Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 5
Role of Social Responsibility in Sustainable Firm Performance: Evidence form Education Sector
Kittisak Jermsittiparsert, Dhurakij Pundit University
Pattanant Petchchedchoo, Dhurakij Pundit University
Abstract
Social responsibility is one of the major practices among the various business organizations. However, this practice is also increasing among the educational institutions. The performance of Indonesian educational institutions in respect to the social responsibility is not satisfactory which has negative role in sustainable firm performance (FP). Therefore, objective of this study is to examine the role of social responsibility in sustainable FP. In this regard, the relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance was examined by the current study. For this purpose, Indonesian educational institutions were selected, and teachers were preferred to get response for the final data analysis. Therefore, by using a questionnaire, data were collected from the teachers of various educational institutions. Finally, data were used for analysis with the help of statistical tool. Results of the study indicated that social responsibility has positive effect on firm image, perceived quality and firm reputation. Furthermore, firm image, perceived quality and firm reputation has positive effect on sustainable FP.
Keywords
Educational Institutions, Social Responsibility, Firm Image, Firm Reputation, Perceived Quality, Sustainable Performance.
Introduction
Social responsibility is one the major concern among the organizations. Along with the different institutions, nations are also working to enhance the social contribution in the society. Companies are majorly working on social responsibility (Jermsittiparsert et al., 2019). The major social responsibility of institution is to enhance the environmental performance (Thongrawd et al., 2019). As in the current decade, due to increase in the performance of technology as well as other developments, the environmental performance is neglected. However, it is one of the major issues globally. Better environment is required for the people to survive. Damage of environment has negative role in the lives of people. That is the reason a healthy environment is required for the people to live healthy lives. The provision of healthy environment is based on the increase in environmental performance. In this direction, the role of social responsibility is most important among the institutions. The environmental safety is one of the major social responsibilities of companies. Now the institutions are also increasing the efforts towards the social responsibility in which the environment has major concern. Therefore, the social responsibility is most popular among the organizations which have several benefits including the environmental safety. The importance of social responsibility is clearly highlighted by the previous research scholars (Ali et al., 2020; Singhapakdi et al., 1994). Hence, social responsibility has several aspects including environmental performance among the various nations.
Social responsibility is also linked with the educational institutions. Although all the organizations are working on social responsibility, the educational institutions are also participating in social responsibility. Nowadays, social responsibility is one of the major concerns of educational institutions. Particularly, in various developing countries, where the environment is one of the major issues, the importance of educational institutions in respect to the social responsibility is quite high. Similarly, in Indonesia, the problem of social issues is high which require high social responsibility by the companies. To decrease the social issues, it is important to increase the efforts of social responsibility. Management of social responsibility is most vital efforts towards the society (Hernández et al., 2020; Uduji et al., 2020). As the efforts of social responsibility decreases the issues in the society. Educational institutions are also playing vital role in the aspect to decrease the social issues by increasing the practices on social responsibility. Indonesian educational institutions are also playing the vital results to increase the efforts of social responsibility. Indonesian educational institutions are involved in different types of social practices. These educational institutions are involved in protecting the environment with different environmental issues. These educational institutions are involved in making efforts to enhance the efforts of poverty reduction. As number of people in Indonesia are facing the issues of poverty and educational institutions are doing various efforts to help the poor people. These efforts of Indonesian educational institutions have major role among the society to help poor people and to handle environmental issues. Indonesian government is also making several efforts to enhance the social responsibility among the organizations. Along with the educational instructions, the role of other organizations also playing major role to protect the society. Therefore, educational institutions have major role in social responsibility (Sepetis et al., 2020).
The performance of Indonesian educational institutions is not satisfactory. These institutions require special efforts to enhance the performance. One of the evidences of low performance of these institutions is the most of the students from Indonesia join the universities in other countries due to the low level of education. Therefore, quality of education must be improved by these institutions to attract the more students. However, the performances of these institutions can be increase with the help of social activities. The focus of these universities on education social responsibility has major role in performance. Along with the other business organizations, the performance of educational institutions can be increased with the help of social responsibility. As the social responsibility and educational institutions has major relationship (Sengupta et al., 2020). Therefore, the focus of this study is to examine the role of social responsibility in sustainable firm performance (FP). Sustainable FP can be increased with the help of social responsibility. Most of the business-related organizations are majorly focusing on social responsibility as the social responsibility has the ability to highlight the business companies in the community and create awareness among people which lead to the higher performance as well as performance sustainability. Therefore, social responsibility is the major which shows positive role in sustainable performance. Given in the previous studies that social responsibility has relationship with performance (Uyar et al., 2020).
Social responsibility has the potential to enhance the firm image. Better practices of social responsibility have the potential to enhance firm image. As the current study is dealing with the educational institutions, therefore, social responsibility can increase the educational institution image in the society. Along with this social responsibility it also has role in perceived quality by the customers. Infect in the educational institutions the perceived quality by the students has major role. Increase in the social responsibility practices shows positive role in perceived quality. Furthermore, the role of social responsibility is also important in case of firm reputation. As the increase in the social responsibility increase the firm reputation. Finally, positive effect of social responsibility on firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality which lead to the sustainable FP.
Therefore, objective of this study is to examine the role of social responsibility in sustainable FP. In this regard, the relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance was examined by the current study. Number of previous investigations shows the corporate social responsibility among various business organizations (Ali et al., 2020; Javed et al., 2020), however, previous studies have not examined the role of firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance along with the role of social responsibility among educational institutions.
Literature Review
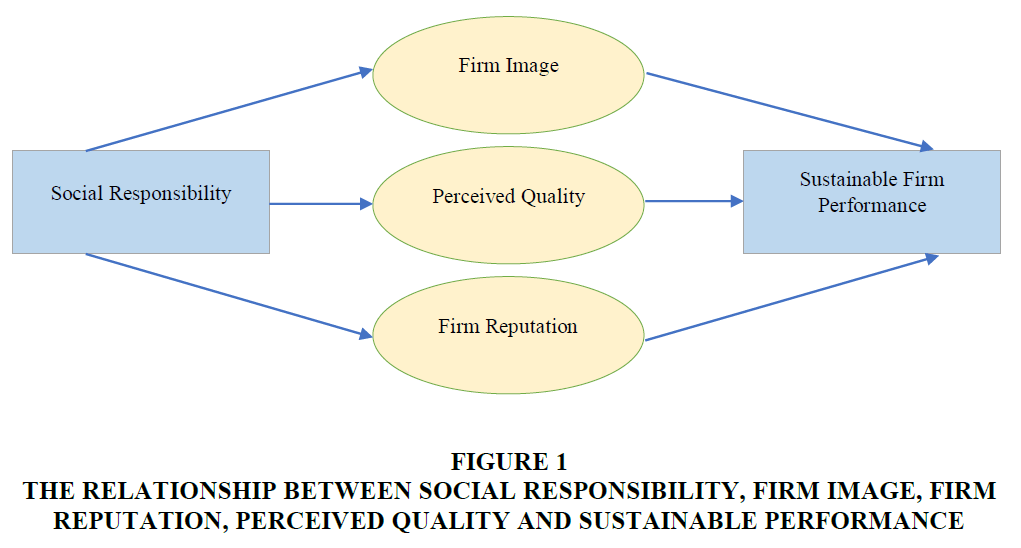
Educational institutions have crucial role in social responsibility. Especially, the higher educational institutions have major role as compared to the other educational institutions. Because higher educational institutions have better resources which help to take part in social responsibility. The role of higher educational institutions has vital among the society as these institutions take part in society welfare with the help of different ways. For instance, these institutions work for the welfare of poor people. They gather the funds and help the poor people. Moreover, these institutions take part in various disaster management activities. Educational institutions take part in disaster management activities. Various educational institutions have strong concern in environmental performance. In this direction, these institutions play their role in various environmental activities. Therefore, the role of education department in social responsibility cannot be neglected (Asrar-ul-Haq et al., 2017; Richards et al., 2019). In this direction, the current study examined the role of social responsibility in sustainable FP. Social responsibility has important role to develop the good firm image which lead to the sustainable FP. It also encourages enhancing the perceived quality of the educational institutions which causes to increase sustainable FP. Furthermore, it has relationship with firm reputation which also has positive role in sustainable FP. Figure 1 shows the relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance.
Figure 1 The Relationship Between Social Responsibility, Firm Image, Firm Reputation, Perceived Quality and Sustainable Performance
Hypotheses Development
Social responsibility is one of an ethical framework and proposes that an individual or organization has a responsibility to act for the different benefit of society at large. Social responsibility is one of the duties every individual as well as organization has to perform so as to preserve a balance between the economy as well as the ecosystems. Social responsibility is not on limited to the environmental activities, but it also has relationship with the other aspects of society. Under the welfare of the society, there are number of aspects which could be the responsibility of educational institutions as well as other organizations. Social responsibility has central role among the organizations to increase firm image. Firm image has major role in company branding. Brand popularity is majorly based on the firm image. As the firm image or corporate image has major role in companies (Ali et al., 2020; Liat et al., 2017; Motilewa et al., 2018). Increase in corporate image has positive role to enhance sustainable FP. Firm image has the direct relationship with sustainable FP. As firm image or cooperate image has significant relationship (Utomo et al., 2020).
H1 Social responsibility has positive influence on firm image.
H2 Firm image has positive influence on sustainable FP.
Another element; perceived quality has relationship with social responsibility and sustainable FP. Perceived quality can be explained as the perception of customer of the general quality or dominance of a product. Perceived quality is the first, a perception by customers. It is the perception of customer in his/her mind related to the concerned company. Companies adopt different ways to increase the perceived quality of the company products which ultimately has influence on firm perceived quality. In this way, social responsibility has major influence to develop firm perceived quality. Perceived quality has major importance among the companies that is the reason companies always focus to enhance the perceived quality (Situmorang, 2020; Susanti et al., 2020). Generally, companies remain involve in number of social activities for the welfare of the company which has the ability to increase the awareness of the company related to the company products in the community and it ultimately lead the customer to purchase the products of concerned company. Therefore, various activities of the educational institutions related to the social responsibility increase the perceived quality of the institutions. As the social responsibility has positive effect on perceived quality, further, perceived quality has positive effect on sustainable FP. Perceived quality has the potential to increase the sustainable FP. Increase in perceived quality increases the FP which is also given in previous studies (Sierra et al., 2017). Social responsibility has positive effect on both financial and non-financial performance. Therefore, social responsibility has important role in perceived quality which further lead to the sustainable FP.
H3 Social responsibility has positive influence on perceived quality.
H4 Perceived quality has positive influence on sustainable FP.
The above discussion shows that firm image has positive relationship with social responsibility and sustainable FP. Moreover, perceived image has positive relationship with social responsibility and sustainable FP. Furthermore, firm reputation also has important relationship with social responsibility which further lead to the sustainable FP. Firm reputation is explained as customers' perceptions of how well an institution takes care of different clients and is genuinely concerned related to their wellbeing. Carefully building as well as preserving this reputation is paramount for constant success in any industry, however, especially significant for service companies where failures are inevitable. Service institutions such as educational sector has important role in this matter. It is given in various studies that firm reputation or corporate reputation has positive role among the companies (Arikan et al., 2016; Arli et al., 2017). Furthermore, improvement in firm reputation has positive role in sustainable FP performance. Therefore, social responsibility effect positively on sustainable FP through firm reputation. Additionally, this study examined the mediating effect of firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality which lead to the below hypotheses;
H5 Social responsibility has positive influence on firm reputation.
H6 Firm reputation has positive influence on sustainable FP.
H7 Firm image mediates the relationship between social responsibility and sustainable FP.
H8 Perceived quality mediates the relationship between social responsibility and sustainable FP.
H9 Firm reputation mediates the relationship between social responsibility and sustainable FP.
Research Methodology
To examine the relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance, the current study designed questionnaire. Therefore, a survey questionnaire is preferred in the current study for data collection. As the survey questionnaire is the suitable tool to collect the data (Bowling et al., 1999). Number of previous investigations used survey questionnaire for data collection and proved that questionnaire is most important tool to collect the primary data. As the survey questionnaire has several benefits, for instance, a survey questionnaire helps to collect the opinion and views of employees. According to the literature, for the collection of primary data from the respondents among the organizations, the survey with the help of questionnaire is best, therefore, the current study also followed survey questionnaire.
This study measured five variables; social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable performance. The measurement of these variables was obtained from the previous studies. After collecting the scale items from previous studies, these scale items were adapted according to the current study and used for data collection. Indonesian educational institutions were selected, and teachers were preferred to get response for the final data analysis. Therefore, by using a questionnaire, data were collected from the teachers of various educational institutions. Among the Indonesian educational institutions, 450 questionnaires were distributed for the data collection among the teachers of these institutions. The purpose of the study was explained before data collection to the teachers. Total 349 questionnaires were returned and used in data analysis. In this whole process, area cluster sampling was applied, and data were collected by using simple random sampling from each cluster (Siuly et al., 2011; Ul-Hameed et al., 2018; Hameed et al., 2019).
Research Findings
First of all, this study insured data screening to examine the error in the data. To fix the errors in the data, this study examined missing value (Aydin & Senoglu, 2018) and outlier in the data. It is given in Table 1 that data is free from missing value as well as outlier which allow the data analysis to proceed further.
| Table 1 Data Statistics | |||||||||
| No. | Missing | Mean | Median | Min | Max | SD | Kurtosis | Skewness | |
| SR1 | 1 | 0 | 3.459 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.251 | -0.786 | -1.466 |
| SR2 | 2 | 0 | 2.993 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.963 | -1.896 | -0.392 |
| SR3 | 3 | 0 | 3.444 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.183 | -0.538 | -0.563 |
| SR4 | 4 | 0 | 3.362 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.28 | -1.854 | -1.41 |
| SR5 | 5 | 0 | 2.976 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.231 | -1.945 | -0.308 |
| SR6 | 6 | 0 | 3.398 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.956 | -0.772 | -0.46 |
| SR7 | 7 | 0 | 3.464 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.193 | -0.594 | -0.451 |
| FI1 | 8 | 0 | 3.52 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.18 | -0.695 | -1.443 |
| FI2 | 9 | 0 | 2.987 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.339 | -0.831 | -0.624 |
| FI3 | 10 | 0 | 3.5 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.231 | -0.785 | -0.463 |
| FI4 | 11 | 0 | 3.408 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 1.256 | -1.853 | -0.28 |
| PQ1 | 12 | 0 | 3.48 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.154 | -0.629 | -0.452 |
| PQ2 | 13 | 0 | 3.51 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.315 | -0.986 | -1.477 |
| PQ3 | 14 | 0 | 3.49 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 0.938 | -0.907 | -0.422 |
| PQ4 | 15 | 0 | 3.51 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.163 | -0.626 | -0.417 |
| FR1 | 16 | 0 | 3.51 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.163 | -1.626 | -0.417 |
| FR2 | 17 | 0 | 2.949 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.175 | -0.482 | -0.59 |
| FR3 | 18 | 0 | 3.398 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.972 | -0.84 | -1.422 |
| FR4 | 19 | 0 | 3.291 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.23 | -0.912 | -0.322 |
| SFP1 | 20 | 0 | 3.495 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.214 | -0.656 | -0.453 |
| SFP2 | 21 | 0 | 3.52 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.18 | -1.695 | -0.443 |
| SFP3 | 22 | 0 | 3.577 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.332 | -0.817 | -1.622 |
| SFP4 | 23 | 0 | 2.99 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.935 | -0.766 | -0.476 |
| SFP5 | 24 | 0 | 3.418 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 1.257 | -0.848 | -0.303 |
| SFP6 | 25 | 0 | 3.474 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.136 | -1.546 | -0.484 |
| SFP7 | 26 | 0 | 4.056 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.91 | 0.501 | -1.889 |
| SFP8 | 27 | 0 | 3.929 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.992 | -0.286 | -0.677 |
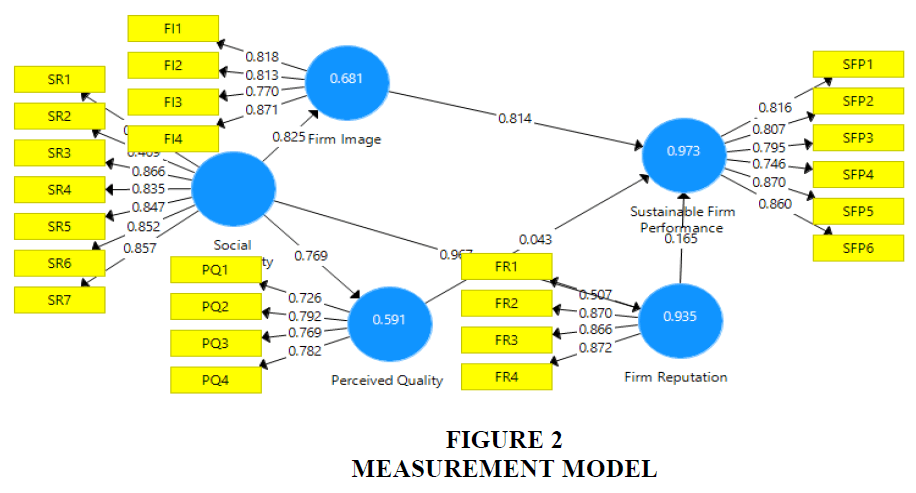
PLS algorithm was used in this study to examine the factor loadings (Henseler & Chin, 2010; Henseler et al., 2014; Henseler et al., 2015; Henseler et al., 2009; Ul-Hameed et al., 2019). It shows that firm image is measured by using four scale items, firm reputation is measured by using four scale items, and perceived quality is measured by using four scale items. Social responsibility is measured by using seven scale items and finally, sustainable FP is measured by using six scale items. All the scale items should have factor loadings above 0.4. Table 2 and Figure 2 shows that all the variables; social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable FP have factor loadings above 0.4 for all scale items.
| Table 2 Factor Loadings | |||||
| Firm Image | Firm Reputation | Perceived Quality | Social Responsibility | Sustainable Firm Performance | |
| FI1 | 0.818 | ||||
| FI2 | 0.813 | ||||
| FI3 | 0.77 | ||||
| FI4 | 0.871 | ||||
| FR1 | 0.507 | ||||
| FR2 | 0.87 | ||||
| FR3 | 0.866 | ||||
| FR4 | 0.872 | ||||
| PQ1 | 0.726 | ||||
| PQ2 | 0.792 | ||||
| PQ3 | 0.769 | ||||
| PQ4 | 0.782 | ||||
| SFP1 | 0.816 | ||||
| SFP2 | 0.807 | ||||
| SFP3 | 0.795 | ||||
| SFP4 | 0.746 | ||||
| SFP5 | 0.87 | ||||
| SFP6 | 0.86 | ||||
| SR1 | 0.514 | ||||
| SR2 | 0.469 | ||||
| SR3 | 0.866 | ||||
| SR4 | 0.835 | ||||
| SR5 | 0.847 | ||||
| SR6 | 0.852 | ||||
| SR7 | 0.857 | ||||
Results in Table 3 shows the convergent validity with the help of average variance extracted (AVE). According to Hair et al. (2017), AVE should be above 0.5. It is given in Table 3 that all the variables; social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable FP has AVE above 0.5. Finally, for all variables; social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable FP, composite reliability (CR) is also above 0.7. This study examined discriminant validity with the help of cross-loadings as given in Table 4 (Fornell & Larcker, 1981).
| Table 3 Reliability and Convergent Validity | ||||
| Cronbach's Alpha | rho_A | CR | (AVE) | |
| Firm Image | 0.836 | 0.839 | 0.891 | 0.671 |
| Firm Reputation | 0.792 | 0.843 | 0.868 | 0.631 |
| Perceived Quality | 0.788 | 0.822 | 0.851 | 0.589 |
| Social Responsibility | 0.874 | 0.903 | 0.905 | 0.587 |
| Sustainable Firm Performance | 0.899 | 0.901 | 0.923 | 0.667 |
| Table 4 Cross-Loadings | |||||
| Firm Image | Firm Reputation | Perceived Quality | Social Responsibility | Sustainable Firm Performance | |
| FI1 | 0.818 | 0.678 | 0.594 | 0.647 | 0.804 |
| FI2 | 0.813 | 0.654 | 0.545 | 0.669 | 0.794 |
| FI3 | 0.77 | 0.658 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.748 |
| FI4 | 0.871 | 0.723 | 0.615 | 0.735 | 0.862 |
| FR1 | 0.384 | 0.807 | 0.782 | 0.495 | 0.386 |
| FR2 | 0.756 | 0.87 | 0.583 | 0.854 | 0.811 |
| FR3 | 0.724 | 0.866 | 0.577 | 0.825 | 0.761 |
| FR4 | 0.698 | 0.872 | 0.574 | 0.838 | 0.728 |
| PQ1 | 0.805 | 0.74 | 0.826 | 0.738 | 0.767 |
| PQ2 | 0.335 | 0.449 | 0.792 | 0.504 | 0.348 |
| PQ3 | 0.357 | 0.434 | 0.769 | 0.464 | 0.362 |
| PQ4 | 0.384 | 0.507 | 0.782 | 0.495 | 0.386 |
| SFP1 | 0.729 | 0.806 | 0.61 | 0.855 | 0.816 |
| SFP2 | 0.821 | 0.677 | 0.596 | 0.846 | 0.807 |
| SFP3 | 0.811 | 0.662 | 0.54 | 0.878 | 0.795 |
| SFP4 | 0.767 | 0.654 | 0.526 | 0.846 | 0.746 |
| SFP5 | 0.874 | 0.737 | 0.616 | 0.881 | 0.87 |
| SFP6 | 0.791 | 0.734 | 0.706 | 0.888 | 0.86 |
| SR1 | 0.292 | 0.394 | 0.635 | 0.514 | 0.81 |
| SR2 | 0.255 | 0.373 | 0.65 | 0.469 | 0.87 |
| SR3 | 0.763 | 0.871 | 0.595 | 0.866 | 0.888 |
| SR4 | 0.741 | 0.863 | 0.599 | 0.835 | 0.778 |
| SR5 | 0.709 | 0.876 | 0.584 | 0.847 | 0.898 |
| SR6 | 0.725 | 0.806 | 0.576 | 0.852 | 0.876 |
| SR7 | 0.728 | 0.805 | 0.611 | 0.857 | 0.884 |
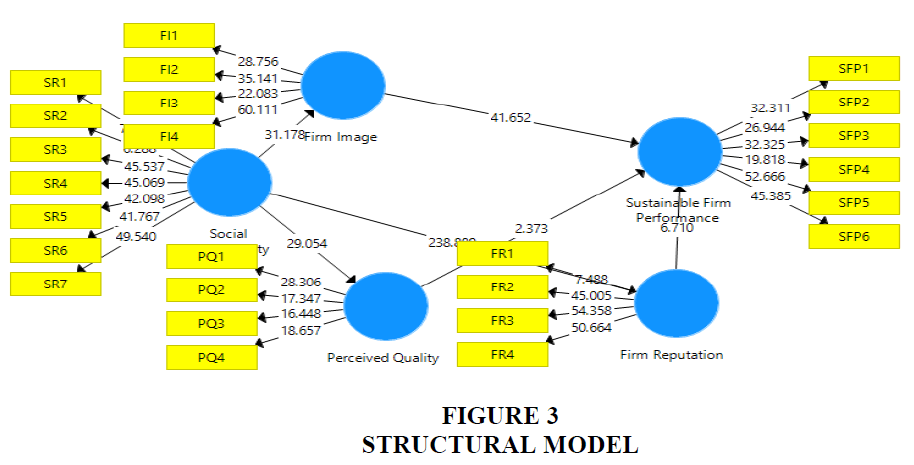
Before, to assess the indirect effect of firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality, this study examined the direct effect. The direct effect of social responsibility is examined on firm image. The direct effect of social responsibility was also examined on firm reputation and perceived quality. The direct effect of firm image is examined on sustainable FP. Moreover, the direct effect of firm reputation and perceived quality was examined on sustainable FP. This relationship was examined with the help of PLS structural model (Hair et al. 2014; Hair et al., 2013; Hair et al. 2012; Hameed et al., 2018; Henseler et al., 2014). Results in Table 5 shows that social responsibility has positive effect on firm image. Social responsibility also has positive effect on firm reputation. Better implementation of social responsibility has the ability to increase firm reputation. Social responsibility also has positive effect on perceived quality. Along with this, firm image has positive effect on sustainable FP. Firm reputation has positive effect on sustainable FP. Finally, perceived quality also shows positive effect on sustainable FP. Hence, social responsibility has positive effect on firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality. Firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality have positive effect on sustainable FP. PLS structural model is given in Figure 3.
| Table 5 Direct Effect Results | |||||
| (O) | (M) | SD | T Statistics | P Values | |
| Firm Image -> Sustainable FP | 0.814 | 0.814 | 0.02 | 41.652 | 0 |
| Firm Reputation -> Sustainable FP | 0.165 | 0.164 | 0.025 | 6.71 | 0 |
| Perceived Quality -> Sustainable FP | 0.043 | 0.043 | 0.018 | 2.373 | 0.018 |
| Social Responsibility -> Firm Image | 0.825 | 0.825 | 0.026 | 31.178 | 0 |
| Social Responsibility -> Firm Reputation | 0.967 | 0.968 | 0.004 | 238.889 | 0 |
| Social Responsibility -> Perceived Quality | 0.769 | 0.77 | 0.026 | 29.054 | 0 |
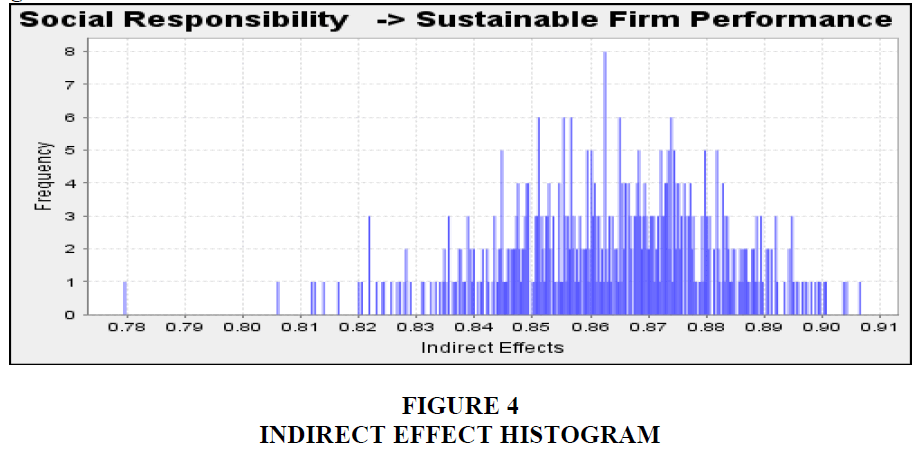
The indirect effect by the current study is given in Table 6. The indirect effect of firm image is examined between social responsibility and sustainable FP. The indirect effect of firm reputation is examined between social responsibility and sustainable FP. Finally, the indirect effect of perceived quality is examined between social responsibility and sustainable FP. All these indirect effect were examined by following the instructions of Preacher & Hayes (2008). The indirect effect of firm image between social responsibility and sustainable FP found t-value 22.597 which is significant. The indirect effect of firm reputation between social responsibility and sustainable FP found t-value 6.67 which is also significant. Finally, the indirect effect of perceived quality between social responsibility and sustainable FP found t-value 2.442 which is also significant. Hence, all the indirect effect is significant which shows that firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality reflect the positive effect of social responsibility on sustainable FB. The indirect effect histogram for all three variables; firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality is given in Table 6. Furthermore, this study examined the r-square value which is 0.973. This r-square value for sustainable FP is strong (Chin, 1998) and showing that all the variables; social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality are expected to bring 97.3% change in sustainable FP. Indirect effect is also given through histogram as shown in Figure 4.
| Table 6 Indirect Effect Results | |||||
| (O) | (M) | SD | t Statistics | P Values | |
| Social Responsibility -> Firm Image | 0.672 | 0.672 | 0.03 | 22.597 | 0 |
| -> Sustainable FP | |||||
| Social Responsibility -> Firm Reputation | 0.159 | 0.159 | 0.024 | 6.67 | 0 |
| -> Sustainable FP | |||||
| Social Responsibility -> Perceived Quality -> Sustainable FP | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.014 | 2.442 | 0.015 |
Conclusion
The objective of this study was to examine the role of social responsibility in sustainable FP. The relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable FP was examined by the current study. Additionally, the indirect effect of firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality was examined between social responsibility and sustainable FP. For this purpose, data were collected from the teachers of various educational institutions in Indonesia by using questionnaire survey. Results of the study provided vital contribution to sustainable FP among the educational institutions. Results of the study indicated that social responsibility has positive effect on firm image, perceived quality and firm reputation. Social responsibility enhances the firm image as the social responsibility has positive effect on firm reputation which shows positive effect on sustainable FP. Increase in social responsibility increases the firm performance as findings shows the significant positive effect of social responsibility on perceived quality of education. Finally, increase in perceived quality increases the sustainable FP. Additionally, firm image, perceived quality and firm reputation has positive effect on sustainable FP. Hence, increase in firm image, perceived quality and firm reputation increases the sustainable FP.
The relationship examined in the current study has major role in sustainable FP which has positive role in theoretical and practical implications. As this study examined the valuable relationship between social responsibility, firm image, firm reputation, perceived quality and sustainable FP. This relationship is first time examined in the educational institutions of Indonesia. Furthermore, this study examined the mediation effect of firm image, firm reputation and perceived quality between social responsibility and sustainable FP which has vital contribution to the Literature. Practically, this study is helpful for the educational institutions of Indonesia as this study proved that social responsibility can increase the performance.
References
- Ali, H., Danish, R., & Asrar-ul-Haq, M. (2020). How corporate social responsibility boosts firm financial performance: The mediating role of corporate image and customer satisfaction. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(1), 166-177.
- Arikan, E., Kantur, D., Maden, C., & Telci, E. (2016). Investigating the mediating role of corporate reputation on the relationship between corporate social responsibility and multiple stakeholder outcomes. Quality & Quantity, 50(1), 129-149.
- Arli, D., Grace, A., Palmer, J., & Pham, C. (2017). Investigating the direct and indirect effects of corporate hypocrisy and perceived corporate reputation on consumers’ attitudes toward the company. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 37, 139-145.
- Asrar-ul-Haq, M., Kuchinke, K., & Iqbal, A. (2017). The relationship between corporate social responsibility, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment: Case of Pakistani higher education. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 2352-2363.
- Aydin, D., & Senoglu, B. (2018). Estimating the Missing Value in One-Way Anova Under Long-Tailed Symmetric Error Distributions. Sigma: Journal of Engineering & Natural Sciences/Mühendislik ve Fen Bilimleri Dergisi, 36(2), 523-538.
- Bowling, A., Bond, M., Jenkinson, C., & Lamping, D. (1999). Short Form 36 (SF-36) Health Survey questionnaire: which normative data should be used? Comparisons between the norms provided by the Omnibus Survey in Britain, the Health Survey for England and the Oxford Healthy Life Survey. Journal of Public Health, 21(3), 255-270.
- Chin, W. (1998). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Modern Methods for Business Research, 295(2), 295-336.
- Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39-50.
- Hair, J., Hollingsworth, C., Randolph, A., & Chong, A. (2017). An updated and expanded assessment of PLS-SEM in information systems research. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 117(3), 442-458.
- Hair, J., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long Range Planning, 46(1-2), 1-12.
- Hair, Jr, J., Sarstedt, M., Hopkins, L., & Kuppelwieser, V. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). European Business Review, 26(2), 106-121.
- Hair, J., Sarstedt, M., Pieper, T., & Ringle, C. (2012). The use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in strategic management research: a review of past practices and recommendations for future applications. Long Range Planning, 45(5-6), 320-340.
- Hameed, W., Basheer, M., Iqbal, J., Anwar, A., & Ahmad, H. (2018). Determinants of Firm’s open innovation performance and the role of R & D department: an empirical evidence from Malaysian SME’s. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 8(1), 29.
- Henseler, J., & Chin, W. (2010). A comparison of approaches for the analysis of interaction effects between latent variables using partial least squares path modeling. Structural Equation Modeling, 17(1), 82-109.
- Henseler, J., Dijkstra, T., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C., Diamantopoulos, A., Straub, D., Ketchen, Jr., D., Hair, J., Hult, G., Calantone, R. (2014). Common beliefs and reality about PLS: Comments on Rönkkö and Evermann (2013). Organizational Research Methods, 17(2), 182-209.
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115-135.
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C., & Sinkovics, R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. In R. Sinkovics & P. Ghauri (eds.). New challenges to international marketing (pp. 277-319). Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
- Hernández, J., Yañez-Araque, B., & Moreno-García, J. (2020). Moderating effect of firm size on the influence of corporate social responsibility in the economic performance of micro-, small-and medium-sized enterprises. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 151, 119774.
- Javed, M., Rashid, M., Hussain, G., & Ali, H. (2020). The effects of corporate social responsibility on corporate reputation and firm financial performance: Moderating role of responsible leadership. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(3), 1395-1409.
- Jermsittiparsert, K., Siam, M., Issa, M., Ahmed, U., & Pahi, M. (2019). Do Consumers Expect Companies to Be Socially Responsible? The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Buying Behavior. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 7(4), 741-752.
- Liat, C., Mansori, S., Chuan, G., & Imrie, B. (2017). Hotel service recovery and service quality: Influences of corporate image and generational differences in the relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty. Journal of Global Marketing, 30(1), 42-51.
- Motilewa, B., Worlu, R., Moses, C., Adeniji, C., Agboola, G., & Oyeyemi, A. (2018). Survey data on employees’ perception of the impact of community development initiatives on the corporate image of oil and gas firms in Nigeria. Data in Brief, 19, 1874-1879.
- Preacher, K., & Hayes, A. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior research methods, 40(3), 879-891.
- Richards, K., Ivy, V., Wright, P., & Jerris, E. (2019). Combining the skill themes approach with teaching personal and social responsibility to teach social and emotional learning in elementary physical education. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 90(3), 35-44.
- Sengupta, E., Blessinger, P., & Mahoney, C. (eds.). (2020). Civil Society and Social Responsibility in Higher Education: International Perspectives on Curriculum and Teaching Development. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Sepetis, A., Goula, A., Kyriakidou, N., Rizos, F., & Sanida, M. G. (2020). Education for the Sustainable Development and Corporate Social Responsibility in Higher Education Institutions (HEIs): Evidence from Greece. Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies, 8(2), 86-106.
- Sierra, V., Iglesias, O., Markovic, S., & Singh, J. (2017). Does ethical image build equity in corporate services brands? The influence of customer perceived ethicality on affect, perceived quality, and equity. Journal of Business Ethics, 144(3), 661-676.
- Singhapakdi, A., Kraft, K., Vitell, S., & Rallapalli, K. (1994). The perceived importance of ethics and social responsibility on organizational effectiveness: A survey of marketers. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(1), 49-56.
- Situmorang, P.P. (2020). The Effect of System Quality and Information Quality on the Satisfaction of User Enterprise Resource Planning-System Application and Product in Data Processing (ERP-SAP) with Perceived Usefulness as a Variable Moderating in PTPN III (Persero) Unit of Labuhan. International Journal of Public Budgeting, Accounting and Finance, 2(4), 1-11.
- Siuly, Li, Y., & Wen, P. (2011). EEG signal classification based on simple random sampling technique with least square support vector machine. International journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, 7(4), 390-409.
- Susanti, V., Sumarwan, U., Simanjuntak, M., & Yusuf, E.Z. (2020). Rational antecedent framework of brand satisfaction in the industrial market: assessing rational perceived quality and rational perceived value roles. International Review of Management and Marketing, 10(1), 19-26.
- Thongrawd, C., Bootpo, W., Thipha, S., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). Exploring the Nexus of Green Information Technology Capital, Environmental Corporate Social Responsibility, Environmental Performance and the Business Competitiveness of Thai Sports Industry Firms. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise, 14(5 Proc), S2127-S2141.
- Uduji, J., Okolo-Obasi, E., & Asongu, S. (2020). The impact of corporate social responsibility interventions on female education development in the rural niger delta region of Nigeria. Progress in Development Studies, 20(1), 45-64.
- Ul-Hameed, W., Mohammad, H., & Shahar, H. (2018). Microfinance institute’s non-financial services and women-empowerment: The role of vulnerability. Management Science Letters, 8(10), 1103-1116.
- Ul-Hameed, W., Mohammad, H., Shahar, H., Aljumah, A., & Azizan, S. (2019). The effect of integration between audit and leadership on supply chain performance: Evidence from UK based supply chain companies. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 7(2), 311-328.
- Utomo, A., Respati, A., & Latil, I. (2020). Effect of Customer Co-Operation Capability and Corporate Image on Firm Financial Performance with Mediating Role of Customer Loyalty. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(1), 233-243.
- Uyar, A., Kilic, M., Koseoglu, M., Kuzey, C., & Karaman, A. (2020). The link among board characteristics, corporate social responsibility performance, and financial performance: Evidence from the hospitality and tourism industry. Tourism Management Perspectives, 35, 100714.