 0.943 | ||
| IQA1 | Environment control influencing the internal quality assessment | 0.823 | |
| IQA2 | Risk assessment influencing the internal quality assessment | 0.793 | |
| IQA3 | Control activities influencing the internal quality assessment | 0.845 | |
| IQA4 | Information, communication and monitoring activities influencing the internal quality assessment | 0.799 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Internal Quality Assessment (IQA) | 0.856 | ||
| EQU1 | Lecturers assured in terms of quantity, excellent professional competence, practical knowledge, and good relationships with enterprises. | 0.933 | |
| EQU2 | Facilities and equipment for teaching and learning are well-equipped and updated to support training and research activities | 0.921 | |
| EQU3 | Feedback on test results and assessments is sent promptly and helps improve the quality of learning for students | 0.929 | |
| EQU4 | The internal quality assessment influencing the educational quality of the private universities in HCMC | 0.913 | |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Educational Quality (EQU) | 0.942 | ||
Table 2 had a cumulative with 80.025%, and the initial eigenvalues are 1.473. Table 2 had a KMO coefficient of 0.832 and the level of significance with 0.000. The above results divided into seven components following: Environment control (ECO); Control activities (CAC); Educational quality (EQU); Monitoring activities (MAC); Risk assessment (RAS), information, and communication (ICO) and Internal quality assessment (IQA).
| Table 2 Total Variance Explained Testing for the Internal Quality Assessment and the Quality of Education at Private Universities in HCMC | |||||||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | |
| 1 | 7.482 | 25.800 | 25.800 | 7.482 | 25.800 | 25.800 | 5.620 |
| 2 | 3.785 | 13.050 | 38.850 | 3.785 | 13.050 | 38.850 | 3.739 |
| 3 | 3.440 | 11.864 | 50.714 | 3.440 | 11.864 | 50.714 | 4.477 |
| 4 | 2.687 | 9.265 | 59.979 | 2.687 | 9.265 | 59.979 | 3.511 |
| 5 | 2.522 | 8.698 | 68.676 | 2.522 | 8.698 | 68.676 | 5.115 |
| 6 | 1.818 | 6.269 | 74.945 | 1.818 | 6.269 | 74.945 | 2.969 |
| 7 | 1.473 | 5.079 | 80.025 | 1.473 | 5.079 | 80.025 | 4.705 |
| 8 | .771 | 2.660 | 82.685 | ||||
| ? | ? | ? | ? | ||||
| 29 | 0.062 | .215 | 100.000 | ||||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy: 0.832; Sig is 0.000 | |||||||
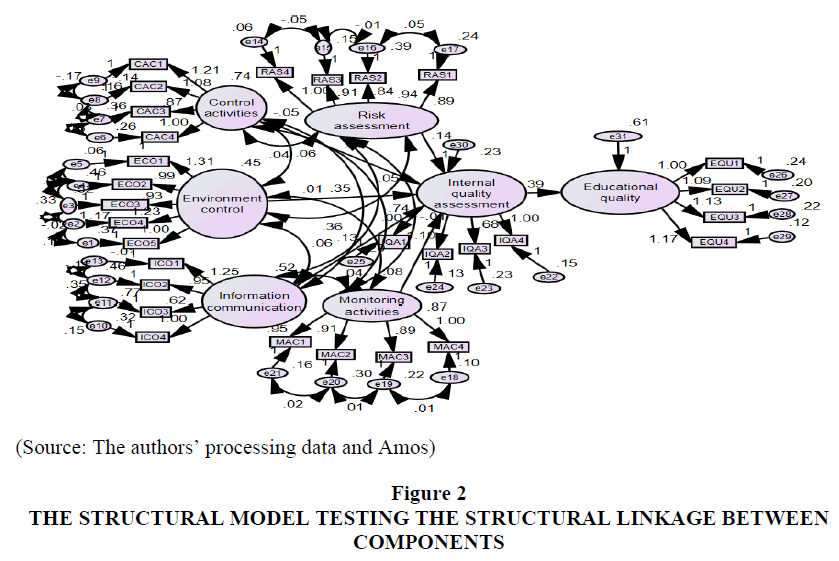
Table 3 showed that P value is 0.000 (<0.01) and hypothesis accepted. Besides, the unstandardized coefficients of environment control; control activities; educational quality; monitoring activities; risk assessment; information and communication and internal quality assessment are positive with significant at 1.0 percent. These results showed that five factors are affecting the internal quality assessment and the internal quality assessment affecting the quality of education at private universities in HCMC with significance level 0.01. Chi-square=1283.767; df=345; p=0.000; Chi-square/df=3.721; GFI=0.971; TLI=0.928; CFI=0.939; RMSEA=0.068 (Figure 2).
| Table 3 Coefficients from Testing Structural Equation the Modeling (SEM) | ||||||
| Relationships of Components | Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | C.R. | P | ||
| Internal quality assessment | <--- | Risk assessment | 0.138 | 0.220 | 4.830 | *** |
| Internal quality assessment | <--- | Control activities | 0.094 | 0.133 | 4.023 | *** |
| Internal quality assessment | <--- | Environment control | 0.352 | 0.388 | 7.859 | *** |
| Internal quality assessment | <--- | Information communication | 0.133 | 0.157 | 4.325 | *** |
| Internal quality assessment | <--- | Monitoring activities | 0.084 | 0.130 | 3.376 | *** |
| Educational quality | <--- | Internal quality assessment | 0.385 | 0.287 | 6.446 | *** |
(Source: The authors? collecting data, SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
Conclusions and Managerial Implications
Conclusions
The primary purpose of quality accreditation of educational institutions is to ensure that specific training standards met and to continuously improve and improve the training quality, to meet the requirements of human resource users. And ensure rights for learners. Through qualitative research methods and quantitative research conducted above, the authors have built a research model and scales used to measure variables of the research model. Through qualitative research, the authors identified and collected 29 elements belonging to seven components of internal quality control. Since then, through quantitative research, the author confirms that the model and the scales used are statistically significant. The results of the study have identified five factors of internal quality control that affect the quality of private schools in HCMC and the importance of internal quality control to the quality of education in descending order are environment control (0.388); Risk assessment (0.220); information and communication (0.157); Control activities (0.133); and Monitoring activities (0.130). Result is scientific evidence which is very important to give views, orientations, and recommendations to enhance the quality of private universities in HCMC.
Managerial Implications
The managerial implication for environment control (0.388). According to the research results, in the control environment, the role, authority, and responsibilities of the school management board are the most important factors affecting the quality of internal control. The University Board needs appropriate qualifications and management to oversee the school's activities. Therefore, the recruitment and appointment of the University Board done carefully. Besides, with the characteristics of non-public school districts, the Board of Directors should have specific and detailed regulations on the rights and responsibilities of the school board. If this stage did, the quality of internal control certainly increased. According to the research results, factors of teaching staff are important and affect the quality of internal control. This factor is in line with reality, because teaching staff is people directly involved in training, teaching, providing educational services for students. The qualifications and competencies of this team have a direct impact on student quality. Therefore, on the one hand, managers need to focus on improving the professional qualifications of faculty members by sending them to study, train, or go on field trips at units and organizations to increase their knowledge. In fact, on the other hand, it is necessary to have good policies to attract and develop high-quality human resources.
The managerial implication for risk assessment (0.220). Private universities need to have provisions on the reporting responsibilities of individuals in the school through the establishment of organizational structure, segregation of responsibilities, and powers. Besides, it is necessary to set up measures for performance evaluation, with incentives and rewards for different levels in the unit. This evaluation should be transparent and fair to all individuals and divisions. Besides, Managers of private continue strengthening and risk control are necessary for private schools in Vietnam. This school sector needs to implement the set of policies, assign tasks to management levels on risk assessment of the above contents. From there, prepare the plans to be ready to deal with the risks that ground out. Private universities need to complete the risk assessment, and the response mechanism is an urgent requirement for all organizations in current socio-political and economic conditions.
The managerial implication for information and communication (0.157). Private universities need to pay attention to currently the internal communication within the unit is done quite well by the schools. Communication carried out in two directions from upper levels of management and lecturers and students up. Individuals in the school receive the necessary information and understand the message from the Board of Directors, the school board. To enhance the effectiveness of internal communication, the school should disseminate documents on regulations, policies, regulations, operating contents as well as communicate instructions to all lecturers. Promptly and fully. Doing this helps lecturers understand the information, understand their duties and tasks, thereby complying with and complying with managers' orders and instructions. Regarding external communication, currently, many private universities have made information on their websites publicly available on the results of educational quality accreditation, reporting on "three public" requirements. Ministry of Education and Training, information related to school activities. Publicity on the mass media increases the confidence of outside parties about the quality of school education. Besides, the school needs to receive feedback from students, alumni, employers, businesses about the quality of education. Based on the processing, analysis, and evaluation of the information collected, university administrators’ review and propose methods for quality improvement.
The managerial implication for control activities (0.133). Private universities need to pay attention to fiscal policy. Public universities must try to increase the income for lecturers with the financial plan that the amount of income increased depends on the study results. Lecturers who conduct a quality study and have international publications must have a better salary than lecturers who do not hold a review. That is why fairness and income gap in such a way create scientific study motivation for lecturers. Public universities need to connect scientific study with doctoral teaching. It is an indispensable trend to improve the quality of science and technology activities as well as teaching high-quality human resources. Experimental research and ethnic minorities have a close relationship with each other.
The managerial implication for control activities (0.133). Research results have shown that loose supervision, bureaucracy is an opportunity for fraud and errors to occur. Therefore, to ensure the improvement of internal quality control, private universities must strengthen their supervision. The supervision at private universities carried out flexibly, combining regular supervision and periodic supervision. Thereby, university managers need to have a review of the results of the monitoring process, specify the deficiencies that occur during the operation, and then develop solutions to overcome them. At the same time, to ensure an effective monitoring process, university should use qualified personnel to participate in the evaluation and evaluation of the implementation of solutions to overcome the consequences of defects. Research results have new points in the research model. However, the research paper is still limited. The subsequent studies should apply probability sampling methods and increases the size of the sample for more accurate analysis results at public universities in other provinces in Vietnam.
References
- Amid, A.A. (2016). Internal control in Tertiary Institutions: Ensuring continuous improvement in the educational system in Nigeria. International Journal of Information, Business, and Management, 8(1), 223-241.
- Andreea, C. (2011). Internal control activities: Cause and effect of a good governance of accounting reportings and fiscal declarations. Annales Universitatis Apulensis: Series Oeconomica; Alba Iulia, 13(2), 339-349.
- Aquila, D.J. (2013). COSO's internal control-integrated framework updating the original concepts for today's environment. The CPA Journal, 8(3), 22-29.
- Benneth, U. (2018). The internal control system as a mechanism for effective fund management of universities in Bayelsa state, Nigeria. Global Journal of Social Sciences, 17(1), 77-91.
- Cenar, I. (2016). Considerations regarding the internal control management system in the university department. Annals of the University of Petro?ani, Economics; Petrosani, 16(1), 61-70.
- Dobre, I. (2015). A brief overview of today's factors impacting the quality of students learning in higher education organizations. The International Scientific Conference eLearning and Software for Education, 3(1), 29-34.
- Ewell, P. (2010). Twenty years of quality assurance in higher education: What's happened, and what's different? Quality in Higher Education, 16(2), 173-175.
- Fazlic, S. (2015). Quality assessment in higher education using the Servqual model. Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 20(1), 39-57.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Haruti, I.S. (2015). Internal control and risk management in ensuring good university governance. Journal of Education and Vocational Research, 6(2), 6-12.
- Kuo, L.C. (2014). Do internal controls improve the operating efficiency of universities. Annals of Operations Research, 22(1), 1-23.
- Michael, O.O. (2016). Internal controls and fraud prevention in non-profit organizations: A survey of selected churches in Lagos, Nigeria. International Journal of Business and Management, 4(6), 240-247.
- Michael, W. (2014). An internal controls tune-up for colleges & universities achieves cost savings & more significant efficiency. Academy of Educational Leadership Journal, 18(4), 245-258.
- Savulescu, I. (2012). Internal control and the impact on corporate governance, in Romanian listed companies. Journal of Eastern Europe Research in Business & Economics, 2(1), 1-10.
- Yusuf, C. (2018). The effects of internal control system on corporate governance: Application in companies within the scope of the best corporate governance index. Mehmet Akif Ersoy University. Journal of Social Science Institute, 10(1), 421-436.