Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 5
Systematic Mapping Study (SMS): Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management and Financial Governance in Indonesia
Riswin Lubis, Universitas Padjadjaran
Mohammad Benny Alexandri, Universitas Padjadjaran
Tetty Herawaty, Universitas Padjadjaran
Pratami Wulan Tresna, Universitas Padjadjaran
Abstract
This article aims to analyze and study literature related to Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management and Financial Governance in Indonesia. Methodology used in this article is written through descriptive research based on analysis of previous documents, studies and literature on Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management and Financial Governance. Journals and articles are obtained from several sources, which are Scopus, Google scholar, science direct and researchgate.com. Data from 40 related articles in this field were collected and statistically analyzed using Systematic Mapping Study (SMS). This study looked at several variables which included authorship pattern, number of published articles, research approach, geographic affiliation, subject and author gender. General The findings of this study indicate that most of the previous studies discussed on the research focuses on the topics that have been researched, methodology and paper type used, and the trend of publication in the future. Finding also compare with other references.
Keywords
Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management, Financial Governance.
Introduction
Reported from an article on the site ayobandung.com, Head of the Office of Cooperatives, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Atet Dedi Handiman in the 2019 UMKM Awards said that according to statistical data he obtained there were 14,000 MSMEs in the city of Bandung but only 6,201 MSMEs which is under the auspices of the Department of Cooperatives and SMEs. Still according to statistical data received by the Office of Cooperatives and MSME states that the Bandung MSMEs contribute 80% of the GDP of the City of Bandung. The number of SMEs in the city of Bandung has increased from year to year. However, business competence is only a small part of MSMEs that are developing. In the midst of intense competition, the MSMEs must move quickly to improve the quality of their business management processes.
Leadership or leadership has the potential to provide encouragement in innovation to give birth to a new way of working in the context of business development. Leadership is generally defined as the process of influencing an organization's employees to achieve organizational goals (Esmer & Dayi, 2016). Entrepreneurs take business risks for top managers about strategic management.
Financial Governance refers to the way companies collect, manage, monitor and control financial information. Financial governance covers the way companies track financial transactions, manage performance and control data, compliance, operations and disclosure (tagetik.com).
In today's global competition, innovation/innovation becomes a very powerful weapon for businesses to be able to excel. According to Prof. Suarez-Villa (1990), the concept of innovative capacity is able to measure the level of discovery and innovation potential in a country, geographical area or in any economic activity. Innovation itself is a renewal that aims to provide more value to a product with new ideas that are different from other products. Innovativeness is defined as a basic desire to move from existing technology or operational processes to move forward away from present conditions. Meanwhile, innovation capacity has been defined as an effort to continuously improve the ability and resources of a company to find opportunities sequentially to be involved in developing new products.
Understanding the work environment according to Armstrong, the work environment consist of the system of work, the design of jobs, working conditions, and the ways in which people are treated at work by their managers and co- workers. Broadly speaking, the work environment is divided into 2 namely, physical environment and non-physical environment. There are several main indicators of work comfort in the physical environment that have been deduced from various opinions of experts, namely: (1) Room coloring; (2) Cleanliness; (3) air exchange; (4) Information; (5) Security; (6) Noise.
Objectives of the research are:
1. What is the focus of research with Systematic Mapping Study?
2. What is methodology and type of articles with Systematic Mapping Study?
3. What is the trend of publication over time with Systematic Mapping Study?
Literature Review
Business Process Management (BPM) has four dimensions:
1) Modeling; Users can define and design the structure of each process. 2) Integration; BPM can connect each element in the process so that these elements can collaborate and exchange information to complete their goals. 3) Supervision; Users can overcome and control the performance of the ongoing business processes and the performance of each person involved in the business process. 4) Optimization; Users can analyze and monitor a business process also take action to improve its efficiency.
Leadership or leadership has the potential to provide encouragement in innovation to give birth to a new way of working in the context of business development. Leadership is generally defined as the process of influencing an organization's employees to achieve organizational goals (Esmer & Dayi, 2016). Entrepreneurs take business risks for top managers about strategic management.
Methodology
Systematic Mapping Study (SMS) is rooted in literature review (SLR) studies introduced in information technology research (Kitchenham, 2004). Research with the SLR approach aims to identify, evaluate, and interpret all available and relevant literature sources related to the research questions that have been formulated (Kitchenham, 2004; Petersen et al., 2008; Banaeianjahromi & Smolander, 2016). The most common reasons for doing SLRs are: first, summarizing existing evidence on the topic; Second, to identify gaps in current research and provide suggestions for future investigations; and third, to provide a background for positioning new research activities (Kitchenham, 2004).
SMS is applied to describe the types of research activities that have been carried out in this study. SMS describes research at a high level and maps research rather than investigating research questions in detail (Petersen et al., 2008). In other words, SMS can be considered as a method to get an overview of a particular research area, because SMS research explores detailed information.
The first step is defining the main keywords. The second step is to examine well-known studies in the field of Entrepreneurship at MSMEs, in this research researcher’s focus on the topics of entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, financial governance. The third is looking for alternative forms of keywords to use in the search process. According to Banaeianjahromi & Smolander (2016a) the final step is to use the operator Boolean whose function is to synthesize into one search string, but in this study, the operator is not used Boolean AND or OR because in the third stage the researcher found that if the string combination is "entrepreneurial leadership" OR "innovation capacity "OR" workplace performance "OR" business process management "OR" financial governance "AND (sme OR smes OR" small and medium enterprises "OR" small and medium enterprises "), researchers found 1,876 results.
Next, the final step is to determine the category of exclusion articles called exclusion criteria and inclusion articles which are one of the mapping study activities to exclude articles that are not relevant and include relevant articles (Petersen et al., 2008). In this research, we formulated exclusion and inclusion criteria to facilitate mapping (Table 1).
| Table 1: Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria | |
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
| 1. Research that focuses on entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, financial governance | 1. Papers that do not discuss entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, financial governance |
| 2. English | 2. Languages other than English |
| 3. Only articles and scholarly journals | 3. Dissertation, thesis, book section, product description, presentation, work report, trade literature, editorial notes, obscure literature |
| 4. Papers that have been peer reviewed 1. Papers that do not discuss entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, financial governance | 4. Papers that have not been peer reviewed |
| 2. Languages other than English | 5. Duplicate research |
| 3. Dissertation, thesis, book section, product description, presentation, work report, trade literature, editorial notes, obscure literature | |
| 4. Papers that have not been peer reviewed | |
| 5. Duplicate research | |
The findings of relevant articles or with inclusion criteria totaled 40 articles. Then the researchers tabulated the data on the Ms. application. Excel 2016 by classifying the findings. The next discussion is the mapping results based on research questions (RQ). Based on the results of mapping from 40 articles on Entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, and financial governance, they are grouped into categories of research focus, methods, paper type, country, years and research developments around the world published by Scopus.
Discussion
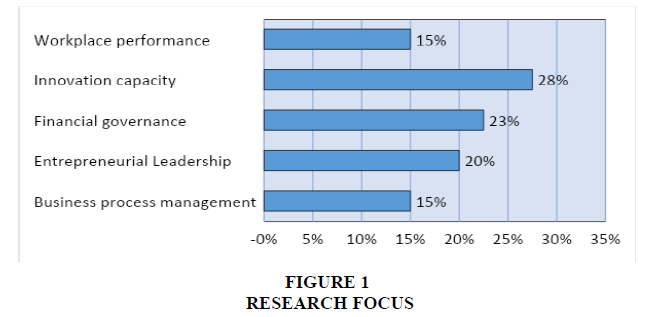
To answer QR1, we classified 40 articles that have been diklaasifikasikan with reference to Kitchenham (2004). The initial stage of calculating articles based on research topic areas (research focus) with categories: Business process management, Entrepreneurial Leadership, Financial governance, Innovation capacity, Workplace performance. Figure 1 is the percentage of the topics studied; the topics that are mostly researched are research with a research focus of Innovation capacity as much as 28%, financial governance 23%, Entrepreneurial leadership 20%, workplace performance 15%, and Business Process management as much as 15%.
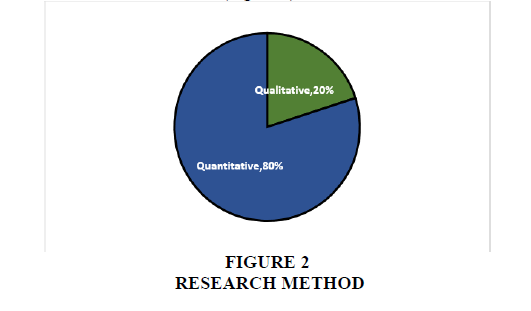
A total of 40 research articles, the majority of previous researchers used a quantitative method approach with a total of 80% of the research results from search results in reputable scientific publications, because of its nature, testing and evaluating. While the qualitative approach was used in 20% of the research (Figure 2).
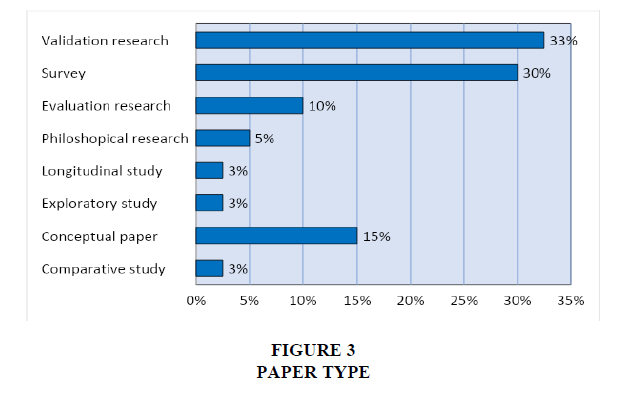
The grouping of articles based on article type categories is based on research from Banaeianjahromi & Smolander (2016a). Figure 3 illustrates the distribution of article types (paper types) based on classification categories according to Banaeianjahromi & Smolander (2016b); Petersen et al. (2008); Wieringa et al. (2006). Based on the results of (systematic mappingsystematic mapping study), the type of research that is most often used is validation research with a total of 33%. The next most frequent type of research is survey type research with a total of 30%.
Research with a conceptual type (conceptual paper) is 15%, evaluation research is 10%, philosophical research is 5%, and research is based on the type of article. Longitudinal study the exploratory study and the comparative study are the types of research that are the least studied, with a percentage of 3% each.
Previous research based on the aspect of the type of article (paper type) shows that research on the focus of entrepreneurial leadership research currently tends to be done with a validation research approach. According to Wieringa et al. (2006), validation research is a new investigative method and has not been applied in practice (experiment/observation). The results of previous research based on the type of articles, validation research. Validation research is currently focused on research on Business process management (23%), Entrepreneurial Leadership (8%), Financial Governance (31%), Innovation capacity (15%), Workplace performance (23%). The research topics were researched in 2009 to 2020. Based on the results of the SMS, the research position was on variables (1) Business process management, (2) Entrepreneurial Leadership, (3) Financial Governance, (4) Innovation capacity, (5) Workplace performance, is being debated critically and exploratively.
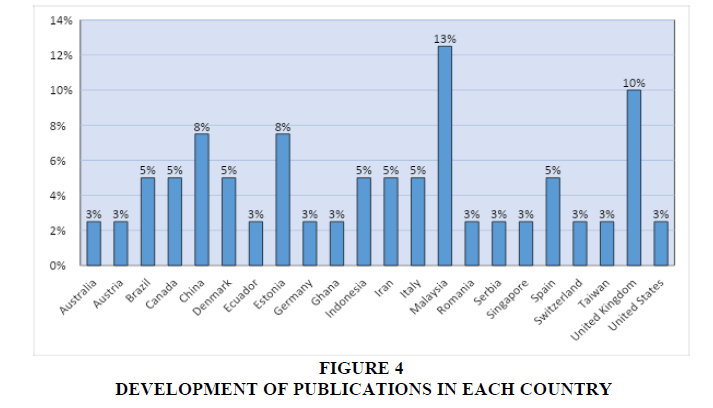
Based on the mapping results, it was found that the most countries producing research on research topics (1) Business process management, (2) Entrepreneurial Leadership, (3) Financial Governance, (4) Innovation capacity, (5) Workplace performance, were Malaysia with a total of 13%, followed by the United Kingdom as much as 10%. Then Indonesia has a research distribution of 5% (Figure 4).
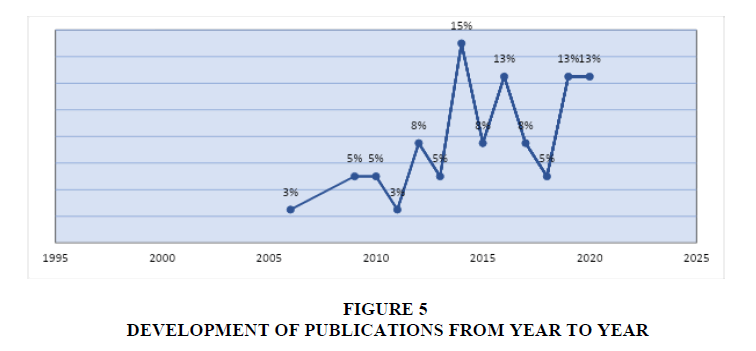
Figure 5 is a trend of research published on electronic database media; DOAJ, EBSCOhost, Emerald, Gale-Cengage, Jstor, ProQuest, SAGE Publisher, Science Direct, Scopus, Springer and Google Scholar, which started from 2006, but from search results we found that research did not continue to increase, namely in 2018 there was a decrease number of publications. However, in 2014, the number of publications continued to increase until in 2019 the number of publications reached 13% of research on entrepreneurial leadership, innovation capacity, workplace performance, business process management, and financial governance.
The relevant determinants that are being debated in the 21st century by MSMEs are (1) Business process management, (2) Entrepreneurial Leadership, (3) Financial Governance, (4) Innovation capacity, (5) ) Workplace performance. SMS is a practical research method for identifying the right topics to research, as well as which areas are needed for more research. The results of this study provide guidelines to assist researchers in planning future research through the discovery of research gaps (Gaps)
State of the Art and Novelty Research
Compiling a State-of-the-art (SOTA) description is the first step to show the novelty of research results (Research Novelty) because it describes the latest map or the most advanced achievements to date. While novelty here is defined as: as many articles have been published and throughout the efforts that have been traced from various sources of research databases or scientific publications, no other researcher has ever presented research results like "that" (Purnomo, 2018).
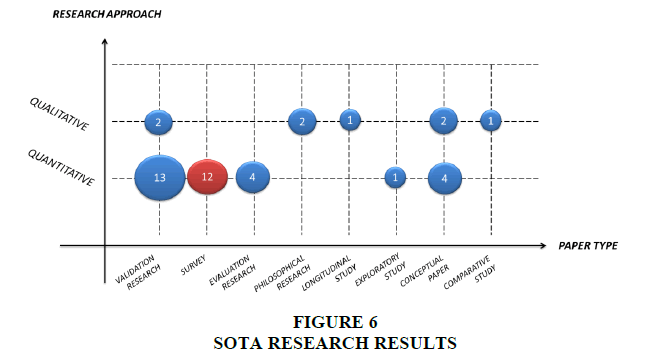
Based on the mapping of 40 articles with a systematic mapping study process or the latest known map of the research results as shown in Figure 6 below this:
Figure 6 above also shows the red circle is the position of this research.
Finding from other literature that relate with this research are Doshmanli et al. (2018) indicated that there was a significantly positive correlation between all four dimensions of economic, legal, ethical and discretionary social responsibility and development of SMEs. Moreover, facilitating legislation and giving more authority to SME owners/managers for developing their enterprises are highly advised.
Salamzadeh et al. (2014a) indicate eight traits, namely: 1) open mindedness; 2) need for achievement; 3) pragmatism; 4) tolerance of ambiguity; 5) visionary; 6) challenge taking; 7) risk taking; 8) internal locus of control, are used to define the entrepreneurial profile of students. Main focus of the research is on elaborating the relationship between these characteristics and the fields of study of the participant students. Results show the extent to which these two are correlated; and explores the entrepreneurship profile of university students. In sum, the difference between entrepreneurial characteristics and fields of study are suggestive. Salamzadeh et al. (2014b) find the best results in the path to achieve agility through work values.
Tajpour et al. (2018 & 2020) find service innovation; administrative process innovation and technological process innovation have a significant impact on organisational performance.
Krisnawati (2019) indicates that financial ability plays a major role in improving the cooperatives’ performance while, and that the other two independent variables also have a significant impact on improving the cooperatives’ performance.
Raharjo & Perdhana (2015). It is suggested that SMEs should gain knowledge and solidify its business process reengineering before implementing ERP.
Hosseini et al. (2020) showed that emotional intelligence and it`sdimensions had a significant positive influence on the organizational innovation in the employees.
Conclusion
The discussion on Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management, and Financial Governance in the Creative Industry in Bandung City is at the meeting point between survey and quantitative. In addition, based on the diagram above and the previous SMS process, the potential novelty of research results (Research Novelty) can be stated in the form of:
1. Entrepreneurial Leadership, Innovation Capacity, Workplace Performance, Business Process Management, and Financial Governance variables were examined individually in a study.
2. Tend to research with Entrepreneurial Leadership variable as a single variable that influences other factors. Meanwhile, this research uses the Entrepreneurial Leadership variable along with the Innovation Capacity variable, and the Workplace Performance variable.
3. Using Financial Governance as the variable sought in research is still rarely done.
4. Tend to use Business Process Management as an independent variable and not as a moderating variable like this study.
5. Tend to use Financial Governance as an independent variable and not a dependent variable.
6. This study uses the unit of analysis of SMEs in Bandung.
7. The selection of the variables studied is more comprehensive and the dimensions and indicators explored reflect the real conditions that occur directly experienced by entrepreneurs, in this case the SMEs in Bandung.
References
- Banaeianjahromi, N., & Smolander, K. (2016a). Understanding obstacles in enterprise architecture development.
- Banaeianjahromi, N., & Smolander, K. (2016b). What do we know about the role of enterprise architecture in enterprise integration? A systematic mapping study. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 29(1), 140–164.
- Doshmanli, M., Salamzadeh, Y., & Salamzadeh, A. (2018). Development of SMEs in an emerging economy: Does corporate social responsibility matter?. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, 17(2), 168-191
- Esmer, Y., & Dayi, F. (2016, September). Entrepreneurial leadership: A theoretical framework girisimci liderlik: Teorik bir çerçeve. International Academic Conference in Paris.
- Hosseini, E., Tajpour, M., Lashkarbooluki, M.(2020). The impact of entrepreneurial skills on manager's job performance. International Journal of Human Capital in Urban Management, 5(4), 361-372.
- Kitchenham, B. (2004). Procedures for performing systematic reviews. Keele, UK, Keele University, 33(2004), 1-26.
- Krisnawati, N. (2019). Assessment of factors affecting cooperatives’ performance in Indonesia: The case of credit union cooperatives. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Business and Economics, 7(2), 80-105.
- Petersen, K., Feldt, R., Mujtaba, S., & Mattsson, M. (2008). Systematic mapping studies in software engineering. EASE'08 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, 68–77.
- Raharjo, S.T., & Perdhana, M. (2015). SME’s enterprise resource planning implementation, competitive advantage, and marketing performance: finding from central Java, Indonesia. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Business and Economics, 4(1)
- Salamzadeh, A. (2020). What constitutes a theoretical contribution?, Journal of Organizational Culture, Communications and Conflicts, 24(1), 1-2.
- Salamzadeh, A., Farjadian, A. A., Amirabadi, M., & Modarresi, M. (2014a). Entrepreneurial characteristics: insights from undergraduate students in Iran. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business, 21(2), 165-182.
- Salamzadeh, Y., Nejati, M., & Salamzadeh, A. (2014b). Agility path through work values in knowledge-based organizations: a study of virtual universities. Innovar, 24(53), 177-186
- Tajpour, M., Hosseini, E., & Salamzadeh, A. (2020). The effect of innovation components on organisational performance: case of the governorate of Golestan Province. International Journal of Public Sector Performance Management, 6(6), 817-830
- Tajpour, M., Moradi, F., & Jalali, S.E. (2018). Studying the influence of emotional intelligence on the organizational innovation. International Journal of Human Capital in Urban Management, 3(1), 45-52.
- Wieringa, R., Maiden, N., Mead, N., & Rolland, C. (2006). Requirements engineering paper classification and evaluation criteria: A proposal and a discussion. Requirements Engineering, 11(1), 102-107.