Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
Using Operation Re-engineering in Raising the Efficiency of Government Spending Programs for Supporting Tourism and Archaeology Sector: Evidence From Iraq
Alaa Shamsallah Noorullah, Mustansiriyah University
Haider Abdulhussein Hameed ALMustawfiy, Mustansiriyah University
Keywords:
Operation Engineering, Government Expenditure Program, Tourism Archaeology
Abstract
Insufficient public funding to implement government activities in Iraq at the time of increasing the state's obligations to serve the social movement of citizens, while at the same time, the state’s commitment to preparing an estimation of current expenditure and capital necessary to implement the government’s commitments using the philosophy of itemized budget. This philosophy does not provide the means and methodologies to produce the required accounting information to measure expenditure productivity in government sectors. For these reasons, this research aims at formulating a model that raises the efficiency of government spending programs based on an accounting perspective using operation re-engineering of these government sectors to support the tourism and archaeology sector in Iraq. This is to be achieved through replacing programs budget and performance accounting as an alternative starting point for itemized budget and final account. Through this research, the researcher concludes a set of results. The most important of these results is the lack of a relationship between the input of the government accounting system and its outputs in support of tourism and archaeology in Iraq. This is due to the lack of a structure that is compatible with the message and objectives of the government organizations. The second result is that the value of the outputs of the governmental organization activities is maximized when operations that do not add an economic value to the tourism and archaeology sector are deleted. When geometrically compatible operations are merged, the cost of the inputs to the governmental organization activities is decreased. As a result, there is a need to describe and identify the structures of activities that are compatible with the mission and objectives of the government units, the necessity to re-engineer the operations of the activities of these units. There is also a need to adopt the philosophy of the program's budget that form these activities and develop accounting manual using government units within the framework of their activity structures. This will be positively reflected in the tourism and archaeology sector in Iraq.
Introduction
The accounting intellect, supported by practical exercises in some countries, including Iraq, has recognized the necessity of looking for a set of mechanisms to maximize decision-making and support. It is rationalizing the strategic decisions that are compatible with the variabilities of the modern business environment (Al-Fatlawi, 2021). Despite the large size of spending and its economic implications, the recent recognition and accounting measurement of the components and results of the spending items do not allow to measure its productivity and effectiveness due to the nature of the accounting environment that is reflected in the accounting laws and the government budget on the elements of the current accounting system. The recent government accounting and budget law do not provide adequate and appropriate accounting information to measure the productivity and effectiveness of this expenditure (Almagtome, 2020). The government’s estimated expenses are based on the mechanism of allocating funds to be spent for government units, simply, on specific purposes that reflect the means of completion or the intermediate outputs to start the implementation of these programs, activities, business, and operations of these units without allowing these units to transfer or exceed the dependencies among these purposes except with the authorization of the financial authorities (Almagtome, 2020). Given the lack of interest in the current government, practices to enhance the governance environment and its relatedness to the efficiency of government spending program decisions based on analyzing the cost-effectiveness of these programs rather than depending on the trade-off between exchange alternatives and the attempt to change its levels. The research seeks to find ways to raise the efficiency of government spending programs by adopting the operations re-engineering approach to modernize, develop, and improve
To achieve the research’s goal, the research is divided into four parts. The first part presents the methodology of the research. The second part explains the basic concepts of the research. The third part is dedicated to clarifying the justifications of re-engineering the implementation steps of the government activities. In contrast, the fourth and final part presents the most crucial research conclusions and recommendations (Al-Wattar, 2019). The tourism and archaeology sector suffers from unintentional negligence due to the lack of attention from current governmental practices to the necessity of improving the governance environment and its implications on the efficiency of government spending programs’ decisions from the perspective of analyzing these programs’ cost-effectiveness rather than depending the trade-off among the spending alternatives and trying to change the levels of these spending alternatives in this crucial economic sector (Amagtome, 2020). Therefore, the research aims to provide objective answers to a set of questions representing the core of the problem this research tries to address and handle. These questions are:
a. How useful is the information of the current government accounting system in measuring the productivity and effectiveness of government spending in the tourism and archaeology sector?
b. Can the shift towards implementing the program budget and accounting for performance in government units help measure the productivity of public expenditure without the need to re-engineering operations in government business centers of the tourism and archaeology sector?
c. Is it possible to formulate a model that can improve the accounting measurement environment for the productivity and effectiveness of government spending within the philosophical framework of introducing the operation re-engineering in tourism and archaeology?
The study focuses on identifying a set of mechanisms that can best help make, support, and rationalize strategic decisions appropriate for a business environment that changes rapidly and sequentially on local and international levels. This reflects the ability of this information to maximize the performance of most government activities, resulting from raising the efficiency of government spending decisions via adopting the operations engineering approach (Amusawi, 2019). This research is manifested through the expansion of government activity, which puts a burden on the financial and accounting intellect in seeking good ways to produce appropriate accounting information that rationalizes the government decisions. This can be done by developing current government accounting methods to the extent that makes them able to measure the cost and return of government activities to calculate the performance of these activities using the productivity and the effectiveness of the size of annual spending on these activities. A framework that represents the viability of the operations of these activities is also required for the measuring. Developing the government budget is associated with developing the approach on which this government budget depends to prepare its estimates rather than addressing the budget structure's varieties and outcomes within a particular framework that it uses.
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
The research is based on the following hypotheses:
a. The ability to improve the accounting environment for the cost and the return of government programs and activities due to structures for these programs and activities raises government spending programs' efficiency in the tourism and archaeology sector.
b. Applying the operation re-engineering approach to make the administrative units formulate their objectives helps build their programs, activities, works, and operations in the tourism and archaeology sector.
Introducing Public Expenses
Public expenses are defined as a financial burden borne by government units to perform sovereign functions and achieve their objectives towards society in all areas, whether social, economic, or political. Public expenses are also known as funds coming out of the state treasury or one of its branches to achieve a public benefit. The amount of funds is limited within the limits of what is planned in the balance sheet. From this definition, we can identify three primary characteristics of public expenditure (Angelino, 2017):
a. Public expenses represent an amount of money, often in the form of cash, spent by government units to obtain the necessary goods and services to keep their activities in check. The amount of money spent is limited in quantity, type, and time to the balance sheet.
b. Public expenses are issued by the state treasury or one of its main branches, such as the monetary department in the accounting department of the Ministry of Finance, the Central Treasury, provincial coffers, or government units applied to the decentralized government accounting system.
c. For example, public expenses are paid to achieve a public benefit, such as security, defence, health, and education, for performing public functions to society (Khaghaany, 2019). Political, economic, and social factors and considerations play a significant role (Hameedi, 2021). For example, the state's appreciation of public benefits reflects the nature of the country's prevailing political and economic system and the level of civilized progress achieved by society.
Expenditure Ingredients
Before regulating the expenditure sheet, in which the accounting record for public expenditures will be fixed, there is a set of conditions to be observed when executing the spending operations for public spending, and these conditions are called "expenditure elements" and are as follows (Chan, 1996):
a. There should be an actual and realistic need for the things to be disbursed, and this need should be included in the activity of the government unit.
b. The disbursements should be based on the availability of the approved allocations, both in type and amount, specified for that expenditure, in the balance sheet and never to exceed them.
c. The sums to be disbursed must be within the authorized financial power of the order or the highest official in the government unit specified by the active legislation.
d. There should be a cash balance in the current account of the unit at the bank enough to pay the amount of the transaction to be disbursed and not exceed it.
e. Suppose the expenses are for the purchase or processing of materials. In that case, expense sheets should be documented in the first copies of the processing lists issued by the seller with the support of the receipt of the store belonging to the government unit for materials purchased under the storage list.
f. Public expenditures should be subject to prior auditing of disbursement before paying the amount once and for all.
g. The expenditure operations must be supported by the employee's signature who organized the expenditure sheet, the accountant or the accounting manager, and the order of spending. It should not be permissible to limit the authority of the expenditure and the accountant and the power to regulate the expense sheet in one person.
h. Expense sheets must be documented in receipts taken from the relevant persons (or the so-called beneficiary) to recognize that he/she has received the sum.
Public Expenditure Productivity Concept
In general, productivity means doing the work correctly as one of the indicators of evaluating the performance of the activities of organizations. The productivity is measured by the relative relationship between the value of the outputs of action and the activity inputs' cost to increase the opportunities for the efficiency of inputs to usable outputs conversion (Kbelah, 2019). There is no point comparing a specific activity's productivity in one organization with the productivity of similar actions in other organizations unless done about the organization's overall productivity or the productivity of the same exercise for a different period or in the future. You should be aware that measuring productivity alone of that activity is misleading unless it is done about other companies or against the productivity of the same activity.
Accordingly, the concept of general expenditure productivity is meant to perform business within the same government activity correctly. The productivity of this expenditure is measured by the relative relationship between the performance units, whether it is several items, time spent, space, distance, or any other approximate form between the costs of inputs paid for these units.
Public Expenditure Effectiveness Concept
The concept of effectiveness means, in general, the extent to which the work has been performed correctly. It is one of the indicators of evaluating the performance of the activities in organizations. Effectiveness is defined by the capacity of the organization to achieve its goals. The effectiveness of public expenditure is measured by the ratio of the actual program's actual achievement to the planned completion (Hasibuan Syahrial, 2019). We feel the need to make the following statement regarding this issue: It is important to note that the unique bond linking the concepts of expenditure productivity and effectiveness in the government sector as a way to organize the expenditure, on the one hand, and as a means to evaluate the effectiveness of government unit activities, on the other.
Operation Re-engineering Concept
The concept of operations means the set of tasks that constitute, in a whole, a value to the beneficiaries of the services provided by the government organization. Implementing a specific service by an administrative unit to the beneficiaries requires limiting the series of tasks that start with receiving a request from the beneficiary and finishing with public service provision to him/her. Operations are the inevitable and logical steps necessary to carry out the job within a particular government activity. Reworking is meant to rethink how the business is carried out or completely redesign one or more job stages. Some steps may be removed, some phases may be merged, and some new processes may be designed or improved to carry out these activities (Wright, 2017).
Based on what is mentioned above, operation re-engineering is intended to rethink how to carry out the business within a particular activity to eliminate what is unnecessary and find better ways to perform what is necessary. In addition, it involves re-engineering procedures to focus on the needs of the government agencies and what the clients desire. Those wishes and preferences demand to change the priorities of these units in providing these services in terms of speed, creativity, flexibility, quality, and cost. However, we should note that re-adapting government units are difficult to these priorities. This adaptation can only be possible using the entrance to re-engineering their operations. Also, it is challenging to prepare the appropriate accounting environment to evaluate the performance of these units within the framework of the productivity indicators and the effectiveness of their expenditures without eliminating the old-style and unable working steps. Therefore, these old-fashioned working steps cannot achieve the desired results, and we must work on designing other steps to carry out these actions correctly and effectively.
One of the important reasons for re-engineering government activities is that the government in Iraq is working periodically to activate economic and social reform policies within the framework of comprehensive and partial restructuring of economic activities in the country. This depends, initially, on the extent of skills in developing the work systems under which these activities operate. As the government's accounting system is one of several systems that have yet to be established, it must be created according to its educational policy. We have discovered that the system's construction is a necessary component in accounting. Requirements Provided, however, that the development of systems should not impact the university's financial management to organize universities and their executive regulations, as well as the laws of balance sheet and government accounting under which these systems operate or rely on shifting to the program and performance (Ruppel, 2009). The mere fact of making some legislative amendments that aim to develop the government accounting system does not add any benefit to its information to help rationalize strategic decisions at the macro and micro levels. Additionally, the speed of replacing the budget of programs in place of the allocation of expenditure without paying attention to the engineering of steps of implementing the government actions will not help the financial authorities in determining the desired volume of expenses required for a specific government program. Furthermore, there will be the inability to measure the efficiency of this program in an objective way that depends on the extent of its contribution to the Gross Domestic Production (GDP) at the cost of production factors of production. Also, this shifting will be unable to explain how to accomplish government programs economically and efficiently or how to accomplish them using the same amount of work but with the highest adequacy the lowest possible cost. Based on those above, it is clear that there is an urgent need to re-engineer the operations within the operation centers that are compatible with the structure of university activities in preparation for developing and improving the environment of preparing the budget of programs accounting for performance. One of the essential justifications that reflect the importance of employing the operation re-engineering approach on the reality of the business, activities, and programs of university units, for example, is (Schaltegger, 2017):
a. There are worries that the itemized budget will be replaced by the program's budget and concerns that these programs and activities are intertwined in a way that causes complications in creating university budget projections.
b. Using programs budget in the public universities sector cannot identify the fundamental areas of rationalizing university spending. This inability is due to processes that do not add economic value, which is easy to characterize and identify when working based on the re-engineering approach mentioned previously.
c. Working with operation re-engineering method in the university units achieves arranging the processes. It specifies the extent of the logical steps of implementing the works within the activities of these units. This will be successful because these steps are integrated and consistent to the extent that they help describe and prepare the structures of these processes, works, activities, and programs in the public universities sector. Also, it will help to design a strategic entry point to measure the financial and non-financial performance of the results of the activities and programs of the units of this sector.
Despite the large size of this expenditure and its economic implications, the current accounting recognition, accounting measurement, and accounting disclosure of the components and results of its items do not allow to measure its productivity and effectiveness due to the nature of the accounting environment reflected by the accounting laws and the balance-sheet on the elements of the current government accounting system, since these elements do not permit providing adequate accounting information that is convenient to measure the productivity and effectiveness of such expenditure (Burritt, 2006). Annual estimates of this kind of expenditures are based on the allocation of funds to government sector units simply for specific purposes that reflect the means of completion or intermediate outputs to start implementing the programs, activities, operations of these units without allowing them to transfer or exceed the amounts of these funds among these purposes without authorization from the financial authorities.
This mechanism is effective because it relies on the qualitative approach or the itemized budget approach. This philosophy serves as the groundwork for these estimates: balance-sheet components and results. Using the qualitative approach philosophy for many years has increased the gap between the resources and uses of the government budget because of the inability of resources to offset the growing spending. The recurrence of this deficit annually and its growth at rates higher than the rates allowed domestically and internationally has triggered the financial, economic, and accounting intellectuals to make many attempts to reduce the increase of this deficit from its permissible limits and to make it at an acceptable proportion of Gross Domestic Production (GDP) at the cost of factors of production. Specialized accounting studies in this field have revealed three types of attempts to address the government budget deficit, which was reflected in the mechanism of allocating funds under the philosophy of the itemized budget approach. The first type is specialized in issuing shouts of pressure, reduction, control, and rationalization of government spending. The second type is specialized in examining the possibility of increasing government resources without increasing government spending. In contrast, the third type has focused on adopting attempts to convert some units of the government sector into business or private sector (Schaltegger, 2017).
Although these attempts make sense in addressing the increase in the government budget deficit from the economically desirable limits, they overlooked the need to deal with the itemized budget approach philosophy that produced this deficit. This is because the itemized budget approach deals with the inputs of the budget without looking at its final outputs. With all of that in mind, it is worth noting that this method does not even bother to consider the actual link between the given inputs and outcomes.
When working on a government budget, you must think about addressing the variety and outputs of its structure and the researcher believes that the itemized-budget approach mentioned above represents the essence of the current accounting system in Iraq. This approach's objectives depend on a mere preparation of a historical record that reflects the movement of funds that government units must spend according to their allocated value on the types, items, groups, and articles of the government budget according to the allocation mechanism mentioned previously. Given this, the itemized budget technique based on the government accounting system's information is only suitable for the legislative review of whether administrative units have followed the guidelines for how much money may be spent on a specific completion means or not. Moreover, the itemized budget approach is not interested in evaluating the final achievement or the final outputs and without the attention of measuring the productivity and effectiveness of these funds. To maximize government accounting information systems' benefit, accounting intellect must search for a mechanism set that enables strategic decisions to be compatible with modern business environments that possess constant and rapid changes at local and global levels. These mechanisms help increase the cost of government projects consistent with technical development in knowledge, information, and communication (Romney, 2000). Accounting information in the government sector has limited usefulness since this information fails to explain poor government activity performance. It is also unable to justify the expenditure of government units on these activities due to the large and overlapping processes involved. Based on one of these mechanisms, these activities must be reengineered as a necessary starting point for improving the accounting working environment.
Results
The philosophy of the government budget based on the itemized budget approach has been subjected to many criticisms. The most important of these criticisms are:
a. It lacks the interest in real goals that the administrative units seek to achieve due to long adherence to the obsolete allocation and usage of the funds. It abides by the limits of these funds. It cannot exceed them when preparing and implementing this budget.
b. Lack of attention to the adverse effects that the spending credits may have on these goals.
c. Insufficient attention to the timely programming of these goals the distribution of these goals to the centers responsible for achieving them.
d. The inability to provide appropriate information to measure the productivity and effectiveness of government expenditure.
e. In addition, the financial authorities' interest under this approach is always shifted to auditing spending items without focusing on the management system responsible for achieving the programs, activities, and the measurement of the implemented actions.
First, to maximize the growth of the country's economy, it is necessary to look for suitable mechanisms, approaches, and non-traditional means capable of developing the government sector's accounting information system (Kbelah, 2019). To improve the accounting working environment in the government sector within these mechanisms, approaches, methods, and policies. It is necessary to design or redesign the evidence procedures for implementing operations related to a particular activity before considering employing one of these mechanisms in developing the government accounting system. One of the most important entry points for the design or redesign of the procedures of this evidence within the framework of the necessary and logical procedures for conducting the business is the approach of operation re-engineering.
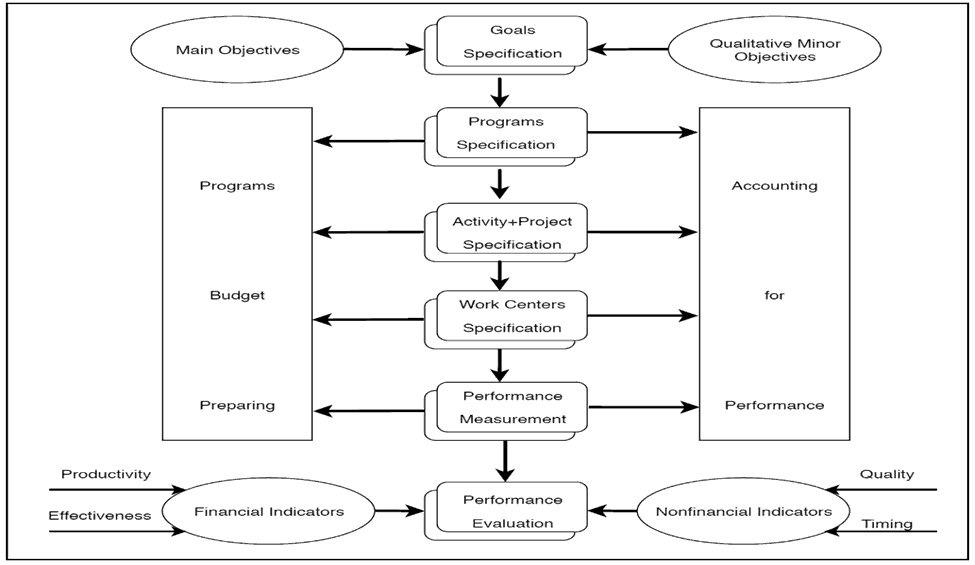
To increase the efficiency and effectiveness of government accounting information system in supporting decisions of performance-evaluation of government activities based on the productivity and effectiveness of spending on these activities depends on the attention of the analysis and management of exercises using the indication of the operation re-engineering approach in order to separate operations that add value to the outcomes of these activities and to make the decision to keep them, while for the processes that do not add value to these outputs, they should be deleted or excluded because they have no necessity in the system of analysis and management of government activities within the framework of this portal in order to provide public services to the public beneficiaries in a better and cost-effective way and also towards adopting the strategy of excellence in producing these services that are depended, precisely, in the implementation of government activities on processes that add value to the outputs of these activities (Dobija, 2010). Since the reform of government administration depends primarily on the philosophy of changing management based on innovation and renewal of the work systems, the entrance to operation re-engineering of operations is the objective orientation towards bringing about the required change in the work systems in the government sector units. To achieve the research’s goal, in the following, the researcher presents the structure of the proposed model to improve the accounting measurement environment for the productivity and effectiveness of expenditure in the government sector based on the philosophy of operation re-engineering approach. The significance of the proposed model in achieving its objectives depends on a group of elements (Hoque, 2004). These elements are:
a. Describing and identifying the major and minor objectives of government units in their operational and strategic dimensions flexibly, free from ambiguity, and quantifiable.
b. Developing the current organizational structures of government units either by reviewing their current divisions to cope with the successive changes in the modern domestic and international business environment or by designing new systems for these units within the framework of these changes.
c. Categorizing public expenditures according to the type of the achieved public service to track spending on these services distributed to various state functions.
d. Describing and identifying the main and sub-programs that government units should implement to achieve their main and qualitative objectives.
e. Describing and identifying the activities and projects that makes up the same program, considering that the action or project is only part of the same program.
f. Describing the activities that make up the activities within performance centers and limited liability, considering that the unit of work within a particular performance center is only partially within the same movement.
g. Describing the processes or steps of carrying out the work within the performance centers and responsibility in government units.
h. Measuring the performance within each performance center and a specific responsibility within the framework of the size of its performance units or the time taken to implement it or using any other approximate basis.
i. Evaluating performance within each specific performance and responsibility center within a set of financial and non-financial indicators needs to pay attention to productivity and effectiveness in this regard.
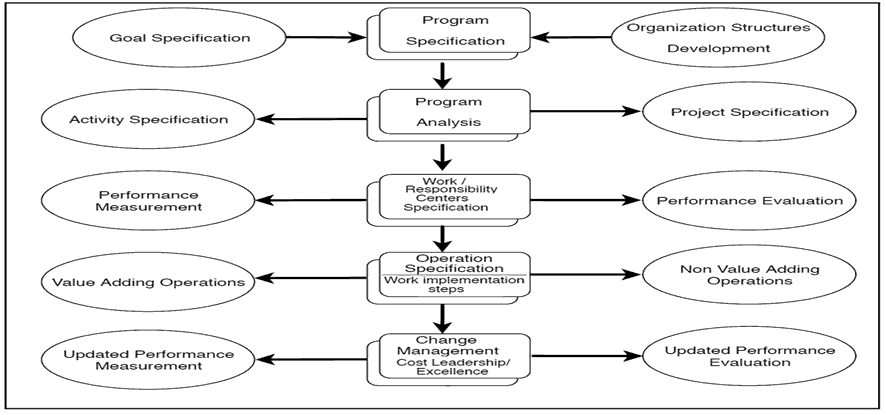
According to the framework of factors in the proposed model that might benefit the productivity and effectiveness of government expenditure accounting measurement environment, the suggested model utilizes such aspects. The research seeks to construct a flowchart to represent the movement of government programs and activities (Figure 1) to help form the framework for the application of the operation re-engineering in government sector units before concentrating on the implementation of the program methodology and performance as inputs to design the government budget in these units:
Figure 1: Government Programs & Activities Flow as A Demand to Prepare The Budget of Programs and Account for Performance
The importance of operation re-engineering related to the government activities to build new information systems on the ruins of existing systems requires the following (Flayyih, 2019):
a. Reengineering has become necessary to improve the measurement and auditing disclosure environment about the reality of the performance of government activities.
b. Reengineering has become necessary to measure the reality of outputs and inputs of government programs and activities and maximize the value of these outputs in line with specific information.
c. Operation re-engineering focuses on the input of government activities carried out by logical and necessary processes or steps.
d. Operations re-engineering is necessary before looking for new methods and approaches to developing accounting information systems in government units within these methods and techniques.
e. Operation re-engineering is necessary to rationalize government resources, maximize their outputs, and improve the planning of these resources in the future.
f. Operation re-engineering is necessary to move from input auditing/control operations to monitoring outputs and performance as a trend imposed by financial and international institutions.
g. Operation re-engineering leads to maximizing the information of the government accounting system for administrative, political, and economic decision-makers in the country due to its active role in improving the accounting measurement environment for the productivity and effectiveness of government spending and establishing objective justifications for its outputs and effects.
Therefore, when the work is completed with the preparation of a structure for each administrative unit's government programs and activities in the government sector, the operation re-engineering approach can be employed to carry out the works within the performance centers and responsibility competent for particular government activity. In this way, maximizing the value of outputs of government activities will be ensured using the cost of their input sought on the necessary and logical processes to implement these activities.
According to the previous, the researcher considers that the improvement of the accounting measurement environment for the performance of government activities depends on the fact of the relationship between the variables of the flow map of government programs and activities and the variables of the operation re-engineering of these activities, which can be shown through the Figure 2.
Conclusion and Discussion
Accounting thought has witnessed a set of attempts to develop the accounting work environment in the government sector in Iraq within the framework of the remarkable development in accounting information systems, especially the administrative-accounting system due to the accelerating and successive changes in the modern economic and industrial business environment, as well as within the framework of the noticeable development in the approaches of preparing the government budgets according to experiences other countries of the world to employ these approaches. As this research extends these approaches and studies, it aims to examine how to raise the efficiency of government spending program decisions depending on operations re-engineering. The article is trying to re-think the accounting system in the government sector by looking at the balance sheets and accounting rules from the government's perspective. The utilization of resources is maximized through programs that optimize resources, notably the sovereign credit, and rationalize using the accounting work environment. Governmental balance-sheet systems can include attempts to implement program and performance estimates based on the need to move from qualitative or itemized approaches to a complete program and performance approach. As part of the effort to improve the measurement environment and improve accounting disclosure of results, efforts are made to bring about government budget systems and auditing performance methods while using the framework of operation re-engineering. The government has experimented with developing and modernizing the governmental accounting system consistent with the proposed approach for developing the government budget based on the unity between the accounting and administrative intellects. To achieve strategic planning, they implement an experiment that other innovations could negate any failure. The existence of variables associated with using the operation re-engineering approach influences the structure of programs and activities, and the procedures followed within operation re-engineering and streamlining. Before planning and implementing the government budget, it is critical to consider how the program and performance strategy should be used. This project is taking place in a public sector setting. It must employ an operation re-engineering strategy when redesigning government operations and processes to include program and performance objectives. Every level of government must prepare a framework for their various programs and procedures based on their strategic vision and operational goals. Measuring the cost of government programs and activities is necessary since many programs and activities are mismanaged. Indicators are essential to evaluate the programs and actions of government entities. As a result of program budgeting and performance accounting basics, the government accounting handbook must be redesigned. Dependence on the existing government budget laws is needed when a new method for preparing and implementing the government budget is considered. Managers of government units who need to learn how to manage government programs need to understand the financial management of government units and program funding and accountability to re-engineer government operations. There is a need for seminars at all levels of government every so often. Participants learn about the program budgeting, performance accounting, and operations re-engineering objectives, regulations, and fundamentals for all government agencies in these seminars.
References
- Al-Fatlawi, Q.A., Al Farttoosi, D.S., & Almagtome, A.H. (2021). Accounting information security and IT governance under COBIT 5 framework: A case study. Webology, 18(S2), 294-310.
- Almagtome, A., Khaghaany, M., & Önce, S. (2020). Corporate governance quality, stakeholders’ pressure, and sustainable development: An integrated approach. International Journal of Mathematical, Engineering and Management Sciences, 5(6), 1077-1090.
- Almagtome, A.H., Al-Yasiri, A.J., Ali, R.S., Kadhim, H.L., & Bekheet, H.N. (2020). Circular economy initiatives through energy accounting and sustainable energy performance under integrated reporting framework. International Journal of Mathematical, Engineering and Management Sciences, 5(6), 1032-1045.
- Al-Wattar, Y.M.A., Almagtome, A.H., & AL-Shafeay, K.M. (2019). The role of integrating hotel sustainability reporting practices into an Accounting Information System to enhance Hotel Financial Performance: Evidence from Iraq. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 8(5), 1-16.
- Amagtome, A.H., & Alnajjar, F.A. (2020). Integration of financial reporting system and financial sustainability of non-profit organizations: Evidence from Iraq. International Journal of Business & Management Science, 10(1).
- Amusawi, E., Almagtome, A., & Shaker, A.S. (2019). Impact of lean accounting information on the financial performance of the healthcare institutions: A case study. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 14(2), 589-399.
- Angelino, A., Khanh, D.T., An Ha, N., & Pham, T. (2017). Pharmaceutical industry in Vietnam: Sluggish sector in a growing market. International journal of environmental research and public health, 14(9), 976.
- Burritt, R.L., & Saka, C. (2006). Environmental management accounting applications and eco-efficiency: case studies from Japan. Journal of Cleaner production, 14(14), 1262-1275.
- Chan, J.L., Jones, R.H., & Lüder, K.G. (1996). Modelling governmental accounting innovations. Research in governmental and non-profit accounting, 9, 1-19.
- Dobija, D., & Klimczak, K.M. (2010). Development of accounting in Poland: Market efficiency and the value relevance of reported earnings. The international journal of accounting, 45(3), 356-374.
- Hameedi, K.S., Al-Fatlawi, Q.A., ALI, M.N., & Almagtome, A.H., (2021). Financial performance reporting, IFRS implementation and accounting information: Evidence from Iraqi banking sector. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 8(3), 1083-1094.
- Hole, Y., Hole, S.P., & Bhaskar, M.P. (2019). The damages of liberal marketing myopia. Restaurant Business, 118(10), 542-556.
- Hoque, Z., Arends, S., & Alexander, R. (2004). Policing the police service. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal.
- Kbelah, S.I., Amusawi, E.G., & Almagtome, A.H. (2019). Using resource consumption accounting for improving the competitive advantage in textile industry. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 14(2), 575-382.
- Khaghaany, M., Kbelah, S., & Almagtome, A. (2019). Value relevance of sustainability reporting under an accounting information system: Evidence from the tourism industry. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 8, 1-12.
- Romney, M.B., Steinbart, P.J., & Cushing, B.E. (2000). Accounting information systems. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Schaltegger, S., & Burritt, R. (2017). Contemporary environmental accounting: Issues, concepts and practice. Routledge.