Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 4
The Analysis of Consumer Value in Choosing Local Coffee Shop
Iin Mayasari, University of Paramadina
Adrian Wijanarko, University of Paramadina
Handrix Chris Haryanto, University of Paramadina
Iyus Wiadi, University of Paramadina
Gilang Cempaka, University of Paramadina
Citation Information: Mayasari, I., Wijanarko, A., Haryanto, H.C., Wiadi, I., & Cempaka, G. (2022). The analysis of consumer value in choosing local coffee shop. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(4), 1-18.
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to analyze the preferences of the local coffee shops. The number of local coffee cafes shows good development. The manager of a local coffee shop shows an interest in developing a business because it also follows increasing consumer preferences in Indonesia related to local coffee consumption. The concepts studied are related to extrinsic and intrinsic consumer values on consumer attitudes. This consumer value refers to the Holbrook typology. The extrinsic value consists of efficiency, service quality, play, and aesthetics, while intrinsic value consists of status, esteem, ethics, and escapism. The attitude of the consumers studied is satisfaction and loyalty. This study also proposes local brand preferences to explain consumer satisfaction.
Design/Methodology/Approach: The research method was a quantitative descriptive study by distributing questionnaires to 450 respondents. However, the number of respondents' data that could be reused was 420. The data were analyzed using partial least squares.
Findings: The results showed that not all proposed hypotheses were accepted based on the research data analysis. Of the ten hypotheses, eight hypotheses were supported. Aesthetics variables affect consumer satisfaction. The escapism variable influences consumer satisfaction. Esteem variable influences customer satisfaction. Local brand preference variables affect consumer satisfaction. The satisfaction variable influences customer loyalty. Service quality variables affect satisfaction.
Keywords
Local Coffee Shop, Extrinsic Consumer Value, Intrinsic Consumer Value, Satisfaction, Loyalty, Local Brand Preference.
Introduction
One way to anticipate the covid-19 pandemic is the emergence of the concept of local coffee shops that grab and go or coffee to go, which shows the development tends to be fantastic. Industries classified as emerging businesses receive a lot of funding from venture capital and provide convenience for consumers to only place orders through applications without being physically present (Aditiya, 2021). On the other hand, according to Euromonitor International (2020), the sales volume of RTD Coffee Indonesia tended to decline before the Covid pandemic. Consumer preferences indicate the existence of a consumer lifestyle supported today by the growth of ready-to-drink coffee (RDT), which shows relatively rapid development during this pandemic. Thus, the development of the coffee business is currently progressing to provide consumers with a variety of opportunities to enjoy coffee-based beverages.
In line with the development of local coffee, both takeaway coffee, and RTD, drinking coffee in the local coffee shop remains a favorite because it can provide services to consumers to come directly as a favorite choice. The number of restaurants or coffee shops increases with consumer demand and lifestyle influence. This is indicated by the number of coffee shops or cafes that reached 3000 outlets in 2019 and 2020 is predicted to grow again by 20% (Arifin, 2021). In 2020, the number of local cafes tended to be stable due to the covid-19 pandemic. There are some reasons for consumers to visit the local coffee shop.
First, the choice of local coffee shops is a destination to fulfill beverage consumption needs. Coffee drinks are a favorite drink of Indonesian people, including consumers from the millennial generation. Secondly, the choice of coffee shops is perceived to have consumer value that not only meets the primary needs. Consumers choose coffee shops because they meet immediate needs and look for other benefits as part of consumer value that can be aspects of service and quality provided by coffee managers. This is supported by research by Dhisasmito & Kumar (2020), which shows that consumer loyalty to local coffee shops is supported by service quality. In addition, consumers also want a location that can be used as a safe place to meet other people, comfort them, and follow their current lifestyle. Third, local coffee cafes selected can also be related to local brand preferences from consumers. The tendency to love local brands or local products is also starting to show attention from consumers. The use of local brands for several product categories is already showing improvement. Along with that, many local entrepreneurs are also starting to grow. Thus, the choice for local brands can at least provide opportunities to local business people to develop their business well. Fifth, the increasing number of local coffee shops will indirectly affect competition with fellow business people. This condition makes it easy for consumers to choose a local coffee café brand and switch from one local coffee café. Of course, consumer satisfaction will be a concern in this study.
Consumers in choosing products will also consider the value of consumers when selecting products. This is especially the selection of restaurants or cafes that provide food, drinks, services, supportive environments. These can be attributes that consumers consider when choosing a point in a food service provider (Jun et al., 2017; Liu & Tse, 2018; Richardson et al., 2019). Gallarza et al. (2017) argue that the concept of value in the context of services is an important aspect. The primary meaning of value is in meeting the immediate needs of consumers. The elements will be directly related to the benefits of using the product. It is also associated with the benefits and costs obtained on a product or service (Beneke & Carter, 2015). Related to this research, this study focuses on analyzing consumer value aspects. Previous research has examined the typology of consumer value with several elements. They are extrinsic aspects consisting of efficiency, excellence, status, esteem. On the other hand, the intrinsic characteristics consist of play, aesthetics, ethics, and spirituality (Hollbrook, 1994). They also include aspects of service quality and sacrifices-price, time, and effort (Cronin et al., 2000); aspects of playfulness (escapism and enjoyment), aesthetics (visual appeal and entertainment); aspect efficiency, service quality, social value, play, aesthetics, time & effort spent (Gallarza & Saura, 2020; Moliner-Velázquez et al., 2019); and parts of quality value, monetary value, novelty value, emotional value, social value, knowledge value (Prebensen & Xie, 2017).
Previous research has focused on the concept of consumer value with several dimensions. This research explores several benefits that meet needs and have several aspects that add value to consumers' lives. The study also shows the measurement of the consumer value, which needs to be further, developed. These studies are essential to understand the consumer values in café service managers (Yoo et al., 2022); the value of consumer experience as the core of the discussion in research (Kim & Stepchenkova, 2018).
Related to local coffee shop options, Dhisasmito & Kumar's research (2020) has also examined local coffee shop options by emphasizing service quality, store atmosphere, and price equity. Wu's research (2017) focuses on experiential loyalty, which includes perceived value experiential trust in explaining the choice consumers consume at Starbuck Coffee. Ahmed et al. (2020) studied CSR programs implemented in local coffee shops to create responsible consumers. Ting et al. (2018) conducted service quality research and its effect on intentions in visits to local coffee shops. Ihtiyar et al. (2019) have also researched the influence of customer satisfaction on the revision of local cafes. Related to consumer loyalty research, Kim et al. (2020) focus on the power of brand credibility and value perception on consumer loyalty.
The study aims to fill the research gap by analyzing consumer value related to local coffee café choices that have not yet been analyzed in the previous studies. The first value is for the consumer that meets consumers’ primary needs, namely drinking coffee, including quenching thirst. However, local cafés have significant benefits; coffees are more valuable than that. The concept of consumer value was examined using the consumer value typology developed by Gallarza et al. (2017), based on Hollbrook's consumer value typology. The study also highlights that consumer value depends on the consumer himself and the consumer's situation (Leroi-Werelds, 2019). The consumer value used as a reference consists of two main aspects: Extrinsic and intrinsic. The inherent value consists of play, aesthetics, ethics, and escapism, while extrinsic value consists of efficiency, service quality, status, and esteem. Both values are seen as an explanation for the choice of consumers at local coffee cafes. Consumers who consume coffee will feel both benefits. These values are also considered to affect consumer satisfaction because the value of consumers can make them comfortable by taking advantage of local coffee cafes. Both values are also considered to meet consumer expectations related to the benefits of local coffee. Secondly, the study also discussed the effect of satisfaction on consumer loyalty in the context of local coffee shops. Third, the study also analyzed local brand preferences as variables that affect consumer satisfaction. The existence of local cafes in major cities in Indonesia shows that consumers prefer local or domestic brands as another research gap in this study. The taste of local coffee brands is perceived to have a better taste than foreign brands. In addition to the taste of local brand coffee, the choice of café has more local strengths related to design, atmosphere, and comfort. Local brand choice is better to create consumer satisfaction than foreign brands. Thus, the purpose of the study was to analyze the effect of intrinsic and extrinsic consumer value on satisfaction. The study also examined the influence of local brand preferences on satisfaction and examined the impact of satisfaction on the loyalty of local coffee cafes.
Literature Review
Consumer Value
The consumer value must be taken into account by the company because, in value, there is a sacrifice issued by consumers to get benefits that are the right of consumers (Kotler et al., 2019). Customer value is what is obtained (benefit) about what has been spent (costs). The value created by the company can be measured by the number of money customers are willing to pay. A marketing transaction shall be considered profitable if the value exceeds the cost of generating the value-added activity. Value can be created by differentiating the activities of the value chain. A company is considered to be competitive if it can offer a better value than competitors. Value is defined as the customer's perceived compromise between cost and benefit and is generally considered relative. The value component can vary between customers or between different purchasing situations. Customer value in the context of local coffee selection is also considered to be what customers receive (benefits, quality, rewards, and benefits) from buying and using the product versus what they pay (price, cost, and sacrifice), resulting in an attitude or emotional attachment to the customer. The perceived value indicates the totality of what the customer gains from consumer behavior.
Consumer sacrifices related to incurred costs include monetary fees, time, energy, and social, psychological, and physical risks. The benefits offered by consumers are propositions that are realized in the functional, experiential, and symbolic aspects. Experiential aspects are part of the consumer value that needs to be considered by the company (Agrawal & Rahman, 2019). Ideally, the company promotes value through the consistency of marketing strategies related to product quality, optimal service, pricing through the received advantages, smooth distribution of products, and communication of ideas by the company’s target consumers.
Gallarza et al. (2017) has developed consumer value based on Hollbrook's proposed typology. Hollbrook's concept of consumer value is considered a broader and comprehensive scope of consumer value concepts. Value for the consumer consists of extrinsic and intrinsic aspects. The extrinsic element is associated with the drive for benefit because of the outside of the individual. In contrast, the intrinsic factor is related to the urge to help the internal side of the individual. The extrinsic aspects are efficiency, service quality, status, and esteem. The elements include play, aesthetics, ethics, and escapism. Leroi-Werelds (2019) also shows valuable aspects, including excellence, quality, esteem, escapism, enjoyment or play, relational benefits, and price.
Play is a variable indicating the presence of activities offered to consumers in the form of playgrounds. In addition, the meaning of the play is also related to service offerings that provide comfort to consumers (Kim & Stepchenkova, 2018), while aesthetic variables describe the external environment with some facilities that support the value of business services such as related to the atmosphere, color, and architecture (Moliner-Velázquez et al., 2019). According to Gallarza et al. (2017), Ethics is associated with companies that pay particular attention to the environment, focus on social aspects, transparent management, and regulatory compliance. Dube & Helkkula (2015) also focused on environmental elements that can create a good experience for consumers to perceive the value of consumers. Escapism is a way to get away from something. Escapism is motivation and is not defined as behavior but psychological self-improvement. Many products offer opportunities for consumers to be more intensive in using them. When consumers have a new challenge and can adapt well, they focus on something serious. Consumers will take advantage of every moment to not pay attention to the surrounding environment (Taylor et al., 2018).
Related to extrinsic consumer value, efficiency is related to the condition of the service support infrastructure. It is also associated with facilities and infrastructure provided by service providers (Moliner-Velázquez et al., 2019). Efficiency is more linked to the external environment that supports delivering services to consumers. Service quality is associated with the operator's advantage. Consumer expectations will vary from consumer to consumer even though the services offered are consistent. Consumer expectations will depend on their experience, knowledge, and needs. As for status, this concept also explains the existence of prestige. Gallarza and Saura (2020) argue that the status aspect shows social appreciation and strengthens the presence of a symbol. In addition, the study also analyzed another external value of esteem was also analyzed in the study. Esteem is a concept that explains the presence of self-esteem in aspects of realizing something and prides (Varshneya et al., 2017).
Local Brand
A local brand is a brand that exists in a region or unique geography and is associated with a particular cultural heritage (Özsomer, 2012). This local brand has a representation of a specific and unique culture. Local brands have cultural proximity (Fritz et al., 2017) and psychological proximity (Guèvremont, 2018). Local brands have a solid value compared to global brands (Riefler, 2020). Related to coffee, Eren-Erdo?mu? & Dirsehan's research (2017) show that local cafes reinforce visual design with local cultural contexts. The physical environment can be a representation of local culture. The most dominant coffee drinking culture originates in the East.
Satisfaction
Consumer satisfaction is part of consumer attitude based on product purchase experience or service utilization and assesses services after consumption (Gallarza et al., 2011). Satisfaction is a comparative feeling that compares actual expectations and experiences (Boonlertvanich, 2019). Consumer satisfaction is linked to interaction with service providers to have a loyal impact. Each company recognizes the importance of satisfaction as the core of an organization's success in serving consumers (Anouze et al., 2018).
Loyalty
Loyalty to the brand is also defined as a preference to repurchase a preferred product in the future, despite the situational influences and marketing efforts that can make behavior move (Ngobo, 2017). Every phase of loyalty is prone to external and internal forces that cannot be avoided, so total loyalty is often inaccessible. These influences can be marketing stimuli, variety search, desire to try another product, changes in needs, and double loyalty. Loyalty in several studies is known to be caused by satisfaction (Kamath et al., 2019; Hoang, 2019; Rambocas et al., 2018; Fernandes & Moreira, 2019).
Based on the above explanation, the following research questions.
RQ 1: Does efficiency influence satisfaction?
RQ 2: Does service quality influence satisfaction?
RQ 3: Does status influence satisfaction?
RQ 4: Does esteem influence satisfaction?
RQ 5: Does play influence satisfaction?
RQ 6: Does aesthetics influence satisfaction?
RQ 7: Does ethics influence satisfaction?
RQ 8: Does escapism influence satisfaction?
RQ 9: Does local preference influence satisfaction?
RQ 10: Does satisfaction influence loyalty?
Hypotheses and Conceptual Framework
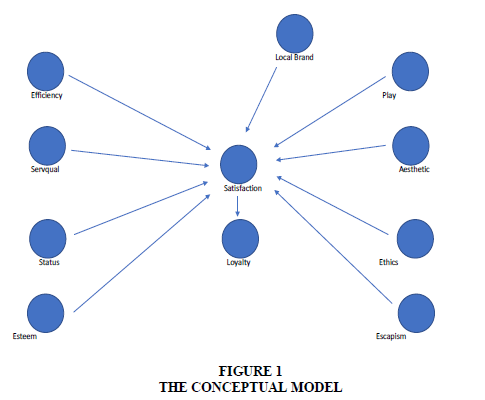
Value for the consumer consists of plays, aesthetics, ethics, and contrasts. On the other hand, extrinsic factors, such as efficiency, quality of service, status, and self-esteem influence consumer satisfaction and loyalty. This satisfaction is linked to fulfilling the benefits consumers need for the costs already paid. Loyalty to the brand is also defined as a preference to repurchase a preferred product in the future, despite the situational influences and marketing efforts that can cause the behavior to move. If the individual is satisfied with the previous brand, then the individual has cognitive consequences for choosing the brand in the future.
H1: Efficiency influences satisfaction.
Efficiency is the infrastructure that should be in a local cafe. Efficiency can be lighting, room temperature, toilets, parking, and locations. Indicators can be factors affecting consumer satisfaction with local coffees. This indicator for efficiency measures has been adapted from Wu & Liang (2009). This dimension is part of the consumer value that can support the performance of services or products offered to consumers. Gallarza et al. (2017) show that variable effectiveness influences satisfaction. Ruiz-Molina et al. (2018) and Moliner-Velázquez et al. (2019) stated that some efficiency aspects could also affect consumer loyalty in the end.
H2: Service quality influences satisfaction.
Quality of service is part of the value to the consumer that includes the reliability of the quality of service, namely assurance, tangible elements, empathy, and responsiveness (Cronin, 2016). It is also related to the ability of employees to provide good service, provide services consistently, provide services promptly, show competent expertise, have attention, and offer good knowledge. Related to local coffee preferences, it appears that consumers enjoy the benefits of local coffee service providers. This reinforces that the quality of services determines consumers’ satisfaction with coffee reasonably. This quality of service will affect satisfaction (Dhisasmito & Kumar, 2020; Jain et al., 2019).
H3: Status influences satisfaction.
Hollbrook (1994) conceptualized consumer values and divided them into economic, social, generous, and hedonic. It is related to social value, the derivative of this term status. Consumer choice of services or products related to social stimulus is considered an external influence. This status aspect can prompt consumers to choose a product or service because an external evaluation is available. Visiting a local cafe is a way that can also show that there is a lifestyle that is being followed today. It is also associated with the consumer's desire to indicate a particular social status or symbol. However, research by Roy & Chau (2011) showed the choice of global brands, more status, and prestige. However, this study assumed that local brands are unique and authentic (Özsomer, 2012). Consumers visiting local cafes will be perceived as individuals who can follow current trends or are considered more "slang.” Many local cafes in large cities can better meet consumers' needs. The status of consumers when visiting local coffee shops affects satisfaction.
H4: Esteem influences satisfaction.
The concept of esteem is a consumer value proposed by Hollbrook (1994). This concept shows a person's confidence in decision-making. Varshneya et al. (2017) describe the aspect of esteem as part of the experience value, which also creates a sense of pleasure. Visiting a local coffee is a way to increase the taste associated with self-esteem. This self-esteem shows how much a person feels able to value him. Drinking coffee in a local coffee could be somewhere that has a prestigious look. This choice can well show the condition of a person in the position. In addition, drinking coffee in a local cafe can show pride because it can follow the current trend. This aspect of esteem in visiting a local coffee shop influences satisfaction.
H5: Play influences satisfaction.
Play is a variable that allows activities that give consumers a place of play or a place to relax. In addition, the meaning of the play is also related to providing services that provide comfort to consumers, and there is an experience value aspect (Chen, 2012). When associated with the local coffee shop aspect, these variables include aspects of children's play, family activities, organizational activities, and additional services that determine the satisfaction of local cafes. When you visit this local café will enjoy the facility and consider it a family place.
H6: Aesthetic influences satisfaction.
This aesthetic is related to the experiential offered by the supplier (Fu & Wang, 2020). Mathwick et al. (2001) argued that aesthetic aspects include visual appeal and entertainment. Al Halbusi et al. (2020) argued that elements of visual appeal are also related to Servicescape, which contains parts of the physical environment, including environmental conditions, designs, signs, or symbols. Leroi-Werelds et al. (2019) also argue that the aesthetic consumer value has a component to think and feel. With the details in the landscape service, consumers will feel satisfied and enjoy the main product or service. This aspect is related to the aesthetics that exist in local cafes. This aesthetic is associated with a good decoration and layout in the coffee. In addition, aesthetics is linked to coffee furniture, coffee sound, color selen, coffee walls, architecture, aroma, and landscape around coffee. Gallarza et al. (2017) show that aesthetics affect satisfaction.
H7: Ethics influences satisfaction.
Gallarza et al. (2017) formulate ethics, including respect and care for the environment and organization, attention to social issues, fair pricing policies, and adherence to rules. Ethics in this study relate to the following aspects: the tendency of cafes to be environmentally friendly, social projects, price transport, and legal aspects that are respected, including rules. The ethical factors applied by local coffee shops will affect satisfaction. Ethics affects satisfaction (Gallarza et al., 2016; Sánchez-Fernández et al., 2020; El-Adly, 2019).
H8: Escapism influences satisfaction.
Escapism is a way to get away from something. Escapism is a concept that can be part of the quality of services and analyzed relatedly in the context of museums (Vesci et al., 2020). Escapism shows a person's condition to focus more on its use or benefits from a product or service. Fu & Wang's research (2020) shows the escapism of choosing services. Visiting a local cafe can be a way to escape routine. Local coffee-coffee supported by several facilities can make it easier for someone to forget the work done for a moment. Visiting a local cafe makes consumers feel relaxed due to a particular job or activity.
H9: Local brand preference influences satisfaction.
Local brand preferences indicate a tendency to choose national brands. Jin et al. (2018) investigated local brand preferences in China regarding product selection. They have an attitude that local brands have an advantage. In connection with coffee, the quality of local brands has a better flavor than brands of overseas coffees. The tendency to love local brands is also motivated by local products' sense of belonging and emotional aspects. Wann et al. (2018) show that local coffee shops are unique by offering local flavors. This local flavor image will bring the natural condition of each coffee. This choice will affect consumer confidence, satisfaction, and loyalty.
H10: Satisfaction influences loyalty.
Several studies have conducted research related to the influence of satisfaction on loyalty (Ing et al., 2020; Ganiyu, 2017; Rather & Sharma, 2017; Jeong & Kim, 2019). Satisfaction is a consumer attitude that includes cognitive, affective aspects, thus encouraging consumers to use the product or service in the subsequent decision-making. Consumers are also willing to choose this brand even though other coffee café brands also offer the same thing regarding local coffee shops. This condition can also be created because consumers can already feel satisfaction first. Consumer satisfaction needs to be made so that consumers are willing to visit the café on their next visit (Dhisasmito & Kumar, 2020). The conceptual model is described as follows (Figure 1).
Data Collection, Research Instrument
The study analyses quantitative approaches of consumers’ extrinsic and intrinsic value, local brand preferences, and satisfaction. The study also examined the effects of satisfaction on loyalty. The aim of this study is a person who already has the experience of consuming at one of the local cafes in several regions in Indonesia, including in Java, Kalimantan, Nusatenggara, Sulawesi, and Sumatra. The sampling was selected based on samples taken according to criteria, namely persons consumed at a local coffee café. The number of questionnaires is up to 450, and the number of questionnaires that can be reprocessed can reach 420. The survey was conducted in consultation with the partners living in these cities. They were asked in every city as academic staff. Then they asked consumers who have experience consuming in a local coffee shop more more than 3 times at the time they had to fill out a questionnaire using a google form. The data were analyzed using PLS-partial least square method. For quantitative research, the study uses measurements from previous research cited in Gallarza et al. (2017), referring to the typology of consumer value from Hollbrook. For the concept of local brand preferences, measurements using Shua et al. (2013), as shown in Table 1. The survey questionnaires used a closed question form throughout the section except in the first part of the questionnaire. The Likert scale used is five levels that aim to respond to respondents based on their opinions (Schindler, 2019).
| Table 1 The Variable Measurement |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable measurement | Source | Number of items | Type of variable |
| Efficiency | Adapted from Wu & Liang (2009) | 8 | Independent |
| Service quality | Adapted from Cronin et al. (2000) | 9 | Independent |
| Play | Adapted from Spark et al. (2008) | 5 | Independent |
| Aesthetic | Adapted from Wu & Liang (2009) | 6 | Independent |
| Status | Adapted from Spark et al. (2008) | 4 | Independent |
| Esteem | Adapted from Spark et al. (2008) | 3 | Independent |
| Ethics | Adapted from Gallarza et al. (2017) | 5 | Independent |
| Escapism | Adapted from Spark et al. (2008) | 4 | Independent |
| Satisfaction | Adapted from Caruana (2002) | 4 | Dependent |
| Loyalty | Adapted from Zeithaml et al. (2020) | 3 | Dependent |
| Local brand preference | Adapted from Shua et al. (2013). | 3 | Independent |
Results
Research Sample Description
The descriptive data in Table 2 of the study showed that the male respondents were 200 people and the female respondents were 220 persons. The majority of respondents under the age of 20 were 60; Respondents aged 20-29 were 196; Respondents aged 30 to 39 were 134; Respondents aged 40-49 are 60; Respondents over the age of 50 are 30 people. The majority of respondents who had taken part in a study were 172 persons, followed by high school-educated respondents - 60 people, and educated postgraduate respondents - 70 people. About work, 87 respondents had a profession as a student; 99 respondents worked as private sector employees, and 65 respondents were self-employed.
| Table 2 Demographic Profile |
||
|---|---|---|
| Demographic Characteristic | Option | Frequency |
| Gender | Male | 200 |
| Female | 220 | |
| Age | 20 – 29 | 196 |
| 30 – 39 | 134 | |
| 40 – 49 | 60 | |
| Above 50 | 30 | |
| Under 20 | 60 | |
| Education | Diploma | 69 |
| Doctoral Degree | 70 | |
| Bachelor Degree | 172 | |
| Senior High School | 109 | |
| Occupation | Housewife | 40 |
| State-owned enterprise | 59 | |
| Private workers | 99 | |
| Students | 146 | |
| Unemployed | 10 | |
| Self-employed | 65 | |
Measurement Assessment
The validation factor analysis is used to analyze the validity and reliability of the data with the PLS 2.0 software. The reliability test determines whether an instrument measures the construct consistently. In contrast, the validity test determines the extent to which the device measures the construct being analyzed. Validity determines whether the sample size represents the actual score in the population (Hair et al., 2021). The load factor coefficient in Table 3 is more significant than 0.50.
| Tabel 3 The Output Of Measurement |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construct | Indicators | Loading | Cronbach's Alpha | Composite Reliability | (AVE) |
| Aesthetics | Aes1 | 0.812 | 0.896 | 0.921 | 0.660 |
| Aes2 | 0.795 | ||||
| Aes3 | 0.851 | ||||
| Aes3 | 0.867 | ||||
| Aes4 | 0.802 | ||||
| Aes5 | 0.742 | ||||
| Aes6 | 0.812 | ||||
| Efficiency | Effi1 | 0.675 | 0.850 | 0.884 | 0.489 |
| Effi2 | 0.597 | ||||
| Effi3 | 0.618 | ||||
| Effi4 | 0.749 | ||||
| Effi5 | 0.780 | ||||
| Effi6 | 0.696 | ||||
| Effi7 | 0.748 | ||||
| Effi8 | 0.711 | ||||
| Escapism | Escape1 | 0.912 | 0.894 | 0.925 | 0.757 |
| Escape2 | 0.836 | ||||
| Escape3 | 0.840 | ||||
| Escape4 | 0.867 | ||||
| Esteem | Esteem1 | 0.898 | 0.896 | 0.934 | 0.826 |
| Esteem2 | 0935 | ||||
| Esteem3 | 0.891 | ||||
| Ethics | Ethic1 | 0.736 | 0.872 | 0.906 | 0.662 |
| Ethic2 | 0.748 | ||||
| Ethic3 | 0.796 | ||||
| Ethic4 | 0.880 | ||||
| Ethic5 | 0.893 | ||||
| Local brand preference | Local1 | 0.873 | 0.745 | 0.834 | 0.578 |
| Local2 | 0.824 | ||||
| Local3 | 0.862 | ||||
| Loyalty | Loyal1 | 0.944 | 0.878 | 0.942 | 0.891 |
| Loyal2 | 0.943 | ||||
| Loyal 3 | 0.876 | ||||
| Play | Play1 | 0.871 | 0.770 | 0.844 | 0.587 |
| Play2 | 0.467 | ||||
| Play3 | 0.880 | ||||
| Play4 | 0.773 | ||||
| Satisfaction | Satisf1 | 0.838 | 0.897 | 0.929 | 0.766 |
| Satisf2 | 0.893 | ||||
| Satisf3 | 0.871 | ||||
| Satisf4 | 0.895 | ||||
| Service Quality | Servq1 | 0.798 | 0.951 | 0.957 | 0.654 |
| Servq2 | 0.782 | ||||
| Servq3 | 0.839 | ||||
| Servq4 | 0.855 | ||||
| Servq5 | 0.801 | ||||
| Servq6 | 0.818 | ||||
| Servq7 | 0.793 | ||||
| Servq8 | 0.764 | ||||
| Servq9 | 0.781 | ||||
| Status | Status1 | 0.809 | 0.870 | 0.911 | 0.720 |
| Status2 | 0.892 | ||||
| Status3 | 0.867 | ||||
| Status4 | 0.823 | ||||
Convergent Analysis
In the context of convergent validity, the issue is to what extent several items measure the same concept in agreement (Ting et al., 2016). Converging validity requires composite loading reliability (CR) and extracted average variants (AVEs). The load for all items is greater than the minimum value of 0.50 (Hair et al., 2021). This model of research measurement in Table 3 meets the requirements of convergent validity. The study applied composite reliability and Cronbach's Alpha related to the reliability. The results shown in Table 3 confirm that the composite reliability values range from 0.884-0.957, more significant than the suggested value of 0.7. At the same time, alpha values range from 0.74to 0.951, more important than the recommended value of 0.6. It can be concluded from this that the measurement of this study is reliable.
Hypothesis Testing
The study partially used Less Square to test 10 hypotheses. The R2 value related to satisfaction is 0.725. This shows that 72.5% of the variation in satisfaction is explained by extrinsic values consisting of efficiency, quality of service, play, aesthetics, and intrinsic value consisting of status, estimation, ethics, and escapism. Related to the loyalty aspect, the value of R2 is 0.735. This indicates a variation of the loyalty values of 73.5% described for each extrinsic and intrinsic value. The hypothesis in Table 4 indicates that efficiency (β=-0.069, p<0.01), quality of service (-0.274, p<0.01), play (β=-0.089, p < 0.01), aesthetics (β=0.196, p<0.01), local brand preferences (-0.287, p<0.01) affect satisfaction. Only the local brand's quality of service, aesthetics, and preferences positively influence satisfaction. Status (β=0.142, p<0.01), esteem (β=0.130, p<0.01), ethics (=0.027, p<0.01), escapism (=0.134, p<0.01) affect satisfaction. Only status, esteem, and escapism positively affect satisfaction. Satisfaction (+0,690, p<0.01) affects loyalty.
| Table 4 Hypothesis Testing |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Sample (O) | Sample Mean (M) | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | T Statistics (|O/STERR|) | Hypothesis Null Testing | |
| Efficiency àsatisfaction | -0.069 | -0.081 | 0.056 | 1.234 | H1 is not supported |
| Service quality à satisfaction | 0.274 | 0.268 | 0.083 | 3.282 | H2 is supported |
| Status à satisfaction | 0.142 | 0.162 | 0.045 | 2.94 | H3 is supported |
| Esteem à satisfaction | 0.13 | 0.122 | 0.071 | 2.822 | H4 is supported |
| Play àsatisfaction | 0.089 | 0.094 | 0.007 | 2.568 | H5 is supported |
| Aesthetic à satisfaction | 0.196 | 0.195 | 0.099 | 2.98 | H6 is supported |
| Ethics à satisfaction | 0.027 | 0.079 | 0.055 | 0.498 | H7 is supported |
| Escapism à satisfaction | 0.134 | 0.338 | 0.046 | 2.98 | H8 is supported |
| Local brand preference àsatisfaction | 0.287 | 0.316 | 0.157 | 2.827 | H9 is supported |
| Satisfaction à loyalty | 0.69 | 0.677 | 0.087 | 7.883 | H10 is supported |
Discussion
Efficiency has no impact on satisfaction; thus, hypothesis 1 is not supported. This efficiency offers the infrastructure that should be in a local cafe. The efficiency is indicated by the lighting, room temperature, room, toilets, parking, and easily accessible places. These indicators are reasonable to exist, so they do not affect consumer satisfaction with local coffee cafes. The quality of service affects satisfaction; Thus, H2 is supported. Indicators used in the research, aspects related to the ability of employees to provide reliable, consistent, timely, competent, accessible, polite, listening, reliable services that attempt to meet the needs of consumers, and attractive appearance affect consumer satisfaction. Related to local coffee preferences, it seems that consumers enjoy the services of the local coffee shop. This reinforces that the quality of services determines consumers’ satisfaction to enjoy coffee well. The condition of local cafes in large cities has a good quality aspect of the service. Consumers feel comfortable with the service. In addition, the level of competition of local cafes in large cities is quite competitive. This competitive situation affects the café managers to provide the best service to maintain consumer satisfaction. This study also agrees with Zietsman et al.’s (2020) results about the impact of quality on satisfaction.
Status affects satisfaction; thus, H3 is supported. This status is linked to the psychological condition of the consumer. The situation in the study was associated with prestige feelings, symbols, or social groups and tried to make a good impression on others. Drinks and food do not just meet the primary needs of hunger and thirst. It is related to the fulfillment of physiological requirements and social conditions. Visiting a coffee is a way that can also show that there is a lifestyle that is followed today. It is also associated with the consumer's desire to indicate a particular social status or symbol. Consumers who visit local cafes will be perceived as individuals who can follow current trends or are considered more "slang.” Many local coffee cafes in big cities can better meet consumers' needs.
Esteem affects satisfaction; So, H4 is supported. This explains that visiting a local cafe is not just to satisfy the thirst, but more than that. Self-esteem includes self-esteem, feelings for achievement, and associated with a certain sense of pride. Visiting a local coffee is a way to increase the taste associated with self-esteem. This self-esteem shows the extent to which a person feels able to value himself. Drinking coffee in a local coffee could be somewhere that has a prestige aspect. This choice can well show the condition of a person in the position. In addition, drinking coffee in a local cafe can show pride because it can follow the current trend. The play variable also affects satisfaction; So, H5 is supported. These variables include aspects of children's play, family activities, organizational activities, and additional services that are essential to determining the satisfaction of the local coffee café. When visiting this local café, they tend to take advantage of the facility and consider this a family place.
About aesthetics, aesthetics affect satisfaction. So, H6 is supported. This aspect is related to the aesthetics that exist in local cafes. This aesthetic is associated with a good decoration and layout in the café. In addition, aesthetics is linked to coffee furniture, coffee sound, color selection, coffee walls, architecture, aroma, and landscape around coffee. This aesthetic is related to the advantages possessed by café companies. This aesthetic advantage is based on today's café trend, which can be used as a photo location for visitors. The current trend is instagrammable. Today, many local cafes reinforce these attributes as an attraction so that consumers do not move to other local cafes. Designers are much needed to give the café a touch to look beautiful. Research by Janssens et al. (2020) shows that aesthetic aspects influence satisfaction in the retail trade. This makes it easier for consumers to feel comfortable making purchases. Ethics does not affect satisfaction; Thus, H7 is not supported. Ethics in this study are related to the following aspects: the tendency of cafés to be environmentally friendly, have social projects, price transparency; there are legal aspects that are adhered to, including regulations. Visiting a local coffee café has nothing to do with ethics because they only want to drink coffee. Consumers have no concerns when it comes to regulatory or socially oriented things.
Associated with escape, escape affects satisfaction; So, H8 is supported. Visiting a local cafe can be a way to escape the routine. Local coffee café supported by several facilities can make it easier for someone to forget for a moment the work done. Visiting a local coffee café makes consumers feel relaxed because of a particular job or activity. Local coffee cafes have a calm atmosphere that affects the psychological condition of consumers. Consumers are ready to stay longer to enjoy the atmosphere while drinking coffee. The big city has many local coffee cafes as it captures the opportunity to provide services to consumers returning home from work.
Local brand preferences influence satisfaction; So, H9 is supported. Local brand preferences indicate a tendency to choose national brands. They have an attitude that local brands have an edge. In terms of coffee, they believe that the quality of local brands has a better taste than brands from overseas cafes. The tendency to like local brands is also driven by local products' sense of belonging and emotional aspects of local products. Local coffee cafes are considered to offer local coffee with a better taste. The image of the cafes is already attached that local coffee has a better quality. Local coffee cafes have become part of the culinary industry in Indonesia. The number of local restaurants in a large city is very diverse. This demonstrates the public's interest in choosing local café preferences.
This study showed that satisfaction with local cafes affected loyalty, so H10 was supported. Consumer loyalty can be formed because there are aspects of prior learning related to the experience owned by consumers. Learning about local coffee can influence consumer attitudes to determine the following attitude. This research is in line with Dhisasmito & Kumar (2020). If this consumer learning is positively linked to local coffee, consumers will want to return. In this case, consumers have a sense of satisfaction and pleasure associated with the local café service. This positive learning can be connected to the rewards that consumers have. Local coffee meets the needs of consumers. Satisfaction in consuming a local brand of coffee can affect long-term loyalty. The choice of coffee flavor and location makes consumers tend to choose the option of coffee. This makes consumers willing to choose a local coffee. In addition, they also want to give recommendations to other consumers to visit the same local coffee.
Conclusion and Implication
The quality of local coffee outlets remains the choice of consumers in product choice. In addition, as coffee consumption at local outlets is a lifestyle, coffee outlets should emphasize the value of status and esteem. The selection of local values on status and esteem can be an option because local brand preferences influence satisfaction. In addition, coffee outlets should be an alternative to drinking coffee at home. Because today, many go to coffee outlets to socialize, the aesthetic factor of coffee outlets must be attractive. Local coffee outlets should utilize Instagramable trends in today's society. Local coffee outlets should also create an alternative environment for consumers. Therefore, the atmosphere in the coffee shop is also a factor that must be observed. Local coffee outlets should create an atmosphere that can be psychologically an alternative for activities because it supports the escape factor. Local value preferences become interesting research to discuss. Consumers have begun to appreciate local and foreign products because they see them as more valuable. Therefore, local value preferences can be studied in later studies on different objects, for example, fashion products. In local cafes, aspects of social value can be variables that can be studied in future research.
Theoretical Implication
This study shows that consumers' intrinsic and extrinsic value can explain consumer satisfaction in the context of a local selection of coffee shops. This explains the existence of a research model that illustrates that satisfaction is caused by the functional value of a product or service and by significance beyond that. Quality of service influences satisfaction. The quality of service determines the satisfaction of consumers enjoying coffee well. The condition of local cafes in large cities has a good quality aspect of service. Consumers feel comfortable with the service. Aesthetic variables influence satisfaction. Today, many local cafes reinforce these attributes as an attraction for consumers not to move to local cafes. The local preferences of the brand affect satisfaction. Local brand preferences indicate a tendency to choose national brands. Local coffee cafes are considered to offer local coffee with a better taste. This research shows that status influences satisfaction. This status is related to the psychological condition of the consumer. Visiting a coffee café is a way that can also show that there is a lifestyle that is followed today. The esteem variable affects satisfaction. This explains that visiting a local coffee cafe is not just to satisfy the thirst, but more than that. Self-esteem includes self-esteem, feelings for achievement, and associated with a certain sense of pride. The play variable also does not affect satisfaction. Associated with escapism, escapism involves the satisfaction of visiting a local cafe may be a way to escape from routine. Local coffee supported by several facilities can make it easier for someone to forget the work done for a moment. This study showed that satisfaction with local coffee cafes affected loyalty.
Practical Implications
This research has implications for the management of the local coffee business. Consumers still have a high tendency to like local coffee products. This offers companies the opportunity to develop local coffee products, including in the management of local coffee cafes. Professional management of local coffees will provide consumers with a better selection of coffee products. The local coffee director is currently facing a variety of competitions at present. First, many franchise coffee companies from abroad. Second, there are new coffee products that offer grab-and-go services. Third, there is a fast-food coffee drink. Local coffee managers should offer breakthroughs so that their business can survive in the long term. Firstly, the choice of coffee products, including coffee beans, is a quality guarantee offered by the coffee manager. The coffee beans made directly will offer a better quality coffee flavor. Local coffee managers benefit from the supply of coffee from Indonesia. This coffee offers has flavor variants from various regions in Indonesia. The existence of this supply of coffee will support the growth of the domestic coffee industry.
Secondly, the manager of the local coffee realized that drinking coffee does not only meet the main needs of eliminating thirst. Coffee consumption is part of a hereditary cultural tradition. Consumers who spend time drinking coffee usually take a long time to sit in a coffee cafe. You will enjoy coffee for a long time. They are willing to spend time with friends or family to discuss at the cafe. The presence of consumer preferences requires that profile managers be more professional and pay attention to the ambiance aspect for café conditions. Coffee managers can also strengthen aspects of experience values that can later be enjoyed by consumers. Thirdly, local coffee design is also expected to meet the current trend. Coffee design that meets aesthetics will be an option for consumers. The use of social media is widely used by vendors and consumers for product promotion. Marketers can strike a certain angle to promote the location of the café for consumers. On the other hand, consumers can also participate in promoting co-creation for other consumers via social media. It is also part of a word-of-mouth strategy for other consumers to come to the café. Fourthly, local coffee-café managers must also strengthen funding for the needs of café expansion. The limited number of local coffees has led to the slow growth of local coffees slow. This is due to the need for greater funding for the procurement of local coffee cafés. The existence of sufficient funds will be too large a business of local coffee cafes to be large. Local coffee cafes will also be able to meet the needs of consumers. Fifth, local coffee managers should optimize social media to promote more optimal products. Professional business management will help local coffee managers become a long-term business that can survive. The manager of this local coffee shop is usually a young businessman who has a passion for coffee consumption. With the opportunity to grow, these companies need to improve their experience in managing coffee better.
Limitation of the Study
This study was carried out in several local cafes in several cities. Future research can not only be carried out in the selected cities. Indonesia is famous for local cafes in each town to explain consumer preferences about local coffees. Each local café has a unique flavor variant based on regional features. This could explain the cultural differences of each region. Future research could also conduct analyses of differences in local and global preferences. These differences in preferences could illustrate a marketer's strategy to make good branding to encourage the other side of a local brand. It can also offer opportunities for local coffee shops to develop better and young entrepreneurs to build their businesses.
References
Aditiya, I. (2021). These are the 6 coffee brands with the most outlets in Indonesia.
Agrawal, A.K., & Rahman, Z. (2019). CCV scale: development and validation of customer co-created value scale in e-services.Current Psychology,38(3), 720-736.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ahmed, I., Islam, T., Rasid, S.Z.A., Anwar, F., & Khalid, A. (2020). As you sow, so shall you reap: finding customer-based outcomes of socially responsible coffee cafes.British Food Journal, 122(9), 3009-3026.
Al Halbusi, H., Jimenez Estevez, P., Eleen, T., Ramayah, T., & Hossain Uzir, M.U. (2020). The roles of the physical environment, social servicescape, co-created value, and customer satisfaction in determining tourists’ citizenship behavior: Malaysian cultural and creative industries.Sustainability,12(8), 3229.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Anouze, A.L.M., Alamro, A.S., & Awwad, A.S. (2018). Customer satisfaction and its measurement in Islamic banking sector: A revisit and update.Journal of Islamic Marketing, 10(2), 565-588.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Arifin, C. (2021). Cafes and coffee shops are opening up opportunities for industrial equipment and raw materials.
Boonlertvanich, K. (2019). Service quality, satisfaction, trust, and loyalty: The moderating role of main-bank and wealth status.International Journal of Bank Marketing,37(1), 278-302
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Caruana, A. (2002). Service loyalty: The effects of service quality and the mediating role of customer satisfaction.European Journal of Marketing, 36(7/8), 811-828.
Chen, K.H. (2012). Experiential value, well-being, and behavioral intention of tourists at Banto (catering) festival events.Humanities and Social Science Research,6(4), 1-25.
Cronin Jr, J.J., Brady, M.K., & Hult, G.T.M. (2000). Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments.Journal of Retailing,76(2), 193-218.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cronin, J.J. (2016). Retrospective: A cross-sectional test of the effect and conceptualization of service value revisited.Journal of Services Marketing, 30(3), 261-265.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dhisasmito, P.P., & Kumar, S. (2020). Understanding customer loyalty in the coffee shop industry (A survey in Jakarta, Indonesia).British Food Journal,122(7), 2253-2271.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dube, A., & Helkkula, A. (2015). Service experiences beyond the direct use: indirect customer use experiences of smartphone apps.Journal of Service Management,6(2), 224-248.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
El-Adly, M.I. (2019). Modelling the relationship between hotel perceived value, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services,50, 322-332.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Eren-Erdo?mu?, ?., & Dirsehan, T. (2017). Exploring local vs global brand associations in an emerging market using BCM technique.Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal,20(3), 266-288.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Euromonitor International. (2020). 2020 impact: Foodservice coffee players turn to retailing RTDcoffee amid covid-19.
Fernandes, T., & Moreira, M. (2019). Consumer brand engagement, satisfaction and brand loyalty: a comparative study between functional and emotional brand relationships.Journal of Product & Brand Management,28(2), 274-286.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fritz, K., Schoenmueller, V., & Bruhn, M. (2017). Authenticity in branding–exploring antecedents and consequences of brand authenticity.European Journal of Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fu, Y.K., & Wang, Y.J. (2020). Experiential value influences authentic happiness and behavioural intention: Lessons from Taiwan’s tourism accommodation sector.Tourism Review,76(1), 289-303.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gallarza, M.G., & Saura, I.G. (2020). Consumer value in tourism: a perspective article.Tourism Review,75(1), 41-44.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gallarza, M.G., Arteaga, F., Del Chiappa, G., Gil-Saura, I., & Holbrook, M.B. (2017). A multidimensional service-value scale based on Holbrook’s typology of customer value: Bridging the gap between the concept and its measurement.Journal of Service Management,28(4), 724-762.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gallarza, M.G., Arteaga-Moreno, F., Del Chiappa, G., & Gil-Saura, I. (2016). Intrinsic value dimensions and the value-satisfaction-loyalty chain: A causal model for services.Journal of Services Marketing,30(2), 165-185.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gallarza, M.G., Gil?Saura, I., & Holbrook, M.B. (2011). The value of value: Further excursions on the meaning and role of customer value.Journal of Consumer Behaviour,10(4), 179-191.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ganiyu, R.A. (2017). Customer satisfaction and loyalty: A study of interrelationships and effects in Nigerian domestic airline industry. Oradea Journal of Business and Economics, 2(1), 7-20.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Guèvremont, A. (2018). Creating and interpreting brand authenticity: The case of a young brand.Journal of Consumer Behaviour,17(6), 505-518.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hair Jr, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C.M., & Sarstedt, M. (2021).A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage publications.
Hoang, D.P. (2019). The central role of customer dialogue and trust in gaining bank loyalty: an extended SWICS model.International Journal of Bank Marketing, 37(3), 711-729.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hollbrook, M.B. (1994). The nature of customer value. R. Rust and R. Oliver (eds).
Ihtiyar, A., Barut, M., & Ihtiyar, H. G. (2019). Experiential marketing, social judgements, and customer shopping experience in emerging markets.Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics,31(2), 499-515.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ing, P.G., Lin, N.Z., Xu, M., & Thurasamy, R. (2020). Customer loyalty in Sabah full service restaurant.Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 32(7), 1407-1429.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jain, N.K., Singh, A.K., & Kaushik, K. (2019). Evaluating service quality in automobile maintenance and repair industry.Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics,32(1), 117-134.
Janssens, K., Lambrechts, W., Keur, H., & Semeijn, J. (2020). Customer value types predicting consumer behavior at Dutch grocery retailers.Behavioral Sciences,10(8), 127.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jeong, Y., & Kim, S. (2019). A study of event quality, destination image, perceived value, tourist satisfaction, and destination loyalty among sport tourists.Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 32(4), 940-960.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jin, T., Shao, W., Griffin, D., & Ross, M. (2018). How young Chinese consumers view Chinese brands.Young Consumers,19(1), 55-69.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jun, J., Kang, J., & Hyun, S.S. (2017). Effects of third-party certification on patrons’ service quality evaluation in the luxury-restaurant industry.British Food Journal, 119(4), 771-789.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kamath, P.R., Pai, Y.P., & Prabhu, N.K. (2019). Building customer loyalty in retail banking: a serial-mediation approach.International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kim, K., Choi, H.J., & Hyun, S.S. (2020). Coffee house consumers’ value perception and its consequences: Multi-Dimensional approach.Sustainability,12(4), 1663.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kim, M.S., & Stepchenkova, S. (2018). Examining the impact of experiential value on emotions, self-connective attachment, and brand loyalty in Korean family restaurants.Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism,19(3), 298-321.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kotler, P., Keller, K., Brady, M., Goodman, M., & Hansen, T. (2019).Marketing Management: 4th European Edition. Pearson UK.
Leroi-Werelds, S. (2019). An update on customer value: State of the art, revised typology, and research agenda.Journal of Service Management, 30(5), 650-680.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Liu, P., & Tse, E.C.Y. (2018). Exploring factors on customers’ restaurant choice: an analysis of restaurant attributes.British Food Journal, 120(10), 2289-2303.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mathwick, C., Malhotra, N., & Rigdon, E. (2001). Experiential value: conceptualization, measurement and application in the catalog and Internet shopping environment.Journal of Retailing,77(1), 39-56.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Moliner-Velázquez, B., Fuentes-Blasco, M., & Gil-Saura, I. (2019). Effects of value and innovation on brand equity in retailing.Journal of Brand Management,26(6), 658-674.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ngobo, P.V. (2017). The trajectory of customer loyalty: An empirical test of Dick and Basu’s loyalty framework.Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,45(2), 229-250.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Özsomer, A. (2012). The interplay between global and local brands: A closer look at perceived brand globalness and local iconness.Journal of International Marketing,20(2), 72-95.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Prebensen, N.K., & Xie, J. (2017). Efficacy of co-creation and mastering on perceived value and satisfaction in tourists' consumption.Tourism Management,60, 166-176.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rambocas, M., Kirpalani, V.M., & Simms, E. (2018). Brand equity and customer behavioral intentions: a mediated moderated model.International Journal of Bank Marketing,36(1), 19-40.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rather, R.A., & Sharma, J. (2017). The effects of customer satisfaction and commitment on customer loyalty: Evidence from the hotel industry.JOHAR,12(2), 41.
Richardson, S., Lefrid, M., Jahani, S., Munyon, M.D., & Rasoolimanesh, S.M. (2019). Effect of dining experience on future intention in quick service restaurants.British Food Journal,121(11), 2620-2636.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Riefler, P. (2020). Local versus global food consumption: The role of brand authenticity.Journal of Consumer Marketing,37(3), 317-327.
Indexed at, Google Scholar , Cross Ref
Roy, R., & Chau, R. (2011). Consumer?based brand equity and status?seeking motivation for a global versus local brand.Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 23(3), 270-284.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ruiz-Molina, M.E., Gallarza, M., & Gil-Saura, I. (2018). A review of value drivers in service settings.Journal of Services Marketing, 32(7), 850-867.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sánchez-Fernández, R., Gallarza, M.G., & Arteaga, F. (2020). Adding dynamicity to consumer value dimensions: An exploratory approach to intrinsic values and value outcomes in the hotel industry.International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 32(2), 853-870.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Schindler, P.S. (2019). Business research methods.International Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill
Shu, S.T., Strombeck, S., & Hsieh, C.L. (2013). Consumer ethnocentrism, self-image congruence and local brand preference: A cross-national examination.Asia Pacific Management Review,18(1).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Taylor Jr, S., DiPietro, R.B., & So, K.K.F. (2018a). Increasing experiential value and relationship quality: An investigation of pop-up dining experiences.International Journal of Hospitality Management,74, 45-56.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ting, H., Lau, W.M., Cheah, J. H., Yacob, Y., Memon, M.A., & Lau, E. (2018). Perceived quality and intention to revisit coffee concept shops in Malaysia: a mixed-methods approach.British Food Journal, 120(5), 1106-1119.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ting, M.S., Goh, Y.N., & Isa, S.M. (2016). Determining consumer purchase intentions toward counterfeit luxury goods in Malaysia.Asia Pacific Management Review,21(4), 219-230.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Varshneya, G., Das, G., & Khare, A. (2017). Experiential value: A review and future research directions.Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 35(3), 339-357.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Vesci, M., Conti, E., Rossato, C., & Castellani, P. (2020). The mediating role of visitor satisfaction in the relationship between museum experience and word of mouth: Evidence from Italy.The TQM Journal, 33(1), 141-162.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wann, J. W., Kao, C.Y., & Yang, Y.C. (2018). Consumer preferences of locally grown specialty crop: The Case of Taiwan Coffee.Sustainability,10(7), 2396.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wu, C.H.J., & Liang, R.D. (2009). Effect of experiential value on customer satisfaction with service encounters in luxury-hotel restaurants.International Journal of Hospitality Management,28(4), 586-593.
Wu, H.C. (2017). What drives experiential loyalty? A case study of Starbucks coffee chain in Taiwan.British Food Journal, 113(3), 468-496.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yoo, S.R., Kim, S.H., & Jeon, H.M. (2022). how does experiential value toward robot barista service affect emotions, storytelling, and behavioral intention in the context of COVID-19?.Sustainability,14(1), 450.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zietsman, M.L., Mostert, P., & Svensson, G. (2020). A multidimensional approach to the outcomes of perceived value in business relationships.European Business Review,32(4), 709-729.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 12-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-11507; Editor assigned: 14-Mar-2022, PreQC No. ASMJ-22-11507(PQ); Reviewed: 21-Mar-2022, QC No. ASMJ-22-11507; Published: 28-Mar-2022