Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
The Role of Ambidextrous Leadership Behaviors in Enhancing Organizational Reputation- Exploratory Research in the General Company for the Distribution of Oil Products in Baghdad
Muthana M. Saeed, University of Fallujah
Mohammed Q. Hamid, University of Anbar
Mahmood J. Awad, University of Fallujah
Abstract
This research aims to verify the extent of the correlation and influence relationship between ambidextrous leadership behaviors (as an explanatory variable) and the organizational reputation of organization (as a responsive variable). The researchers have adopted in finalizing their research on the descriptive and analytical approach. The applicability of this research has been executed in the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products in Baghdad. The study has chosen a random sample consisting of (70) members of its community of (79) individuals by relying on a as a basic tool in collecting the data that was processed and analyzed using the statistical program (spss) using a set of statistical methods (such as the arithmetic mean, standard deviation, correlation coefficient, coefficient of variation, relative importance and regression analysis). The research has reached a set of results; the most important of which is the existence of a direct positive correlation with a moral significance between ambidextrous leadership and organizational reputation, This means that the company's leaders work properly and to take the advantage of their leadership skills that they own in strengthening the organizational reputation of their organization in order to innovate and develop services which will reflect positively on the reputation of their organization, the research has come up with a set of recommendations, notably the need to manage the company to take advantage of leadership skills possessed by the company's leaders in order to enhance its reputation and organizational contributing to the role of strengthening the company's position at the local level due to their ability and and familiarity with the study of the environment and organizational knowledge of the strengths and weaknesses experienced by their organization as well as for their important role in improving their products by their ability to invest the capabilities and capabilities of employees within the company.
Keywords
Ambidextrous Leadership, Oil Products, Baghdad
Introduction
The recent development of leadership theories is due to a prevalent interest in the positive model leading by writers and researcher. Being the best style for the implementation of leadership behaviors that come in line with contemporary organizations management requirements in the absence of a leadership style can be generalized to represent all organizations because of the complexity of the environment and the uncertainty experienced by organizations. Hence the need for today's organizations to find a leadership pattern that has a sufficient amount of behavioral and cognitive complexity that enables it to implement its multiple roles simultaneously to enhance the reputation of the organization, which is considered today a controversial topic in both the domains of academia and administration. As the growing sophistication of the stakeholders and the environment resulted in a serious competition and the growing demand for transparency organizations and social responsibility to increase attention to the reputation of the organization with the new challenges of the twenty first century and the twenty-represented not only the attention it is virtual and intuitively by its leaders, but has become the issue has been taken into account by all dealers with organizations, and the rapid collapse of some organizations today only as a result of the loss of confidence by clients and thus become part of the past.
In the academic world, the reputation of the organization is an important concept, and for its importance, comprehensive and in-depth research has been conducted on the theoretical and experimental levels. As it must be recognized that despite the global recognition of the importance of the organization's reputation and its considerable ability to influence the success or failure of its strategy, However, the organization's reputation in the area of research is still lacking a deeper perception of investigation because of the fragmented and lack of a multidisciplinary approach built how they work.
Hence the idea of research has been crystalized, trying to shed light on the study of the role of the ambidextrous leadership that make up the modern trend of the management of public organizations in strengthening the organizational reputation. it has chosen the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products in Baghdad, being one of the important organizations in Iraq, which is directly in contact with the citizen through the products offered by companies for electric power generation and other products offered directly to the citizen.
The Methodological Framework for Research
Research Problem
The contemporary business environment, large and rapid changes imposed great pressure on organizations of different types in their quest to enhance their competitiveness and the continued survival and growth in the long term. These circumstances made the Oil Products Distribution Company in Baghdad as one of these organizations, are not far away from such pressures. As it made it suffer from a state of contradiction, some dating back to the need for these companies to practice their traditional activities as well as its desire to explore new opportunities that allow them to excellence and expansion of a local company with the biggest potential company able to overcome the country's borders and the trend towards global marketing. However, the harsh conditions that Iraq is experiencing and the disruption operations to which the company's production and distribution lines are exposed, have made difficult choices trying to overcome in order to maintain its reputation as a well-established company that provides its services on a daily basis to all citizens.
The basis for the question that arises here is about what kind of leadership can deal with these two types of opposing activities..? And what kind of behaviors that must be shown by the leaders to promote creative behavior of employees in the company in order to keep its reputation in a particular position? Hence, the problem of the study is exemplified in the following questions:
1. The fact that the role of the ambidextrous leadership in the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products, and is able to manage the controls of the organization right direction, despite all the obstacles and circumstances provoked?
2. Can the leaders of the distribution of the company's oil products in question to maintain the status of their organization in the country's current conditions of intense competition exercised by some companies of neighbouring countries that entered the on line under the pretext of support the shortfall in the production and distribution of oil produced in Iraq.
3. What is the level of perceived Organizational reputation enhancement in the State Company for Petroleum Products Distribution under consideration?
The Research Significance
The practical importance of research lies in raising the public interest in the company for the distribution of petroleum products and its leaders and its members attitude leadership ambidextrous which represents present intangible assets as well as the importance of the Organizational reputation of the company the importance of research can be summarized as follows:
1. Introducing the General Company for Oil Products Distribution with the latest developments in management thought in the field of ambidextrous leadership behaviors and organizational reputation.
2. Helping the leaders of the organization in question to identify the most important leadership characteristics to be used in order to enhance the prestige and reputation of their organization in the long run.
3. Identifying the level of availability of the dimensions of the process of leadership ambidextrous observed in the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products.
4. Enriching the managerial thought with a set of ideas related to the themes of ambidextrous leadership and organizational reputation, as well as the benefit provided to students later.
Research Objectives
The research seeks generally to achieve a set of the most important aims:
1. A statement on whether there is a correlation and impact relationship between the ambidextrous leadership in its dimensions and the organizational reputation within the researched company.
2. Determine the relationship between the ambidextrous leadership in strengthening the organizational reputation perceived in the public company for the distribution of petroleum products.
3. The current research seeks to expose what are the strengths and weaknesses of the ambidextrous leadership behaviors and ambidextrous organizational in the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products, as well as marking the necessary means to address and strengthen each of them.
4. To provide a set of recommendations for the management of the General Company for the distribution of petroleum products to enhance organizational reputation and leadership ambidextrous.
Hypotheses
The research hypotheses as to draw a practical idea of what might be reached by the research, as it is the first opinion to solve its problem, and adopted the research hypotheses represented its boss what it aims to reach, and formulated as follows:
1. The first major hypothesis: There is a correlation between leadership behaviors ambidextrous dimensions (open leadership and leadership closed) positively correlated with a statistically significant indication of the organizational reputation dimensions.
2. The second main hypothesis: There is an influence relationship between ambidextrous leadership behaviors in its dimensions (open leadership and closed leadership) with a positive, statistically significant effect on organizational reputation in its dimensions.
The Scheme for Research
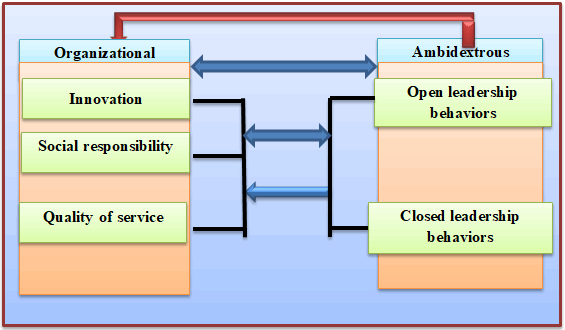
The scheme accounted for researching a picture expressed by a range of logical relations, and in terms of this, a scheme included in all major and sub-relations, which represent the research problem and objectives expected to be achieved and according to the following variables:
1. Independent variable (Independent Variable): Increased behavior of ambidextrous leadership, which includes dimensions (open leadership and closed leadership), depending on the study of (Voigt 2014).
2. Certified variable (dependent variable): The Organizational reputation, which includes dimensions (creativity, social responsibility, quality of service) is based on the study (Šontait & Kristensen, 2009).
Research Method
The researchers adopted an analytical descriptive curriculum in achieving their research aims. The description is used to collect data and information required by the study and analysis for the purpose of determining the results and diagnosis of the leading indicators and then determining the characteristics of the phenomenon as well as the quality of the relationship between its variables and factors.
Participants
Every research is a genuine society and basic components that are clearly and accurate by researchers. The current research community has included the General Company for the distribution of oil products - Baghdad, which is from (83) people, such as higher and central leaders in the company's organizational pyramid. The researchers distributed (83) questionnaires to the research individuals in a random way, and (79) of them were retrieved, while (9) of them were invalid for statistical analysis, so that the total of the remaining (70) questionnaires valid for statistical analysis represented the research sample.
Research Limits
- Spatial boundaries: The spatial boundaries were given for research by the General Company for the Distribution of Petroleum Products in Baghdad, represented by the senior and middle leaders in the company's organizational hierarchy.
- Temporal limits: covered the temporal limits of research in the year 2020/2021.
Theoretical Framework
Ambidextrous Leadership
The Concept of Dexterity Ambidextrous Leadership
Today, ambidextrous leadership is one of the important terms in management science in general. This type of leadership is due to the increasing complexity, which accompanied the strategies used in organizations. The need for leaders today called for adequate behavioral and cognitive complications that enable them to exercise several roles at the same time. This pattern is "Ambidextrous Leadership" and its first model was developed by the worlds (Vera & Crossan, 2004; AL-Eida, 2020). Before addressing the concept of leadership, we have to show the general concept of dexterity, when using the term " ambidextrous " for the first time by (Duncan: 1976) in his research paper, Organization ambidextrous: Design of dual structures for innovation, He pointed to the stages of innovation to be identified and implemented, the Organization's structures are different and require distinctive degrees of complexity (2013: 43 Pearce). And ambidextrous was defined by Ahsan, et al., (2020) as “the ability of a person to use both hands easily.” As for administrative ambidextrous, it was defined by (Dwidienawati et al., 2020) as “the ability to find a balance between the organizational and exploratory strategies of the organization”. The concept of ambidextrous leadership was defined by (Rosing et al., 2010) as the ability to "enhance exploration by opening behaviors and exploitation by closing behaviors and flexibly switching between these behaviors according to the requirements of the position and the task". Denis (2007) defines ambidextrous leadership as "the ability of the individual (leader) to distribute their interests, resources and time simultaneously and with equal skill for both expansion and exploration activities for the purpose of overcoming the paradoxical tensions of learning and achieving success at work" (Abdelkrim, 2015). Ambidextrous leadership is defined as "the leader's ability to employ open and closed behaviors to enhance the organization's investment and exploration activities, enhancing its efficiency and effectiveness in achieving the desired aims" (Mezher, 2017). In addition, we can define ambidextrous dexterous leadership as "the ability of a leader to adapt and find a balance between changes within and around the organization and the leadership methods that must be followed to cope with these changes". The main idea of ambidextrous leadership is that the complexity of innovation activities within organizations must be matched by an equally complex leadership pattern (Zacher & Rosing, 2015). In other words, ambidextrous leadership is a more complex leadership style that tries to keep the organization in a state of permanent stability despite the rapid and successive changes that occur in the organization and the leadership styles used to counter this change. While exploratory innovation attempts to create new knowledge for the organization and expand its existing knowledge base, exploitative innovation seeks to develop and control existing knowledge (Wang et al., 2020). This requires ambidextrous leaders to be able to support both exploration and exploitation activities in their employees ' behaviors and to demonstrate these behaviors in time to support the organization's long-term work (Wen et al., 2020). ambidextrous leaders are important for the ability to continuously change between the more open leader behaviors that help independence and tolerance and the more closed leader's behaviors by setting specific aims and strict guidelines that are followed up by monitoring the progress of the organization's work and taking any corrective action if necessary (Cunha, 2019).
Objectives of Ambidextrous Leadership
Introduced the concept of ambidextrous leadership for the first time in the field of management science to describe the ability of organizations to run business efficiently and effectively as well as its ability to accommodate future changes in the organization (Wu et al., 2020). Ambidextrous leadership as a leadership aims to strengthen and develop relationships between the leader and members of the organization in order to help them solve complex management problems (Guo et al., 2020). It is working to help leaders to provide support to their followers in an attempt to make them proficient in the field of work (Rosing et al., 2011). Ambidextrous leadership also aims to promote innovation behaviors among employees as well as reducing the contrast or increase depending on the situation experienced by the organization by showing leadership behaviors opening and closing and switch between them flexibly (Oluwafemi, 2020). It also shows (Seetge, 2012) that ambidextrous leadership aims to enhance creativity within organizations, with its two types, exploratory and exploitative, so that leaders can practice different work patterns according to the circumstances experienced by their organizations. For our part, we believe that ambidextrous leadership aims to enhance the skills of the leader and his ability to deal with the changes that his organization is exposed to, which helps him to find better alternatives for the work of the organization.
Dimensions of Ambidextrous Leadership Behaviors
Behaviors of Open Leadership
A leader’s introductory leadership behavior can be defined as “a set of skills that a leader uses for the purpose of encouraging employees to work and try new things, allowing them to think independently, and providing them with support for challenging tiring methods and procedures at work” (Alkhawaldeh, 2020). As it shows (Coleman, 2016) that the driving behavior of open leaders used for the purpose of helping employees to work and the use of methods, tasks and diverse ideas and give them ample space for independent thinking and provide them with support and follow-up work on ways to do business. Behaviors leadership openness encourages exploration with the use of the style of open work within the organization i.e., they ask staff to think diverse and work on the experience of different ideas, and that leaders who demonstrate the behavior of openness in the implementation of the organization works allow their employees using work methods of varying (Strobl, 2019: 20). It's a clever approach followed by the leaders to give staff a great deal of freedom which helps them to integrate the Organization's work faster as well as mentally, brought to reveal the creative ideas they hold.
Closed Leadership Behaviors
Closed leadership behavior is defined as the behavior followed by the leader to limit the varying behaviors of subordinates by setting specific instructions, taking corrective actions and monitoring the achievement of the organization's aims (Alghamdi, 2018). “Lockdown” indicates that leaders tend to use activities that reduce change in the organization and work to establish pre-determined timelines, principles, and aims for the purpose of accomplishing them, i.e., they only allow to have things done with a specific goal in mind that is under their control (Hafeez, 2019). Also, (Rosing et al., 2011; Coleman, 2016) show that closed leadership behaviors are used by organizational leaders in order to ensure that employees in organizations carry out the tasks entrusted to them correctly because the process of implementing them will be accompanied by the presence of Guidelines as well as taking corrective measures in the event of a deviation. Closed leadership behaviors are closer to the internal instructions specified in the organizational structure of the organization, which the leaders of the organization work to bring to the lower levels, and the employees must abide by them.
Organizational Reputation
The Concept of Organizational Reputation
The concept of the reputation of the organization dates back to the year (1997) when it was established reputation (RI) and academic journal "Review of the reputation of the organizations" devoted to this subject only, and is considered (van Riel), as a key scientists and most influential in this topic (Šontait? & Kristensen, 2009). As issues focused on the ongoing research within the literature of the reputation of organizations on the definition of building reputation and what way is activated and how in turn contribute to the success of the organization (Inglis & Sammut, 2006). The organization's reputation also has become today the subject is important in academic circles and the business world, and despite the global recognition of the importance of the reputation of the organization as an asset strategic and large potential impact on the success of the organization's strategy, the reputation still lacks the deeper concepts (Adeosun & Ganiyu, 2013). Organizational reputation has been defined by (Ewing & Newton, 2010) as "the collective judgments of observers of an organization based on assessments of the financial, social, and environmental impacts attributed to the organization over time". He also defined it (Bartikowski & Walsh, 2011) as a temporal accumulation of the results achieved by the organization in the internal and external environment in a way that achieves loyalty and belonging by its customers. For our part, we believe that the organizational reputation is "a state of mind and morale that the organization reaches as a result of the good results it achieved in providing services to its clients during a previous period". Nowadays, reputation is the most valuable and decisive factor for the competitive advantage of organizations because there is evidence that the good reputation of the organization is associated with various tangible and intangible interests, well-known organizations scandals that dominate the media and a decline in public opinion among organizations, the reputation of the organization has also become a reality in the past few years (Beheshtifar & Korouki, 2013). Organizational reputation is an overall assessment of the organization that is socially transferable and reconciled among stakeholders over a long period of time representing an expectation of the organization’s business and its level of trustworthiness, validity and recognition compared to its competitors (Smaiziene & Jucevicius, 2009). It Shows (Bass, 2018) that the regulatory reputation today is one of intangible assets owned by organizations that allow them to expectations and needs of different organizations better manage stakeholders as well as creating differentiation and barriers to competitors.
The Importance of Organizational Reputation
The concept of organizational reputation plays an important role for organizations today as is a simple, attractive intuitive idea, that an idea of simplicity is that after a period of time organization can become well known in the minds of clients, which does not allow them to be judged either positively as good or it is not good (Lange, 2011). Considering the organizational reputation of the most important strategic assets intangible that can be owned by the Organization which must constantly strive to build them in a manner commensurate with the nature of the internal and external environment, they are one of the most important measures of success for attracting customers by creating an impression of my mind is good to it, and therefore the main source of excellence Which supports the services provided by the organization and distinguishes it from its competitors (Keshta et al., 2020). A good reputation is an effective tool for organizations to achieve their strategic aims of creating value, increasing growth and profitability, and achieving a sustainable competitive advantage that contributes to their overall survival. It is believed (Smaiziene & Jucevicius, 2010) as the positive reputation brings the organization a range of benefits: including the possibility of achieving distinctive profits and attract new customers and give the product or service extra value as well as increased employee satisfaction and loyalty to the organization in which they work and easy access to the best professionals, such as service providers premium advertising agencies, And enhancing the strength of the organization in attracting new business partners and investors and improve the Organization's relationship with suppliers, distributors and direct stakeholders. He adds (Testa, 2008) that one of the benefits and advantages of organizational reputation are: Attracting and retaining qualified human competencies to work in the organization. In addition, it serves as a barrier to entry for new potential competitors.
The Dimensions of Organizational Reputation
The topic of determining the dimensions of the organization's reputation has received great attention due to the recognition of its importance in academic literature and business, In addition, it was found that most writers and researchers varied their opinions in determining the main dimensions of the reputation of the organization, namely (Innovation, social responsibility, quality of service), these dimensions were chosen for the agreement of most writers and researchers on them and because they are consistent with the nature and objectives of the research, namely:
Innovation
Innovation is essential for organizations as it is concerned with the production of creative and useful ideas, products, procedures and administrative practices, Individuals must be more creative when faced with a high level of self-motivation, i.e., they must be enthusiastic and interested in participating in the work activity. It is expected that conditions and practices affect contextual creativity through their effects on intrinsic motivation, and this means that the conditions that foster internal motivation must promote creativity (Zhou & Oldham, 2001). Innovation means “coming up with new ideas, reconstituting existing knowledge, or finding new entrances to solve specific problems "(Al-Shama, 2007). Creativity, innovation and development have become critical for organizations seeking strategic competition in the new global economy-oriented business environment (knowledge economy), Innovation has therefore become important for organizations in all their directions, and even the basis for distinguishing their goods and services (Keshta et al., 2020). Individuals can access new perspectives and ideas and develop creative outcomes by connecting with others. Some researchers perceive Innovation as a social process in social networks, and consider the social aspect of creativity as an essential part of these processes (Chae, 2016). In order to enhance Innovation, employees need to participate not only in behaviors that help them to generate ideas but also in behaviors that can be used to convince others drawing their ideas and presenting them as Innovation and support for its implementation (Gupta & Singh, 2015).
Social Responsibility
The concept of social responsibility of organizations nowadays shows that organizations voluntarily incorporate social and environmental concerns into their operations and interaction with stakeholders, it involves the application of the concept of sustainable development through which organizations that respect and listen to stakeholders should naturally be concerned about their growth and profitability (Kumar, 2019). The European Commission defines the social responsibility of organizations as "the responsibility of organizations for their effects on society and determines what the organization must do to meet that responsibility", and this concept shows that the social responsibility of organizations is the way in which the organization strikes a balance between economic, environmental and social imperatives, i.e., it is the process of assessing the impact of the organization on society and CSR has long been a strategic concern for organizations worldwide in response to interest from both consumers and investors and commentary on significant stakeholder pressure to adopt CSR policies (Albuquerque et al., 2019). A properly implemented CSR concept can deliver a variety of competitive advantages, such as enhanced access to capital and markets, increased sales and profits, savings in operational costs, improved productivity, quality and human resource base efficiency, improved brand image and reputation, enhanced customer loyalty, better decision making and risk management processes (Sarkar, 2019).
Service Quality
Over the past few decades, quality of service has become one of the main areas of concern for practitioners, managers and researchers due to its strong impact on business, performance, low costs and customer satisfaction as well as customer loyalty and profitability (Seth, 2005). Definition of quality of service is as the degree and direction of contradiction between consumer perceptions and expectations. As part of the perception, expectations are perceived as wishes or wishes of consumers (Camilleri, 2021). In the same regard, the quality of service includes three important dimensions of service operations, personal factors, physical evidence. It also defines service quality as “a procedure or activity that can be provided by one party to another party”. It is basically intangible and cannot affect any property. The service may be related to a tangible product or an intangible product. On the one hand (Alamgir & Shamsuddoha, 2004). The quality of service within organizations is a concern for diverse sect oral actors around the world because the service cannot be touched or seen as with products, the quality of service to be provided is not expressed by concrete measures or weights, but the quality of service provided is expressed by customer satisfaction (Magembe & Njuguna, 2019). It is determined by directing customer management and quality of service in general as one of the most effective means (albeit difficult) to build a competitive position in the service industry and improve organizational performance (Ennew & Binks, 1996).
The Practical Aspect
Presentation and Analysis of the Dimensions of Ambidextrous Leadership
Analysis of the vertebrae after (obvious ambidextrous leadership)
It is clear from the data in Table (1) that the total score of the sample answers for the paragraphs related to the dimension of (open-minded leadership) came with a high value Its mean was (3.90), standard deviation (0.68), and coefficient of difference (17.55) The highest answer came to Paragraph No. (1), which states (it is allowed to adopt a variety of methods to accomplish work in the company), where the arithmetic mean reached (4.04), which is higher than the hypothetical mean (3), which is a value around a very high, while the standard deviation is (0.60), and this indicates. The answers to the sample were different. While the coefficient of variation for this dimension was (14.85). Paragraph (11) came in the last place of importance on the level of this dimension, which states (it encourages subordinates in the company to take risks). The arithmetic mean reached (3.72), which is a high value. This is due to the fact that the company has the ability to encourage employees to take risks in an environment to ensure, but not in a way that enables them to face the challenges they face in the external environment, As for the standard deviation for this paragraph, it was (0.75), which is a homogeneous ratio to a species. As for the coefficient of variation, it reached (20.38).
| Table 1 Percentages, Frequency Rate, Mean, Standard Deviation, And Coefficient Of Variation for the Open-Attractive Driving Dimension |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Totally agree | Agreed | Neutral | I do not agree | I don't totally agree | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Coefficient of difference | ||||||
| Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | |||||
| Ambidextrous leadership open | 1 | 13 | 18.6 | 48 | 68.6 | 8 | 11.4 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 4.04 | 0.6 | 14.85 |
| 2 | 9 | 12.9 | 50 | 71.4 | 11 | 15.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.97 | 0.54 | 13.54 | |
| 3 | 13 | 18.6 | 45 | 64.3 | 10 | 14.3 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.99 | 0.67 | 16.81 | |
| 4 | 9 | 12.9 | 48 | 68.6 | 12 | 17.1 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.93 | 0.59 | 15.21 | |
| 5 | 11 | 15.7 | 42 | 60 | 17 | 24.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.91 | 0.63 | 15.21 | |
| 6 | 13 | 18.6 | 43 | 61.4 | 14 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.98 | 0.62 | 15.69 | |
| 7 | 15 | 21.4 | 38 | 54.3 | 17 | 24.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.97 | 0.68 | 17.13 | |
| 8 | 16 | 22.9 | 38 | 54.3 | 14 | 20 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.97 | 0.74 | 18.67 | |
| 9 | 12 | 17.1 | 38 | 54.3 | 15 | 21.4 | 5 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 3.81 | 0.8 | 21.07 | |
| 10 | 11 | 15.7 | 41 | 58.6 | 15 | 21.4 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.85 | 0.72 | 18.87 | |
| 11 | 9 | 12.9 | 37 | 52.9 | 20 | 28.6 | 4 | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.72 | 0.75 | 20.38 | |
| 12 | 10 | 14.3 | 35 | 50 | 19 | 27.1 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.7 | 0.82 | 22.23 | |
| The total to open after the ambidextrous leadership | 3.9 | 0.68 | 17.55 | |||||||||||
Analysis of paragraphs after (the ambidextrous leadership closed)
It is clear from the data in Table (2) that the total score of the sample answers to the paragraphs related to the (closed ambidextrous leadership) dimension came with a high value. Where its arithmetic mean is (3.81), standard deviation (0.77), and coefficient of difference (20.86), the highest answer came to Paragraph No. (18) Which states (works to monitor the implementation of the company's aims), where the arithmetic means reached (3.85) and is higher than the hypothetical mean (3). This is due to the fact that the company has a clear interest in monitoring the implementation of its own aims in a way that enables it to proactively take the necessary correction. The standard deviation of it is (0.68), and this indicates that the answers of the sample were homogeneous to some extent, while the coefficient of variation for this dimension was (17.81). Paragraph (17) ranked last in importance on the level of this dimension, which states (exerting pressure on workers to complete work within the specified period. The arithmetic mean was (3.54), which is a high value. This indicates that the administration has strict methods that it uses to pressure workers to complete their work on time while the standard deviation for this paragraph is (0.86), which is a somewhat homogeneous percentage, as for its coefficient of variation, it reached (24.35).
| Table 2 Percentage Rate Frequencies, The Arithmetic Average, Standard Deviation and Coefficient of Variation of Leadership Ambidextrous The Closed Adept |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Totally agree | Agreed | Neutral | I do not agree | I don't totally agree | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Coefficient of difference | ||||||
| Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | |||||
| Ambidextrous leadership open | 1 | 11 | 15.7 | 39 | 55.7 | 16 | 22.9 | 4 | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.81 | 0.76 | 20.10 |
| 2 | 10 | 14.3 | 36 | 51.4 | 16 | 22.9 | 8 | 11.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.68 | 0.86 | 23.34 | |
| 3 | 9 | 12.9 | 38 | 54.3 | 12 | 17.1 | 11 | 15.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.64 | 0.90 | 24.74 | |
| 4 | 9 | 12.9 | 39 | 55.7 | 12 | 17.1 | 10 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.67 | 0.88 | 23.97 | |
| 5 | 8 | 11.4 | 31 | 44.3 | 22 | 31.4 | 9 | 12.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.54 | 0.86 | 24.35 | |
| 6 | 9 | 12.9 | 45 | 64.3 | 13 | 18.6 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.85 | 0.68 | 17.81 | |
| 7 | 7 | 10.0 | 38 | 54.3 | 23 | 32.9 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.71 | 0.68 | 18.41 | |
| 8 | 6 | 8.6 | 41 | 58.6 | 21 | 30.0 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.72 | 0.65 | 17.63 | |
| 9 | 8 | 11.4 | 40 | 57.1 | 19 | 27.1 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.75 | 0.71 | 18.92 | |
| 10 | 7 | 10.0 | 41 | 58.6 | 18 | 25.7 | 4 | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.72 | 0.72 | 19.33 | |
| After the total closed ambidextrous leadership | 3.71 | 0.77 | 20.86 | |||||||||||
Dimensional Analysis of Organizational Reputation
Analysis of Paragraphs after (Innovation)
It is clear from the data in Table (3) that the total degree of the sample answers to the paragraphs related to the creativity dimension came with a high value, where the arithmetic mean was (3.71) with a standard deviation (0.47) and a coefficient of variation (19.98), and the highest answer came to paragraph No. (23) Which states (the company’s management seeks to provide a positive climate that stimulates employees to creativity and innovation), as the arithmetic mean for it reached (3.98). It is higher than the hypothetical mean (3).This is due to the fact that the company's management encourages employees to innovate and be innovation by creating a positive atmosphere that enables them to demonstrate their core competencies. As for the standard deviation (0.69), this indicates that the answers of the sample were homogeneous. While the coefficient of variation for this dimension was (17.34). Paragraph (26) ranked last in this dimension, which states (the company’s management is concerned with the employees’ creative ideas and works to benefit from them). The arithmetic mean reached 3.58, which is a high value. This is due to the fact that the company is interested in the suggestions and ideas of their workers, but it is not in a way that enables it to take advantage in making its decisions and investing in a way that makes the company advance proactively, while the standard deviation for this paragraph is (0.67), which is an acceptable dispersion ratio. As for the coefficient of variation, it reached (18.68).
| Table 3 Percentages, Frequency, Arithmetic Mean, Coefficient of Variation and Standard Deviation of The Innovation Dimension |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Totally agree | Agreed | Neutral | I do not agree | I don't totally agree | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Coefficient of difference | ||||||
| Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | |||||
| Quality of service | 1 | 13 | 18.6 | 46 | 65.7 | 8 | 11.4 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.98 | .690 | 17.34 |
| 2 | 5 | 7.1 | 43 | 61.4 | 17 | 24.3 | 4 | 5.7 | 1 | 1.4 | 3.67 | 0.75 | 20.59 | |
| 3 | 4 | 5.7 | 44 | 62.9 | 19 | 27.1 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.70 | 0.64 | 17.43 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1.4 | 45 | 64.3 | 18 | 25.7 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.58 | 0.67 | 18.68 | |
| 5 | 9 | 12.9 | 34 | 48.6 | 21 | 30.0 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.65 | 0.81 | 22.27 | |
| 6 | 5 | 7.1 | 41 | 58.6 | 16 | 22.9 | 8 | 11.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.61 | 0.78 | 21.73 | |
| 7 | 12 | 17.1 | 38 | 54.3 | 14 | 20.0 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.80 | 0.82 | 21.76 | |
| Total innovation dimension | 3.71 | 0.47 | 19.98 | |||||||||||
Analysis of Paragraphs after (Quality of Service)
It is clear from the data in Table (4) that the total degree of the sample answers to the paragraphs related to the quality of service dimension came with a value around the mean, Its mean was (3.81) with a standard deviation of (0.71) and a coefficient of variation (18.55), The highest answer came to Paragraph No. (32) which states (the company's management contributes with new ideas and constructive suggestions that will improve the quality of services provided and appropriate training), where the arithmetic mean reached (3.88), which is higher than the hypothetical mean (3). This is due to the company's keenness to improve the quality of its services by providing training programs for employees and adopting bright and new ideas that contribute to the development of their company. As for the standard deviation (0.73), it indicates that the answers of the sample were different, while the coefficient of variation for this dimension was (18.86). Paragraph (35) ranked last in importance on the level of this dimension, which states that (the company's appointees are subject to a probationary period that determines their eligibility to occupy these jobs, The arithmetic mean was (3.71), which is a high value. This indicates the extent of the company's interest and enthusiasm in qualifying its employees and giving them a period to test their abilities to fill jobs. And the standard deviation for this paragraph is (0.70), which is a somewhat acceptable percentage of dispersal. As for the coefficient of variation, it reached (18.92).
| Table 4 Percentages, Frequency, Arithmetic Mean, Coefficient of Variation and Standard Deviation of The Service Quality Dimension |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Totally agree | Agreed | Neutral | I do not agree | I don't totally agree | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Coefficient of difference | ||||||
| Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | |||||
| Quality of service | 1 | 13 | 18.6 | 46 | 65.7 | 8 | 11.4 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.98 | 0.690 | 17.34 |
| 2 | 5 | 7.1 | 43 | 61.4 | 17 | 24.3 | 4 | 5.7 | 1 | 1.4 | 3.67 | 0.75 | 20.59 | |
| 3 | 4 | 5.7 | 44 | 62.9 | 19 | 27.1 | 3 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 3.70 | 0.64 | 17.43 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1.4 | 45 | 64.3 | 18 | 25.7 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.58 | 0.67 | 18.68 | |
| 5 | 9 | 12.9 | 34 | 48.6 | 21 | 30.0 | 6 | 8.6 | 0 | 0 | 3.65 | 0.81 | 22.27 | |
| 6 | 5 | 7.1 | 41 | 58.6 | 16 | 22.9 | 8 | 11.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.61 | 0.78 | 21.73 | |
| Total service quality dimension | 3.81 | 0.71 | 18.55 | |||||||||||
Analysis of Paragraphs after (Social Responsibility)
It is clear from the data in Table (5) that the total degree of the sample answers to the paragraphs related to the dimension of social responsibility came with a high value. Where it had an arithmetic mean (3.84), a standard deviation (0.66), and a coefficient of variation (17.10).The highest answer came to Paragraph No. (43) which states (the company owns a system that can facilitate communication and communication with all parties from unions and federations), where its arithmetic mean reached (3.94), which is higher than the hypothetical mean (3.(This is due to the fact that the company has a high interest in communicating between it and the external environment through its advanced systems. As for the standard deviation (0.67), this indicates that the answers of the sample were homogeneous. While the coefficient of variation for this dimension was (17.21). Paragraph (38) ranked last in importance on the level of this dimension, which states (the company participates in events, events, seminars and conferences held by civil society organizations; (the arithmetic mean was (3.72), which is a high value. This is a clear indication that a company has an interest in participating in events, occasions, seminars and conferences held by civil society organizations, but not in the desired manner. The standard deviation for this paragraph is (0.67), which is an acceptable percentage of qualitative dispersion As for the coefficient of variation, it reached (18.22).
| Table 5 Percentages, Frequency, Arithmetic Mean, Coefficient Of Variation And Standard Deviation Of The Social Responsibility Dimension |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Totally agree | Agreed | Neutral | I do not agree | I don't totally agree | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Coefficient of difference | ||||||
| Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | Repetition | The ratio % | |||||
| Quality of service | 1 | 6 | 8.6 | 55 | 78.6 | 7 | 10.0 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.92 | 0.54 | 13.92 |
| 2 | 3 | 4.3 | 50 | 71.4 | 15 | 21.4 | 2 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.77 | 0.56 | 15.09 | |
| 3 | 5 | 7.1 | 45 | 64.3 | 16 | 22.9 | 4 | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.72 | 0.67 | 18.22 | |
| 4 | 11 | 15.7 | 42 | 60.0 | 16 | 22.9 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.90 | 0.66 | 16.99 | |
| 5 | 6 | 8.6 | 45 | 64.3 | 18 | 25.7 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.80 | 0.60 | 15.90 | |
| 6 | 8 | 11.4 | 44 | 62.9 | 15 | 21.4 | 2 | 2.9 | 1 | 1.4 | 3.80 | 0.73 | 19.32 | |
| 7 | 11 | 15.7 | 39 | 55.7 | 16 | 22.9 | 4 | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 3.81 | 0.76 | 20.11 | |
| 8 | 13 | 18.6 | 41 | 58.6 | 15 | 21.4 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.94 | 0.67 | 17.21 | |
| The total dimension of social responsibility | 3.84 | 0.66 | 0.1017 | |||||||||||
Testing and Analyzing Research Hypotheses and Their Interpretation
This part of the current research aims from its beginning to test the distribution of the answers of the research sample, through the use of appropriate statistical tools in the analysis. The prepared Statistical Program (SPSS) has been relied upon in order to extract the value of the Pearson correlation coefficient and simple linear regression.
Test Data Distribution
Knowing the quality of the data distribution (normal or abnormal) is a prerequisite in statistical analyzes in order to use the appropriate statistical tools It has been found by conducting a (Normality Test) that the distribution of the data for the research was normal. The value of (Kolmogorov-smirnov) for the ambidextrous leadership dimension was (0.131), with a significant level of (sig.) (0.05, (As in Table (6), as for the organizational reputation variable, it reached a value of (Kolmogorov-smirnov) (0.104) and a significant level of (sig.) (0.056, (through the results, it becomes clear to us that both of the significant values were higher than the significant value (0.05), which is the minimum to consider the data with an abnormal distribution. Therefore, the data distribution in this case is normal.
| Table 6 Data Distribution Test |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | (Kolmogorov -smirnov) | Sig. | DF | Distribution type |
| Ambidextrous leadership | 0.131 | 0.05 | 70 | normal |
| Organizational reputation | 0.104 | 0.056 | 70 | normal |
Testing and Interpreting Hypotheses for the Association between Ambidextrous Leadership and Organizational Reputation
Verifying the correlation hypotheses (acceptance or rejection) is a basic condition in scientific research Therefore, we will test the main hypothesis of the correlation of the research, which states (there is a significant correlation between ambidextrous leadership and organizational reputation) and through table (7) it shows us that there is a significant correlation between ambidextrous leadership and organizational reputation that reached (0.226 *) at the level of significance (0.05, (Based on these results, it becomes clear to us that any positive change in ambidextrous leadership leads to a change in the same direction in the organizational reputation and by an amount of (0.226 *), meaning that the dependent variable moves by the same amount as the independent variable, whether positively or negatively, and this shows that the oil company realizes the importance of leadership, ingenious, open- minded, albeit weakly, Thus, the main correlation hypothesis is accepted.
| Table 7 Correlation Hypothesis Test |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent variable | Correlation coefficient | Morale | Sample volume | Dependent variable |
| Independent variable | Correlation coefficient | Morale | Sample volume | Dependent variable |
| Ambidextrousleadership | 0.262* | 0.028 | 70 | organizational reputation |
Testing and Interpreting Hypotheses about the Impact of Ambidextrous Leadership on Organizational Reputation
In order to accept or reject the hypotheses of the research with the direct influence relationship, we must test them and interpret the results related to them. This will be done through the use of the statistical program (SPSS) and the linear regression equation, and as follows:
Y= a+βi xi
Y: is the dependent variable
a: is the constant value
βi: is the regression coefficient
X: is the independent variable
We can now test the validity of the main impact hypothesis, which states (there is a significant effect of strategic foresight on organizational reputation, (Through table (9), it appears that the calculated value of F) is (5.016), which is greater than its tabular value, which is (3.98, (As for the level of morale, it reached (0.028b, (This means that ambidextrous leadership has a significant impact on organizational reputation. This indicates that any change (up or down) in leadership will lead to a change in organizational reputation. As for the linear regression equation, it was as follows:
x1+0.115 (organizational reputation) 0. 257+0.262=(ambidextrous leadership) Y
From this, it turns out that the organizational reputation exists even if the ambidextrous leadership is equal to zero, and the indication of this is the constant value a, which amounted to (0.262), but if ambidextrous leadership is present, any change in it (by one unit) will be offset by a change in the organizational reputation of (0. 257), and the significance of this is the value of b, which amounted to (0.257).
As for the coefficient of determination or the value of the reliability of the approximation, R^2, it reached (0.069), and this indicates the percentage of variance in the dependent variable that was explained by the variance of the values of the independent variable, and this means that ambidextrous leadership explains (7%) of the organizational reputation, while the remaining (93%) there are other factors that explain organizational reputation that the researcher did not take into account in this research, and from the above we can accept the main hypothesis that (there is a significant effect of ambidextrous leadership on organizational reputation).
| Table 8 Impact Hypothesis Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent variable | Regression coefficient | R2 | F | Sig | Dependent variable | |
| Ambidextrous leadership | A | B | 0.069 | 5.016 | 0.028b | organizational reputation |
| 0.262 | 0. 257 | |||||
Conclusion
1. It has been found through the field study that the General Company for the Distribution of Petroleum Products is concerned with ambidextrous leadership.
2. The company is interested in leadership the ambidextrous open high, and this is due that the company has the ability to encourage workers to take risks in uncertainty environment, but not in the position facing the challenges faced in the external environment.
3. It is noted that the General Company for the Distribution of Petroleum Products is highly concerned with the ambidextrous leadership dimension, and this is an indication that the administration has strict methods that it uses to pressure the workers to complete their work on time.
4. The management of the company encourages employees to innovation and creativity, but not in the position to take advantage of it to take its decisions and invest in a way that advanced the company proactively.
5. The results of the analysis that attributed the company's enthusiasm to improve the quality of its services through the provision of a training programs for workers and the adoption of the bright and new ideas that contribute to the development of their company.
6. It indicates the extent of the company's interest in qualifying its employees and giving them a period to test their abilities to fill jobs.
7. The social responsibility dimension is of high importance in the direction of its environment and the external environment through the Advanced Systems owned by the company.
8. The company has an interest in participating in events, seminars and conferences held by organizations of civil society, but not particularly desirable.
9. Research results showed that there is a relationship link between the ambidextrous leadership and organizational reputation, as the more general company for the distribution of petroleum products possess ambidextrous leaders and participate in the creation and improvement of services as this led to the formation of a good reputation for the company.
Recommendations
1. The need for administrative leaders to encourage employees of the company to accomplish their self-reliance and to enable them to carry the spirit of risk.
2. Empower workers and give them the freedom to think and provide them the freedom of the application of creative ideas that may contribute to the development of the company.
3. Enhancing the company's interest in the social responsibility dimension by paying attention to social activities that express its responsibility towards the community, such as the hiring of engineers and administrators who possess skills and experience in the oil sector and interest in the environment through the allocation of an amount of annual profits to charity projects to benefit those with low incomes.
4. The management of the company must encourage employees to innovation and creativity by creating a positive atmosphere they can show core competencies as well as that the company is concerned with proposals and ideas of their employees and employ them in the company that makes advanced proactively.
5. The necessary attention to the company's participation in the events, events, seminars and conferences organized by the community organizations that contribute to the sense of social responsibility, as well as helping to develop the expertise of employees.
6. The company should pay attention to providing services that will raise the level of the company and make it have a good reputation among other companies.
7. The company must establish an effective communication network that enables it to build positive relationships with it and the external environment.
8. The company's management are necessary to take advantage of the nature of the relationship between ambidextrous leadership owned by the company its reputation and development, which contribute to the company in strengthening its investment capabilities and possibilities of employees within the company.
References
- Abdel-Karim, S. (2015). Leadership styles and their relationship to organizational commitment among implementing workers, a field study in the national corporation for casting and transforming non-ferrous metals in Al-Musaliyah, published master’s thesis, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Mohamed Boudiaf University - M’sila, Algeria.
- Al-Shama`a, K.M.H. (2007). "Management principles with a focus on business management", (5th Edition). Dar Al Masirah for Publishing, Distribution and Printing, Amman - Jordan.
- Adeosun, L.P.K., & Ganiyu, R.A. (2013). Corporate reputation as a strategic asset. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 4(2), 220-225.
- Alamgir, M., & Shamsuddoha, M. (2004). Service quality dimensions: A conceptual analysis. The Chittagong University Journal of Business Administration, 19.
- Albuquerque, R., Koskinen, Y., & Zhang, C. (2019). Corporate social responsibility and firm risk: Theory and empirical evidence. Management Science, 65(10), 4451-4469.
- Alghamdi, F. (2018). Ambidextrous leadership, ambidextrous employee, and the interaction between ambidextrous leadership and employee innovative performance. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 7(1), 1-14.
- Alkhawaldeh, S.S.A.R. (2020). The ambidextrous leadership and its impact on organizational performance in the Jordanian government schools from the viewpoint of teachers. British Journal of Education, 8(2), 63-73.
- Bartikowski, B., & Walsh, G. (2011). Investigating mediators between corporate reputation and customer citizenship behaviors. Journal of Business Research, 64(1), 39-44.
- Bass, K. (2018). "Organizational reputation: For public organizations". Media literacy: How the era of fake news affects public service.
- Beheshtifar, M., & Korouki, A. (2013). Reputation: An important component of corporations' value. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 3(7), 15.
- Camilleri, M.A. (2021). Evaluating service quality and performance of higher education institutions: A systematic review and a post-COVID-19 outlook. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences.
- Chae, S.W. (2016). Perceived proximity and trust network on creative performance in virtual collaboration environment. Procedia Computer Science, 91, 807-812, 810(16).
- Ching-Wen, K., Jin, F.U., & Shou –Chi, L. (2020). Ambidextrous leadership and employee innovation in public museums. Chinese Management Studies, Emerald Publishing Limited, 1750-614X .
- Coleman, N.J. (2016). An exploration of the role of leadership behaviors and ambidexterity in online learning units (Doctoral dissertation, The George Washington University).
- Cunha, M.P.E., Fortes, A., Gomes, E., Rego, A., & Rodrigues, F. (2019). Ambidextrous leadership, paradox and contingency: Evidence from Angola. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30(4), 702-727.
- Diena, D., Mts, A., Dyah, G., & Y.D.P. (2020). Ambidextrous leadership influent Toce on team creativity, team innovation and team performance. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(03), 6268 – 6279.
- Ennew, C.T., & Binks, M.R. (1996). The impact of service quality and service characteristics on customer retention: small businesses and their banks in the UK 1. British Journal of management, 7(3), 219-230.
- Ewing, M.T., Windisch, L., & Newton, F.J. (2010). Corporate reputation in the People’s Republic of China: A B2B perspective. Industrial Marketing Management, 39(5), 728-736.
- Guo, Z., Yan, J., Wang, X., & Zhen, J. (2020). Ambidextrous leadership and employee work outcomes: A paradox theory perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 11.
- Gupta, V., & Singh, S. (2015). Leadership and creative performance behaviors in R&D laboratories: Examining the mediating role of justice perceptions. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 22(1), 21-36, 3(1).
- Inglis, R., Morley, C., & Sammut, P. (2006). Corporate reputation and organisational performance: An Australian study. Managerial Auditing Journal.
- Keshta, M.S., El Talla, S.A., Al Shobaki, M.J., & Abu-Naser, S.S. (2020). Perceived organizational reputation and its impact on achieving strategic innovation.
- Kumar, N. (2019). Corporate social responsibility: An analysis of impact and challenges in India. International Journal of Social Sciences Management and Entrepreneurship (IJSSME), 3(2).
- Lange, D., Lee, P.M., & Dai, Y. (2011). Organizational reputation: A review. Journal of management, 37(1), 153-184.
- Magembe, C., & Njuguna, R. (2019). Service characteristics and service quality of organizations within the telecommunications sector: A case of Safaricom public limited in Nakuru county. International Journal of Current Aspects, 3(V), 57-75.
- Oluwafemi, T.B., Mitchelmore, S., & Nikolopoulos, K. (2020). Leading innovation: Empirical evidence for ambidextrous leadership from UK high-tech SMEs. Journal of Business Research, 119, 195-208.
- Pearce, D.L. (2013). Implementing innovation with ambidextrous leadership in small and medium enterprises, Ralph C. Wilson, Jr. School of Education St. John Fisher College.
- Rosing, K., Frese, M., & Bausch, A. (2011). Explaining the heterogeneity of the leadership-innovation relationship: Ambidextrous leadership. The leadership quarterly, 22(5), 956-974.
- Rosing, K., Rosenbusch, N., & Frese, M. (2010). Ambidextrous leadership in the innovation process. In Innovation and international corporate growth (191-204). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Roy, S.K., & Roy, S. (2015). Corporate social responsibility in India: A study in the light of the companies Act, 2013. Corporate Social Responsibility, 18.
- Saeed, N.S.M.Al-E. (2020). The impact of ambidextrous leadership on organizational excellence: An applied study in small and medium enterprises in Qatar. International Journal of Business and Management, 15(9), ISSN 1833-3850 E-ISSN 1833-8119.
- Sarkar, R. (2019). Corporate social responsibility: An Indian perspective. Parikalpana: KIIT Journal of Management, 15(1/2), 141-152.
- Seetge, J. (2012). Leading innovation in fast-growing firms: A multiple case study in the internet industry (Master's thesis, University of Twente).
- Seth, N., Deshmukh, S.G., & Vrat, P. (2005). Service quality models: A review. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
- Smaiziene, I., & Jucevicius, R. (2009). Corporate reputation: Multidisciplinary richness and search for a relevant definition. Engineering Economics, 62(2).
- Smaiziene, I., & Jucevicius. (2010). Facing multidimensional nature of corporate reputation: Challenges for managing reputation. social science/Socialiniai Moksiai, Nr. 3(69), 1 – 9.
- Šontait?, M., & Kristensen, T. (2009). Aesthetics based corporate reputation management in the context of higher education. Organizational Management: Systematic Research, 51, 129-146.
- Strobl, R. (2019). The role of ambidextrous leadership for innovative outcome/Author Ruby Strobl, BSc (Doctoral dissertation, Universität Linz).
- Testa, M. (2008). Corporate social responsibility and reputation risk analysis. In corporate responsibility research conference.
- Wang, S., Eva, N., Newman, A., & Zhou, H. (2020). A double-edged sword: The effects of ambidextrous leadership on follower innovative behaviors. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 1-22.
- Wu, M., Wang, R., He, P., Estay, C., & Akram, Z. (2020). Examining how ambidextrous leadership relates to affective commitment and workplace deviance behavior of employees: The Moderating role of supervisor–subordinate exchange guanxi. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(15), 5500.
- Zacher, H., & Rosing, K. (2015). “Ambidextrous leadership and team innovation”. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 36(1), 54-68.
- Zainab, A., Syed, A.H., & Umar, N.K. (2020). Impact of ambidextrous leadership on project success with the mediating role of innovation and moderating role of self-efficacy. Abasyn Journal of Social Sciences, 13(1).
- Zhou, J., & Oldham, G.R. (2001). Enhancing creative performance: Effects of expected developmental assessment strategies and creative personality. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 35(3), 151-167,152( 10).