Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 4
Second Order Confirmatory Factor Analysis of Guidelines for the Elderly Business in Thailand
Thanin Silpcharu, King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok
Wongtawat Boonrattanakul, SS Prosperity Group Co. Ltd.
Abstract
Aim: As Thailand is becoming Aged Society nowadays, business sectors must therefore adjust themselves for changes of target customers who are the elderly. This research aims to study second order confirmatory factor analysis of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand.
Methodology: Mixed method (qualitative and quantitative research) was carried out in this research by surveying qualitative data via in-depth interview with 9 experts and quantitative data from 500 entrepreneurs who run aging-related business by qualitative research using purposive sampling and descriptive statistics using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), and multivariate statistics analysis using Analysis of a Moment Structures (AMOS).
Finding: Research results showed that the second order confirmatory factor of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand consisted of 5 components; innovation and technology, resource, internal process, marketing, and learning growth. Analysis results of developed model were found corresponded to the evaluation criteria and fit to empirical data with 0.092 Chi-Square Probability Level, 1.116 of Relative Chi-Square, 0.955 of Goodness of Fit Index, and 0.015 of Root Mean Square Error of Approximation.
Keywords
Second Order Confirmatory Factor Analysis, Business, Guideline, Elderly.
Introduction and Literature Review
The United Nations (UN) defines the word “the Elderly” that both male and female population who are older than 60 years old. Aged society is classified into 3 levels; 1) Aging Society, 2) Aged Society, and 3) Super-Aged Society. Their differences are that they are the society or country having population who are older than 60 years old more than 10%, 20%, and 28% of total population or population who are 65 years old or older more than 7%, 14%, and 20% of total population, respectively (Prompak, 2013).
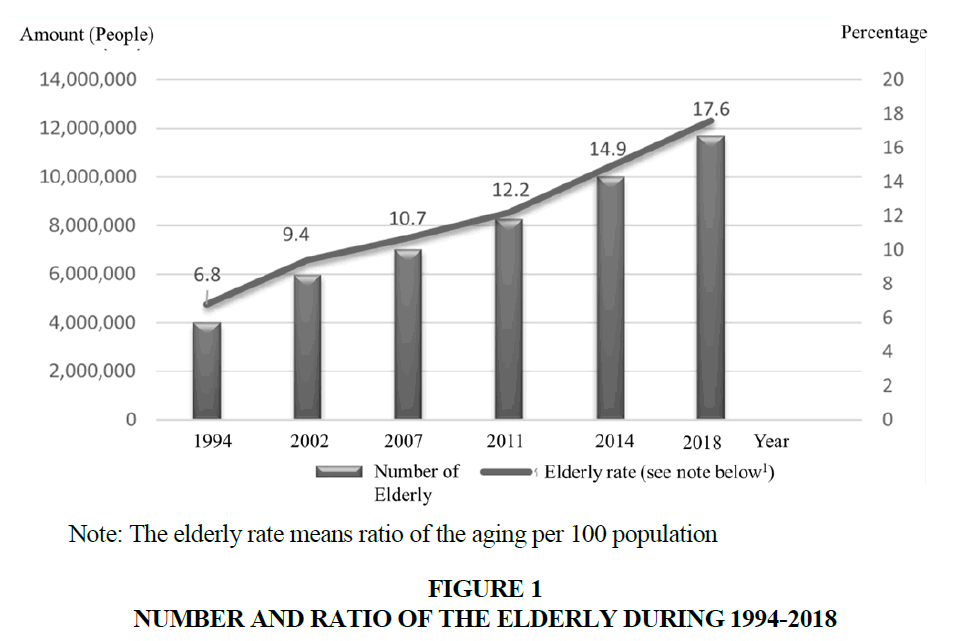
Trend of the elderly increased during 1994 – 2018. As shown in Figure 1, the elderly increased 6.8% in 1994 and 9.4%, 10.7%, 12.2%, 14.9%, and 17.6% in 2002, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, respectively (National Statistics Office, 2018).
Situations in Thailand were found that the elderly ratio continuously increased in 2018. The population excluding migrant workers was 66 million and 11.70 million of them were elderly citizen which was 17.60% of total population. The figure implied that Thailand is becoming Aged Society in 2021. Therefore, the country should be prepared for changes. It had been expected that value of market of elderly business and services in Thailand in 2017 was 1,000 million Baht with 15% annual growth rate. The trend of this market in the next 6-10 years will grow up to 3,000 – 4,000 million Baht. Becoming Aged Society causes health vulnerability following to age groups and lack of caregivers. Rapidly increased ratio of the elderly effects on characteristics of economic dependence among different ages of population. Moreover, due to the progressive development of advanced medical general practice and medicines, the number of death rates is reduced with better life quality and longer life span. In spite of longer life, physical fitness is getting worse. Accident is easy to take place. Sickness from non-communicable diseases appears. Disability might be found and causes self-incapability (Srisuk, 2018). According to the population structural changes, unavoidable impact on economy and society are certainly met. Having high ratio of the elderly in a country also reflect the lower number of labors. These effects on national potential of products and services production. In addition, the government has burden and expenses on welfare for the elderly and this might affect on financial status of the country (Thailand Development Research Institute, 2017).
According to such problems, future situation should be greatly focused and will affect on national economic and social systems. It is urgent to plan and be prepared for being aged society so that the higher number of the elderly will have good life quality. Industrial business sector should be ready for elderly market in order to manufacture products and provide services that meet fundamental needs according to elderly groups and create new innovation and technology. This is considered great business opportunity to best enhance products and services for the aging group. Therefore, guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand to increase competitive potential for industrial business sectors need to be studied.
Innovation & Technology
The study of Kale (2017) showed 2 sources of innovation and technology for business; 1) internal discovery for new concepts of products and services is often carried out by establishing Research and Development (R&D) agencies and finding people who are talented in thinking of new things which might be the development of new products and services for added value., and 2) knowledge sharing and getting external or open innovation; good concepts do not have to only come from internal personnel. It is to accept new external ideas leading to more rapid and diverse ideas including lower costs and expenses than self-development as the experts who are specifically specialized might be scattered outside the organization.
Marketing
The study of Lies (2019) and the research of “Digital Marketing Techniques on Their Way to Becoming Social Engineering Techniques in Marketing” from International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence explained customer’s true behaviors which change rapidly. High marketing competition is such an important factor that entrepreneurs must adjust their marketing strategies. To succeed in marketing in digital society 5.0 corresponding to consumer’s behaviors, 3 key strategies, heart of marketing 5.0, are needed; Conversion, Experience, and Data.
Internal Process
Mclvor (2016) mentioned that significance of internal process is internal process improvement or development, correction, and change for better internal process by discovering causes, analyzing, finding solution, including setting up work practice or manual to be good work standards. Meaning of internal process improvement or the manual is always reviewed when a problem is found. The internal process improvement will be able to lessen internal conflicts between departments including internal and external customer’s complaints.
Learning and Growth
The research of Karlinsky-Shichor and Zviran, M. (2016) on knowledge management (KM) and its framework was carried out by having literature review about development of concepts of knowledge management and showing KM elements for establishing a system. The 3 KM elements are KM resource, KM activities, and KM impact. Its collaborative framework can be achieved from the results of expert, academician, and entrepreneur’s opinions, reviews, and suggestions. KM must rely on 3 key components; 1) human or personnel; It is the most important factor for KM operation. Human is the most significant knowledge source and the one who applies all knowledge for organizational development., 2) technology; It is an assistant for searching, sharing, and collecting data and allows people to rapidly and conveniently apply such data for organizational development., and 3) KM process; In every KM process equally and efficiently relates among one another.
Resources
The study of Jensen et al. (2016): World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology on The Resource-Base View of Organization and Innovation: Recognition of Significant Relationship in an Organization was about strategic management by showing the relationship between organizational resource and innovation. Resource drives organizational capacity which leads to innovation ability and achievement according to suitable guidelines. Resource is strength of the organization and significantly effect on competitiveness. It consists of 4 attributes; valuable resource, rare resource, imperfectly imitable resource, and non-substitutable resource.
Second-order Confirmatory Factor Analysis (SCFA)
A multiple statistical method starting from Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) which groups highly-related variables in the same group and verifies them by using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) to confirm grouping correctness between observative variables and each latent variable. After that, the variable will be re-verified in order to confirm the correctness of each latent variable whether it suits for the research or not (Silpcharu, 2020).
Objectives
Objective of this study is to analyze components of second-order confirmatory factor of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand.
Methodology
1. Qualitative research using in-depth interview technique; 9 experts were the population of this research. Purposive sampling was used by determining qualification of experts. The experts were therefore divided into 3 groups; 3 experts in a group of entrepreneur or executives in business organizations, 3 experts in a group of elderly-related public sectors or agencies, and 3 experts in a group of academicians. Data were collected for setting a questionnaire.
2. Quantitative research; Population of this research is executives or owners of active commerce-registered business according to Business Registration Act. 272,803 elderly-related businesses (Department of Business Development Ministry of Commerce, 2019) are classified following to business categories by using criteria of component analysis research. 500 samples were determined in very good level (Silpcharu, 2020) Multi Stage sampling was used and consisted of cluster sampling with 2 groups of business categories; service business and non-service business. Probability sampling was then used for collecting data from the sample groups (Silpcharu, 2020).
3. A tool for component analysis research was a 100-question rating-scale questionnaire by determining weighing criteria into 5 scales of Likert (David & Sutton, 2011). Test results of tool quality showed 0.60-1.00 Index of Item Objective Congruence: IOC, 0.31 – 0.78 Corrected Item–Total Correlation by individually analyzing discrimination value, and 0.973 Cronbach’ Alpha Coefficient from content validity analysis.
4. Data collection in this research was carried out by interviewing the sample groups. Descriptive statistics using SPSS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis using AMOS were used for data analysis with the 4 following values for evaluating the data-model fit; 1) Chi-square Probability Level was more than 0.05., 2) Relative Chi-square was less than 2.00., 3) Goodness of Fit Index was greater than 0.90., and 4) Root Mean Square Error of Approximation was less than 0.08 (Silpcharu, 2020).
Results
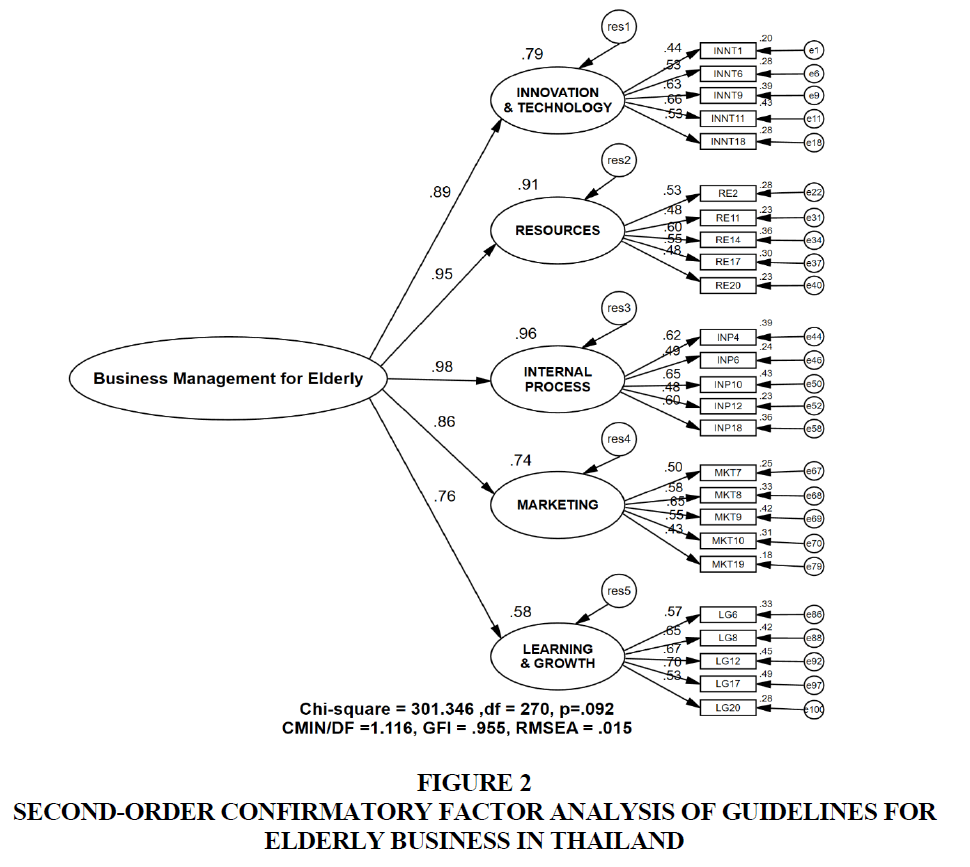
Analysis results of second-order confirmatory factor analysis of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand are as shown in Figure 2.
According to Figure 2, it showed statistical values evaluating the fit of post-improvement second-order confirmatory factor analysis model of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand by considering Modification Indices (MI) according to the study of Arbuckle. It was found that Chi-Square probability level (CMIN-P) value equaled to 0.092 which was greater than 0.05. Relative Chi-Square (CMIN/DF) was 1.116 which was less than 2. Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) was 0.955 which was greater than 0.90 and Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was 0.015 which was less than 0.08. These can be concluded that all 4 statistical values were qualified. Therefore, the second-order confirmatory factor analysis model of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand was fit to the empirical data.
Guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand consisted of 5 latent variables which could be ascendingly prioritized according to its weight as follows; 1) Internal Process; Regression Weight=0.98, R2=0.96, 2) Resources; Regression Weight=0.95, R2=0.91, 3) Innovation & Technology; Regression Weight=0.89, R2=0.79, 4) Marketing; Regression Weight=0.86, R2=0.74, and 5) Learning & Growth; Regression Weight=0.76, R2=0.58.
Analysis results of levels of significance of post-improvement second-order confirmatory factor analysis model of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand showed mean and Standard Deviation (S.D.) values of each component as shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Mean and Standard Deviation (S.D.) Values of Guidelines for Elderly Business in Thailand | |||
| Guidelines for Elderly Business in Thailand |  |
S.D. | |
| OVERALL GUIDELINE FOR ELDERLY BUSINESS | 4.18 | 0.36 | |
| 1. INNOVATION & TECHNOLOGY | 4.24 | 0.40 | |
| INNT1 | Design products or services by considering independent elderly’s self-assistance | 4.18 | 0.63 |
| INNT6 | Focus on innovation development by teamwork | 4.33 | 0.65 |
| INNT9 | Allocate time for personnel in the organization to create and develop products or services for elderly | 4.21 | 0.71 |
| INNT11 | Keep up with innovation idea to make it become concrete benefit | 4.21 | 0.70 |
| INNT18 | Collaborate with public sector, research networks, and educational institutes to discover new innovation and technology | 4.24 | 0.59 |
| 2. RESOURCES | 4.17 | 0.42 | |
| RE2 | Provide experts in elderly psychology | 4.19 | 0.72 |
| RE11 | Develop purchase system in order to obtain qualified raw materials for product or service production | 4.07 | 0.75 |
| RE14 | Regularly evaluate tool, machine, and equipment suitability to consider making decision in buying or improving them | 4.19 | 0.67 |
| RE17 | Use internal and external information for analysis and decision making | 4.07 | 0.69 |
| RE20 | Coordinate with external organizations to co-use elderly-related big data together | 4.07 | 0.74 |
| 3. INTERNAL PROCESS | 4.23 | 0.39 | |
| INP4 | Set Cross-functional team collaboration in the organization to develop products and services to fit the elderly in each age gap | 4.17 | 0.68 |
| INP6 | Determine short-term and long-term plan to support elderly-related business | 4.15 | 0.71 |
| INP10 | Coordinate with all sector to have consistent work operation to mutual goal | 4.19 | 0.67 |
| INP12 | Collaborate with external organizations to set up elderly-related business platforms | 4.28 | 0.63 |
| INP18 | Determine departments/units/divisions/personnel to be responsible for products or services specifically for the elderly | 4.27 | 0.68 |
| 4. MARKETING | 4.22 | 0.38 | |
| MKT7 | Set the price by considering worthiness because the elderly has financial restrictions | 4.24 | 0.63 |
| MKT8 | Never take advantage from setting exaggerated price of elderly-related products | 4.25 | 0.64 |
| MKT9 | Apply quantitative discount policy for big order of products or services | 4.17 | 0.70 |
| MKT10 | Establish agencies for product and service demonstration at user’s place | 4.17 | 0.68 |
| MKT19 | Analyze internal and external situations to adjust strategies in design planning and products or services production | 4.07 | 0.78 |
| 5. LEARNING & GROWTH | 4.05 | 0.48 | |
| LG6 | Clearly determine goals of knowledge sharing and relate them to business goals | 4.05 | 0.71 |
| LG8 | Set up human networks who experiences from actual practices | 4.13 | 0.70 |
| LG12 | Provide manner training course for personnel in the organization | 4.09 | 0.74 |
| LG17 | Provide training courses for knowledge and ability development to apply in organizational development | 4.02 | 0.76 |
| LG20 | Create culture of learning organization to urge everyone’s creativity | 3.98 | 0.81 |
According to Table 1, it was found that overall significance of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand was high with 4.18 mean values. Considered individually, significance of all components was high. The significance of innovation and technology, internal process, marketing, resource, and learning and growth was 4.24, 4.23, 4.22, 4.17 and 4.05, respectively. Individual analysis results of levels of significance of second-order confirmatory factor of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand. Significance of individual analysis results was high with 3.98 – 4.33 mean value and the top 3 components could be ascending put in order as follows:
i. Innovation & Technology; 1) focuses on innovation development by teamwork, 2) collaborates with public sector, research networks, and educational institutes to discover new innovation and technology, and 3) keeps up with innovation idea to make it become concrete benefit with 4.33, 4.24, and 4.21 mean values, respectively.
ii. Resource; 1) regularly evaluates tool, machine, and equipment suitability to consider making decision in buying or improving them, 2) provides experts in elderly psychology, and 3) uses internal and external information for analysis and decision making with 4.19, 4.19, 4.07 mean values, respectively.
iii. Internal process; 1) collaborates with external organizations to set up elderly-related business platforms, 2) determines departments/units/divisions/personnel to be responsible for products or services specifically for the elderly, and 3) coordinates with all sector to have consistent work operation to mutual goal with 4.28, 4.27, and 4.19 mean values, respectively.
iv. Marketing; 1) never takes advantage from setting exaggerated price of elderly-related products, 2) sets the price by considering worthiness because the elderly has financial restrictions, and 3) establishes agencies for product and service demonstration at user’s place with 4.25, 4.24, and 4.17 mean values, respectively.
v. Learning and Growth; 1) sets up human networks who experiences from actual practices, 2) provides manner training course for personnel in the organization, and 3) clearly determines goals of knowledge sharing and relate them to business goals with 4.13, 4.09, and 4.05 mean values, respectively.
Discussion
1. The component most effecting on guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand is internal process with 0.98 Standardized Regression Weight and 0.001 statistical significance. This is in accordance with performance management. KPI is important for the operations of online stores who sell products for the elderly. The Key Performance Indicator (KPI) from Balanced Scorecard (BSC) showed that internal process was in the first place, followed by learning and growth, customer, and finance, respectively (Tsai & Cheng, 2012).
2. Innovation & Technology aspect of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand was the most significant component with 4.24 mean value. The figure reflects the importance of using innovation and technology as an important role of operation for the elderly business in Thailand in order to help the elderly who have poor health, stay independently, or sick by non-communicable disease to live well and happily. This was in accordance with the study of mHealth which showed that the rapidly higher number of aging populations comes with chronic diseases. Therefore, there are a number of challenges to meet elderly group’s complicated requirement. mHealth mobile technology shows the determination of elderly assistance to manage chronic diseases. Using mHealth technology to develop innovation of elderly home health care (Matthew-Maich et al., 2016) and new value presentation lead to the adjustment of mutual understanding among relating people and the elderly such as the elderly and caregivers so that they realize value of the robot that assists and helps the elderly. The robot might help the family member feel safe, however; the elderly might be stressed when they have to rely on the technology. This is therefore the obstacle of service acceptance (?ai?, 2018).
3. Innovation development by teamwork was individually focused and the most significant with 4.33 mean value. However, as the teams from diverse and various professions cooperate to develop integrated concept of innovation for responding the elderly’s complicated requirement from theories to practices by encouraging practitioners to change their vision and be the center of management and helping them to develop their new roles and be able to share their knowledge among experts (de Stampa, 2014).
Suggestions for Further Study
According to second-order confirmatory factor analysis of guidelines for the elderly business in Thailand, the author would like to suggest 3 issues of guidelines for the elderly business as described below:
1. Education; the government by Ministry of Education should provide learning plan and prepare elderly’s care procedure starting from childhood. Children should learn and understand the elderly, learn their restrictions, abilities, and physical fitness, and deeply reach their minds in order to live with them happily. Moreover, the society must be campaigned and implanted with values of realization of elderly’s value following to the culture focusing on gratitude. For working-age group, caregiver should have knowledge and abilities to take care and live with the elderly happily. Elderly’s expense supporter should have financial and time plan to take care of their parents and even themselves in the future. The elderly should be encouraged to learn technology and innovation which rapidly change so that they will be able to accept and not refuse assistance from supporter or caregiver.
2. Business entrepreneur; Business guidelines for the elderly are 1) focusing on innovation development by teamwork, 2) collaborating with external organizations to set up elderly-related business platforms, 3) determining departments/units/divisions/personnel to be responsible for products or services specifically for the elderly, 4) never taking advantage from setting exaggerated price of elderly-related products, and 5) collaborating with public sector, research networks, and educational institutes to discover new innovation and technology. Therefore, the business entrepreneur should adjust their business operational plan to be more suitable for elderly services.
3. Social development and human security; Public sectors should prepare the development of suitable environment and public services for the elderly’s lifestyle, the development of accommodation adjustment prototype so that the elderly or caregiver will be able to conveniently and safely utilize it and help the elderly to be able to live when they have to be alone., comprehensive, sufficient, and convenient healthcare service so that the elderly are able to easily, conveniently and safely access to it with qualified standards., financial planning and adequate saving for the elderly themselves and their offspring, the development for caretaker’s knowledge, and provision post-retired jobs both in public and private sectors.
References
- ?ai?, M., Odekerken-Schröder, G., & Mahr, D. (2018). Service robots: value co-creation and co-destruction in elderly care networks. Journal of Service Management, 29 (2), 178-205.
- David, & Sutton. (2011). Social research: An introduction, 2nd ed. SAGE, London, UK: 259
- De Stampa, M., Vedel, I., Trouvé, H., Ankri, J., Saint Jean, O., & Somme, D. (2014). Multidisciplinary teams of case managers in the implementation of an innovative integrated services delivery for the elderly in France.BMC Health Services Research,14(1), 1-8.
- Department of Business Development Ministry of Commerce. (2019). The Statistic of the Juristic Person's Registration in 2019. Retrieved from www.dbd.go.th
- Jensen, J.A., Cobbs, J.B., & Turner, B.A. (2016). Evaluating sponsorship through the lens of the resource-based view: The potential for sustained competitive advantage.Business Horizons,59(2), 163-173.
- Kale, D. (2017). Sources of innovation and technology capability development in the Indian automobile industry.Institutions and Economies, 121-150.
- Karlinsky-Shichor, Y., & Zviran, M. (2016). Factors influencing perceived benefits and user satisfaction in knowledge management systems.Information Systems Management,33(1), 55-73.
- Lies, J. (2019). Marketing intelligence and big data: Digital marketing techniques on their way to becoming social engineering techniques in marketing. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia & Artificial Intelligence,5(5).
- Matthew-Maich, N., Harris, L., Ploeg, J., Markle-Reid, M., Valaitis, R., Ibrahim, S., & Isaacs, S. (2016). Designing, implementing, and evaluating mobile health technologies for managing chronic conditions in older adults: a scoping review. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 4(2), e29
- McIvor, R. (2016). An analysis of the application of process improvement techniques in business process outsourcing.International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 33(3), 321-343.
- National Statistical Office Thailand. (2018). The Report on the 2018 survey of older person in Thailand, Statistical Forecasting Division National Statistical Office.
- Prompak, C. (2013). Aging Society in Thailand. Bureau of parliamentary studies of the secretariat of the senate.
- Silpcharu T. (2020). Research and Statistics Analysis by SPSS and AMOS. 18th edition, Nonthaburi : Business R&D Part., Limited.
- Srisuk, A. (2018). Lived experiences of sons being caregivers for dependent elderly parents.
- Thailand Development Research Institute. The estimated increasing cost of the elderly compared with government revenue 2012 - 2021.
- Tsai, Y.C., & Cheng, Y.T. (2012). Analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) for E-commerce and Internet marketing of elderly products: A review.Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics,55(1), 126-132.