Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 4
Strategy of Innovative Development as an Element to Activate Innovative Activities of Companies
Liudmyla Zavidna, Uzhhorod Trade and Economics Institute
Petro M. Makarenko, Poltava State Agrarian Academy
Ganna Chepurda, Cherkassy State Technological University
Olena Lyzunova, Donetsk National Technical University
Nadiia Shmygol, Zaporizhzhya National University
Abstract
Innovative activity becomes a factor determining the strategic success of the company in the market of goods and services, the stability of its development. This research is aimed at analyzing the practice and assessment of the innovative activity of companies with the aim of forming an innovative development strategy. In order to achieve this, the authors compared theoretical opinion with empirical testing methods. In this study, the methods of statistical studies, expert assessments were used, which allowed to determine the system of coefficients for the assessment of innovative activity in justifying the choice of innovative development strategies. The identified results are: (1) the specifics of the strategy of innovative development of a company depends on the profile of its activities, the level of production and technical development, research work on the introduction of innovations, (2) the specific type of innovative strategy depends on the state of the processes of interaction of the enterprise with the external environment and is determined by the innovative activity, (3) the system of indicators for assessing innovative activity must meet the requirements of universality and simplicity for practical use, (4) when forming a system of indicators for assessing innovative activity, resources are analyzed for the current production of innovations in all areas of company activity (production, finance, research and development, marketing, etc.).
Keywords
Innovative Activity, Strategy of Innovative Development of a Company, Strategic Management, Innovative Activity.
JEL Classifications
M5, Q2
Introduction
The main characteristic of the post-industrial type economy is the intensification of innovative processes, which are a factor in ensuring the long-term economic growth of companies. Active scientific and practical studies show that the development of a strategy for innovative development of a company is related to the size and structure of their innovative potential, the level of innovative activity (Goffin et al., 2019). When shaping the strategy of innovative development of the company's management, it is necessary to consider not only the possibilities of the innovation sphere, but also to analyze the sufficiency of resources for the current production of innovations in all directions of activity (Juntunen et al., 2019). However, despite the theoretical and practical achievements, the issues of formation of the company's innovative development strategy require further research, taking into account the factors ensuring the effective formation and implementation of the company's innovative development strategy, as well as the principles for its development.
Literature Review
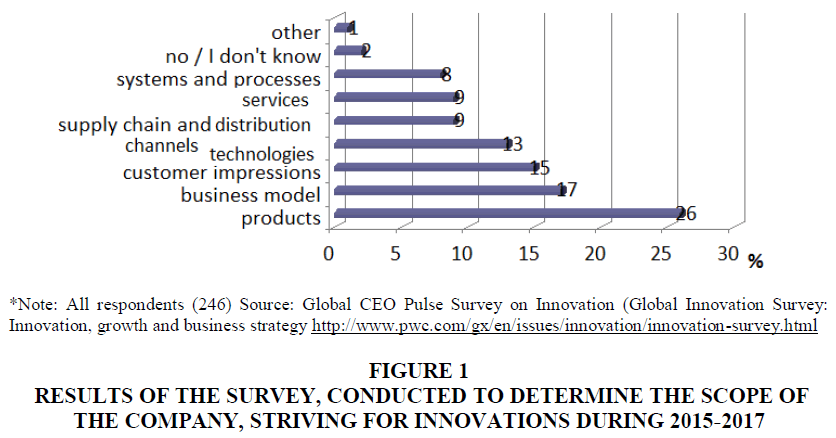
Statistical studies confirm that the liveliest innovations are in big companies, because they have significant advantages in financing, production technologies, and intellectual resources. Data of a survey of 246 company executives from around the world conducted by Global CEO Pulse Survey on Innovation Global CEO Pulse Survey on Innovation shows that almost half of the surveyed executives (51%) consider innovation an important condition for maintaining the competitiveness of their organizations, a driver of fast and profitable revenue growth (14%), necessary condition for maintaining long-term business development (35%) (http://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/innovation/innovation-survey.html). The surveys conducted in order to determine the company's activities, striving for innovations, among which products (48%), technologies (45%), customer impressions (44%), systems and processes (43%), business model (41 %), services (37%), supply chain and distribution channels (33%) (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Results of the Survey, Conducted to Determine the Scope of the Company, Striving for Innovations During 2015-2017
With the effective use of innovations, their transformation into certain commercial results is one of the important conditions for economic growth. Innovation business is looking forward to continuous modifications in production technology, new products and much more.
According to Kriz & Welch (2018), corporations with a widely diversified business portfolio should build, maintain, and implement a system of strategies that takes the form of a hierarchy. The specificity of the company's innovative strategy, Stattev et al. (2019) determines as dependent on the following factors: activity profile, level of production and technical development, focus and scope of work in the innovative cycle, the scope of innovation. We agree with Drobyazko et al. (2019) that the need to form a strategy for innovative development of a company is conditioned by changes in the external environment, namely: market saturation and lower demand; radical changes in technology and production technology; diversification of production, expansion of the market range of innovations; emergence of fundamental innovations in the market; emergence of new competitors.
Thus, the innovative strategy is aimed at clarifying specific corporate goals, to achieve which tools for working with innovations, as well as identifying the resources necessary to achieve these goals, and creating (maintaining) patterns of work with innovations are required (Perevozova et al., 2019).
Zhong (2018) determines that the development of an innovative strategy must answer the question: how to achieve goals, how to remove competitors, how to secure competitive advantages, how to strengthen a firm's long-term position, how to make a managerial strategic vision a reality. Karpenko et al. (2018) note that the implementation of innovations creates particularly difficult conditions for project, firm and corporate management, since it is associated with an increased degree of uncertainty of results and offers management tools: SWOT analysis, PEST analysis, coefficient and matrix analysis. According to Bondar & Iershova (2015), the development of a company's innovative development strategy begins with an assessment of innovative activity based on strategic management accounting data. We agree that feedback information significantly affects the effectiveness of a company's innovative strategy. Glaeser (2018) determines the components of an innovative strategy: sources of innovative ideas, tools for accumulating information and knowledge management, principles for building innovation assessment mechanisms, research and development, and the intellectual potential of a company.
Hypothesis
Innovative development is the fundamental basis for the positive dynamics of company performance indicators. The strategy of innovative development of a company is formed according to a hierarchical approach and depends on the indicators of innovative activity.
Methodology
The methodology of the study was based on the theory of strategic management. The main methods that formed the conceptual basis of the study are: comparison, analysis and synthesis, as well as expert-econometric, empirical generalization and statistical processing. Managers and heads of the Polish companies producing household appliances with a parallel study design were selected for the survey. Telephone interviewing, analysis of publicly disclosed information, data from the Internet and insider information were used. The study involved 60 respondents. Interviewing was used to diagnose the main problems that hinder the innovative development of the Polish companies and the questionnaire to select the coefficients of innovative activity in determining the type of strategy for innovative development of companies.
Results and Discussion
The leading role in the Polish industry is assigned to the processing industries. In 2017, it occupies 87.2% of industrial products sold. The production of household appliances in 2017 remained one of the main branches of the Polish engineering, which is made up of both the Polish enterprises of its own (for example, Amica) and enterprises of the largest foreign companies, such as BSH (brands Bosch and Siemens), Electrolux, Whirlpool, Indesit, Samsung, Beko and Fagor Mastercook. In 2017, the production of washing machines increased by 3.6% to 6,712 thousand units, refrigerators and freezers - by 2.1% to 3,221 thousand units, vacuum cleaners - by 59.8% to 1,194 thousand units, electric stoves - by 2.6% to 1377 thousand units. (https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database) In 2017, Poland mainly retained its position as a major manufacturer of household appliances in the European Union, specializing in the average price category. The method of questioning managers and heads of household appliances companies revealed the main problems that hinder the innovative development of companies (Table 1).
| Table 1 Survey Results Distributed by Status Groups on the main issues that Hinder the Innovative Development of the Polish Companies in the Production of Household Appliances | ||||
| Main problems | Status group of respondents | |||
| Managers | Heads | |||
| % | Rank | % | Rank | |
| Lack of managerial levers to stimulate the company's innovative activities, which do not allow developing an effective innovative strategy, determining the ways of innovative development of the company | 22 | 6 | 24 | 7 |
| Insufficient financing from external sources (it is difficult for a company to develop innovative activity in full, since it requires significant financial expenditures not only for the creation, but also for the development and implementation) | 26 | 7 | 16 | 5 |
| The need to create conditions for reducing the energy intensity of production, supply of the necessary equipment and reduce in the wear on production | 15 | 5 | 9 | 2 |
| Alienation of innovation | 13 | 4 | 10 | 3 |
| Lack of experienced managers in the field of innovation for the effective and productive construction of management policies for innovation (a problem may arise at all levels of management). | 8 | 2 | 20 | 6 |
| The lack of a full study of innovative developments, which leads to the difficulty of building a real picture of the demand for innovative products | 10 | 3 | 8 | 1 |
| Lack of a clear organizational mechanism in the company’s management structure | 6 | 1 | 13 | 4 |
Managers of companies for the production of household appliances consider the main problem that hinders rapid innovation development, insufficient funding, and managers - the lack of managerial levers to stimulate the company's innovative activity. The development and implementation of innovative development strategies for a company requires a combination of interests and accountability of strategic, scientific, technical, financial and industrial management, as well as marketing decisions.
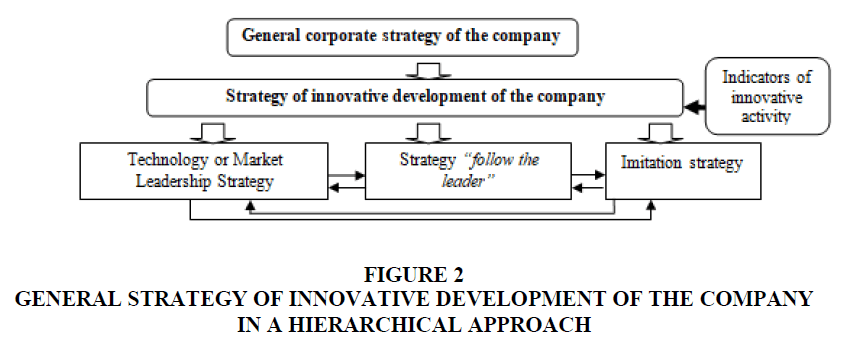
From the point of view of a hierarchical approach to the formation of a corporate strategy, the strategy of innovative development is an integral part of the overall corporate strategy (including the level of SBU (Strategic business unit) and is focused on achieving common goals; while it has its own tools that allows you to achieve goals using special methods and techniques. In the study, the authors identified four managerial levels. At the first level, a corporate-wide strategy is determined, at the second level-a set of business strategies, at the third level-functional strategies and at the fourth-production (operational) strategies (Figure 2).
The formation and choice of the strategy of innovative development of the Polish company for the production of household appliances depends on the indicators of innovative activity. We proposed a system of coefficients for assessment of the innovative activity, based on the use of real economic indicators, and aimed at analyzing innovative resources of an enterprise, including intellectual, personnel, property, technological and investment resources, which allows to determine the type of innovative development strategy (Table 2).
| Table 2 Coefficients of Innovative Activity in Determining the Type of Innovative Development Strategy and the scale of their Assessment | |||
| Coefficients | Technology or Market Leadership Strategy | Strategy “follow the leader” | Imitation strategy |
| Coefficient of intellectual property supply | More than 0.1 | 0.1 | Less than 0.1 |
| Coefficient of personnel engaged in research and development | More than 0.2 | 0.2 | Less than 0.2 |
| Coefficient of property assigned for the research and development activity | More than 0.3 | 0.3 | Less than 0.3 |
| Coefficient of development of new technology | More than 0.4 | 0.4 | Less than 0.4 |
| Coefficient of development of new products | More than 0.5 | 0.5 | Less than 0.5 |
| Coefficient of innovation growth | More than 0.6 | 0.6 | Less than 0.6 |
| Total indicator | Σ more than 2.1 | Σ 2.1 | Σ less than 2.1 |
The results of the assessment of the innovative activity of the Polish company for the production of household appliances to determine the type of innovative development strategy are presented in Table 3.
| ??ble 3 Matrix of the Results of the Assessment of the Innovative Activity and the type of Innovative Strategy of the Polish Company for the Production of Household Appliances | |||
| Company/Strategy | Technology or Market Leadership Strategy | Strategy “follow the leader” | Imitation strategy |
| Amica | 1.4 | ||
| Beko | 1.8 | ||
| Electrolux | 2.7 | ||
| Indesit | 2.1 | ||
Approbation of the methodology allowed an adequate assessment of the innovative activity of the Polish company in the production of household appliances and readiness for innovative transformations. On this basis, it is recommended to choose the strategy of innovative development for a specific company in order to strengthen its own positions in the market. And also this technique can be used as a basis for rating positioning of competing companies in the market of home appliances in Poland.
Recommendations
It is recommended to evaluate the innovative activity of the company for the production of household appliances in Poland using a system of calculated indicators. With this approach, it is possible to substantiate the choice of the type of innovative development strategy. The selected indicators system meets the requirements of universality and ease of its use and provides objective information that is adequate to the object under study.
The system for assessment of the innovative activity, based on the use of real economic indicators, and aimed at analyzing innovative resources of an enterprise, including intellectual, personnel, property, technological and investment resources allows to determine the type of innovative development strategy.
Conclusion
The practice of the world's leading companies shows that an innovative development strategy creates undeniable competitive advantages in the long term. Today, when creating an innovative potential, it is necessary to consider not only the possibilities of the innovative sphere, but also to analyze the sufficiency of resources for the current production of innovations in all areas of activity of companies (production, finance, research and development, marketing, etc.). The use of statistical research methods, expert assessments, and the coefficient method in this study made it possible to determine a system of indicators for evaluating innovative activity in determining the type of innovative strategy of the Polish company for the production of household appliances. The main problems that hinder the innovative development of the Polish companies in the production of household appliances with the aim of further developing the practice of strategic management of innovative activity were analyzed.
References
- Bondar, M., & Iershova, N. (2015). Strategic management object as an object of scientific research. Baltic Journal of Economic Studies, 1(1).
- Drobyazko, S., Hryhoruk, I., Pavlova, H., Volchanska, L., & Sergiychuk, S. (2019). Entrepreneurship innovation model for telecommunications enterprises.
- Glaeser, S. (2018). The effects of proprietary information on corporate disclosure and transparency: Evidence from trade secrets. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 66(1), 163-193.
- Goffin, K., Åhlström, P., Bianchi, M., & Richtnér, A. (2019). State?of?the?Art: The Quality of Case Study Research in Innovation Management. Journal of Product Innovation Management.
- Juntunen, J.K., Halme, M., Korsunova, A., & Rajala, R. (2019). Strategies for integrating stakeholders into sustainability innovation: a configurational perspective. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 36(3), 331-355.
- Karpenko, L.M., Serbov, M., Kwilinski, A., Makedon, V., & Drobyazko, S. (2018). Methodological platform of the control mechanism with the energy saving technologies. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 17(5), 1-7.
- Kriz, A., & Welch, C. (2018). Innovation and internationalisation processes of firms with new-to-the-world technologies. Journal of International Business Studies, 49(4), 496-522.
- Perevozova, I., Savchenko, M., Shkurenko, O., Obelnytska, K., & Hrechanyk, N. (2019). Formation of entrepreneurship model by innovation activity of industrial enterprises. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22, 1-6.
- Stattev, S.V., Boiarchuk, A., Portna, O., Dielini, M., & Pylypiak, O. (2019). Formation of a System of Anti-Crisis Entrepreneurship of Services Companies. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22, 1-6.
- Zhong, R.I. (2018). Transparency and firm innovation. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 66(1), 67-93.