Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 3
Total Quality Management (TQM) as a Tool for Sustainable Customer Loyalty in a Competitive Environment: A Critical Review
Rowland E. Worlu, Covenant University
Anthonia A. Adeniji, Covenant University
Tolulope M. Atolagbe, Covenant University
Odunayo P. Salau, Covenant University
Abstract
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a set of guiding principles and philosophies that represents the underpinning of an excellent organization. It ensures the survival of firms in the competitive economy. In view of this, this paper seeks to show how the implementation of TQM serves as a precursor to sustainable customer loyalty in the competitive business environment by utilizing the manufacturing industry In Nigeria. A structured approach was used to determine the source of materials for review and reviewed articles were combined to develop propositions in this paper. Based on the literature reviewed, the factors necessary for the satisfactory implementation of TQM were identified and these include; top management commitment, continuous improvement on the product, team-work, training of employees and control. A conceptual model was also developed to show how total quality management (TQM) can affect customer’s loyalty. Thus, managers should ensure they define quality policy and develop specific measurable goals to meet customers’ expectations and to improve organizational performance.
Keywords
Customer, Loyalty, Satisfaction, Total Quality Management.
Introduction
The demand for quality is emerging as one of the most critical factors in today’s competitive global market. The demand for quality has become one of the indispensable components and strategic tools for measuring business performance. With the intensity of global competition, increasing demand by customers for better quality in the marketplace has encouraged many companies to provide quality products and services. The essence of providing quality product and service is to satisfy their customers, secure repeated purchase and possible recommendation of the product by the customers that have used it to others. One of the major reasons that have made quality to gain such prominence is because organizations have more understanding of the cost and adverse implications of poor quality on market performance and customer patronage (Dapper et al., 2015).
Kantardjieva (2015) showed that TQM is one of the most effective means to increase product and service quality, productivity and profitability. However, many organizations are still overly involved in “quality confusion”. This scenario is a common phenomenon in Nigeria. Nigeria’s manufacturing sectors in the face of increasing competition are currently facing enormous challenges, which have made survival increasingly difficult. Dapper et al. (2015) stated that the continual wave of technical and environmental changes easily turn products obsolete hence, loss of customer’s confidence and patronage, which may be as a result of the failure in organizational processes. The existing research on quality management and customer loyalty perspectives are mainly concentrated on service quality and customer satisfaction. In view of this, this paper tends to examine how continuous product improvement can sustain customer loyalty and how top management commitment to TQM can enhance customers’ patronage.
The broad objective of this study is to show how the implementation of TQM serves as a precursor to sustainable customer loyalty in a competitive business environment. The specific objectives are to firstly, examine how continuous product improvement can sustain customer loyalty and secondly, to determine how top management commitment to TQM can enhance customers’ patronage.
Literature Review
An Overview of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Traditionally, quality is viewed as “the degree of conformance to a standard”. Total Quality Management (TQM) is a philosophy and driving force that characterize the basis for successful organization and to ensure the survival of organizations especially in the competitive economy of today. Margaret & Oluwakayode (2014) opined that TQM is a system of management that focused on the philosophy that every stakeholder must be committed to promoting stimulating continuous improvement and high standards of work in a company's operations.
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Customer satisfaction develops customer’s loyalty towards products and service of organization (Cummings & Worley, 2014). It is the attitudes and experience of the individuals that are in closest contact with customers that determine whether or not customers are willing to return to the company and are satisfied. (Montasser & Al-Manhawy, 2013) which in turn impacts the service quality delivered. One of the most vital factors that contribute to the formation of customer loyalty is customer satisfaction.
The Relationship between TQM and Customer Loyalty
TQM is a quality-based strategic tool of management. It promotes enterprise-wide quality through a strong focus on environment, dynamics and customer orientation (Kantardjieva, 2015), For an organization to achieve competitive advantage, it has to differentiate itself in terms of cost and quality of products and services; that is, if TQM is effectively evidence in the quality of product and low pricing, customer loyalty is automatically be enhanced.
The Deming’s Theory of TQM
Deming's theory was propounded in 1986 (Deming, 1986) and this theory of TQM rests upon fourteen points of management. Deming believes that the ability of an organization to provide quality service requires a change in philosophy. Deming perceives that TQM as a set of management practices that enable companies to increase their productivity and quality. He also identified fourteen points which include the adoption of a new philosophy; ability to create constancy of purpose for improving products and services; stop reliance on inspection to attain quality among others. By implications, the theory allows individuals and organizations to plan and continually improve themselves, their relationships, processes, products, and services.
Methodology
Conceptual research approach has its purpose and target to develop concepts and analyze them mainly by reasoning. The explanatory design was adopted because the paper aimed at putting together different ideas or perspectives relating to the subject understudy in a bid to understand and explain “what’’ “why’’ and “how’’ total quality management translates to sustainable customer loyalty. However, in this paper efforts are geared towards attending to these limitations by relying on literature that captures the subject matter. The literature utilized in this paper comprised of academic articles, journals, research working papers, sustainability reports collected from reputable sources. In collating the relevant literature, articles that undergo peer review process before being published were included while those that do not undergo peer review process were excluded.
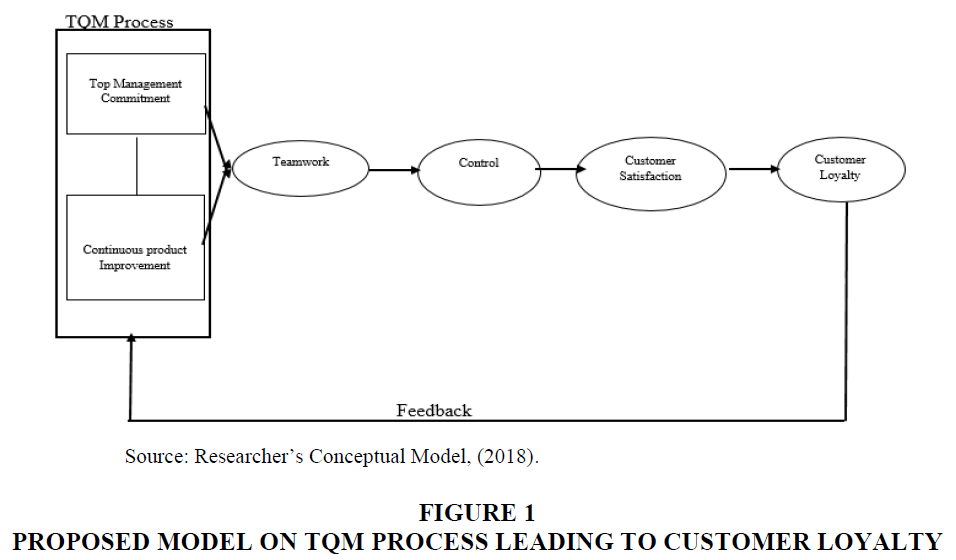
Propositions Continuous product improvement and customer loyalty Studies such as Dapper et al. (2015) have revealed that essential to all TQM systems is improving the quality of the products and services provided by an organization. Chen & Mau (2009) opined that customer loyalty is the most critical issue to be measured in an organization and it is necessary to create customer loyalty due to the intense competition and saturated market situations because the world is turning towards the loyal customers from satisfied ones as it is the most integral part of the present businesses. Based on the above discussion it is observed that the literature supports the link between continuous product improvement and customer loyalty. Therefore, this study proposes the first hypothesis in a new context that: P1: Continuous product improvement can sustain customer loyalty. Top management commitment and customer patronage Previous research in TQM practices emphasizes that top management commitment plays a very crucial role in driving TQM implementation and the overall success of the organization (Zakuan et al., 2010). Top management must initially believe in TQM and thereafter show its commitment in order to implement TQM successfully. When top management is fully committed, a high-quality product will be produced and it will lead to customer satisfaction and once customers are satisfied they remain loyal. Top management commitment will also help enhance maintaining of customers and offering of higher value products in order to attract new customers and to uphold the loyalty of customers (Lee, 2010). Based on the above, it is proposed that: P2: Top management commitment to TQM can enhance customers’ patronage. Proposed Model Extant studies like Munizu (2013), Margaret & Oluwakayode (2014) and Dapper et al. (2015) have shown how TQM affects organization performance and how it leads to customer satisfaction but limited research has been done on how TQM can lead to customer loyalty which goes beyond satisfaction. The proposed model presented in Figure 1 integrates the TQM process and how it can lead to customer satisfaction and loyalty. It shows that top management commitment and continuous product improvement are the backbone for successful implementation of TQM and it requires the cooperation of top managers in all departments and divisions of the organization (Teamwork) and there must be effective control for monitoring and measuring the real performance of the business. Once all these are in place, it will lead to customer satisfaction thereby enhancing sustainable customer loyalty and there must also be room for feedback from customers. The model represents two propositions which were examined in this study. Proposition 2 examines how top management commitment to TQM can enhance customers’ patronage and proposition 1 explains that continuous product improvement can sustain customer loyalty. Gap in Literature Studies such as Seth et al. (2006) and have carried out research on service quality and management in developed countries, however, there are limited studies that focus on manufacturing especially in Nigeria’s context. Studies in Nigeria such as Munizu (2013) and Fapohunda (2012) focus on TQM and or Customer Satisfaction but there are few studies on TQM and Customer Loyalty. Conceptual models have ignored customer loyalty which is the final purpose why firms engage in the relationship with their customers. Most of the models focus on customer satisfaction which is one of the most important factors that contribute to the formation of customer loyalty. Managerial Implications 1. Managers should ensure they define quality policy and develop specific measurable goals to meet customers’ expectations and to improve organisational performance. 2. Managers should invest in resources particularly in time, in order to implement TQM process. The implementation of TQM process would lead to the production of quality products thereby leading to customer satisfaction and loyalty. In conclusion, TQM is seen as a means to change some economies into a more competitive one, but the TQM implementation is lengthy, difficult, and complex, it involves huge efforts from employee’s top management and organizations as a whole. The implementation of TQM can be seen as a process of transformational change within the organization. In order to cope with this change, it is necessary that the leadership of the organization encourage, uphold enthusiasm throughout the organization and also identify useful ways to overcome barriers in order to successfully complete the implementation of TQM system. The role of top management is an important factor in implementing TQM in the organization. Therefore, the success or failure of TQM implementation in the organization is part of top management responsibility.Results
Discussion
Conclusion
References