Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 1
Islamic Corporate Culture in Enhancing Employee Engagement
Muhammad Fahri Farid, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Billy Tunas, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Dedi Purwana, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Citation Information: Farid, M.H., Tunas, B., Purwana, D. (2022). Islamic corporate culture in enhancing employee engagement. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S1), 1-8.
Abstract
This study aims to investigate direct and indirect effects of Islamic corporate culture in an effort to improve employee engagement through job satisfaction in a Sharia Bank in Indonesia. This research was conducted with a quantitative approach by using surveys in research. The number of respondents in this study was 274 employees working at a Sharia Bank. This study uses a Likert scale to measure the perspectives of Sharia Bank employees in an effort to create employee engagement. The analytical tool used is the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with the AMOS 24 application’s help. This study is different from previous studies because it involves the effect of variables of Islamic corporate culture and job satisfaction on employee engagement and is carried out at a Sharia Bank. The results of this study significantly indicate an indirect effect of Islamic corporate culture on employee engagement through job satisfaction. However, direct effect of Islamic corporate culture on employee engagement is not significant.
Keywords
Employee Engagement, Islamic Corporate Culture, Job Satisfaction.
Introduction
Islamic banking is one of the driving forces of Indonesia's national economy. The potential of Indonesia's Islamic financial service sector is very large, with a domination of the Muslim population as much as 88.1 percent. Referring to Financial Services Authority (OJK) data, even during the Covid-19 pandemic, the Islamic banking industry continues to grow positively. Evidently, throughout last year, the growth of Islamic banking financing reached 8.08 percent. This growth continued in January 2021 which reached 8.17% on an annual basis. The contribution of Islamic banking assets in the midst of national economic recovery efforts showed an increase of 13.11 percent per year. In order to maintain and improve its performance, Islamic banking is very concerned with the development and improvement of the quality of Human Resources (HR).
A well-functioning organization is the outcome of health, committed and always motivating human resources called “engaged employee” (Siddhanta & Roy, 2010). Companies with engaged employees have high employee retention, decrease employee turnover, increase productivity, profitability, growth and customer satisfaction (Kompaso & Sridevi, 2010). Research on organizational culture or Islamic companies has not been done much, especially in terms of its effect on employee engagement. Some of those who have done so are: Al Shehri et al. (2017), Byarwati (2016); Hoque et al. (2013); Karim & Rehman (2012); and Hakim (2012). They found that Islamic corporate culture has its own characteristics, including: belief in Allah, justice, accountability, honesty, morality, cooperation, ihsan and itqan, in which these characteristics are in line with indicators on employee engagement.
From previous studies as far as the research results, there is no topic that examines the influence of Islamic corporate culture and job satisfaction on employee engagement. Likewise, when viewed from the place used as the object of research, this research is the first research conducted to examine the employees of an Islamic bank in Indonesia as the unit of analysis. In addition, the research variable of Islamic corporate culture is a relatively new variable to be studied, so it provides interest for research, and can be a reference on the influence of Islamic corporate culture on employee engagement.
One of the leading Islamic banks in Indonesia wants to ensure that its organization can effectively support the achievement of its vision and mission. The Bank realizes the importance of keeping the Employee Engagement Index (EEI) at an engaged level, as an indicator of organizational effectiveness. The results of the survey and preliminary interviews show that the level of employee engagement is still not satisfactory at certain levels such as: corporate culture and job satisfaction. In order to maintain and increase the level of employee engagement, through this research, we want to know how the level of employee engagement is and how it affects the company culture and job satisfaction.
This paper consists of five parts. The second part describes various components of theoretical background and hypotheses development on employee engagement, Islamic corporate culture, job satisfaction. The third part discusses research methods on framework, data and measures while the fourth part analyses the findings. Finally, this paper ends with a conclusion and recommendation for future research. The contribution of the research is to create awareness on corporate culture and job satisfaction in order to improve management and operational quality of Sharia banking.
Literature Review and Hyphotheses
Employee Engagement
According to Armstrong &Taylor (2014), the importance of the concept of employee engagement is the heart of the working relationship. According to Gary (2010), poor absenteeism, high turnover, and psychological problems reflect reduced employee engagement. Employee engagement is one form of key work attitudes, namely forms of employee work behavior that can assist management in achieving company performance targets (Kreitner & Kinicki, 2010). In this study, employee engagement is thought to be influenced by Islamic corporate culture and job satisfaction.
Islamic Corporate Culture
According to McBain (2007), one of the factors that supports the formation of employee engagement is organizational culture. Lockwood (2007), also states that organizational culture is one of the factors that influences employee engagement. Organizational culture supports the work and development of employees as well as leads to friendly and helpful working conditions which eventually help shape the nature of being engaged in their work. Hoque et al. (2013) state that organizational culture in an Islamic perspective is a set of values based on the Qur'an, Sunnah, Ijma, and Qiyas that help its members in relation to their understanding of what the organization means, how it works and transforms it. Qudamah (1997) also states several values and work behavior of organizations, such as sincerity, earnestly, empathetically, patiently, consistently, honesty, responsibility, enthusiasm, improvement of work quality, feeling of being watched by Allah at work (muroqobah), always remembering life after death without ignoring the world and communicating as a leader in an effective way. According to Byarwati (2016) those values derived from Islamic principles can be simplified into two main standards of Islamic corporate culture, namely: ihsan and itqan. Ihsan is a picture of one's feelings towards Allah's supervision when doing work (Qudamah, 1997). In a further understanding, it means that an individual strives to be serious in his work, with a relentless dedication to optimization, so as to obtain maximum results. As for Itqan, is to make or do something seriously and carefully so that it is neat, beautiful, orderly and coincidental with each other. The meaning and implementation of ihsan and itqan are indicators of employee engagement. According to Al Shehri et al. (2017), the Islamic organizational culture has an influence on employee engagement. Based on the results of the discussion above, the following are the hypotheses to be tested.
H1 Islamic corporate culture directly has positive influence on employee engagement
Job satisfaction is a person's attitude towards his work which is influenced by the values he adheres to. Job satisfaction criteria for employees in organizations that adhere to Islamic values are certainly expected to follow or comply with Islamic rules or shariah (Yousef, 2000; Markos & Sridevi, 2010). According to Ariyanto (2014) the influence of Islamic organizational culture on employee job satisfaction partially has a significant effect. Based on the results of the discussion above, the following are the hypotheses to be tested.
H2 Islamic corporate culture directly has positive influence on job satisfaction
Job Satisfaction
According to Colquitt et al. (2011), job satisfaction is a pleasant emotional state resulting from job appraisal or work experience. In other words, job satisfaction is a picture of how a person feels about his own job and what he thinks about his job. The same thing is stated by Kinicki & Williams (2011) who argue that job satisfaction is the extent to which he feels positive or negative about various aspects of his job. Their overall satisfaction depends on how they feel about several components, such as the job itself, pay, promotions, co-workers and supervision (Kinicki & Williams, 2011). Based on research by Karim & Rehman (2012) that one of the forms of job satisfaction to increase engagement is to provide salaries according to what employees demand. Although salary is not the only factor, it can be said that job satisfaction can increase employee engagement. Based on the results of the discussion above, the following are the hypotheses to be tested.
H3 Job satisfaction has directly positive influence on employee engagement
According to Ariyanto (2014) Islamic organizational culture has an effect on employee job satisfaction while Karim & Rehman (2012) reveal that job satisfaction can increase engagement. Islamic corporate culture comes from Islamic values that are manifested in the nature of ihsan and itqan. Ihsan is a relentless dedication to work optimistically in order to obtain maximum results. The itqan which is the embodiment of employee engagement defined as doing work professionally. Islamic corporate culture can increase employee engagement if supported by employee work professionalism which is the implementation of the increased job satisfaction. Based on the results of the discussion above, the following are the hypotheses to be tested.
H4Islamic corporate culture indirectly has positive influence on employee engagement through job satisfaction
Methodology
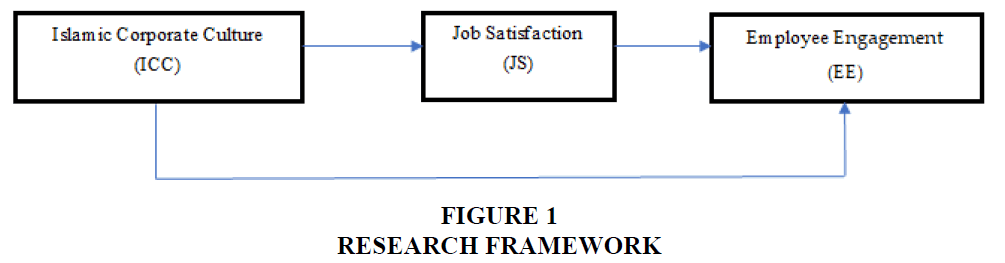
This research is a causal and effect research that looks for the influence between variables. The study uses a survey method using analysis techniques of Structural Equation Model (SEM), by AMOS 24 program and the maximum likelihood estimation approach. Based on the previous studies and the formation of hypotheses, the following is the framework that will be used in this study (Figure 1).
Research Framework
The following is the research framework used:
Sample and Data Collection
The sample in this study includes 274 employees working at a Sharia Bank. The sampling technique is a probability sampling using simple random sampling, regardless of the strata in the population.
Measures
The variables in this study consist of Islamic corporate culture, job satisfaction and employee engagement. Each variable used is measured based on the previous research works. The Islamic corporate culture is measured using following indicators: trustworthiness, excellence, cooperation, sacrifice and Islamic work environment (Qudamah, 1997; Miller & Miller, 2002; Hoque et al., 2013; Byarwati, 2016). The job satisfaction is measured using following indicators: the job itself, quality of supervision, relationship with co-workers, promotional opportunities and salary (Kreitner & Kinicki, 2010; Colquit et al., 2011; Robin dan Judge, 2005). The employee engagement is measured using the following indicators: high energy, persistence, enthusiasm about work, pride in work, totality in work (Dressler, 2013; Armstrong & Taylor, 2014; Hewitt, 2005; W.B. Schaufelli, Bakker dan Salanova, 2006; Gallup, 2004). All questionnaires are measure using a 1-5 Likert scale (Never=1 up to Always=5) and (Strongly Disagree=1 up to Strongly Agree=5).
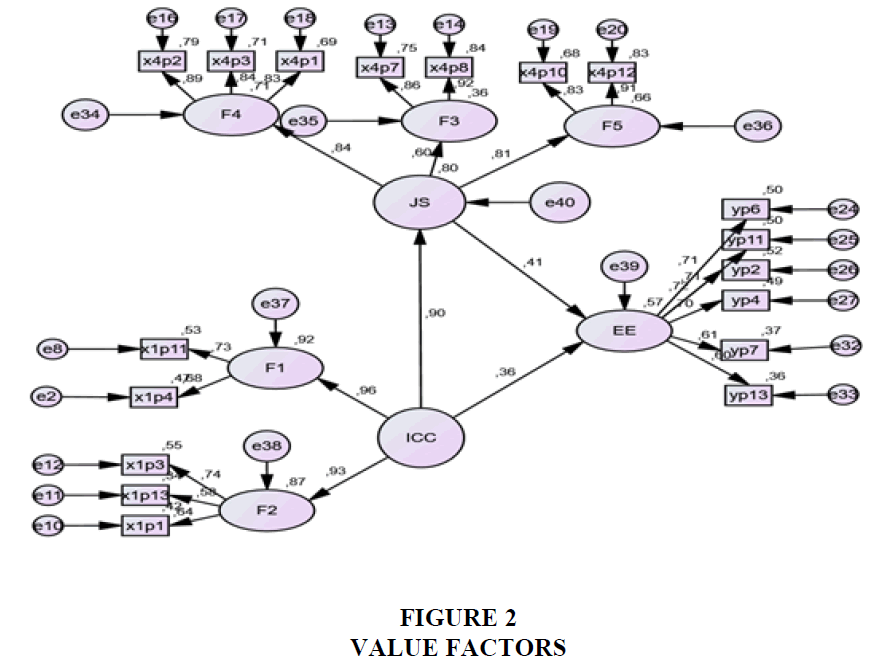
The test results (Table 1 and Figure 2) show that the full model can be categorized to meet the criteria of fit, it’s based criteria have been fulfilled several criteria of goodness of fit. The results of Value CMIN / DF amounting to 1.211 (good) is still below value 2.00. TLI value of 0.986 (good) above 0.90. CFI value of 0.989 (good) whose value is above 0.90. RMSEA value of 0.028 (good) because it is below 0.08. IFI value of 0.989 (good) since it is above 0.90. P value of 0.053 (good) as the value is above 0.050.
| Table 1 Goodness of FIT | |||
| Goodness of Fit Index | Cut off Value | Test Result | Fit/Not |
| P | > 0.05 | 0.194 | Fit |
| CMIN/DF | ≤ 2.00 | 1.149 | Fit |
| CMIN | < 5546.313 | 73.554 | Fit |
| RMSEA | ≤ 0.08 | 0.023 | Fit |
| TLI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.991 | Fit |
| CFI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.994 | Fit |
| NFI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.956 | Fit |
| IFI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.994 | Fit |
| PNFI | ≥ 0.60 | 0.673 | Fit |
| AIC | < 1056.000 | 183.554 | Fit |
Value factors loading all indicators (Table 2) show the estimated value of which the ranges are between of 0.573 and 0.915. This means that this value is above the limit value of 0.5 used as the criteria. According to Hair et al. (2014), a factor loading value above 0,5 is considered good so that all indicators are able to be explained to construct, nothing is dropped and so the model is considered fit and able to be continued to the next test.
| Table 2 Standardized Regression Weights | |||
| Estimate | |||
| x1p4 | <--- | ICC | 0.678 |
| x1p11 | <--- | ICC | 0.744 |
| x1p1 | <--- | ICC | 0.645 |
| x1p13 | <--- | ICC | 0.573 |
| x1p3 | <--- | ICC | 0.752 |
| x4p7 | <--- | JS | 0.870 |
| x4p8 | <--- | JS | 0.913 |
| x4p2 | <--- | JS | 0.885 |
| x4p3 | <--- | JS | 0.837 |
| x4p1 | <--- | JS | 0.829 |
| x4p10 | <--- | JS | 0.821 |
| x4p12 | <--- | JS | 0.915 |
| yp6 | <--- | EE | 0.705 |
| yp11 | <--- | EE | 0.705 |
| yp2 | <--- | EE | 0.720 |
| yp4 | <--- | EE | 0.706 |
| yp7 | <--- | EE | 0.619 |
| yp13 | <--- | EE | 0.601 |
Hypothesis Test and Discussion
In testing the research hypothesis seen from table 3 the p-value testing must be smaller than 5%, whereas the indirect effect test is done with a Sobel test. The following are an estimate and probability table in the results of this study (Table 3).
| Table 3 Hypothesis Test (Direct N Indirect Effect) | |||||
| Est | SE | CR | P | ||
| H1 | Islamic Corporate Culture à Employee Engagement | -0.532 | 0.305 | -1.744 | 0.081 |
| H2 | Islamic Corporate Culture àJob Satisfaction | 0.940 | 0.103 | 9.110 | *** |
| H3 | Job Satisfaction àEmployee Engagement | 1.149 | 0.307 | 3.741 | *** |
| H4 | Islamic Corporate Culture à Job Satisfaction àEmployee Engagement * |
1.080 | 3.442 | ||
The first hypothesis (H1) is rejected because Islamic corporate culture does not have a significant effect on employee engagement (the value of 0.081 means above 0.05), while the magnitude of the effect of Islamic corporate culture on employee engagement amount to 0.532. The results of this study are not in accordance with research conducted by Byarwati (2016).
In testing the second hypothesis (H2), Islamic corporate culture has a significant effect on job satisfaction (because the value is 0.000, meaning below 0.05), while the magnitude of the effect of Islamic corporate culture on job satisfaction amount to 0.940. The results of this study are consistent with research conducted by Yousef (2000) and Ariyanto (2014) which state that Islamic corporate culture has a positive effect and significantly influences job satisfaction.
In testing the third hypothesis (H3), job satisfaction has a significant effect on employee engagement (because the value is 0.000, meaning below 0.05), while the magnitude of the job satisfaction on employee engagement is 1.149. The results of this study are consistent with research conducted by Karim & Rehman (2012) which state that job satisfaction has positive effect on the employee engagement.
For the indirect relationship between Islamic corporate culture and employee engagement through organizational culture (H4), the results of a Sobel test (Table 3) show a value of 3.443 which mean above 1.98, and a p value of 0.000 far below 0.05. So, the indirect influence of Islamic corporate culture on employee engagement through job satisfaction has a significant effect. These results are consistent and support the idea of Ariyanto (2014) and Karim & Rehman (2012) which stating that Islamic corporate culture has a positive effect and significantly influences on employee engagement through job satisfaction.
Conclusion, Recommendations and Future Research
This study has a purpose to analyze direct and indirect effects of Islamic corporate culture that is claimed to be a significant factor to improve employee engagement through job satisfaction in a Sharia Bank in Indonesia. After analysis, this research concludes that Islamic corporate culture does not provides a significant positive influence on the employee engagement. Instead, Islamic corporate culture provides directly positive significant influence on the job satisfaction. The job satisfaction provides a directly positive significant influence on the employee engagement; The Islamic corporate culture provides an indirectly positive significant influence on employee engagement through job satisfaction among employees at a Sharia Bank in Indonesia. In this study, Islamic corporate culture has no direct effect on employee engagement. One of the contributing factors is the Islamic corporate culture that is currently cultivated in general, is still limited to normative Islamic companies (company rules) that have not penetrated and taken root in the hearts of employees. As an example, the sacrifice indicator which has the lowest average indicator (4.164) could be understood that the level of employee sacrifice at work is still standard and has not yet reached the optimal level. At the optimal level of sacrifice, an employee often has to prioritize the interests of the company over other interests.
The problem of employee engagement is a complex, and many factors influence it. In this study, the problem is limited to three main variables, according to the phenomena that arise in the company: employee engagement, Islamic corporate culture, and job satisfaction,
The findings in this study are expected to contribute and provide solutions to various problems faced by the community and can be developed in further studies, especially those related to employee engagement, Islamic corporate culture and job satisfaction.
In an effort to increase employee engagement related to Islamic corporate culture, changes can be made to provide employees with an understanding of the importance of sacrifice in order to achieve company goals. One way to do this is by having the leaders’ gives examples (qudwah). Sacrifice to the company does not mean putting aside family interests or social interests. Furthermore, job satisfaction can be increased by considering the 'salary' indicator because it has the lowest average indicator value. The payroll system should be developed by considering the employee performance and competence factors. Meanwhile, employee engagement can also be increased by considering the indicator of enthusiasm with work because it has the lowest average value of the indicator.
This study is tentative. There are some limitations in terms of data, thus future study can develop similar research by comparing corporate culture of several Islamic banks, not only in Indonesia but in other countries, especially among Islamic banks in South East Asia. This study is making contribution to the research which will create awareness on corporate culture and job satisfaction in order to improve management and operational quality of Islamic banking. This is very crucial as Islamic banking has double roles to improve not only its commercial performance but also social performance.
References
Ariyanto, A. (2014). The influence of Islamic organizational culture and spiritual leadership on employee job satisfaction MQ Corporation Bandung. Scientific Journal of Management Muhammadiyah Aceh, 2(1).
Armstrong, M., & Taylor, S. (2014). Armstrong’s handbook of human resource management practice. Great Britain and the United States: Kogan Page Publishers.
Colquitt, J., Lepine, J.A., Wesson, M.J., & Gellatly, I.R. (2011). Organizational behavior: Improving performance and commitment in the workplace (Vol. 375). McGraw-Hill Irwin New York, NY.
Gary, D. (2010). Fundamentals of Human Resource Management: Content, Competencies and Applications.
Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R.L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis 6th Edition.
Karim, F., & Rehman, O. (2012). Impact of job satisfaction, perceived organizational justice and employee empowerment on organizational commitment in semi-government organizations of Pakistan. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, 3(4), 92-104.
Kreitner, R., & Kinicki, A. (2010). Organizational behavior, 9th Editon. New York: McGraw Hill
Kinicki, A., & Williams, B.K. (2011). Management a practical introduction (6th Edition).New York: McGraw Hill.
Lockwood, N.R. (2007). Leveraging employee engagement for competitive advantage. Society for Human Resource Management Research Quarterly, 1(1), 1-12.
McBain, R. (2007). The practice of engagement: Research into current employee engagement practice. Strategic HR review.
Miller, W.C., & Miller, D.R. (2002). Spirituality: The emerging context for business leadership. USA: Global Dharma Center.
Qudamah, I. (1997). Minhajul qashidin: The path of the guided. Pustaka Al Kautsar.
Siddhanta, A., & Roy, D. (2010). Employee engagement engaging the 21st century workforce. Asian Journal of Management Research.