Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 2S
Risk Management Strategies and Impact on Sustainability: The Disruptive Effect of Covid 19
Saad Darwish, Kingdom University
Anjali Mary Gomes, Kingdom University
Umair Ahmed, Kingdom University
Keywords
COVID-19, Pandemic, Risk Management, Sustainability, Quarantine, Micro and Medium sized endeavors.
Abstract
The intent of this paper is to assess the impact on sustainability due to the outbreak of pandemic. The paper has been carried out on the basis of theoretical review. The outbreak of COVID-19 threw the whole world into a deep crisis. In this time of crisis during the pandemic, enterprises have been through many challenges, so as to say; to the degree that impact of sustainability needed engaging attention. As a result, this avant-garde paper attempts to do a studyof the extent to what COVID-19 all in all; as well as specifically lockdown has impacted sustainability. The researchers have carried out discussion on the many challenges faced by the organizations and economy as a whole and the need to overcome it. The research carried out additionally summaries the lessons learnt from this outbreak and investigate the risk management strategies that emerged as a result of this catastrophic pandemic.
Introduction
December 2019 is the month of pneumonia; this was first knowledgeable in South China in Wuhan's well-known Hubei Province fish market. This pandemic, which widely spread this infection, had influenced countless numbers of individuals in China and foreign nations. The widespread of this infection, on January 23 2020, the Chinese Government had no way out than to hinder all passage and leave in and out of Wuhan (Yue et al., 2020). The remarkable ascent in diseases continued flooding high as it is on record that as of February 15 2020, the amount of affirmed patients with the infection was 68,500 (Sina News, 2020). The current daily number of COVID contaminations worldwide is increasing (Wang et al., 2020). The central issue currently is; how businesses will face the difficulties presented due to COVID-19 in consideration, and what should indeed be possible?
In the United States of America, the previous US Defense Secretary, Rumsfeld, expressed that they are not generally up to date on the forthcoming assaults, which has overwhelmed the world. Between 5 to 10 years, it currently appears that we experience new infections that come in various structures; take, for example, influenza, SARS in 2003 (Wagner, 2020), H1-N1, in 2009; MERS, in 2012; and Ebola, which was also well known in 2014. They are putting forth a valiant effort in countering the impact of this infection. However, such advances and exploration do not yield prompt outcome as they need to go through various testing, particularly for created immunizations to be utilized by people. (World Health Organization, Situation Report – 86) from Figure 1.
In comparing this with free and open societies with no restrictions of movements and interactions, it is evident that network devices consist of people, things and places. Several activities can be happening at a particular time dynamically. Several persons can access the world map from different locations simultaneously on the go, and we are looking at a growing population of not less than 5 billion worldwide. Thus, modern gadgets like mobile phones, which use GPS, have brought about much information and communication. Interaction is a must for humans, but in times like this, where we face a pandemic of this nature, we need to improve social distancing, do more of stay at home jobs, limit our human contacts, and lead to little virus spread. There is a need for dealing with the complexities of networks. Data collected and rightly analyzed can help understand the virus and slow down its spread as its propagation pattern will be understood. With this approach, health care institution will better respond to cases coming up (Ching et al., 2020).
What we learned from this phenomenon is that firstly, businesses have to accept the immediate change. In many business places, social distance has always been an issue. These businesses have also learned to focus on work from home and have a more robust online presence to make more profit than in the conventional working environment of working days and attending to clients. Businesses began to care more about the health of both their customers and employees and also the general public. Organizations have cut cost in expenses as they do not need to travel for business meetings and pay for certain services needed for their offices' daily running (Fu et al., 2020).
Secondly, there has been a need to rethink how to perform smartly; how well they can remember things and balance work-life activities and keep everyone safe (employees and families) is a top priority. A striking question now is; how best can a company's workforce be reshaped to meet their clients' productive needs? Advancement in new technology has also brought about a shift in how connected workers can be in times like this. Thirdly, how a pandemic can bring about a synergy between the general public, businesses and government as they all work towards finding solutions to problems coming up due to COVID-19. It is not the first virus infection that the world has seen, as stated earlier, but this has shaken the world in general as it cut across nations (Richter et al., 2020). Everyone's collective approach during this period has shown how connected we can be in crisis, which has led to the progress experienced in this short time. In the future, we are hopeful enough to be very much aware and observant of threats that can come up and find ways to mitigate them on time before becoming full-blown and risky enough to lead to people's death (Ashraf, 2021).
Importance of this Research
Discussion is carried out in this paper on the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that will uphold the sustainability and to get the greater benefit of such current technology. This will also support in the management of such disruption in the future. Due considerations on micro and medium sized endeavors is also given by the researchers, as in how micro and medium sized endeavors are managing with the disruptions that has been the result of the pandemic - COVID-19.
Objective of this Research
The extremely unpredictable environment acknowledges for some risk management strategic approaches regarding micro and medium sized actions accord, on to pursue the obligations. The study highlights the scope that might be put into action to treat and control any such similar situation if and ever it arises in future.
Research Methodology
Since this issue of the pandemic is not well-defined this research is carried out in order to gain a clearer understanding of the current risk management strategies during the pandemic era. The findings will not be definitive as the research adopts broad concept and uses the logical analysis to define problems that can be the subject of future study.
Research Problem
Many organizations were forced to alter and revise their business models to adjust to the uncertain economic environment. Many of the conspicuous economies on a global basis imposed a complete lockdown. From then the attention has switched to the challenge faced by the economies. This research will highlight how the pandemic has rattled the normal channel of communication amidst many other things and this has caused the negative effects on enterprises such as business meeting and long -term events planning.
Literature Review
Historical Review of Viruses Transfer to Humans
Chinese state media revealed on January 9, 2020, about a group of scientists whom XuJianguo drove, and they had recognized the microorganism behind a strange episode of pneumonia in Wuhan, which today we call COVID or COVID-19.
The name Coronavirus has come through from unmistakable spikes of adjusted tips that design their surface. This construction helps researchers remember the sun's environment, which is otherwise called its crown. Different Corvids contaminate various species, albeit the principal human Corvids, during the 1960s (Williams, 2020). As expressed by pediatrician Jeffrey Kahn of the University of Texas Southwestern, who considers respiratory infections:
"As around then, two Corvids were distinguished as; OC43 and 229E. Since they were new, much exploration was not made on them, as expressed in an audit on Covid by Kahn on SARS in 2003. He expressed that "I do not accept there was a major exertion to make antibodies against these because it is to a greater degree a disturbance than anything else." (Williams, 2020).
The sicknesses cause average infection results like a sensitive throat, nasal congestion, coughing, especially customary. One early appraisal analyzed that 3% of illnesses in Georgian adolescents suffered respiratory complications (Williams, 2020).
Origin of Corona Viruses
While SARS was not as bad as Coronavirus in as much as it was also deadly, COVID-19 has appeared to be more problematic as its mode of spread, and possible symptoms are caused by its widespread.
During the SARS outbreak, a few experts looked out for possible traces to a more significant virus, and in 2004, Netherland researchers found a novel Covid. Youths were the carriers as they suffered pneumonia and another respiratory sickness. Kahn discovered that illness came to be known as NL63, who worked with Yale University School of Medicine (Williams, 2020).
Covid comes with signs, according to Kahn, and its root is not well known. Regardless, it is a known fact that our body has a way of fighting diseases and infections, but viruses most times are challenging to fight. It is worthy to note that cold is associated with several respiratory problems.
Risk Management Role in Controlling Epidemics
The alarming report in the specialist's board worldwide trade; showed the entire evasion segment and broad critical threat decline. The fundamental aspect of preparation lies in reducing neighbourhood flare-ups, which hinders the plague and spreads the pandemic.
There is a need for a new approach that will ensure prosperity and rapidly respond to individuals' needs regarding the security & essentials of communities. This approach can also help pandemic outbreaks like covid19, and it is called the "cost-efficiency approach". COVID-19 is no longer a story, it has widely spread across borders, and its effect, which has hampered transportation of goods and services, has succeeded in cutting off trades; although the strategy was to reduce its spread globally in 2009 with the H1N1, which was delicate as a pandemic based on its certified representation, and it was not easy preventing its spread. An emergency approach was called "The emergency-based availability and response model" (Sirkeci et al., 2020). The idea was to drastically reduce the pandemic's worldwide spread, focusing on ways to hinder its further spread and contain and examine the animals that were transmitting the virus. Brilliantly, with such a proposition, there was great concern about the cost implications and questions like; can countries tap into this idea quickly? Profitability without feasibility has no importance. Sensibly, the "emergency preparation and response" model is in a manner non-plausible. In any case, the emergency perspective is absolutely and typically unsuitable for rapidly changing contamination speed (Fu et al., 2020).
Complex variety & ordinary assurance adds to complicating the cycle by irrefutably joining those introduced worldwide by human science and advancement. Microorganisms and powerful ailments are doubtlessly an enduring peril to human prosperity and security. Hence, pandemics are not sporadic emergencies but instead an expected and endless groundbreaking risk. This reality alone affects both humans and animals' health as it makes it fundamental enough in managing the risk of pandemics as they ought to be an exceptionally fundamental level grounded effort to keep them safe at all times (Reperant et al., 2017). Availability as an overall perspective is open as it sets off a genuine scene of ailment in the public space.
The "availability and response strategy" are customary, and they fail to consider shortcomings of the socio-economic system (power, water and transportation) (Heffron et al., 2017). Generally, the "12 human-animal prosperity response" is related to the model and does not sufficiently look into the broader complexities of interminably, immovably, risks for both animals and human's prosperity. Honestly, to date, coordinators will overall acknowledge homeostatic security of the overall structure and, as needs be, disparage that guideline systems can be well operationalized. In any case, as contended below, such notions will be challenging to hold on to, as those social systems give signs of increasing stress. The usually happening different pandemic waves would subsequently find social orders legitimately more exposed and less solid. Finally, managing the perils of groundbreaking microbial; turn of events, return, and resistance is a specific resource concentrated undertaking. It is much more overpowering thinking about the intrusion of creating "transient stressors" like total financial stagnation, the solicitations for creating population, little essential ordinary resources and related conflicts, huge, grouped impact of ecological change, the upsetting risk and costs of antimicrobials, and characteristic degradation. These upgrade threats and the cost of status response will further test social adaptability at general or standard levels. To these stressors, debts tend to increase primarily personal debts, which are corporate debts.
Based on the need for more resources, there is a need to source more money to carter for daily needs that come to bear during disastrous outbreaks. The current critical perspective probably could be missing, deficient, and outlandish. Consequently, even with the aforementioned "stressors", it can be seen that they are neither convincing nor capable of tackling cataclysmic shocks, upgraded by increasing weights and conditions of the "21st Century" human instinct. The task using logically insufficient calamity the chief resources is as of now genuinely bent and senseless. It is on record that "All around, only 4% of use on catastrophes goes towards calamity avoidance and planning, with 96% spent on response. It requires change by Kristalina Georgieva, the former acting CEO of World Bank, current European Commission Vice-President, and Disaster Risk Reduction Champion. To effectively use limited resources in a crisis centered planet, interest in significantly preventive, the proactive threat is critical to developing clever strategies with the most substantial benefit from the investment. The current model no longer working because of insufficient funding for responses. There is a need for better responses towards overwhelming infection cases through legitimate measures, and it will reliably remain a need. Regardless, an overall method for a high-result, threatening civilization problems like genuine pandemics demand good preventive circumstances determinedly based on an intensive examination and efficient, progressive decline of threats.
In the same way, organized, highly centered risk reduction, fundamental expectation, and availability should be in place before flare-ups. Such 13 global systems are required, possible, yet for the most part, non-existent (Cotula, 2021).
Corona Virus Catastrophic Risks
In 2020, COVID-19 shot disastrous dangers and their administration into the worldwide cognizance. The admonition signs have been progressively solid as people upset biodiversity, come into close contact with infection conveying elements and travel seriously worldwide (Sirkeci et al., 2020). The Global Challenges Foundation's Annual Report attempts to outline the relative multitude of most noteworthy dangers to humankind, following improvements in the issues, feature their inter-connectivity, and investigate how they are at the worldwide level. The papers show, like never before, the unpredictable links between these worldwide dangers and how they can build up one another. The current year's review of worldwide calamitous dangers accompanies added importance. If at any point there were a contention for upgraded worldwide collaboration to handle calamitous dangers, COVID-19 is it.
The pandemic regards no lines and underlines our interdependence. Nobody is genuinely protected until everybody is which implies antibodies and treatment should arrive for everybody, a vast collective endeavor (Gao et al., 2020). However, what of other equally essential risks, strikingly the environment emergency which at last was highlighted among the worldwide issue a year ago yet has since been generally dominated by the competition to contain the infection? The pandemic will probably prompt a decrease in worldwide fossil fuel byproducts in 2020 (Heffron et al., 2021). Be that as it may, how is it possible to influence environmental change in the medium to long run? There is a genuine danger that political and public consideration for environmental issues will drastically decrease despite the pandemic's intense financial and social outcomes (Ching et al., 2020).
However, a few of us accept that this emergency can be a defining moment, offering ascent to a greener future as the monetary recuperation bundles set up by numerous nations offer a chance to re-form economies and social orders towards feasible methods of creation and utilization. As discussions proceed about the ideal approach to deal with the most pressing dangers to our species' presence, one thing is sure: we should construct new types of worldwide administration, more critically and more inventively than any other time in recent memory imagined. The Global Challenges Foundation will keep on advancing the agreement and signed up, pondering how we oversee and administer these dangers. We will take care of progressing worldwide conversations on these subjects. As the United Nations denotes its 75th commemoration this year, during a period of extraordinary interruption for the world, UN Secretary-General António Guterres has dispatched the 'UN 75' activity. It vows to be the biggest and most extensive worldwide discussion to date on "The future we need the UN we need". We are adding to this discussion by supporting the UN and the significant work of one of the groups that won our 2017 'New Shape Prize' to rebuild worldwide administration for the 21st century. This worldwide group of specialists - financial analyst Augusto Lopez Claros, researcher Arthur Dahl and global attorney Maja Groff - is looking at the necessary primary changes required for the UN to successfully address the best difficulties within recent memory. They are building up an incorporated arrangement of proposition to survey the UN Charter, which would plan to give the UN the limiting authoritative, legal and requirement capacities to viably address cataclysmic dangers, while as yet reserving most functions to states as well as UN change, GCF is explicitly tending to environment administration by setting up a Climate Governance Commission. The Commission will analyze hindrances to successful environment activity and propose worldwide administration reactions. It means creating and assembling upheld for various recommendations to improve worldwide decision-making and collaboration to animate successful answers for the environmental emergency. The Commission will incorporate mastery from environment specialists and specialists on financial matters, sociology, global administration, public strategy, tact, business, and the work market. The point is to launch progress in the weak global interaction to end cataclysmic environment changes (Martin et al., 2020).
Threats & Financial Ramifications
The COVID-19 pandemic tends to the best preliminary of the post-crisis money related system to date. The pandemic sets up a tremendous overall full-scale financial stagger, driving the overall economy into a plunge of questionable significance and term. The overall financial structure faces the twofold test to help the credit movement amidst declining improvement and control perceived threats. This exogenous stagger has put the related money system under strain. Dropping revisions of expected financial development and elevated risk shirking have incited a huge re-assessing and repositioning in overall money related business areas. From one perspective, the providers of financing have a growing tendency for transient safe assets from Figure 2.
On the other hand, credit risks are rising distinctly. As a result, the solicitations on the financial system's capital and liquidity have risen. Raised operational risks are adding to shortcomings (Hafiz et al., 2020).
Corona Virus is devastating nations worldwide. However, for some low-pay and delicate states, the monetary stun will be amplified by the deficiency of settlements cash sent home by traveller and visitor labourers utilized outside nations.
Transmission of Shocks
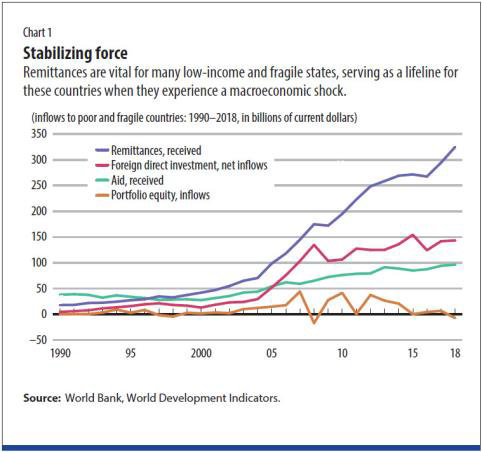
Remittances are income flows that sync the business example of various recipient countries with those of sending countries. During good times, this relationship is a shared advantage, furnishing actual work to fuel host countries' economies and turning out truly substantial income to families in the drifters' countries of the starting point. Regardless, this close by business cycle linkage among host and recipient countries has a burden peril. Shocks to the economies of explorer have countries as of late such paralyzes achieved by the Covid pandemic can be shipped off those of the settlement recipient countries. For example, significant substantiation country that gets settlements tending to in any occasion 10% of its yearly GDP, a 1 per cent decrease in the host country's yield opening (the difference among real and conceivable turn of events) will overall reduce the recipient country's yield opening by close to 1% (Barajas et al., 2012). Settlements address generously over 10% of GDP for specific countries, driven by Tajikistan and Bermuda, at an abundance of 30% (see Chart 2, Source: IMF, World Economic Outlook).
The pandemic will give a hit to reimbursement streams that might be incredibly more loathsome than during the cash related emergency of 2008, and it will come similarly to weak nations as they are wrestling with the effect of COVID-19 on their economies. Explorer labourers who lose their business will probably decrease settlements to their families back home. Beneficiary nations will lose an essential kind of pay and commitment pay when they need it most (Abdih et al., 2012) (see Chart 3, Source: IMF, World Economic Outlook).). Financial and exchange changes would be affected, and nations' capacity to back and maintain their responsibility becomes minimal.
Banks are, as of now, obligated to see their cost of exercises increase, and their ability to extend credit whether or not to the private territory or to finance Government, insufficiency will be unimaginably diminished (Barajas et al., 2018). Besides, the customarily credit-obliged private territory by and large, including autonomously utilized people and micro and medium-sized endeavors, will probably lose settlement sponsoring, just as overseeing impressively more close credit conditions from banks. It will come on top of lower interest for their organizations and things due to the crisis.
That is not all, a lengthened crisis could increase pressure in rich countries' labour markets, and jobless drifters could lose their tenant status in countries and be constrained to get back. For example, in Gulf states, for instance, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, which rely upon short work from the Middle East, North Africa, and Southeast Asia, the drop in the expense of oil and financial activity could achieve voyagers (some of whom are as of now corrupted with the disease) getting back. They are presumably going to join the jobless in their countries of cause in labour features already flooding with jobless youth similarly as pressed successfully fragile general prosperity structures. It could elevate the overall burden in nations effectively poorly set up to manage the pandemic, and perhaps at the same time, fuel overflows past their boundaries. Individuals getting away from predicaments in their nations are probably going to look for different shores. However, likewise amidst battling the infection, more extravagant nations may want to permit travellers inconceivably prompting a much more major displaced person emergency (Heffron et al., 2021).
Hazardous World Environment
This pandemic represents a significantly more noteworthy danger to nations that depend intensely on settlement pay. This emergency's worldwide idea implies that not exclusively will beneficiary nations see remittance flow slow to a trickle. They will simultaneously experience an outflow of private capital and possibly decrease aid from benefactors in similar situations. Usually, when private capital escapes a country due to a macroeconomic stun, regardless of whether environment related or due to a crumbling in the nation's terms of exchange, financial settlement streams come in to diminish the impact of capital flight. Alternately, in this current crisis, vulnerable countries may experience the two marvels of capital outflow similarly as a drop-in settlement stream (Wu et al., 2020)
With worldwide interest possibly suffering, it would be hard for settlement beneficiary nations to export right out of this emergency. Cash deterioration cannot be relied upon to spike interest for their fares or pull in the travel industry since this stun is fundamental (Barajas et al., 2010). The monetary shortfall will probably deteriorate the monetary circumstance for many of these low-pay and delicate states whose obligation is in unfamiliar cash, further discouraging neighbourhood interest and bringing about more prominent shrinkage of nearby economies.
Losses due to Economic Downturn
An exceptional calamity, the COVID-19 pandemic, has achieved an incredibly high number of deaths. Gatherings were prohibited, Countries locked down.
Quarantine was introduced and became a part of life to control the widespread of COVID-19 though it does not guarantee to control the epidemic. Lifting the quarantine would be unlikely to bring down the cumulative mortality rate considerably (Morgello, 2020). As compared to lifting the quarantine at one go, a two-step quarantine lifting according to the age group was more effective. It would substantially lower cumulative mortality. Besides, it will also lower ICU-bed occupancy. Though post-quarantine examining was linked to diminish epidemic rebound at the same time, it is not a plan of action for preventing overcrowded ICUs (Sterpetti, 2020)
At the corona virus resource centre, Johns Hopkins (https://coronavirus.jhu.edu) stated that identifying the quantum of the most imperative ways for COVID-19 concern is through the mortality rate. Due to the different ways of calculating and different factors of calculation, the death rates have biases (Bousquet et al., 2020). At the same time, some countries have standardized method of calculating death rates across the nation. It can get more harmful after a 2-step quarantine lifting according to age unless the younger generation's immunity is not strong enough once governments lift the older population's quarantine (Figure 3). The consequences of Corona virus can be reduced only with effective treatment, significantly if health officials increase the capacity of ICU.
As it is evident that soon after the pandemic's announcement, the country's economy is shutting down; several economic shocks faced the world. The pandemic displays, and it is evident that there has been an international catastrophe that has touched every country, a high degree of awareness on such global interdependencies will lead to the involvement of stakeholders, which is very much needed to strengthen the economy of every country. To overcome this, designing critical infrastructure for the future is essential, such as food, health, electricity systems (Martin et al., 2020).
Nations subject to the development business, travel, warmth, and pleasure for their progression encounter huge aggravations. Making business regions and making economies face extra difficulties with great inversions in capital streams, general danger requiring foggy spots, and money pressures while acclimating to more fragile thriving frameworks and more bound financial space to offer help. A few economies entered this emergency in a weak state with drowsy unforeseen development and high responsibility levels.
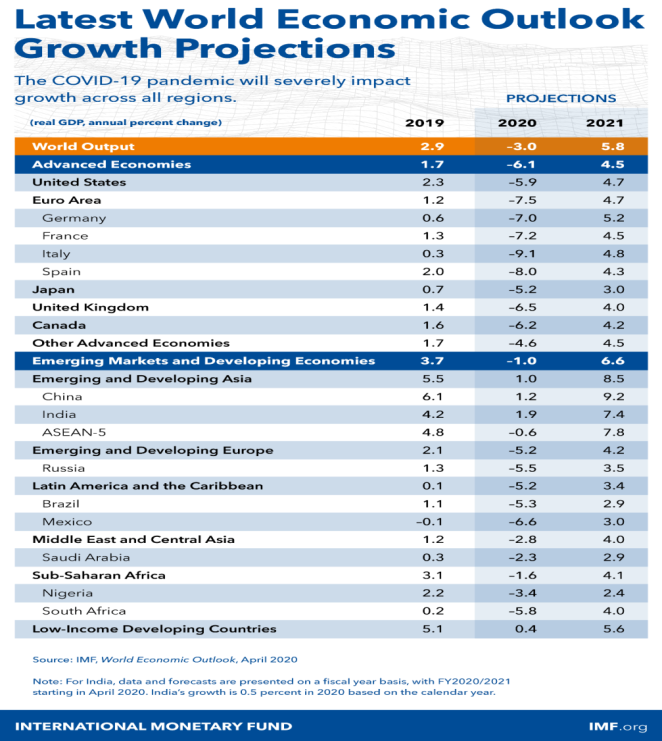
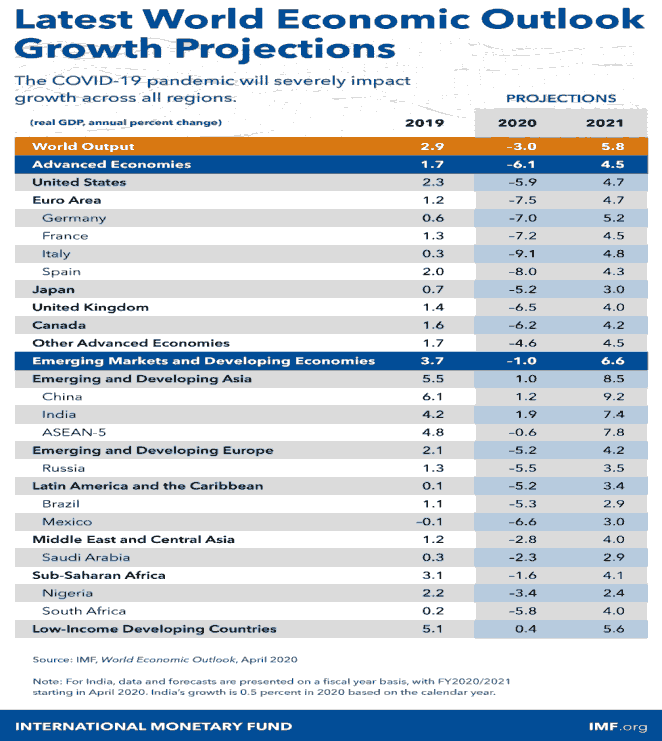
Unusually since the Great Depression, both progressed economies and making progressing business region and making economies are in decrease. During the current year, progression in front line economies reached - 6.1 per cent. Making business zone and making economies with standard progression levels well above cutting edge economies are in like way projected to have negative improvement paces of - 1.0 % in 2020 and - 2.2 % in the USA. The income per capita expected to reduce for more than 170 nations. Both developed economies and new business markets and growing economies are relied on somewhat recuperate in 2021 (Kilic et al., 2020). The pandemic may not subside in the second half of this current year, inciting longer terms of rule, self-destructing cash related conditions, and further breakdowns in general hold chains. In such cases, by and large, GDP would fall broadly further: an extra 3 per cent in 2020 if the pandemic is more loosened up for this current year, while, if the pandemic proceeds into 2021, it might fall one year from now by an extra 8 per cent (Khan et al., 2020)
There is no trade-off between saving lives and saving positions. Countries should continue spending generously on their flourishing structures, perform never-ending testing, and quit trade constraints on clinical supplies. An overall effort should ensure that both rich and powerless nations have quick access to vaccinations (Mina et al., 2020). There are sure signs that this crisis will end. Countries are winning concerning containing the contamination using social-discarding chips away at, testing, and contact following, in any occasion until extra warning, and arrangements and immunizations may develop sooner than expected.
Comparable with the scale and speed of the crisis, neighborhoods and significant strategy responses ought to be immense, expeditiously sent, and quickly recalibrated as new data opensup. The solid exercises of arranged specialists and clinical specialists ought to be made by policymakers any and put on the world so we can together vanquish this crisis (Figure 4).
Facing the Epidemic
Pandemics are known for changing people's way of life due to restrictions that, by and large, are not sensible concerning what they were used to do regularly. Unquestionable in nature is what this pandemic comes as, with unique excellence in strategies for expectation. Better systems for life spread torments other New and additional pivotal parts update the transmission of issues, as the disease gets sent starting with one individual then onto the next contact or among animals and individuals. In a speedy period by and large change, these territories' goliath degrees are on a fundamental level inevitable. Among them are the main impetus and uncommon adaptability of individuals, with broadened vehicles and common travel, and more key between tremendous metropolitan networks' responsiveness with significant vehicular vehicle associations like planes, trains, street vehicles, and boats. Simultaneously, globalization incites augmented exchange among nations correspondingly as more obvious improvement of individuals inside and between them. For a hugely long time, a dependably widening number of individuals have been moving from the field into metropolitan affiliations, looking for better positions and improved theories for customary comforts (Yang et al., 2020). These dangers apply, at any rate, to thickly populated regions, on the verge, of metropolitan affiliations where common area covers them. Here, close and recurrent contact, a hugely individuals and animals, nearby creatures, and untamed life raise the probability hazard of new torture. These per-metropolitan districts will be considered less respected, and neighbourhood individuals have less choice of clinical advantages. The twofold danger here is that their issues may go undetected and untreated, whilst al. choices for the region, avoiding and control are lessened. The Ebola scene in 2014 has, on a fundamental level, showing this. Upsettingly, the early part of the 21st century has seen certain liberal crises, the grand removal of masses, standard pity, political shortcoming, clashes, wars and dramatic events. Potentially risky changes are in like way occurring, in the utilization of land, neighborhood ties, and food creation - as live poultry and creature business zones, as well as deforestation – which, likewise, prompts extended contact among individuals and real life. Some of these creatures, such as monkeys, most likely are wellsprings of new microorganisms. At last, ordinary changes, such as brand name change, add to disorder transmission. Different parts add to create mortality of pandemic ailments. In returning to standard control checks, we have seen that unquestionable standard rule measures are not prevalent. The utilization of microbes to treat contaminations has been a fundamental event in the twentieth century. Antimicrobial opposition is, as of now, out voyaging. It is an enormous concern considering how polluting may execute, spread to other people, and find better approaches to manage direct regulate, treat and breaking point of the spread of the illness. Antimicrobial check happens for what it is worth, yet some improper usage of medications, for instance utilizing contradicting microbial for viral contaminations like cold or influenza or utilizing executing specialists' harms for creature improvement in the creature district. Among major shocking pollutions, the treatment of tuberculosis is the most influenced. As of now, there are strains of the microorganism that are multi-drug resistant. The value and coarseness issues are ceaselessly key for the image: consent to clinical countermeasures stays hypnotizing, particularly for low-pay nations and nations going toward unselfish crises (Gao et al., 2020).
Market parts do not guarantee a reasonable development of assets subject to general accomplishment requests. Overall portions are relied on to guarantee reasonable choice to life-saving interventions during emergencies. Among them is the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), the International Coordinating Group, GAVI, the Vaccine Alliance, and the Pandemic Influenza Preparedness Framework. (Krishnan et al., 2020). Another risk to drive another word has entered, the when in doubt flourishing language: "infodemics". These can be depicted as the snappy spread of data, thinking about everything, including reports, nark and fascinating data. They are spread quickly and worldwide through the utilizing cells, electronic media, the web and other correspondence sorts of progress. An increment of electronic "arranged subject trained professionals" with accumulated and consistently annihilating perspectives can make issue, worry and even tumult during certifiable baffling flare-ups. Counterfeit or misleading data is perilous. The clarification risk correspondence. Progress coordinated arranged specialists relentlessly utilize an enormous heap of present-day limits, and working conditions organized prepared experts and expert succeeding work power. It is more focal now than any time in late memory to learn and apply them. The most recent and most exact data should be reliable, and insufficiencies identified with a scourge should be recognized to keep up the reliability and public trust. Along these lines, we see the unusual considered '21st-century plagues' and their evasion and control. It requires new kinds of progress frameworks and new cutoff habitats, and new perspectives of the whole course across the general accomplishment area. Danger correspondence is poorly down at more perceptible length in a later piece of this handbook. One such intervention is among the program leaders. The pandemic has questioned the program leaders to act very quickly to the changes taking place in the health care delivery, ensure trainee safety, and remodel educational activities. The countless threats to trainees' well-being due to the pandemic, the program directors, were expected to address them. Remodeling education so that program leaders can effectively deal with trainee well-being needs can also reflect how to improvise training programs. During the COVID-19 pandemic, certain education systems respond to online learning, and it was very advantageous to stay connected, which will be critical to continue and expand upon post-COVID-19 (Weiss et al., 2020).
Fundamental Risk Management Lessons to Learn from Corona virus Pandemic outbreak
COVID-19 has come with so much tragedy worldwide; its impact has affected millions of lives negatively as it has continually led to substantial economic disruptions and hunger. We ought to keep working towards a safer future, as this pandemic has also helped reshape risk management in organizations methods of doing business, in as much as the full impact of Corona virus is still unknown to the world (Khanna et al., 2020). As of April 2020, an investigation by Sunday Times revealed that a lack of proper understanding of the virus and actions led to the outbreak of the virus. As a result of the outbreak of this Covid 19 pandemic six critical lessons are considered:
• Identify actions
• Work and have confidence inplanning
• Look into current and future development
• Examine lessons from the actions taken
• Be imaginative -expecting the worse
• Understand the limitations
Identify Actions
Based on records available, we have seen that "pandemics a possible threat to nations' sustainability for many years". A living document known as a risk log is needed to reflect the changes that happened as time passes. Such a document must focus on solutions. Understanding the problem and subsequent actions to curtail its effect is very important. Emphasis on understanding what risks are there and that everyone understands this hazardous situation. It is essential to ensure that the actions taken should lead to having more control over the risks. In risk management, straight to the point actions can lead to better results and timely outcomes (Richter et al., 2020).
Work and have Confidence in Planning
An article by Sunday Times says that almost every plan is not active as of February. This lack of confidence in the outlined steps can lead to slow actions and jeopardize the Risk management process. Instances that lead to movement from earlier stated plans could lead to consequences not planned for or expected at all. Taking time to comprehensively state, and agreeing on the stated risk management strategy, will help at the early stages of organizational development and growth process. There is the need for regular testing of risk management plans to ensure that they remain viable to the organization, for the ever-improving organizational structure modified regularly (Hua et al., 2020).
Look into Current and Future Development
A good example of this is the as happened in UK,the form of assessments of previous happening. It is on record that in the same period that there was a Coronavirus outbreak, the Government was bent on focusing on the Brexit deal, which was still in 2020. Short term risks usually come with an understanding of urgency, but this is not the case for Long Term risk as their approach can be implemented in a considerably longer time. Although, in some instances, a distant problem can end up turning into an urgent problem that can call for immediate actions to be taken, if not, its impact can be massive as they take everyone by surprise (Richter et al., 2020).
In a book written by Michael Lewis titled "The Fifth Risk", he noted that 'in cases of a bomb explosion, those with a longer detonator can take a long time before they detonate, but their impact will still be as those with a shorter detonator'. Imagining the consequences of risk are significant to stakeholders to think about their future long-term impact on society.
An overall analysis related to the risks of the COVID-19 pandemic requires a decision support system and its consecutive medium- and long-term impacts, particularly in the virus COVID-19 around the world. Hence it can be applied to various types of risk management (Bai, 2021).
Examine Lessons from the Actions Taken
As far back as 2016, the Government had looked into what pandemic outbreaks can bring about. Organizers of projects are likely to understand what can happen. It is imperative that adequately considered steps during the process of putting up the risk strategy plan as regular testing can bring forward limitations that can affect the future need of the plans (Khanna et al., 2020).
Be Imaginative -Expecting the Worse
In Risk management framework planning, the process is carried out by unadventurous and inquisitive persons. For decisions relating to Risk management, it is expected that the approach should be bold and imaginative, as stated by Sunday Times.
All aspects of an organization are supposed to have fair risk management policies but adequately positioned to ensure that the organization functions in optimum service delivery to the client's needs. Industry planners usually try to think of what next can significantly affect an organization. A statement that reads is;
"Managing risks is an act of imagination. Moreover, the human imagination is a poor tool for judging risk. People are good at responding to the crisis that just happened, as they naturally imagine that whatever just happened is most likely to happen again. They are less capable of imagining a crisis before it happens – taking action to prevent it.".
Understand the Limitations
To every organization, there are limitations to what they can do. Most organizations usually reflect more on what they would have done differently than they had done. It is not easy to imagine all events that can come up and plan appropriately for them as they can be unforeseen events that can become a big reality for an organization. Such can be like planning for a nuclear disaster which no one knows when it can happen or the magnitude of destruction that can come with it. In most cases, organizations have a limited budget and scope of operations. As a result, they mainly plan for what they can do based on their limitations.
It is pertinent to understand how risk management processes can mitigate risks that can come up anytime. The use of the already existing flexibility in the 3P's design has helped in accelerating/decelerating, scaling up/down, shifting resources or pause activities when needed. More organizations are currently moving towards agile ways of getting work done, and they have been getting remarkable results. The in-built agile structure has led to a swifter response to risk control while still providing quality service. Secondly, a systematic process helps in a better risk management approach by using its interconnected structures.
With the prevalence of Corona virus, there has been a need to understand why good risk management is essential; this is not just because of putting strategies and mechanisms in place earlier but also because it has helped bring about innovations. In as much as we wish we had a risk-free world, businesses need to get used to taking steps that can prevent a further economic break down as has been experienced in different countries (Cotula, 2021). This writing period seems to have experienced a reduced infection rate in COVID-19. If organizations improve their proactive nature in analyzing their risk management strategies, it will go a long way even in time of another pandemic.
Future Lessons Learned
Researching the not so unattainable future containing the COVID-19 plague is likely going to require some time. General achievement intercessions will be empowered towards social discarding and improving hygienic practices. Testing, contact following, separation of the infected, and preliminary self-isolation of contacts was basic in decreasing the proportion of new cases (Forman et al., 2020).
Little to no data is available so far on help transmission approaches, unequivocally by procedures for sewage, dirtied water, or cooling systems. Other than insufficiently known whether people, who have recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection, would be protected from reinfection (Yang et al., 2020). The effects of temperature, season, and dampness on COVID-19 affects the COVID-19 discharge results from various parts of the world are expected.
Various starters are in progress to make novel treatment decisions and an immunizer to treat the respiratory condition. At any rate, results are still awaited. Moreover, several months are needed before vaccination is possible and requested. Progressed instructional and web learning can be extricated up for a gigantic long time. Telemedicine and unequivocally teleophthalmology ought to be applied. In the coming years, overwhelming difficulties will probably be included among essential achievement hazards caused by antagonistic microbial resistance. In like way, apt certification, gifted end, lively division, and clinical affiliation would remain at the forefront (Gao et al., 2020).
Pandemics have changed in the new past, and it keeps doing appropriately. Different new factors add to an improvement in the genuineness of unexpected illnesses. Better methodologies for life spread illnesses and other new and more momentous parts redesign the transmission of sicknesses, either by considering how they increase their contacts between individuals or among creatures and individuals. In a time of quick general change, extraordinary measures of these are fundamental.
Conclusion
COVID-19 had been acknowledged, as a general health hazard, all over the globe. The infections added to the list of epidemic disease outbreaks, such as; the Bovine Spongiform Encephalitis outbreak in 1986, the Avian flu of 1997, the SARS outbreak in 2002, the Swine Flu 2009, and the Ebola Virus outbreak in 2014. These epidemics are a constant reminder that we live in an ecosystem where respecting the relationships between animals, our social life, and the environment is necessary to survive and thrive. Rapid development, and daily shift into forest lands, has resulted in a new interface between humans and wildlife. Also, it has exposed humans to foreign organisms, often involving the consumption of exotic wildlife. As stated by the UN Environment Chief, Inger Anderson: "Our continued erosion of wild space has brought us uncomfortably close to animal and plants that harbor diseases that can jump to humans. She said, "If we do not take care of nature, we cannot take care of ourselves". COVID-19 is nature's way of telling us that we need to recognize and respect our relationship with animals, including pets, livestock, and other natural and wildlife elements. The trans-disciplinary 'One Health approach, involving professionals from many disciplines, such as medicine, veterinary, environmental health, and social sciences, should be advocated to help control new infectious outbreaks. The economic burden of disease should be minimum, and understanding disease mechanisms, health problems, disease emergence, and reemergence should be improved to facilitate a timely response. It will aid in the notification, prevention, and treatment of future pandemics relying on experience garnered from the COVID-19 outbreaks. There is an utmost need to develop risk management strategies at high levels for government’s, institution’s and public. The formulation of robust governance of risk will help facing future calamities which is not expected to end with science and technology advancement. The adoption of policies that respects the environment and preserving the lives of humans is inevitable. Risk management model must prevail so no sudden hazardous attack of various risk that may occur since we live in an unpredictable world.
References
- Ashraf, A. (2021). Lessons learned from COVID-19 response for disaster risk management. Natural Hazards, 1-6.
- Bai, S. (2021). Modeling a decision support system for risk management of COVID-19. Advances in Simulation and Process Modelling, 1(10), 23-39.
- Bousquet, J., Anto, J.M., Iaccarino, G., Czarlewski, W., Haahtela, T., Anto, A., ..., & Costa Domínguez, M.D.C. (2020). Is diet partly responsible for differences in COVID?19 death rates between and within countries? Clinical and translational allergy, 10(1), 16.
- Ching, J., & Kajino, M. (2020). Rethinking air quality and climate change after COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5167.
- Cotula, L. (2021). Towards a political economy of the COVID-19 crisis: Reflections on an agenda for research and action. World Development, 138, 105235.
- Forman, R., Atun, R., McKee, M., & Mossialos, E. (2020). 12 Lessons learned from the management of the corona virus pandemic. ScienceDirect, 577-580
- Fu, L., Wang, X., Wang, D., Griffin, M.A., & Li, P. (2020). Human and organizational factors within the public sectors for the prevention and control of epidemic. ScienceDirect, 104929.
- Gao, J., Tian, Z., & Yang, X. (2020). Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Bioscience trends.
- Hafiz, H., Oei, S.Y., Ring, D.M., & Shnitser, N. (2020). Regulating in pandemic: Evaluating economic and financial policy responses to the corona virus crisis. Boston College Law School Legal Studies Research Paper, (527).
- Heffron, R.J., Körner, M.F., Schöpf, M., Wagner, J., & Weibelzahl, M. (2021). The role of flexibility in the light of the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond: Contributing to a sustainable and resilient energy future in Europe. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 140, 110743.
- Hua, J., & Shaw, R. (2020). Coronavirus (Covid-19) "infodemic" and emerging issues through a data lens: The case of China. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(7), 2309.
- Khan, N., & Naushad, M. (2020). Effects of Coronavirus on the world community. Available at SSRN 3532001.
- Khanna, R.C., Cicinelli, M.V., Gilbert, S., Honavar, S.G., & Murthy, G.V. (2020). COVID-19 pandemic: Lessons learned and future directions. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 68(5), 703.
- Krishnan, L., Ogunwole, S.M., & Cooper, L.A. (2020). Historical insights on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the 1918 influenza pandemic, and racial disparities: Illuminating a path forward. Annals of internal medicine, 173(6), 474-481.
- Kilic, K., & Marin, D. (2020). How COVID-19 is transforming the world economy. VoxEU. org, 10.
- Martin, A., Markhvida, M., Hallegatte, S., & Walsh, B. (2020). Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Economics of disasters and climate change, 4(3), 453-479.
- Mina, M.J., Parker, R., & Larremore, D.B. (2020). Rethinking Covid-19 test sensitivity—A strategy for containment. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(22), e120.
- Morgello, S. (2020). Coronaviruses and the central nervous system. Journal of Neurovirology, 26(4), 459-473.
- Naudé, W. (2020). Artificial intelligence vs COVID-19: Limitations, constraints and pitfalls. AI & Society, 35(3), 761-765.
- Rajkarnikar, L., Shrestha A.S., & Shrestha, S. (2021). AI applications to combat COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, 4(1), 1-10.
- Richter, A., & Wilson, T.C. (2020). Covid-19: Implications for insurer risk management and the insurability of pandemic risk. The Geneva Risk and insurance review, 45(2), 171-199.
- Reperant, L.A., & Osterhaus, A.D. (2017). AIDS, Avian flu, SARS, MERS, Ebola, Zika… what next? Vaccine, 35(35), 4470-4474.
- Rodríguez, C.P., Carballido, B.V., Redondo-Sama, G., Guo, M., Ramis, M., & Flecha, R. (2020). False news around COVID-19 circulated less on SinaWeibo than on Twitter. How to overcome false information? International and Multidisciplinary Journal of Social Sciences, 9(2), 107-128.
- Sirkeci, I., & Yucesahin, M.M. (2020). Coronavirus and migration: Analysis of human mobility and the spread of COVID-19. Migration Letters, 17(2), 379-398.
- Sterpetti, A.V. (2020). Lessons learned during the COVID-19 virus pandemic. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 230(6), 1092-1093.
- Wang, C., Cheng, Z., Yue, X.G., & McAleer, M. (2020). Risk management of COVID-19 by universities in China.
- World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Situation report, 86.
- Wang, Q., Guo, Y., Ji, T., & Li, P. (2021). Towards combatting COVID-19: A risk assessment system. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 99, 1-1.
- Wagner, D., (2020). Risk management lessons from Coronavirus. Risk Management Magazine.
- Weiss, P.G., & Li, S.T.T. (2020). Leading change to address the needs and well-being of trainees during the COVID-19 pandemic. Academic pediatrics, 20(6), 735-741.
- Wu, D.D., Olson, D.L. (2020). Pandemic risk management in operations and finance. Modeling the impact of COVID-19.
- Williams, S., (2020). A brief history of human corona viruses. The Scientist.
- Yang, Y., Peng, F., Wang, R., Guan, K., Jiang, T., Xu, G., ... & Chang, C. (2020). The deadly coronaviruses: The 2003 SARS pandemic and the 2020 novel coronavirus epidemic in China. Journal of autoimmunity, 109, 102434.