Review Article: 2018 Vol: 22 Issue: 3
A Review on Providing Loyalty Discounts to Customers in Retail Stores
Sanmoy Paul, NMIMS University
Sameer Acharya, NMIMS University
Kashyap Bhuva, NMIMS University
Abstract
Facial recognition systems were first explored in the security system to identify and compare with other biometrics, iris recognition etc. from the database. Recently it has been added in many fields of study and has become a commercial form of identification and marketing tool. This paper describes the study of different types of algorithms being commonly used for face recognition. Our study will help in the retention of customers who adds customer value and thereby increasing the customer lifetime value. The facial recognition system could be set up at the billing desk. The faces of the customers would be stored as image automatically in a database along with their purchase history, which is then matched with any incoming customer. Accordingly, the frequency of each customer would be stored in the database & loyalty discounts could be provided to them on the basis of their purchase frequency. This data could also be used to predict the sales, market basket analysis and other marketing analytics applications for the retail store. We will use the algorithm that yields better accuracy in order to detect potential customers purchasing in a retail store.
Keywords
Eigen Values, Fishers Face, Viola Jones, Facial Recognition, PCA.
Introduction
The purpose of this study is to provide some benefits to the customers in retail stores in the form discounts coming to their stores regularly keeping a fair bit of loyalty or trust on them. This will help the retail owners not only to attract new customers but also retain their existing customers. Here we keenly look through the purchasing behaviour of each customer and then provide discounts depending on their maximum likelihood of their purchase.
Customers largely impacts in any type of business by retaining existing customers is the most important in any type of business because not only it increases the business but also helps in growing business by bringing more and more new customers. In recent times discounts to customers are provided in terms of sale or as general discounts but there is no scope of discounts based on loyalty or trust that customers show on their purchase irrespective of any age group.
The platform to achieve our target is through scanning each customer’s face through facial recognition technique and then provide discounts instantly on real time basis after giving a thorough study of their past purchasing history. We will also try to provide discounts by predicting their next purchases. This will help us to give importance to customers purchasing behaviour and the trust they show.
This literature review will advance through the different techniques and methods to track and identify loyal and potential customers. This study also advances through by predicting when their next purchase will happen and the maximum likelihood of purchase on which category.
Research Background
System Architecture
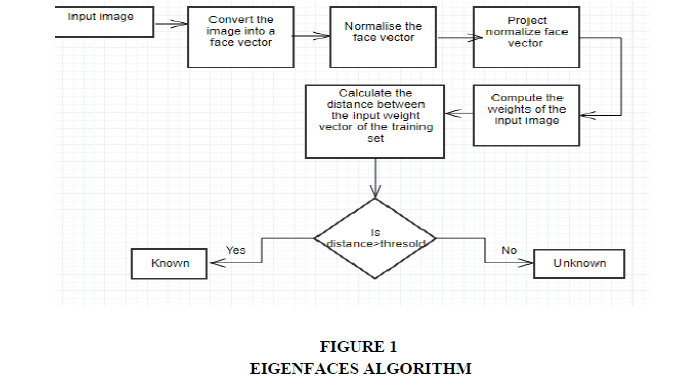
The system architecture diagram of the study, describes that, the camera in the bill desk will start detecting faces using face recognition. Given the circumstances that there are faces detected, it will verify if the customer’s face is registered or a new customer. Only the registered customer’s faces are verified, if so, it will study the past purchasing history and the number of times he visited the store. After satisfying necessary condition set by the administrator the system will automatically provide discounts on their next purchases.
System Design
First process is to identify the loyal customers who are authorized to avail the system generated real time discounts by filling up the basic necessary conditions. Prior studies reveal the following methods and techniques to identify the loyal customers.
Literature Review On Various Methods Of Facial Recognition Techniques
Eigen Faces Algorithm with PCA
The Eigen faces Algorithm is the most commonly used methods in the field of facial recognition. Muge and Figen (2012) have researched on Eigen faces method with smallest Euclidian distance is the person that resembles the most. We split the set of images into training and test set. Convert the face images in training set to face vectors ?i. We normalise the face vectors by computing the mean of the face vectors then subtract the mean face from each of the face vectors to get as normalised face vector ?i.
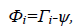
Where 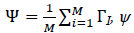 is the average face vector.
is the average face vector.
The Covariance matrix C is given by,
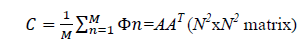
Where 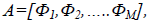 each normalised vectors in each column makes up A, where A is N2xM matrix. Now to choose k significant vectors from the Eigen vector space becomes a problem. Therefore, in order to solve this we use dimensionality reduction, where we assume face vector space as a lower dimensional subspace and recomputed the covariance matrix as follows:
each normalised vectors in each column makes up A, where A is N2xM matrix. Now to choose k significant vectors from the Eigen vector space becomes a problem. Therefore, in order to solve this we use dimensionality reduction, where we assume face vector space as a lower dimensional subspace and recomputed the covariance matrix as follows:
C=ATA, now the covariance matrix becomes of MxM dimension. Similar methods has been further researched down by Jiachen and Kenneth (2017). Now it becomes easier to find the k significant Eigen vectors from the face vector space. The covariance matrix now returns M Eigen vectors each of Mx1 dimension. After dimensionality reduction of the covariance matrix k best Eigen faces are selected such that k<M which can represent the total training set. But the selected k Eigen faces must be of the original dimensionality of the face vector space i.e. we have to map it back into the original dimensionality by
ui=A*vi,
where: ui is the Eigen vector of higher dimensionality and
vi is the Eigen vector of lower dimensionality.
Detsing and Ketcham (2017) also used PCA with Eigen faces in their research. The dimensionality reduction not only made computational problem easier but also helped in the reduction of noise which could have impacted our result. Now we represent each face in the training set as a linear combination of all k Eigen vectors along with the average face vector multiplied by the weights w. The weight vector is represented as Ω=[w1, w2,……..wk], this is the Eigen face representation of the ith face and the weights for each face is calculated. Debasmita and Debtanu (2013) also used PCA with Eigen faces for their research of Facial Expresions. The flowchart of our Eigen faces algorithm is mentioned (Refer to Figure 1).
Fisher Faces Algorithm (FLDA)
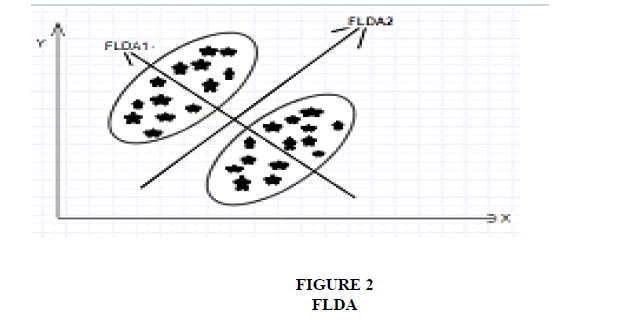
The Fisher face method is an enhancement of the Eigen face method that it uses Fisher’s Linear Discriminant Analysis (FLDA or LDA) for the dimensionality reduction. Jiachen and Kenneth (2017) also used LDA method in order to compare the accuracy between Eigen faces method and LDA. In Fisher faces we assume that the images are normally distributed and contains only facial region. Shereena and Ashok (2014) have used FLDA where a multidimensional data is transformed into single dimensional data. Each image starts with the two-dimensional mxn array of intensity values I (x, y), we construct the lexicographic vector expansion 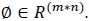 This vector corresponds to the initial representation of the face. Thus, the set of all faces in the feature space is treated as a high-dimensional vector space. As different faces fall in different classes in the training set, we establish a framework for performing a cluster separation analysis in the feature space. Also, Quan-xue, Lei and David (2008) applied a singular value decomposition (SVD), wherein an image is decomposed into a general appearance image.. The dataset must be associated with class. FLDA maximises between class variance and minimises within class variance given by direction of the Eigen vector associated with maximum Eigen value. It shapes the scatter with the aim to make dataset suitable for classification transformation of matrix resulting in maximising the ratio of between class scatter (Figure 2).
This vector corresponds to the initial representation of the face. Thus, the set of all faces in the feature space is treated as a high-dimensional vector space. As different faces fall in different classes in the training set, we establish a framework for performing a cluster separation analysis in the feature space. Also, Quan-xue, Lei and David (2008) applied a singular value decomposition (SVD), wherein an image is decomposed into a general appearance image.. The dataset must be associated with class. FLDA maximises between class variance and minimises within class variance given by direction of the Eigen vector associated with maximum Eigen value. It shapes the scatter with the aim to make dataset suitable for classification transformation of matrix resulting in maximising the ratio of between class scatter (Figure 2).
Let X be a random vector with samples drawn from c classes,
X={X1, X2,………Xc}
Xi={X1, X2,………Xn}
The scatter matrices Sb and Sw are calculated as,
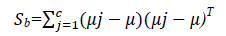
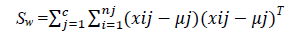
Where xij is the ith sample of class j, μj is the mean of class j, and nj the number of samples in class j.
Where μ is the total mean.
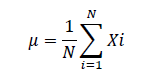
μi is the mean of class 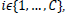 N is the number of samples.
N is the number of samples.
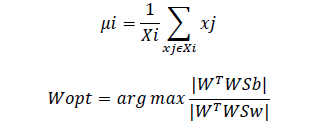
solving the General Eigenvalue Problem:
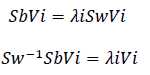
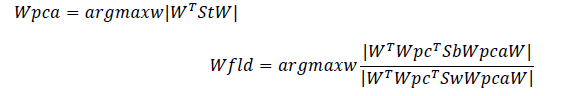
The transformation matrix W that projects a sample into the (c-1) dimensional space is then given by:
W=WTfldWTpca
Viola Jones
This algorithm is a combination of three algorithms:
1. Viola Jones for detection.
2. HOG for recognition.
3. SVM for classification.
Viola Jones for detection:
The Viola-Jones face detector is based on the following ideas:
1. The image integral.
2. Classifier learning with Ada Boost.
3. Attentional cascade structure.
The main objective of Viola-Jones face detection algorithm is to transform the input image into an integral image. The integral image scaled from 0 to 10 depending on the darkness. Integral image efficiently computes the sum of pixels in a rectangular subset to finally make a decision of considering it to be a haar like feature. The Viola Jones uses Adaptive Boosting to select a small set of features to train the classifier. A single AdaBoost classifier consists of a weighted sum of many weak classifiers, where each weak classifier is a threshold on a single Haar-like rectangular feature. The weight associated with given sample is adjusted on the basis of whether or not weak classifier correctly classifies the sample. Also Cascading can be used instead of an AdaBoost. Ebenezer and Qi (2014) have used neural-AdaBoost .The Viola Jones Algorithms could thus be used to crop the faces and get rid of extraneous part of the image.
Histogram of Gradients (HOG) & Support Vector Machines (SVM)
The most frequent problem in recognizing the face arises due to pose variations, and different illumination conditions and so on. Arya et al. (2016) has used HOG and self-organizing maps for facial recognition. Julina and Sharmila (2017) have researched on facial recognition using histogram of gradients and support vector machines. The combination of HOG and SVM can overcome all of these challenges. The HOG descriptor is invariant to lighting conditions. Hence it can overcome the problem of varying illumination. It is used to extract the magnitude of edge information and it works well even during the variations in poses and the illumination conditions. HOG works well under such challenging situations as it represents directionality of edge information thereby making it significant for the study of pattern and structure of the interested object. The combination of HOG and SVM yields improvement of detection accuracy. The HOG technique counts the number of occurrences of gradient orientation in the normalized portions of an image called detection window.
The implementation HOG descriptor algorithm is as follows:
1. We first divide the input image into small connected regions called cells, and for each cell a histogram of gradient directions or edge orientations for the pixels within the cell is computed.
2. Then convert each cell into angular bins according to the gradient orientation.
3. Each pixel of a cell contributes weighted gradient to its corresponding angular bin.
4. The adjacent group of cells is then treated as spatial regions known as blocks. Each block of grouped cell is considered as the basis for grouping and normalization of histograms.
The normalized group of histograms represents the block histogram and the set of these block histograms represents the descriptor.
Methodology to test the above combination of algorithms:
1. Reading images from the databases.
2. Partitioning the database into training set and test set to perform cross validation.
3. Feature Extraction using HOG.
4. Build a classification model using the SVM classifier.
5. Predict the test images.
Statement Of Contribution
Every customer desires for better offerings and discounts whenever he/she visit any retail stores. Due to lack of proper channels and techniques consumers do not get proper recognition and benefits. This article uses the facial Recognition framework to distinguish between different customers based on facial features. Having identified and distinguished the faces through different techniques from the database based on his/her brand loyalty and number of the visits to a retail store he/she availed benefits or discounts. We are creating an algorithm to capture customer’s facial features based on different techniques for face detection such as Eigenfaces algorithm and Fisher's LDA mechanism in order to classify the buyer's as high, mid and low potential groups and accordingly take a decision. Further time series analysis will be used to predict person's probability of his/her next purchase. Further, our research will use different types of regression to determine the significant variables affecting person’s purchasing behavior.
Conclusion
This research review’s purpose is to help the reader to understand different algorithms in order to detect the face of an individual. The most commonly and used mechanism for face detection is Eigen faces algorithm but however we will go through a couple of other algorithms in order to determine better accuracy in face recognition which will our prime goal. Then we will use Fisher’s LDA mechanism in order to classify the buyer’s as high, mid and low potential groups and accordingly take decision based on that. A time series analysis will be done in order to predict person’s probability of his/her next purchase. We will further move our research in using different types of regression to determine the significant variables putting an effect on a person’s purchasing behaviour.
Acknowledgement
We thank Prof. Dr. Siba Panda, for his comments on an earlier draft of this paper, his insights and experiences added considerable valuable.
References
- Arya, K.V., Upadhyay, G., Upadhyay, S., Tiwari, S., & Sharma, P. (2016). Facial recognition using histogram of Gabor phase patterns and self-organizing maps. 11th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Roorkee.
- Debasmita, M. (2017). Detection and facial recognition for investigation. King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok.
- Ebenezer, O., Yongzhao, Z., & Qi R.M. (2014). A neural-AdaBoost based facial expression recognition system, Jiangsu University.
- Jiachen, C., & Kenneth, J.W. (2017). Facial recognition with PCA and machine learning methods. School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Pennsylvania State University.
- Julina, J.K.J., & Sharmila, T.S. (2017). Facial recognition using histogram of gradients and support vector machines. International Conference on Computer, Communication and Signal Processing (ICCCSP), Chennai.
- Muge, C., & Figen, O. (2012). A face recognition system based on Eigen faces method. Halic University,Turkey.
- Quan-xue, G., Lei, Z., & David, Z. (2008). Face recognition using FLDA with single training image per person, Applied Mathematics and Computation. A Biometrics Research Centre, Department of Computing: The Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
- Shereena, T.K., & Ashok, B. (2014). Face recognition system by integrating PCA, FLDA, Artificial Neural Networks & Minimum Euclidean Distance. School of Computer Sciences, M G University, kerela.