Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 1
Strategic Management of Intellectual Capital of the Enterprise in the Framework of Informatization of the Economy
Oleksiy Svistunov, Khmelnytskyi National University
Kateryna Polozhentseva, Donbass National Academy of Civil Engineering and Architecture
Alla Panchenko, Borys Grinchenko Kyiv University
Mykola Stadnyk, National Academy for Public Administration under the President of Ukraine
Marina Li, Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers
Abstract
In the course of the research, one has determined the scientific and theoretical approaches, related to the identification of the directions and tools needed to improve strategic management; one also provided the main directions of the intellectual capital formation and development within the enterprise, which include the state of the capital at the present stage and the requirements to it from the future knowledge economy: the introduction of human capital into the assets of the enterprise, the promotion of the creative activity of the employees of the enterprise by using factors of human and social capital activation, as well as the establishment of an accounting system and evaluation of intangible assets. We have highlighted a range of specific principles of the intellectual capital management at the enterprise: the establishment of a partnership between all participants of the production process within the enterprise, namely, its owners, managers, and employees; the determination of criteria for assessing the contribution of every employee into the final result of the enterprise activity; the arrangement of an integrated network of the workers’ mass participation to identify the potential reserves, improve the production efficiency, and the product quality; the development of measures upon the principles’ implementation; and the primary task orientation of management on the future competition. One formulated the scientific and methodological foundations regarding the development of measures, aimed to improve the management of the intellectual capital of an enterprise, which include a sequence, the procedure of determination, the justification, the evaluation of the appropriateness of particular measures, the involvement of a wide range of workers in their development via the methods of interrogation and questioning.
Keywords
Intellectual Capital, Strategic Management, Network Schedule, The Intellectualization of Work, Innovative Development.
JEL Classifications
M5, Q2
Introduction
The transition to the knowledge-based economy and the increase of the human factor involvement into production are the distinctive features of the current state of development of the enterprises in the developed countries around the world. The use of the employees’ intellect becomes a prevailing tool in the provision of high efficiency and competitiveness of the enterprise.
The revision of the matter point of a problem and the structure of the capital of the enterprise, and the increase of the intellectual capital leading role, as its constituent, contributed to the fundamental changes in the production relationship. The concept of enterprise management becomes a more widespread phenomenon. According to it, the enterprise is considered to be a system. The human is regarded as the main working factor in it. These changes require the revision of the old methods of operations management and the adoption of new standards of the enterprise activity.
A lack of adaptedness to the new realia and requirements of the modern economy causes ineffective activity and thwarts the progress of the enterprise. This raises the question about the urgent need to change the accents of the operating policy and the methods of the enterprise’s economic growth provision in the directions of intellectualization and innovative development.
One of the most significant factors of intensification of intellectual capital development is the establishment of the corresponding infrastructure, principally, the intellectual one, and the provision of the innovation and knowledge transfer. The development of the intellectual capital of the enterprise and its constituents slows down by the underdeveloped market infrastructure. The services of the infrastructure components, available at the market, are either of poor quality or do not match the needs of the enterprises, or are too pricey for them. At the same time, the availability of the corresponding external conditions of intellectual capital formation and development alone is not sufficient to make it the driving power for the development of the enterprises and provision of their competitiveness.
The research objective is the development of theoretical and methodological background and application systems of intellectual capital management at the enterprise.
Review of Previous Studies
It is noteworthy that modern economic literate analyses intellectual capital based on the four interrelated aspects:
• The value, defined as an asset, which can bring income (Drobyazko et al., 2019a & b; Durmanov et al., 2019).
• The system that is an assembly of interrelated elements (Secundo et al., 2018);
• The process, reflecting the availability of reproductive characteristics, which have a relation to the circular movement (Kianto et al., 2017);
• The result, which denotes a priority in the process of consumption (Hilorme et al., 2019 a & b; Sokolova et al., 2019).
The global experience shows: the living standard of all social groups of people and the overall economic and social situation in the country are determined by the level of education of the society and its attitude towards the intellectual valuables (Obeidat et al., 2017). Only an intellectually rich society can become a guarantor of the high living standards of its residents and prosperity of the entire country, even if it has no energy producing stations, minerals, and other treasures of nature. Neither the riches of the Earth’s depths, nor fertile soil, nor ideal climate, nor popularity with tourists can compete with the power and social significance of the potential of the human mind.
The intellectual capital is the system of relationship between the employees within the enterprise, including the interaction between the employer and his workers about capitalization of their knowledge and skills, directed at the provision of efficient activity and development of the enterprise, and the creation of the competitive product, based on the available knowledge (Matos et al., 2017).
Thus, in the realia of the modern market set by the enterprise activity, one pays particular attention to the role of the intellectual capital. It lies in the mutual influence of each constituent of this type of capital on the economic results of the enterprise activity, in particular, on the improvement of effectiveness of use of the available resources and, as a result, on the effectiveness of the company’s activity, development of its innovative potential, strengthening of competitive abilities, and increase of the market value. The task of the intellectual capital management improvement requires clarification of its content as a management object and determination of its structural elements and features.
Methodology
The research was held using the general scientific and special methods, principles, and research techniques based on the system, process-centric, and situational approaches.
The author used the following general scientific methods of theoretical and empirical study in his research: the analysis and synthesis – to determine the state and tendencies of intellectual capital development of the enterprise; a systematic approach – to highlight the place and role of the intellectual capital in the formation of the company’s total capital; methods of theoretic generalization – to specify the principles of the enterprise intellectual capital formation; the induction and deduction – to form the methodological principles of the intellectual capital establishment and development at the enterprise; a terminological analysis – to show and clarify the terms, which fully reflect the essence of the intellectual capital; a semantic and structural analysis – to clarify the conceptual and categorical apparatus of the enterprise capital and its elements; the method of classification and typology – to systematize the approaches to interpretation of the intellectual capital of the enterprise, its objects, and entities; and the statistic methods of comparative analysis – to learn the state and compare the figures of intellectual capital formation at the enterprises, which carry out different types of economic activity.
The information basis of the research study comprises the official statistic data, the reporting information of the enterprise, personal social research, and analytical calculations.
Results and Discussion
The informatization of the economy and the intellectualization of work become crucial elements in the stuffing structures shifts. They give rise to the need for the formation of an intellectual elite and highly qualified specialists, which can generate scientific and technological innovations and use them effectively, as well as highly qualified transmitters, the distributors of information in the system of education, communication, press, mass media, etc. Significant changes are also needed in the area of the technical personnel training, which is in charge of the maintenance of the information machines, the workers of the mass professions of material production, and the service sector, the computer literacy for which becomes quite necessary.
The intellectual capital has its peculiar features, which should be taken into account in the process of its improvement:
1. The skillful use of intellectual capital allows to reduce the cost of production material means or maximize the income from their use;
2. The intellectual capital has a diverse choice of opportunities at the time when the material resources draw the enterprise to barriers in their further development in a certain period;
3. The intellectual capital is not amortized in the course of its usage; on the contrary, it loses its cost in the case if it is not engaged in the process;
4. The priority orientation of the intellectual capital on the future, the basis for its evaluation is the cost that will be established in the course of its use in the future;
5. The intellectual capital is evaluated using its pricing and non-pricing figures;
6. The investments into the intellectual capital provide their owners with a higher income.
By emphasizing the role and the place of the human capital in the development of the enterprise economic potential, we keep to the idea that the economy innovative development strategy is the only right sequence of events, which relies on one of the key competitive advantages – the intellectual capital of employees, the development of human resources, on the most effective application of knowledge and skills of people for continuous improvement of technologies.
We are impressed by the price approach of the author to the evaluation of the efficiency of the intellectual capital management of the enterprise. These and some other provisions, proposals, and recommendations of the author can be used as a basis for works on the formation and enhancement of the intellectual capital mechanism management of the enterprise.
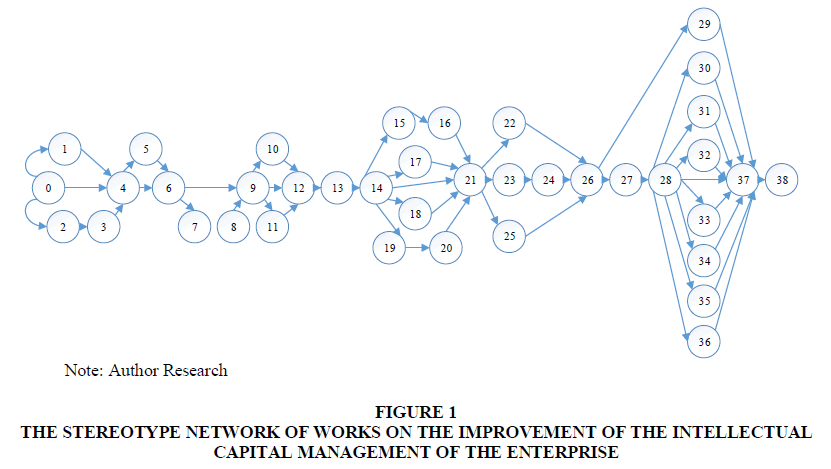
Figure 1 reflects the stereotype network of works on the improvement of the intellectual capital management of the enterprise.
Figure 1 The Stereotype Network of Works on the Improvement of the Intellectual Capital Management of the Enterprise
Annotation: events: 0-1 The study of the theory and practice of the intellectual capital management within the industry, region, country, global experience of management under the conditions of knowledge economy; 0-2 The program development on the study of conditions and factors which take part in the formation of the intellectual capital of the enterprise; 2-3 The conduction of a survey among the employees of the enterprise, analysis of conditions and factors of intellectual capital formation; 0-4 The study of the experience on the management of the intellectual capital at the enterprise within other industries of the country; 4-5 The formulation of the target goals and tasks of the action plan on the intellectual capital improvement; 4-6 The development of proposals and substantiation of methodological approaches to improve the enterprise’s intellectual capital management system; 6-9 The development of the GDR improvement program; 6-7 he definition of the place of the program in the in the system of measures for managing the business activity of the enterprise; 7-6 The preparation of proposals about the order of the program engagement into the system of measures on the enterprise management; 9-10 The definition of the main organizational forms and methods of the intellectual capital development of the enterprise; 9-11 The determination of actual methodological support for the formation and development of the intellectual capital of the enterprise; 9-12 The determination of ways of achievement the goals of development of intellectual capital of employees and intellectual capital of the enterprise; 12-13 The development of an action plan on improvements; 13-14 The development of a concept ad general structure; 14-15 The development of a planning subsystem; 15-16 The development of accounting and control subsystem; 14-17 The development of a subsystem on the improvement of knowledge level, professional competence, qualification of employees of the enterprise, and making them aware of the production problems solving methods; 14-19 The development of the organizational mechanism and determination of its place in the economic mechanism of the enterprise; 19-20 The development of a subsystem of stimulation the production and creative activity of employees; 14-18 The development of other subsystems; 14-21 The establishment of a complex; 21-23 The approbation of new organizational forms and methods of formation of intellectual capital of the enterprise; 21-22 The study of social aspects of implementation; 21-25 The examination of the economic aspects and the implications of implementation; 23-24 The approval by public organizations, associations of employees of the enterprise and its approval by the management of the enterprise; 24-26 The study of the processes and ways of further enhancement; 26-27 The generalization of experience on the engagement and improvement of elements in the structural units of the enterprise; 27-28 The distribution of the best working experience of the enterprise units; 26-29 The clarification of the computer program for the task “Social development and personnel management” based on the requirements; 28-30 The clarification of the computer program and conducting the research about the influence on the economic development of the enterprise; 28-31 The clarification of the computer program and conducting a research about the influence on the level of production activity of the workers; 28-32 The clarification of the computer program and holding a research about the level of social activity of employees; 28-33 The clarification of the computer program and the conduction of a research on the level of the employees’ involvement in the production management; 28-34 The clarification of the computer program and holding a study about the influence on the workers’ professional competency; 28-35 The clarification of the computer program and conduction of a study about the influence on the level of knowledge of the employees; 28-36 The clarification of the computer program and conducting a study regarding the formation and development of consumer and structural capital of the enterprise; 28-37 The evaluation of the operating efficiency; 37-38 The improvement of the elements of EI KMS based on the informatization of the productive and social activity.
The organizational and economic mechanism of enterprise management should include, as a subsystem, the mechanism for managing the intellectual capital of the enterprise, based on the essence of the concept of the intellectual capital and its structure. It assumes the existence of means, forms, methods, quantitative and qualitative indicators, etc., with the help of which the objective laws of production and social relations are carried out. We should emphasize on the importance of the subsystem elements, related to the social regulations, including the formation and use of the component of the intellectual capital of the enterprise.
The availability of the management subsystem on the intellectual capital and all its components – human, social, structural, and consumer capital – are an obligatory condition of the efficient formation and full use of the intellectual capital of the enterprise (Stoyanova et al., 2019).
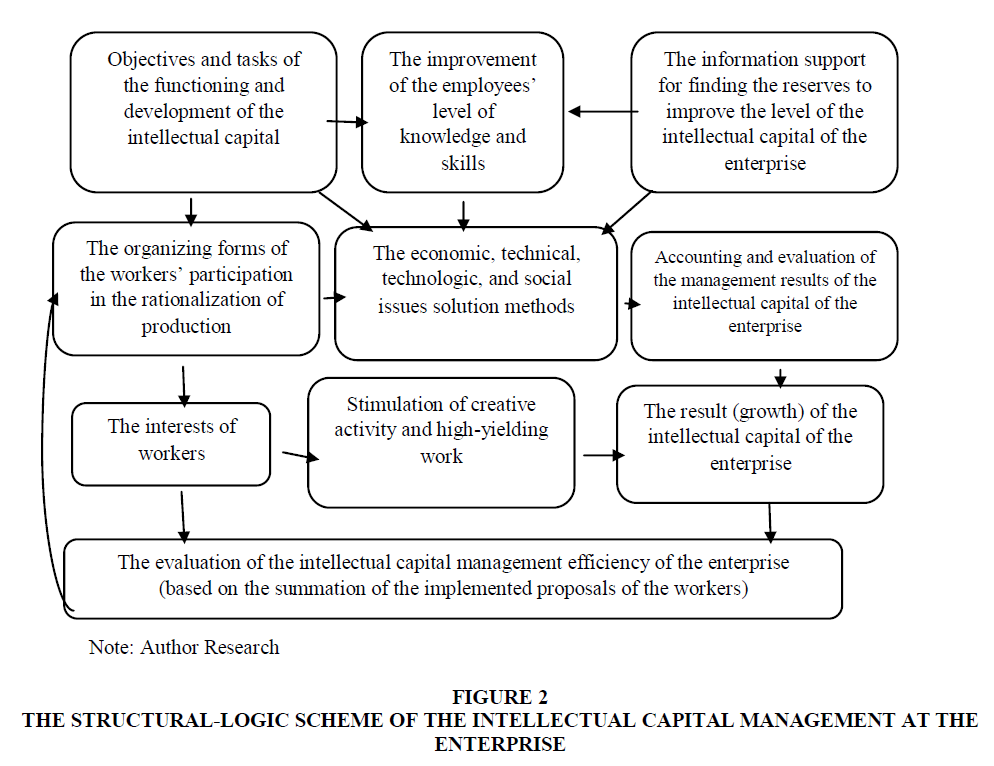
The structural-logic scheme of intellectual capital management at the enterprise is shown in Figure 2.
The tasks and goals of functioning and development of the intellectual capital of the enterprise are formed based on the goals of socio-economic development. One of the ways to realize them is to increase the level of knowledge and skills of the employees as the necessary condition for the development of their intellectual capital. Thus, the company provides conditions for the realization of employees’ creative potential to solve production problems. This is done concerning the personal interests of the employees.
One has determined that the various methods of the economic, technical, technological and social problem solving of the enterprise are the crucial elements of management of the intellectual capital of the enterprise. In particular, one provided an economic and mathematical model for the selection and evaluation of the proposals regarding the production problem-solving in a certain situation, obtained by modifying the model of subjective optimality of business decisions, taking into account the specificity of such an object as an intellectual proposal. By combining these methods with the forms of material, social, moral stimulation of creative activity, and highly productive work, one provides the desired result, which is the growth of the intellectual capital of the enterprise.
Thus, it is possible to conclude that the accounting and evaluation of the results of the search and realization of the reserves of the enterprise are the crucial elements of management. They based on the principles of the worker’s input evaluation into the overall results of the intellectual capital activity at the enterprise and the choice of the corresponding forms of the creative activity promotion.
One of the conditions of effective use of the intellectual capital of the enterprise is the control over the interaction of the components of the enterprise’s intellectual capital management system, as well as adherence to a certain strategy, including the promotion of the employees’ knowledge and skill improvement, and gaining new experience, which can be put it into practice.
Recommendations
The knowledge economy forms new demands and interests of workers at the enterprise. The current needs of a worker regarded as basic will further stay basic and will be supplemented with the priorities of the perspective character. The employees pay more interest in obtaining new knowledge, professional reorientation, skills upgrading, etc. Intellectual skills, professional knowledge, universalism, which determine the amount of financial reward for his activity, determine the social status of an individual and forms of his realization. In the structure of the economic interest, the importance of the social component of intelligence and the opportunities for the development of the individual, and the fulfillment of his needs increase sufficiently. The study of the interest structures shows that high-qualified workers, which are the basis of the workforce of the new economy, pay great attention to their interests, determining their social status.
Special prerequisites are needed to transform the employees’ intellectual resources within the enterprise into their intellectual capital, and then into the intellectual capital of the enterprise or society (it is a general indicator of the level of knowledge, creativity, experience, relationships, and skills development of society). In response to the informatization of society, traditional labor activity is replaced by the creativity and self-actualization of an individual. The process of cognition and creativity becomes a necessity. A creative person finds pleasure in the process of his creative activity. His work always receives a special individual character.
One of the most significant factors of intensification of intellectual capital development is the establishment of the corresponding infrastructure, principally, the intellectual one, and the provision of the innovation and knowledge transfer. The development of the intellectual capital of the enterprise and its constituents slows down by the underdeveloped market infrastructure. The services of the infrastructure components, available at the market, are either of poor quality or do not match the needs of the enterprises, or are too pricey for them.
At the same time, the availability of the corresponding external conditions of intellectual capital formation and development alone is not sufficient to make it the driving power for the development of the enterprises and the provision of their competitiveness.
The company’s management team should, first of all, realize the role of the intellectual capital and develop an efficient set of actions for its development. In particular, the enterprise should promote the processes of effective accumulation, knowledge distribution, and use, advance training, promotion of skills on self-development, programming the employees’ career, the program of setting the personnel reserve, and the development of teamwork skills.
Conclusions
One has formed the key directions of formation and development of the intellectual capital of the enterprises, which are based on the current state and requirements of the knowledge economy: the inclusion of the human capital into the assets of the enterprise; the promotion of the creative activity of the employees of the enterprise using the factors of human and social capital activation; the establishment of the system of formation of pricing and non-pricing assets, based on the notion of the intellectual capital.
The research justifies the expediency of applying specific principles of the enterprise’s intellectual capital management: the strategic partnership of the owners of the enterprise, the management team and the employees; partnerships between all participants of the production process; taking into account the interests of each employee of the enterprise; determination of criteria for assessing the individual contribution of employees into the overall results of the enterprise; the organization of the diverse network of the forms for participation of the workers to identify the reserves for improving the production efficiency and product quality, the development and implementation of measures; the orientation of the management team of the enterprise on the competitiveness of their company for the future, and not for currently existing markets.
One justified the stages and developed a typical network schedule of the works on the improvement or formation of the system of the intellectual capital management of the enterprise, and gave a detailed description of the plan of works upon each stage of its implementation.
The results of this research can be used to solve the issues related to the improvement of the intellectual capital management at the enterprises within other industries of the economic complex of the country, in particular, in mining, energetic, transport, trade, and consumer services area.
In the course of the study, one determined the scientific problems of the accounting and evaluation of a piece of the intellectual property, the evaluation of intellectual capital cost, and the market value of the enterprise, which can be the directions for further research on the topic.
References
- Drobyazko, S., Makedon, V., Zhuravlov, D., Buglak, Y., & Stetsenko, V. (2019a). Ethical, technological and patent aspects of technology blockchain distribution. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues.
- Drobyazko, S., Potyshniak, O., Radionova, N., Paranytsia, S., & Nehoda, Y. (2019b). Security of organizational changes via operational integration: ensuring methodology. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues.
- Durmanov, A., Bartosova, V., Drobyazko, S., Melnyk, O., & Fillipov, V. (2019). Mechanism to ensure sustainable development of enterprises in the information space.
- Hilorme, T., Sokolova, L., Portna, O., Lysiak, L., & Boretskaya, N. (2019a). Smart grid concept as a perspective for the development of Ukrainian energy platform.
- Hilorme, T., Sokolova, L., Portna, O., Lysiak, L., Boretskaya, N. (2019b). The model of evaluation of the renewable energy resources development under conditions of efficient energy consumption.
- Kianto, A., Sáenz, J., & Aramburu, N. (2017). Knowledge-based human resource management practices, intellectual capital and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 81, 11-20.
- Matos, F., & Vairinhos, V.M. (2017). Intellectual capital management as a driver of competitiveness and sustainability. Journal of Intellectual Capital.
- Obeidat, B.Y., Tarhini, A., Masa'deh, RE., & Aqqad, N.O. (2017). The impact of intellectual capital on innovation via the mediating role of knowledge management: a structural equation modelling approach. International Journal of Knowledge Management Studies, 8(3-4), 273-298.
- Secundo, G., Massaro, M., Dumay, J., & Bagnoli, C. (2018). Intellectual capital management in the fourth stage of IC research. Journal of Intellectual Capital.
- Sokolova, L.V., Guillermo, T.V., Portna, O.V., Lisyak, L.V., & Boretska, N.P. (2019). The model of the evaluation of renewable energy resources development under conditions of efficient energy consumption.
- Stoyanova, T.A., Koev, S.R., Stoyanov, P.P., Zhyvko, Z., & Laptiev, V. (2019). Strategic Management of the Personnel Development of Industry Companies. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 18(3), 1-6.