Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 4
The Impact of Organizational Culture on the Strategic Development of Tourism and Hospitality Enterprises
Elena Yurievna Nikolskaya, Plekhanov Russian University of Economics
Svetlana Georgievna Fedorchukova, Moscow State Institute for Physical Culture, Sports and Tourism named after Yu. A. Senkevich
Ivan Petrovich Kulgachev, Moscow State Institute for Physical Culture, Sports and Tourism named after Yu. A. Senkevich
Tatyana Vladimirovna Simonyan, Don State Technical University
Galina Victorovna Tretyakova, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Sergei Vladimirovich Feoktistov, Amur State University
Abstract
The article deals with assessing the impact of organizational culture on the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises. It is determined that organizational culture plays a key role in the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises. Organizational culture is the lever that ensures the long-term success of a tourism and hospitality enterprise rather than immediate achievements. It is proven that in the process of strategic development management in the tourism and hospitality industry, staff need to timely and appropriately responds to changes in the external environment, including seasonal fluctuations in demand, legislative changes, and national currency fluctuations. These issues are supposed to be alleviated by the organizational culture which will not be perfunctory but rather will have actual leverage over the development and competitiveness of a tourism and hospitality enterprise. It is established that efficient organizational culture is a significant internal resource for the development of a tourism and hospitality enterprise. Understanding the features of the organizational culture of successful tourism and hospitality enterprises allows one to adopt and reinterpret their experience as well as forecast, prevent and constructively solve organizational contradictions at different management levels at the early stages of strategic development.
Keywords
Organizational Culture, Strategic Development, Enterprise, Tourism and Hospitality Industry, Diversification, Service, Product, Efficiency.
Introduction and Literature Review
In the current geopolitical situation which is a consequence of globalization processes in society and the economy, increasingly more attention is paid to the development of non-manufacturing enterprises. For example, the tourism industry has acquired the status of one of the most profitable in the world in recent years, which has a positive effect on the diversification of the economy through the generation of related industries involved in the creation and sale of tourism products and related services on the tourism market.
Moreover, the issues of strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises require significant attention due to the high competition in the tourist services market and significant changes in tourist demand. There is a need to explore the demand for tourist and related services. First, this is possible only in the case of innovative development of tourist enterprises, for example, through the diversification of tourist products and individual tourist services, the formation of an efficient organizational culture, and changes in behavioral factors.
The aspects of the functioning of tourism and hospitality enterprises were described in the works by Agamirova et al. (2017); Alrawadieh et al. (2019); Bashynska et al. (2019); Jafari & Cai (2018); Cherkasov et al. (2017); Dzhandzhugazova et al. (2017); Fedulin et al. (2017); Frolova et al. (2020); Fu et al. (2019); Kosevich et al. (2020); Lin & Cantoni (2018); Markova et al. (2018); Mirzayeva (2018); Nikazachenko et al. (2018); Nikiforov et al. (2018) and others. At the same time, the existence of tourism enterprises is impossible without looking into the future, without strategic planning and management. It should be noted that strategic management is not a closed process. Researchers have found a significant number of factors influencing this process, but most agree that the most impactful factors are those that are related to the factors of the internal environment of the tourism and hospitality enterprise.
Nevertheless, when studying the problems associated with the strategic management of a tourism and hospitality enterprise, researchers pay great attention to external factors, which are almost impossible to control at the level of these enterprises but can only be considered, and out of all the variety of internal factors, the researchers focused on strategic potential. We believe that researchers are overlooking factors, the degree of influence of which on the strategic management of tourism and hospitality enterprises cannot be underestimated. It is these factors that include organizational culture which is the core that determines the state of the internal environment of a tourism and hospitality enterprise (Nikolskaya et al., 2017; Rahimi & Akgunduz, 2017; Seredina et al., 2017).
Methodology
As the main research method, the authors used the abstract-logical method, which was used for the structural justification of the components of organizational culture. The procedure included the formalization of the development strategy of tourism and hospitality enterprises, which made it possible to strengthen and formulate a clear development plan for the development of detailed measures.
As a theoretical subject of the study of the impact of organizational culture on the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises, the analysis was used, which includes the collection and processing of the necessary information? In this case, the uncertainty of the external environment, its constant variability and unpredictability, as well as the specificity of the internal environment, is due to the special importance of the tourist services market for various business structures.
As an empirical direction, the process of developing a strategy for the development of an enterprise in the tourism and hospitality industry was used, which is based on the development of a pilot development strategy, evaluation of the results of strategic development, fully reflecting all aspects of the development of the market of tourist services for various enterprises in modern conditions.
In the course of the study, we plan to highlight and characterize the impact of organizational culture on the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises, determine the formalization of the development strategy of subjects in the industry and formulate a clear development plan within the framework of a new organizational culture.
Results and Discussion
Practice has shown that recently there has been a decline in the number of citizens who visit the Russian Federation for tourism purposes and travel abroad. In the context of the socio-political and, consequently, the economic crisis that the country is experiencing, the already fierce competition between tourism and hospitality enterprises has intensified further. For tourism and hospitality enterprises, the problem of survival is the main one, which causes the need to optimize all business processes and minimize the costs of all business procedures.
The crisis led to a shortage of clients, and one of the survival goals was to retain the client by maintaining the client's loyalty to the tourism and hospitality enterprise. At the same time, tourism and hospitality enterprises, which, due to the established management traditions cannot make price compromises, work for the client's sake, optimize prices, are not viable in the current realities of doing business. At the same time, most of the enterprises of the tourism and hospitality industry work on the trust of consumers and service providers.
Therefore, trust is a state due to which the consumer of tourism and hotel services relies on some opinion that seems reputable. Trust is the expectation that a partner can be relied on for their obligations, predictability of their behavior and good faith in actions and negotiations, even if the partner has the opportunity to behave in bad faith. It is trust that is the lever that ensures the consumer's choice of tourism and hospitality enterprise, as well as tourist and hotel services. The extent to which customers, partners and employees are loyal to the tourism and hospitality enterprise is an indicator of the impact of the organizational culture of a particular enterprise in the industry.
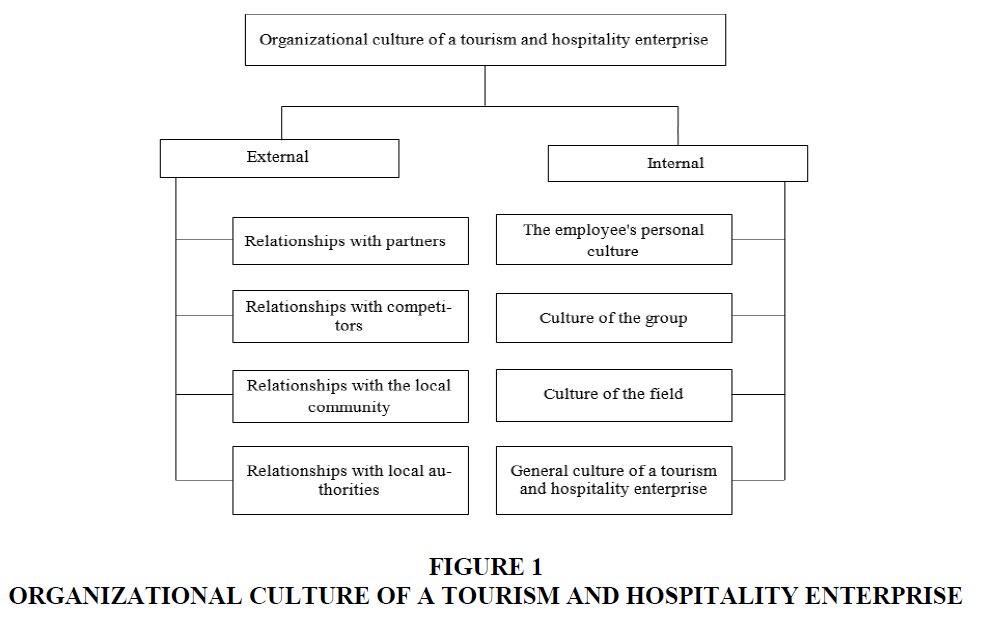
At the same time, organizational culture is a consequence of the correct positioning of business and strategic planning, which were laid down at the stage of founding the tourism and hospitality enterprise and is maintained during its operation. At the same time, the organizational culture of the tourism and hospitality enterprise takes into account the relationship with partners, competitors, as well as the employee's personal culture (Figure 1).
Consciously or chaotically, organizational culture is formed at every tourism and hospitality enterprise and either supports the chosen strategy or, over time, becomes an obstacle to its implementation. Therefore, leading tourism and hospitality enterprises consider organizational culture a key resource for development, a foundation for future achievements and a guarantee of stable dynamic progress towards the implementation of the strategy and achievement of the set organizational goals.
Practice has shown that the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises can have two directions, the first is development as growth (range of goods, services or expansion of the enterprise), and the second direction includes long-term operation in the selected segment of the market with a timely and adequate response to changes concerning the chosen segment – this is how the strategy is chosen by small tourism and hospitality enterprises.
At the same time, factors that introduce an element of uncertainty and affect strategic planning and implementation of decisions can be divided into external and internal. These factors are fully taken into account in most studies; however, the existing approaches that determine the factors of the internal and external environment of a tourism and hospitality enterprise require supplementation, considering the influence of the organizational culture.
Most tourism and hospitality enterprises are just beginning to master the technology of strategic management, therefore, the developed strategic development plans prepared using a significant amount of time and money, as a result, remain unrealized. At the same time, the presence of a strategy does not mean that an enterprise in the tourism and hospitality industry is focused on strategic management and, as a result, development.
In this case, the following negative factors can be identified that reduce the efficiency of strategic management at tourism and hospitality enterprises in the Russian Federation:
- The influence of the bureaucratic system in obtaining permits for the implementation of entrepreneurial activities in the field of tourism and hospitality;
- High interest rates on credit resources required for business activities and short repayment periods for these loans;
- Sale of land for building objects in the tourism sector (hotels, camping sites, restaurants, bars, cafes) at unreasonably high prices;
- Low motivation of entrepreneurs due to frequent changes in tax policy;
- Low professional level of staff in tourist and hotel enterprises;
- Unpredictable policy of the central bank of the Russian federation, currency fluctuations;
- A standard approach to determining interest rates when different entrepreneurs obtain loans;
- Failure to fully use resource-saving technologies when constructing tourist facilities;
- Low purchasing power of the population;
- Tourists' insufficient awareness about cultural values;
- Tourist safety issues;
- Low quality of service at the enterprises of the tourism and hospitality industry;
- Inefficient pricing policy.
The identified negative factors also include inefficiency of existing organizational mechanisms which are timely changed adequately for the chosen strategy; the managers' lack of understanding of the need for changes; low efficiency of tools for monitoring the results of strategic changes occurring at the tourism or hospitality enterprise; the staff's lack of a sense of responsibility for the result of strategic changes, for the achievement of strategic goals, for the constant reproduction of the acquired skills and the preservation of the achieved positions; the inability of staff to develop a new tourist product; the inability of leaders to overcome resistance when introducing changes.
In modern conditions, organizational culture makes it possible to increase the efficiency of a tourism and hospitality enterprise, contributes to the growth of motivation and loyalty of employees, the quality of their working life, and positively affects the establishment of interaction with the external environment (Karaulova et al., 2017; Lebedev et al., 2018; Zhetpisbaeva & Zholzhanova, 2018). In this case, an efficient organizational culture should provide for decentralization, efficient and quick decision-making, and flexible procedures (Table 1).
| Table 1 Features of Organizational Culture in an Efficient Tourism and Hospitality Enterprise | ||
| Type of enterprise | Approaches to management | Organizational culture |
| An efficient tourism and hospitality enterprise | Decentralization Independent and quick decision-making Flexible procedures Focus on value creation Analysis of problems and results |
Confidence Entrepreneurship and calculated risk Extensive exchange and use of information Personal responsibility for the result Free access to the management Versatile and motivated staff Attracting and retaining talent Using skills Coaching and mentoring Search and elimination of losses |
| A traditional tourism and hospitality enterprise | Centralization Slow decision-making Strict formal hierarchy Focus on the result Control over plans and hushing up problems |
Lack of trust Avoiding uncertainty and risk Concealing information Apathy and lack of initiative No education Diffusion of responsibility High distance to power Cost level protection Loyalty to the detriment of talent and professionalism |
Practice has shown that strategic management is such management of a tourism and hospitality enterprise, which relies on human potential as the basis of the organization, focuses service activities on consumer requests, reacts flexibly and makes timely changes that respond to the environment and allowing to achieve competitive advantages, which together enable the tourism and hospitality enterprise to survive in the long term while achieving its goals (Hasaballah et al., 2019; Konovalova et al., 2020; Zavalko et al., 2017).
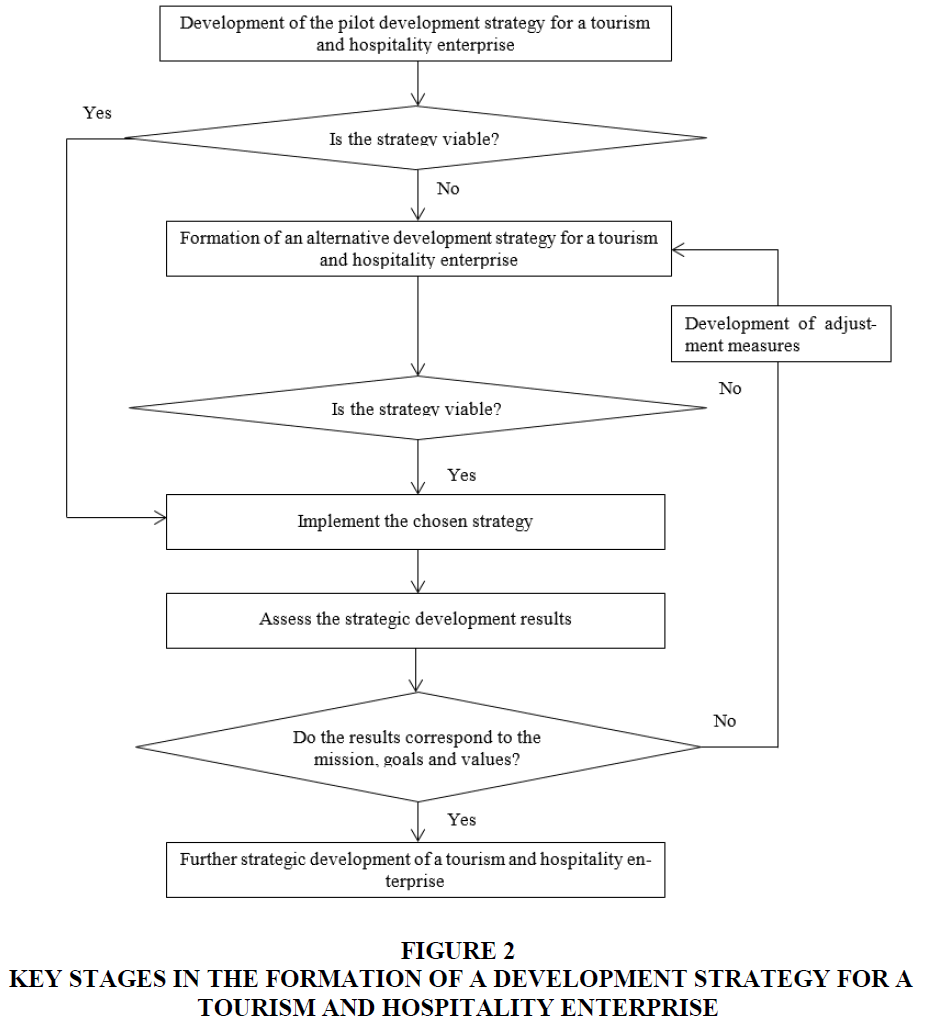
One can also note that the strategy makes it possible to ensure efficient motivation, control and accounting for compliance with the standard of the tourism and hospitality enterprise, which determines its development and performance. In this case, the algorithm for developing an enterprise management strategy for the tourism and hospitality industry is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Key Stages in the Formation of a Development Strategy for a Tourism and Hospitality Enterprise
Therefore, after examining the enlarged stages of the process of developing and implementing the management strategy, it can be noted that the implementation of almost all the stages of the process under consideration depends on the strength of the organizational culture and its characteristic features. However, the assessment of the role of organizational culture in achieving the strategic goals set by the tourism and hospitality enterprise remains a rather difficult task. To solve this problem, one must study the culture of a tourist enterprise through the prism of implementing the key functions: increasing the efficiency of activities, consolidation and improving the quality of employees' working lives, creating a positive image and increasing the market value of a tourism and hospitality enterprise.
In this case, the organizational culture can be considered efficient when the specified functions are implemented. In the case of enterprises in the tourism and hospitality industry, we will use a methodological approach, which is based on studying the trend of economic indicators for the implementation of each of the proposed functions to prove the feasibility of forming and developing culture and to assess its efficiency.
The practice of enterprises in the tourism and hospitality industry has proven that the formation and development of an efficient organizational culture support the implementation of the strategy and contributes to the achievement of success in the long term. An analysis of the websites of leading tourism and hospitality enterprises in the Russian Federation showed that not only the staff of these enterprises demonstrate impressive stereotypical loyalty, but also service consumers show absolute loyalty instead of hidden loyalty which is more common among tourism service consumers.
All this testifies to the attractiveness of the strategic values in the cultures of these enterprises to society, namely, to employees, consumers, business partners, government and public organizations. We believe that an efficient organizational culture makes it possible to neutralize the effect of the human factor which can manifest in mistakes in strategic and managerial decisions. Furthermore, organizational culture, on the one hand, allows one to preserve and transfer knowledge about business processes to new employees, and, on the other hand, forms consumer loyalty at the level of trust in the tourism and hospitality enterprise, which is manifested in the willingness to forgive minor shortcomings in the service organization.
It is the basic values and principles that allowed the leading enterprises of the tourism and hospitality industry to attract qualified staff, form a system of relationships within the enterprise, and also establish efficient interaction with the constantly changing external environment. It is an efficient organizational culture that promoted the development of tourism and hospitality enterprises and positioned them as reliable counterparties, forming a positive attitude towards them from society and government agencies.
Leading tourism and hospitality enterprises constantly demonstrate that organizational culture is a fairly efficient argument in the competition. Organizational culture determines the management style, behavior with the client, the expected consequences of certain actions, social relations, and the quality of services. Moreover, recently, society is increasingly demanding tourism and hospitality enterprises to respect universal human values.
In this case, most tourism and hospitality enterprises prioritize meeting the needs of their customers but the desire for innovation and development at the level of goals is voiced by only a few enterprises (ICS Travel Group, Intourist, Anex Tour). Also, most enterprises mention conscious humanity (for example, TUI, Coral Travel, Tez Tour, Pegas Touristik, etc.), associating long-term success in the tourism market with this value.
Almost all surveyed tourism and hospitality enterprises industry also position themselves as responsible corporate participants. This is primarily because tourism and hospitality enterprises, working in a certain territory, knowingly or unwittingly harm communities. The harm can be manifested in upsetting the ecological balance in the country or paving the way for a conflict of cultures. Therefore, enterprises, for their own reasons, focus on what the community and consumers can get from their activities in a given area.
This approach relieves the tension in relation to the perception of the tourism and hospitality enterprise on a particular territory, improves the image and, as a result, has a positive effect on the economic results. The missions of such enterprises as Coral Travel, TUI, Tez Tour, Pegas Touristik, ICS Travel Group and Intourist quite specifically describe their orientation towards cooperation with communities to improve the citizens' quality of life.
Moreover, all of the above enterprises are a fusion of bureaucratic and informal cultures. This happened because the goal of culture is not only to fulfill the aforementioned functions but also to contribute to the improvement of business operations. All the considered enterprises are transnational and in various areas of work support the development of the most efficient model of cultures in terms of the implemented development strategies.
Conclusion
All in all, it can be noted that organizational culture plays a key role in the strategic development of tourism and hospitality enterprises. Organizational culture is the lever that ensures the long-term success of a tourism and hospitality enterprise rather than immediate achievements. That is why, in the process of strategic development management in the tourism and hospitality industry, staff need to timely and appropriately respond to changes in the external environment (seasonal and fashion-related fluctuations in demand, legislative changes, national currency fluctuations). These issues are supposed to be alleviated by the organizational culture which will not be perfunctory but rather will have actual leverage over the development and competitiveness of a tourism and hospitality enterprise.
Moreover, efficient organizational culture is a significant internal resource for the development of a tourism and hospitality enterprise. Understanding the features of the organizational culture of successful tourism and hospitality enterprises allows one to adopt and reinterpret their experience as well as forecast, prevent and constructively solve organizational contradictions at different management levels at the early stages of strategic development.
It is worth noting that the imperatives of forming organizational culture remain hardly explored, and research remains at the periphery of the interest of economics. However, despite the publications that examine the formation and development of organizational culture, until now there have been no works that presented reliable and efficient methods of assessing the impact of organizational culture on economic indicators of tourism and hospitality enterprises or analyzed the features of transformations in the organizational culture under external influence.
References
- Agamirova, E.V., Agamirova, E.V., Lebedeva, O.Y., Lebedev, K.A.E., & Ilkevich, S.V. (2017). Methodology of estimation of quality of tourist product. Calitatea, 18(157), 82-84.
- Alrawadieh, Z., Karayilan, E., & Cetin, G. (2019). Understanding the challenges of refugee entrepreneurship in tourism and hospitality. The Service Industries Journal, 39(9-10), 717-740.
- Bashynska, I., Lytovchenko, I., & Kharenko, D. (2019). Sales tunnels in messengers as new technologies for effective Internet-marketing in tourism and hospitality. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(12), 594-598.
- Cherkasov, I.L., Seredina, M.I., Mishurov, O.I., Adashova, T.A., & Lebedeva, O.Y. (2017). The effect of international tourism on the development of global social-economic processes. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 8(6 (22)), 1166-1170.
- Dzhandzhugazova, E.A., Blinova, E.A., Orlova, L.N., & Romanova, M.M. (2017). Intellectual resources used in developing tourism and hospitality industry. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 12(5b), 705-722.
- Fedulin, A.A., Zgonnik, L.V., Lebedeva, O.Y., Dukhovnaya, L.L., & Ilkevich, S.V. (2017). Methodological approaches to the assessment of historical and cultural resources in tourist destinations. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 8(6 (22)), 1198-1204.
- Frolova, E.V., Kabanova, E.E., Rogach, O.V., Vetrova, E.A., & Ryabova, T.M. (2020). A spotlight on Russian tourism and hospitality industry. International Transaction Journal of Engineering, Management and Applied Sciences and Technologies, 11(4), 1104.
- Fu, H., Okumus, F., Wu, K., & Köseoglu, M.A. (2019). The entrepreneurship research in hospitality and tourism. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 78, 1-12.
- Hasaballah, A.S., Zenad, Y.S., & Shlaka, J.K. (2019). The role of fundamental analysis in determining the market value of hospitality, tourism and companies’ shares. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 8(4).
- Jafari, J., & Cai, L.A. (2018). Quality services and experiences in hospitality and tourism. Bridging Tourism Theory and Practice, 9, 301-306.
- Karaulova, N.M., Silicheva, L.V., Antonenko, V.V., Konovalova, E.E., & Lebedev, K.A. (2017). Methodical approaches to forecasting tourist streams. Revista Espacios, 38(48).
- Konovalova, E.E., Shelygov, A.V., Artamonova, L.S., Dolina, O.N., & Boikov, A.I. (2020). Development of Forms of the Hotel Business Organization in Modern Conditions. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 11(4 (44)), 857-862.
- Kosevich, A.V., Novikova, N.G., Gladkikh, V. I., Sharonin, P.N., & Smirnov, M.A. (2020). Improving Economic and Legal Regulation in the Tourism Sector. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 11(4 (44)), 979-984.
- Lebedev, K.A.E., Reznikova, O.S., Dimitrieva, S.D., & Ametova, E.I. (2018). Methodological approaches to assessing the efficiency of personnel management in companies. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 9(4(34)), 1331-1336.
- Lin, J., & Cantoni, L. (2018). Decision, implementation, and confirmation: Experiences of instructors behind tourism and hospitality MOOCs. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 19(1), 291-293.
- Markova, O.V., Zavalko, N.A., Kozhina, V.O., Panina, O.V., & Lebedeva, O.Y. (2018). Enhancing the quality of risk management in a company. Espacios, 39(48), 25.
- Mirzayeva, A. (2018). E-tourism and social media in tourism and hospitality. International Journal of Humanities and Natural Sciences, 11-3, 36-45.
- Nikazachenko, A.L., Yudashkina, E.E.E., Vlasov, G.V., Novikova, V.V.E., & Lebedev, K.A.E. (2018). Modern approaches to assess tourism industry-related environment. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 9(2 (26)), 298-303.
- Nikiforov, A.I., Ryazanova, N. Y., Shishanova, E.I., Lyzhin, D.N., & Lebedeva, O.Y. (2018). Economic and legal support for the use of coastal territories in a tourism-recreation sector. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 9(13), 1048-1054.
- Nikolskaya, E.Y., Pasko, O.V., Volkova, I.A., Dekhtyar, G.M., & Lebedeva, O.Y. (2017). Boosting the competitiveness of hotel business operators in current conditions. Journal of Environmental Management & Tourism, 8(8 (24)), 1617-1622.
- Rahimi, R., & Akgunduz, Y. (2017). Driving force analysis of East European students to study tourism and hospitality in the UK. Anatolia, 28(2), 224-238.
- Seredina, M.I., Tretjakova, G.V., Oberemko, T.V., Kozhina, V.O., & Lebedev, K.A. (2017). Impact of external labor migration on labor market development. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 8(2), 596-600.
- Zavalko, N.A., Panina, O.V., Kovalev, V.A., Zhakevich, A.G., & Lebedev, K.A.E. (2017). Improving financial control over the government system. Espacios, 38(29), 15-22.
- Zhetpisbaeva, A.T., & Zholzhanova, N.T. (2018). The impact of innovation on the competitiveness of enterprises of tourism and hospitality industry. Colloquium Journal, 5-6(16), 29-30.