Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 1
The Effect of Transformational Leadership Style, Organizational Culture and Work Motivation toward Employee Performance (Study on Developer Companies in Makassar)
Muhammad Idris, STIE Nobel
Maryadi, STIE Nobel
Saripuddin D, STIE Nobel
Ahmad Firman, STIE Nobel
Muhammad Hidayat, STIE Nobel
Citation Information: Idris, M., Maryadi, Saripuddin, D., Firman, A., & Hidayat, M. (2022). The effect of transformational leadership style, organizational culture and work motivation toward employee performance (Study on developer companies in makassar). Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S1), 1-15.
Abstract
The aims of this study is to examine and to analyze the influence of Transformational Leadership Style, Organizational Culture, and Work Motivation on Employee Performance and the influence of transformational leadership styles, organizational culture through mediating work motivation on employee performance at developer companies in Makassar. The current research design applied quantitative approach and data collection was conducted survey method by using questionnaire instrument. The study involved 101 developer employees chosen by proportional simple random sampling. Data analysis method used in testing the hypotheses is Generalized Structured Component Analysis (GSCA). Result of this study indicates that transformational leadership style has a positive and significant effect on organizational culture. Transformational leadership style has a positive and significant effect on work motivation. Transformational leadership style has a positive and significant effect on employee performance. Organizational culture has no effect on work motivation. Organizational Culture has no effect on Employee Performance. Work motivation has a positive and significant effect on employee performance. Transformational leadership styles may have a direct effect on employee performance as well as through work motivation. Work motivation is not a mediating variable (non-mediation) of the relationship between organizational culture and employee performance.
Keywords
Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, Work Motivation, Employee Performance.
Introduction
Rapid change requires organizations to have employees and leaders who are able to adapt effectively, focus on consumers and improve performance for getting profit. Human resources have a very strategic role and function for the achievement of company goals. The competitive world economy, rapid progress in various fields where boundaries between countries are not an obstacle and the level of competition is getting tougher require a paradigm shift particularly a change in leadership which will be a key factor in the success of an organization. This condition is largely determined by quality of organizational leadership (business, government, social). Thus it requires new leadership in the organization (Bass, 1998). The new leader is called a transformational leader in which they have to create new things from the old one.
Bass (1998) describes 3 (three) main characteristics of a transformational leader, namely: charismatic, caring, and intellectual. Charismatic leaders are leaders who are able to foster enthusiasm and loyalty of members of the organization, encourage them to express opinions, ideas and notion, have far-sightedness, have a strong commitment to change, are broad-minded, are able to build networking and are able to direct attention to the vision and anticipating situations and conditions in the future. An attentive leader is a leader who is willing to pay attention to the problems encountered and needs of the organization members as well as helpful to solve problems of his subordinates.
Bass (1985) explains in his book Leadership and Performance beyond Expectations that transformational leadership is a leadership model that aims to encourage extra effort followers in order to achieve the expected performance. Transformational leadership is able to encourage subordinates to achieve the targets that exceed what has been set. Conger & Kanungo (1988) asserts that transformational leadership is able to change ordinary people to do extraordinary things. Personal power legitimacy involves special relationship between them on the basis of trust, reward, and recognition of competence. For this reason, besides his roles as motivator, coach, and mentor, transformational leadership is also a wise person who is assertive and authoritative.
(Stoner et al. (1996) suggest that charismatic leadership has a very high level of power and part of that power comes from their desire to influence others. Charismatic leaders have a level of self-confidence and a strong belief in moral truth and the ability to convince his followers to increase loyalty toward the organization.
Researches that link leadership style with employee performance are Davis (1997); Goleman (2017); < Bass et al. (2003 & 2006); Vigoda‐Gadot (2007). They found out that leadership style has a significant and positive effect on employee performance.
Leaders encourage, preserve, maintain, and increase work motivation and employee performance. In order to improve employee performance, leaders are expected to consider their leadership style. The most important thing in leadership is an effort to influence subordinates to work according to their abilities and expertise, so that the organization can grow, develop and be able to compete.
Literature Review
Leader
A leader is an attempt to influence social behavior through planning, organizing, controlling others through prestige, strength and ability. Leaders plan, organize, direct, and control through their abilities to achieve organizational goals.
Luthans (2002) describes the characteristics of leaders in XXI century namely: Innovation (creating something new); An original (original from the leader); Development (to develop); Focus on people (focus on humans); Inspires trust (foster a sense of trust); Long-range perspective (long-term perspective); Asks what and why (asking what why); Eye on the horizon (looking ahead); Originility (having authenticity); Challenges the Status quo (opposing the Status quo); Own person (responsible); Does the right thing (behave righteously).
Various studies of organizational behavior especially on the topic of leadership (leadership) have been carried out, from the history of studies on the topic of leadership are described in the following sections, including the IOWA Study, the Ohio Study, and the Michigan Study which then underlie subsequent leadership theories, both classical leadership theory / traditional as well as modern leadership theory (Luthans, 2002).
Transformational Leadership Style
Transformational leadership style put forward by states that: “Transformational leadership is a condition in which the followers of a transformational leader feel that there is trust, admiration, loyalty, and respect for the leader, and they are motivated to do more than they originally expected”.
Transformational leadership is the ability to inspire and motivate followers to achieve greater results than originally planned and for internal rewards.
According to Robbins, a transformational leadership style is a leader who engages and inspires (transforms) his followers for extraordinary things. By this transformational leadership, followers feel trust, admire, loyal and respect to the leader, as well as they are motivated to do more than they expect.
A transformational leader is a type of leader who inspires his followers to put their personal interests aside and has extraordinary influencing abilities. Transformational leadership inspires their followers not only to believe in themselves personally, but also to believe in their own potential to envision and create a better future for the organization. Transformational leaders create big changes within themselves as well as their organizations.
Based on the above definition, it can be concluded that transformational leadership changes followers' awareness of problems by helping them to see the old problems in new ways, and they are able to excite, awaken, and inspire followers to give extra efforts of the followers to achieve goals of the organization.
Four characteristics of a leader to possess transformational qualities, those are:
•1. Idealized influence is behavior that evokes strong emotions and identifications from followers to leaders.
•2. Individualized considerations include providing support, encouragement, and training for followers.
•3. Inspirational motivation includes delivering an attractive vision, using symbols to focus the efforts of subordinates.
•4. Intellectual stimulation is behavior that increases followers' awareness of problems and influences followers to view problems from a new perspective.
There are several characteristics of transformational leadership, namely:
•1. Have a clear strategy. Leaders carry out and have a big change plan and directed towards the vision, mission and strategy of the organization and it is well communicated to their members.
•2. Concern. Leaders pay attention to every problem faced by members. He will motivate and care of them.
•3. Stimulate members. Leaders stimulate and help members for positive goals and avoid things that are not productive.
•4. Maintain team cohesiveness. The leader always keeps solidarity of team and do not let his thinking lead by the members’ point of view.
•5. Appreciate differences and beliefs. Leaders value every differences of opinion for the purpose of a better direction, and invite all members to respect differences and beliefs.
Some indicators of transformational leadership:
•1. Ideal influence. The ideal influence is considered to be a combination of charm and personal attractiveness that contributes to an extraordinary ability to get others to support the vision and promote it passionately as well.
•2. Inspirational Motivation. Inspirational motivation describes leaders passionate in communicating the idealistic future of the organization. Leaders use verbal communication or use symbols that are intended to stimulate subordinates' enthusiasm. The leader motivates subordinates to the importance of the organization's vision and mission so that all subordinates are encouraged to have the same vision. This common vision encourages subordinates to work together to achieve long-term goals optimistically. So that the leader does not only arouse individual spirit but also team spirit.
•3. Intellectual Stimulation. Intellectual stimulation describes the leader as being able to encourage employees to solve old problems in new ways. The leader seeks to encourage attention and awareness of subordinates to the problems encountered. The leader then tries to develop ability of subordinates to solve problems with new approaches or perspectives.
•4. Individual Considerations. Individual attention illustrates that leader always pay attention to their employees, treat employees individually, train and advise. Leader invites employees to be observant about the abilities of others. Leader focuses employees on developing personal strengths.
Organizational Culture
C Organizational culture is a number of important understandings, such as norms, values, attitudes and beliefs, which are shared by members of the organization (Stoner et al., 1996). Each organization has culture that is different from each other, thus organizations can be differentiated between one and another. Culture will encourage someone to behave in a certain way in an organization. Culture can affect all the activities of organizational employees, whether they work, how to view work, work with colleagues, or how they perceive the future (Gibson et al., 1973). Culture is a complex mix of assumptions, behaviors, values, beliefs and order that are inherent in an organization and affect the organization.
Work Motivation
S The success of an organization in achieving its objectives is not only determined by the form of complete organizational structure but is also influenced by the placement of individuals in the right position according to their abilities and expertise (the right man on the right place), each individual have different motivations for work. Individuals differ not only in their ability to work but also in their willingness to do something (motivation).
Employee Performance
The ability of an organization to develop lies on individuals within the organization, thus performance of an organization is result of an effort from all members of the organization. Employee performance is the result of employee work in a certain period. Employee performance is closely related to the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization in achieving vision and mission of the organization. Individual performance has influence on improving group performance and contributes to the overall organizational performance.
Performance is result or output of a process, performance is closely related to productivity because it is the most important thing that determines the achievement of a high level of productivity in an organization. Performance is part of motivation and ability function. Performance shows degree of success in carrying out tasks and ability to achieve goals that has been set by the organization. Performance is the quality and quantity of tasks achievement, individuals, groups and companies.
Performance is a function of the interaction of abilities (A), motivation (M) and opportunity (O), or performance = f (A x M x O). This means that performance is a function of ability, motivation and opportunity (Robbins, 2003).
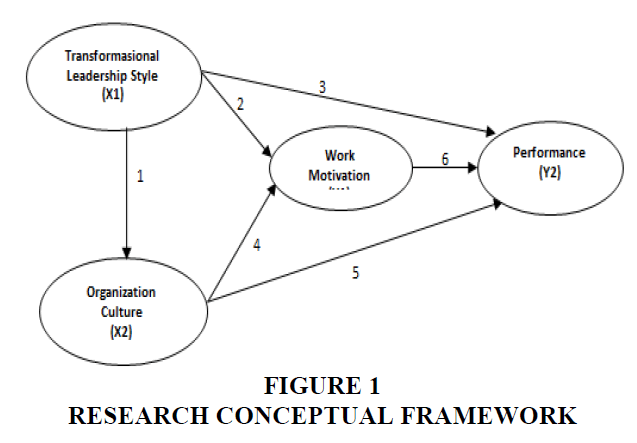
Based on the description above, the conceptual framework of this research is shown as follows (Figure 1):
Research Hypothesis
H1Transformational leadership style has a significant effect on work motivation
The influence of transformational leadership styles on employee motivation, Conger & Kanungo (1998), suggests that transformational leadership is a visionary, coach, and mentor as well as a motivator.
H2Transformational leadership style has a significant effect on employee performance.
The influence of transformational leadership styles on employee performance. Bass (1985) suggests a leadership model that is able to provide solutions in understanding what makes leaders have a great influence on followers and makes the performance of a number of organizations experience continuous improvement is a transformational leadership model, this model aims to encourage extra effort of employees to achieve high performance as expected. Several research results conducted by Bass et al. (2003); Sudarto (2004); and Vigoda‐Gadot (2007); Jung & Avolio (2000) indicate that leadership style directly affects employee performance.
H3 Organizational culture has a significant effect on employee motivation.
A strong culture is influential and become a driving force for employees to behave positively, dedicatively, and productively to improve employee performance. Gibson et al. (1973) and Schein (1990) explains that organizational culture must refer to several things such as norms, groups, basic values that are believed to be true in the organization, formal philosophy, rules of the game in organizations, climate and behavior based on habits within the organization.
H4 Organizational culture has a significant effect on employee performance
Organizational culture is related to long-term economic performance of company (Kotter, 2008). This is one of the reasons that organizational culture is used as a strategic tool in dealing with change and is expected to be one of the pillars of competitive advantage for the organization. In the context of organizational culture as a management tool, organizational culture can be considered as part of the organization's strategy in achieving goals. Some research results on organizational culture and employee performance were carried out by; Ojo who stated that organizational culture is very important in every company and that it has a positive impact on employee performance whereas Ahmad (2012) stated that there is a significant and positive influence between organizational culture and performance.
H5 Work motivation has a significant effect on employee performance.
Lussier & Achua (2015) presented a study which found that one of the theories of motivation, namely theory of expectation, can predict accurately work effort, level of satisfaction and performance of an employee, while Suprihanto (1987) states a person's performance depends on the person's motivation for the work being done, the higher a person's motivation to do a job the higher performance can be achieved, and vice versa, the lower a person's motivation to do a job, the lower his performance.
H6 Transformational leadership style has a significant effect on employee performance mediated by work motivation
The influence of transformational leadership styles on employee performance is mediated by work motivation. Leadership style is related to the ways implemented by managers to organize and influence their employees to improve their performance in order to achieve company goals. Leaders have a very close relationship with work motivation and employee performance (Hersey & Blanchard 1993; (Siagian et al., 1994).
H7 Organizational culture has a significant effect on employee performance mediated by work motivation
Organizational culture has a strategic role in the success of organization. Robbins (2003) states that an organization that has a weak culture means that individuals belong to the organization are not prepared for a change. Employees prefer individual values and group values that they already have. They also prefer the way they work and resist changes, especially with regard to new abilities and skills to meet expected demands and obligations.
Some researches on organizational culture and performance have been carried out by Aluko (2003). They reveal the positive and significant relationship between organizational culture and performance.
Research Methodology
Research Sample
This study involved 5 developer companies, namely, PT. Timurama, PT. Dayaprima Nusawisesa, PT. Prima Nusa Bakti Makassar, PT. Baruga Asri Nusa Development, PT. Nusa Sembada Bangunindo. 101 employees at 5 companies were chosen as research samples.
Measurement
Variables measured in this study are leadership style (X1), organizational culture (X2), work motivation (z) and employee performance (Y) which can be explained operationally in the Table 1:
| Table 1 Research Variable Operationalization Summary | ||||
| Variable | Indicator | Item | Source | |
| Transformasional Leadership Style | charismatic | 1 | Faith | Bass (1998) |
| 2 | Mutual respect | |||
| 3 | Mission | |||
| Attentive | 4 | Attentive | ||
| 5 | Attention to needs | |||
| 6 | Problem Solver | |||
| 7 | Respectful | |||
| Intellectual Leader | 8 | Thinking Rationally | ||
| 9 | Using Data | |||
| 10 | Describing Vision | |||
| 11 | Achievement of objectives | |||
| 12 | Proper decision | |||
| Organizational Culture | Norma | 13 | Freedom of behavior | Stoner et al. (1996) |
| 14 | Loyality to the organization | |||
| 15 | Regulations are adjusted to the interests of the company | |||
| Value | 16 | Maintain alignment | ||
| 17 | Avoiding confrontation | |||
| Attitude | 18 | Pleasant behavior | ||
| 19 | Duty based treating | |||
| Belief | 20 | Concern | ||
| 21 | Prioritizing company interests over personal interests | |||
| Changes | 22 | Mindset Change | ||
| 23 | Inovation | |||
| 24 | Discussing work | |||
| Work Motivation | Expectation | 25 | Developing new method of working | Robbins (2003) |
| 26 | Work according to company regulations | |||
| Instrumentality | 27 | Work Achievement | ||
| 28 | Jobs based on education | |||
| Valence | 29 | Ability based work | ||
| 30 | As per Quantity Standards | |||
| Employee performance | Quantity of work | 31 | Exceeding the target | Amstrong & Baron (2005) |
| 32 | Meet quality standards | |||
| Quality of work | 33 | Organizing work | ||
| 34 | employee development | |||
| Desire | 35 | suitability of salary | ||
| 36 | suitability of bonus | |||
The essence of the current study is to get the best model to explain relationship between the independent variable of transformational leadership style (formed by 3 indicators), the dependent variable of organizational culture (formed by 5 indicators), work motivation variable (formed by 3 indicators) and employee performance variable (formed by 3 indicators). Based on these considerations, Generalized Structured Component Analysis (GSCA) technique was applied in the analysis of the data. By its modeling through GSCA, it is expected to obtain a powerful structural model for confirmation purposes. Therefore, GSCA method is equivalent to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) of analysis. GSCA is also powerful for testing theory-based models, or in other words to confirm theories about the relationship between variables contained in the structural model.
Measures of Fit Model Evaluation of GSCA
In GSCA Measures of Fit analysis can be conducted on measurement models, structural models and overall models are measurement of the combined goodness of fit between measurement models and structural models, especially reflective indicators.
Measures Model Evaluation
Latent variables in this study are measured by reflective and formative indicators; evaluation of the measurement model can be conducted as follows:
Latent construct is considered to have convergent validity, if the estimated loading value is ≥ 0.40 and the critical point value (critical ratio / CR) is significant at 95% confidence level or α = 0.05 (Ferdinand, 2002; (Solimun, 2012).
Testing discriminant validity of GSCA method by looking at AVE (Average variance Extracted) value. It is recommended that AVE values are greater than 0.50 which means that AVE values above 0.50 can be said that latent variables have good discriminant validity.
The latent variable has good internal composite reliability if the composite reliability value is greater than or equal to 0.60 ((Solimun, 2012).
Evaluation of Goodness-of fit structural Model and Overall Model
Measure of fit Evaluation on the structural model and the overall model is a measure of goodness of fit, namely a combination of measurement models and structural models with FIT, AFIT, GFI and SRMS tests.
Evaluation of the Goodness-of fit of the structural model and the Overall Model
Measure of fit structural model, measured by using FIT and AFIT.
FIT shows the total variable of all variables that can be explained by structural model. The greater the FIT, the greater the proportion of variable variance that can be explained by the model.
AFIT (Adjusted FIT) can be used for model comparisons. Models with AFIT, value can be seen among the good models.
Measure of fit Overall Model, aims to see the structural model and measurement model as an integrated whole model. Examination of the overall goodness-of-fit model aims to find out SMRS value with a cut-off ≤ 0.08 and GFI value with a cut-off ≥ 0.90.
Research Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing in this study aims to answer whether the proposed hypotheses are accepted or rejected. Testing is conducted by using a critical point (CR); p-value≤0.05 (α=0.05) which means that significance level of parameter estimation in hypothesis testing is set at 95% or α=0.05. Thus hypothesis testing is based on probability values with the following conditions:
Ho p> α 0.05 or 95%; there is no significant effect between exogenous variables on endogenous variables.
Ha p<α 0.05 or 95%; there is a significant influence between exogenous variables on endogenous variables.
The basis for consideration of decision making in this study are:
•1. If p<α=0.05, then Ho is rejected, Ha is accepted, meaning that there is a significant influence between exogenous variables on endogenous variables.
•2. If p>α=0.05, then Ho is accepted, Ha is rejected, meaning that there is no significant influence between exogenous variables on endogenous variables.
Examination of Mediation Variables Effect
Method of examining the mediating variables by using approach of coefficient and significance values (Solimun, 2012) in the following ways: (a) examining direct effect of independent variable toward dependent variable on the model by involving the mediating variable, (b) examining the effect of independent variable toward dependent variable on the model without involving mediating variable, (c) examining effect of independent variable on mediating variable, (d) examining mediating variable toward dependent variable (Solimun, 2012). These goals can be fulfilled by:
•1. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is not significant, then it is proven that there is a complete mediation variable;
•2. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is also significant, where the coefficient of (a) is lower (down) than (b) then it is proven that there is a partial mediation variable;
•3. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is also significant, where the coefficient of (a) is almost the same as (b) then it is proven that it is not a mediating variable;
•4. If either (c) or (d) both are not significant, it is proven that it is not mediating variable.
Research Result
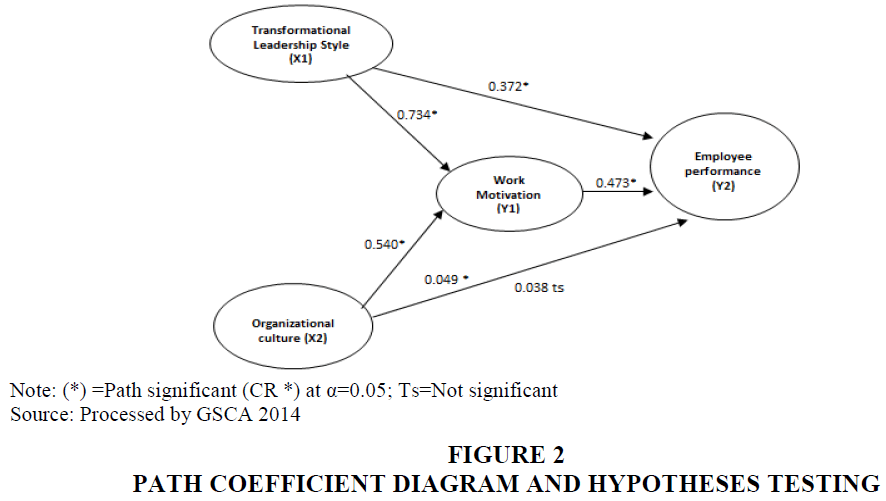
Test results in Figure 2 showed that from the six direct effects between tested variables, there are four significant effects, namely: (1) transformational leadership style has a significant effect on work motivation, (2) transformational leadership style has a significant effect on employee performance; (3) work motivation has a significant effect on employee performance. While there are two variables tested that have no significant effect, namely: (1) organizational culture has no effect on work motivation, (2) organizational culture has no effect on employee performance. Testing of structural models and hypotheses is carried out to determine the relationship between latent variables in this study. From the output of GSCA model, structural model testing and hypotheses were carried out by looking at the estimated value of the path coefficient and critical point value (CR *) which were significant at 95% confidence level. The complete analysis results are contained in the results of GSCA analysis, which can be seen in Table 2.
| Table 2 Path Coefficient of Direct Effect and Hypotheses Testing | |||||
| Hypotheses | Direct Effect | Path Coefficient | C.R | Conclusion | |
| H1 | Transformational Leadership (X1) → Work Motivation (Y1) | 0.734 | 7.01* | Significant | Accepted |
| H2 | Transformational Leadership (X1) → Work Motivation (Y1) | 0.372 | 3.15* | Significant | Accepted |
| H3 | Organizational Culture (X2) → Work Motivation (Y1) | 0.049 | 0.35 | Not Significant | Rejected |
| H4 | Organizational Culture (X2) → Employee Performance (Y2) | 0.038 | 0.41 | Not Significant | Rejected |
| H5 | Work Motivation (Y1) → Employee Performance (Y2) | 0.473 | 3.74* | Significant | Accepted |
Source: Processed by GSCA 2014
Hypotheses Testing and Path Coefficient of Indirect Effect (Mediation)
Testing the indirect effect (mediation) aims to detect the position of intervening variables in the model. Mediation testing is carried out to determine the nature of relationship between variables, either as a complete mediation variable, or as a partial mediation or non-mediating variable.
The assumption of audit result refers to the following criteria:•1. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is not significant, then it is proven that there is a complete mediation variable;
•2. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is also significant, where the coefficient of (a) is lower (down) than (b), it is proven that there is a partial mediation variable;
•3. If (c) and (d) are significant and (a) is also significant, where coefficient of (a) is almost the same as (b) then it is proven that it is not a mediating variable (non-mediation);
•4. If either (c) or (d) both are not significant, it is proven that it is not a mediating variable (non-mediating);
H6 The effect of transformational leadership style through mediating work motivation on employee performance
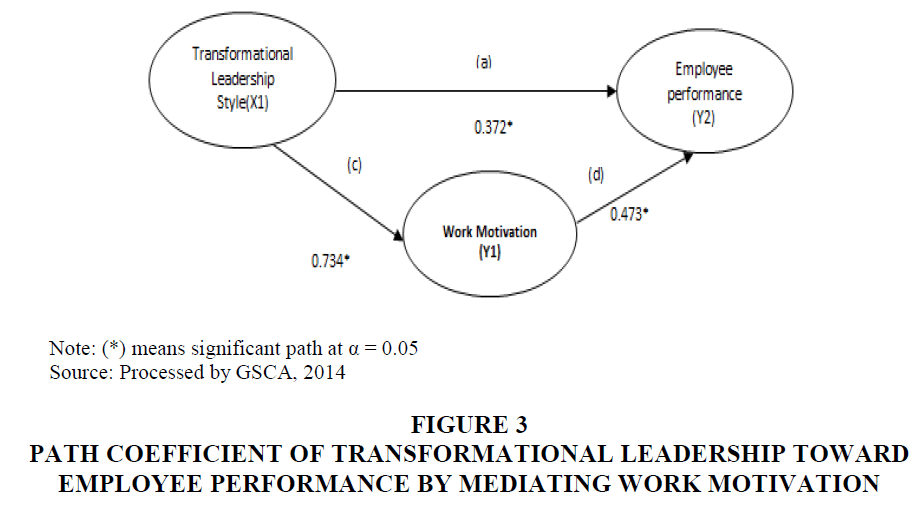
Results of testing the effect of transformational leadership style on employee performance (a) in the initial model were found to be significant. In the second model involving work motivation as a mediating variable shows that transformational leadership style directly has a significant effect on work motivation (c). Then work motivation variable on employee performance also has a significant effect (d). The nature of relationship on mediating variable can be concluded by re-examining the transformational leadership style variable in relation to employee performance by not involving the mediating variable in model (b). The test results are shown in the path diagram in Figure 3.
Based on the two models, Figures 3 and 4 show that path coefficient values (a), (c), and (d) are significant with the initial model, the coefficient value (a) is lower (down) than the coefficient value (b). Nature of mediation of transformational leadership style effect on employee performance through work motivation is partial mediation. These results mean that transformational leadership style on employee performance can have a significant and positive effect either directly or indirectly through work motivation. Results of the examination show that there is sufficient empirical evidence to accept the hypothesis (H7) which shows that transformational leadership style has a significant effect on employee performance, which is mediated by work motivation or work motivation acts as a partial mediating variable.
Figure 3 Path Coefficient of Transformational Leadership Toward Employee Performance by Mediating Work Motivation
Figure 4 Testing Path of Transformational Leadership Style Toward Employee Performance Minus Work Motivation Mediating Variable
H7 The influence of organizational culture on employee performance, which is mediated by work motivation
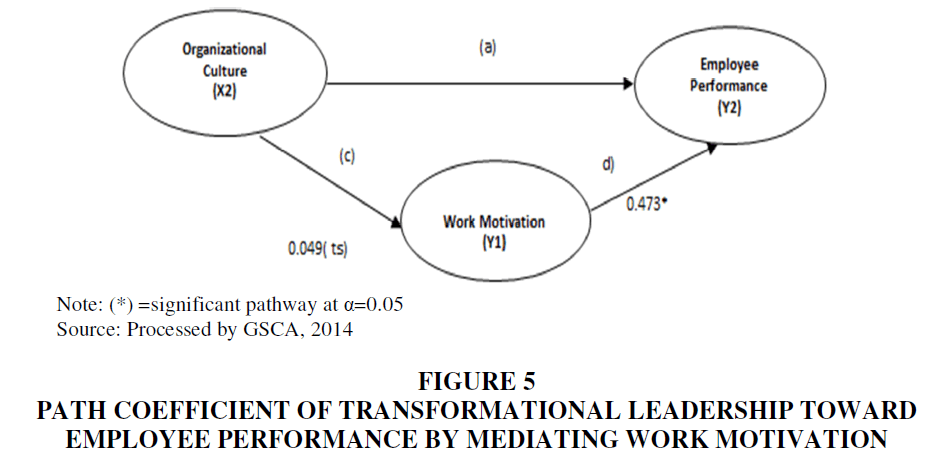
The results of testing the influence of organizational culture variables are not significant on employee performance (a). Then the effect of organizational culture is not significant on work motivation (c). Furthermore, work motivation is significant on employee performance (d). Based on the results of this analysis, it can be concluded that work motivation is not a mediating variable (non-mediating) of the relationship between organizational culture and employee performance. The path diagram in Figure 5 is presented in more detail below.
Figure 5 Path Coefficient of Transformational Leadership Toward Employee Performance by Mediating Work Motivation
Results of this examination reveal that hypothesis (H7) is rejected which means that transformational leadership style has a significant effect on employee performance, which is mediated by work motivation.
Results of coefficient testing of the influence of work motivation mediating variable are presented in Table 3.
| Table 3 Path Coefficient of Influence of Mediation and Hypothesis Testing | |||||||
| No | Correlation of Variable | Mediation Variable | Path Coefficient | Conclusion | |||
| C | d | a | B | ||||
| 1 | Transformational Leadership (X1) → Work Motivation (Y2) | Employee Performance (Y2) | 0,734 | 0,473 | 0,372 | 0,777 | Partial Mediation |
| 2 | Organizational Culture (X2) → Work Motivation (Y2) | Employee Performance (Y2) | 0,049 | 0,473 | 0,038 | - | Not Mediation |
Based on Table 3, it can be explained that nature of the influence of mediating variables in the model is as follows:
Transformational Leadership Style on Employee Performance through Mediation of Work Motivation
Testing results of transformational leadership style on employee performance at the initial model involving mediating variable show that transformational leadership style on work motivation has a significant effect (c) and employee performance (a). Work motivation has a significant effect on employee performance (d). Estimation of mediating variable can be identified by re-analyzing relationship between transformational leadership styles (b), no work motivation involved (mediating variable) in the model. Results of the analysis of the second model show that coefficient value of (a) is lower (down) than the value of (b), thus, nature of the relationship between transformational leadership and employee performance through work motivation is partial mediation. These results suggest that transformational leadership styles can have a direct effect on employee performance and work motivation.
Organizational Culture on Employee Performance is Mediated by Work Motivation
Analysis results of the influence of organizational culture variables on employee performance in the initial model involving mediating variables showed that organizational culture has no significant effect on work motivation (c) and employee performance (a), but work motivation on employee performance has a significant effect (d). Results of the model analysis show that relationship of (c) and (a) is not significant but relationship of (d) is significant in the model. Thus, relationship between organizational culture and employee performance through work motivation is non-mediation. This result means that organizational culture does not directly affect employee performance or work motivation.
Discussion
This research shows that the two independent variables, namely leadership style and organizational culture have influences on company performance. This result is supported by empirical facts if the leader indeed have a strong enough influence in bringing the organization to achieve successful leadership goals, then it will lead every individual in the company to be able to achieve the expected performance.
Likewise organizational culture, which is an organizational life structure that is continuously adhered by all members of the organization, this culture will form loyal character of the individual toward organization's operational. Finally the built in organization characteristics directs the organization and individuals within to achieve performance in accordance with duties and responsibilities.
Leadership implemented in the organization will be able to influence work motivation of people within the organization as well as work culture. Work convenience which is developed and influenced by the culture adopted by the organization will also affect the motivation level of people who work in the organization. Thus, it is clear that leadership style and organizational culture will be able to influence motivation and at the same time motivation will affect performance.
Conclusion
Based on hypothesis testing, discussion results and research findings, several conclusions can be made as follows:
Transformational leadership style can increase employee motivation. This result is reflected in the implementation of transformational leadership style that makes a real contribution to increasing employee motivation at developer companies in Makassar.
Transformational leadership style is able to improve employee performance. These results are reflected in the application of a transformational leadership style that makes a real contribution to employee performance at developer companies in Makassar.
Organizational culture has no real effect on increasing employee motivation. The results of this study indicate that organizational culture does not influence work motivation.
Organizational culture does not contribute significantly to improve employee performance. Dominant organizational culture is reflected by beliefs, while employee performance is seen as the most important and dominant, reflected by quality of work. This means that belief as measured on caring for employees, prioritizing the interests of the company so as improving employee performance.
Work motivation can improve performance of the developer company employees. This result means that work motivation makes a real contribution in improving employee performance.
The influence of transformational leadership style on employee performance through work motivation mediation is partial mediation. These results suggest that transformational leadership styles can affect employee performance either directly or indirectly through mediating influence of work motivation.
The influence of organizational culture through work motivation mediation on employee performance is not mediation (non-mediation). This is because organizational culture has no effect on employee performance.
References
Armstrong, M., & Baron, A. (2005). Managing performance: performance management in action. CIPD publishing.
Bass, B.M., & Riggio, R.E. (2006). Transformational Leadership, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Mahwah, NJ.
Bass, B.M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectations. Collier Macmillan.
Bass, B.M. (1998). TL: Industry, military, and educational impact.
Davis, M.L. (1997). Assessment of the effects of leadership on productivity. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Baker College, Michigan.
Gibson, J.L., Ivancevich, J.M., & Donnelly, J.H. (1973). Organization Structure, Processes, Behavior, Business Publications.
Goleman, D. (2017). Leadership that gets results (Harvard business review classics). Harvard Business Press.
Hersey, P., & Blanchard, K.H. (1969). Management of organizational behavior: Utilizing human resources.
Kotter, J.P. (2008). Corporate culture and performance. Simon and Schuster.
Lussier, R.N., & Achua, C.F. (2015). Leadership: Theory, application, & skill development. Cengage learning.
Robbins, S.P. (2003). Organizational behavior.
Schein, E.H. (1990). Organizational culture. American Psychological Association.
Siagian, S.P., Kepemimpinan, T.D.P., & Ke, C. (2004). Motivation theory and its application, PT. Rineka Cipta. Jakarta.
Solimun, S., (2012). Generalized structural component analysis (GeSCA) modeling. Statistics study program, FMIPA, PDIM FE Universitas Brawijaya.
Stoner, J.A.F., Freeman, R.E., & Gilbert, D.R. (1996). Management. Pearson education.
Sudarto, T. (2004). The influence of work motivation, ability, leadership, and organizational culture on work performance.
Suprihanto, (1987). Human resource management. CV Karunia. Open University. Jakarta.