Review Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
A Study on Consumer's Perception towards Digital Payments In Rural and Urban Areas
Balaji Ch, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Meghana K., Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Dheeraj Sai V, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Citation Information: Balaji, C.H., Meghana, K., & Dheeraj Sai, V. (2022). A study on consumer’s perception towards digital payments in rural and urban areas. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(5), 1-10.
Abstract
Demonetization of Rs. 500 and Rs. 1000 currency notes was one of the most significant international events of the year 2016. The last few years has seen tremendous growth in use of digital payments in India. Demonetization created huge growth opportunity for digital payment in India and the digital wallet companies garbed the opportunities with both the hands to expand their market share. In recent days many changes took place in the payment system like digital wallets, UPI and BHIM apps for smooth shift to digital payments. Payment gateways have emerged as the most significant contributor in pushing Cashless and electronic payments. The financial transaction has increased due to digital payment in India. The structured questionnaire was used as research tool for understanding consumer perception of digital payment. The objective of this research paper is to study the positive impact that Digitization of payment system. The present paper focuses on the analysis of the adoption level of these digital payment systems by customers using survey method to know opinion of the people regarding digital payment in rural and urban areas.
Keywords
Digital Payments, Demonetization, E-Payments, Online Payments.
Introduction
Digital Payments
The Government of India has been taking several measures to promote and encourage digital payments in the country. As part of the ‘Digital India’ campaign, the government aims to create a ‘digitally empowered’ economy that is ‘Faceless, Paperless, and Cashless’. There are various types and modes of digital payments. Some of these include the use of debit/credit cards, internet banking, mobile wallets, digital payment apps, Unified Payments Interface (UPI) service, Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD), Bank prepaid cards, mobile banking, etc. A digital payment occurs when goods or services are purchased through the use of various electronic mediums. There is no use of cash or cheques in this type of payment method.
These initiatives have provided extensive boost up to the digital payment system in the country. Government’s other initiatives like BHIM and UPI are supporting in transition and faster adoption of digital payments. Electronics Consumer transaction made at point of sale (POS) for services and products either through internet banking or mobile banking using smart phone or card payment are called as digital payment.
Review of Literature
Demonetization created huge growth opportunity for digital payment in India and the digital wallet companies garbed the opportunities with both the hands to expand their market share. In recent days many changes took place in the payment system like digital wallets, UPI and BHIM apps for smooth shift to digital payments. Payment gateways have emerged as the most significant contributor in pushing Cashless and electronic payments. The study is conducted in Hyderabad region. A sample size of 200 was selected using the convenience sampling. Out of which 183 were responded. Structured questionnaires are used for collecting data. The responses from the respondents were analysed using the simple percentage analysis and Chi square test. It indicate that the deployment of technology for digital payments have improved the performance of banking sector and able to achieve the motive cash less country. It gives emphasis to the percentage of awareness on maximum utilization of technology. Banks should take effective measures in creating awareness towards the effective usage of technology and security.
The present development of ITC in rural Karnataka by Government bodies as well as private sectors was studied through primary data collection. The variables that influence the customer’s adoption of Digital Payment System was identified from literature and verified through a questionnaire survey from two rural areas in Karnataka, viz. Nelamangala & Bidadi. The data collected through survey underwent a statistical analysis to arrive at the major difficulties in adoption of DPS at Nelamanagala & Bidadi. It indicate that the deployment of technology for digital payments have improved the performance of banking sector and able to achieve the motive cash less country. It gives emphasis to the percentage of awareness on maximum utilization of technology. Banks should take effective measures in creating awareness towards the effective usage of technology and security (Murali 2006).
The debit/credit card is one of the popular modes for digital payment among samples. Afterwards people preferred UPI for digital payments. The most of people are satisfied by using various modes of digital payments. The many people satisfied from mobile banking used. The most of people used digital payment for online shopping, reason behind that online shopping various discounts are available on digital payment. The second purpose of digital payments is money transfer.
Methodology
Need for Study
Digital Payments is the most popular platform for usage of money. It communicates with the entire world which can result in recognition. As my project is management consumer’s perception towards digital payments, this study is helpful in finding the consumer’s perception and causing factors behind the perception. This study is useful in identifying whether the perception of consumers is positive or negative.
Problem Statement
1. The problem of the study was to determine is there any impact of demonetization in rural and urban areas.
2. The problem of the study was to determine is there any impact of consumer perception on digital payments.
Objectives of the Study
3. To compare the usage of digital payments in rural and urban areas.
4. To determine the difficulties encountered in adoption of digital payment system and the technological drawbacks associated with it in rural and urban areas.
5. To suggest various measures to promote digital payments in rural areas.
Scope of the Study
6. The research is confined to only in and around Gudivada region.
7. This study is based on consumer’s perception towards digital payments in rural and urban areas.
8. The activities involved in this study are knowing the perception of the consumer’s and impact of demographic profile towards these payments.
Limitations of the Study
9. The main limitation in this study is considering only five types of digital payment platforms.
10. The second limitation is this study is confined to in and around Gudivada region.
11. There is limited sample size and limited time in research.
Research Design
The research design used in this study are EXPLORATORY RESEARCH DESIGN. Exploratory research, as the name implies, intends merely to explore the research questions and does not intend to offer final and conclusive solutions to existing problems. This type of research is usually conducted to study a problem that has not been clearly defined yet.
Method
Descriptive Research Method is used in this study Descriptive research is defined as a research method that describes the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This methodology focuses more on the "thing" of the research subject than on the "why" of the research subject. In other words, descriptive research focuses mainly on the description of the nature of a demographic segment, without focusing on "why" a particular phenomenon occurs. In other words, it "describes" the subject of the investigation, without covering "why" it happens.
Data Collection Techniques
Primary data is collected from the closed ended questionnaire and secondary data from articles, journals and industry report. Here primary data is collected for the analysis. Here I used self-administrated survey as the primary data. A primary data source is an original data source, in which the researcher collects the data in the first person for a specific purpose or a research project. The collection of primary data is quite expensive and time-consuming compared to the collection of secondary data.
Data Collection Instrument
Schedule tool is used for gathering the data. A program is a structure of a series of questions about a particular topic that the interviewer or researcher asks them personally. The order of the questions, the language of the questions and the arrangement of the parts of the program are not changed. However, the researcher can explain the questions if the respondent faces some difficulty and contains direct questions and questions in tabular form. The schedule includes open-ended questions and closed-ended questions and questions used in this study are closed-ended questions.
Sampling Technique
Convenient sampling is considered best for this study. The sampling of convenience is a non-probabilistic sampling technique in which the subjects are selected because of their convenient accessibility and proximity to the researcher.
Sample size: Sample size is 200 and the sample size is a count of individual samples or observations in any statistical environment, such as a scientific experiment or a public opinion survey.
Respondents: Respondents from my study are employees who are working in different companies Table 1.
| Table 1 The Frequency Tables and Bar Charts are Obtained for Demographic Factors | |||
| Variable | Characteristics | Frequency | Percentage |
| Gender | Male | 108 | 72 |
| Female | 42 | 28 | |
| Age group | 20-30 yrs | 66 | 44 |
| 31-40 yrs | 42 | 28 | |
| 41-50 yrs | 24 | 16 | |
| 51 yrs & above | 18 | 12 | |
| Education | Post-Graduation | 12 | 8 |
| Graduation | 78 | 52 | |
| 10+2 | 55 | 22 | |
| Matriculation or below | 27 | 18 | |
| Profession | Student | 15 | 10 |
| Private Sector Employee | 66 | 44 | |
| Public Sector Employee | 36 | 24 | |
| Self Employed | 21 | 14 | |
| Others | 12 | 8 | |
| Annual Income | Upto 2.5 Lacs | 8 | 5.3 |
| 2.5-5 Lacs | 6 | 4 | |
| 5-7.5 Lacs | 32 | 21.3 | |
| 7.5-10 Lac | 95 | 63.3 | |
| 10Lacs & above | 9 | 6 | |
Data Analysis
Descriptive Analysis
Statistically Analysis
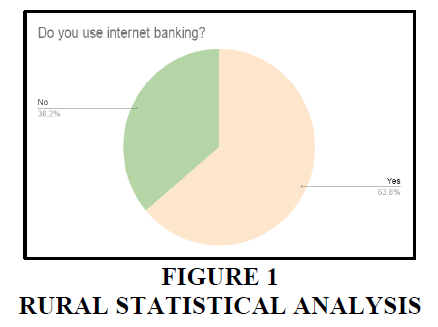
Rural
1. 63.8% of the people in rural areas are using internet banking. 36.2% people in rural areas are yet to use the internet banking. The percentage of usage of internet banking in rural areas is very less compared to urban areas.
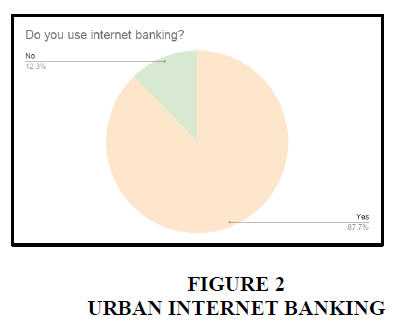
Urban
2. 87.7% of the people are using internet banking. 12.3% people of the people do not use internet banking. The percentages of people using internet banking in urban areas are more compared to rural areas.
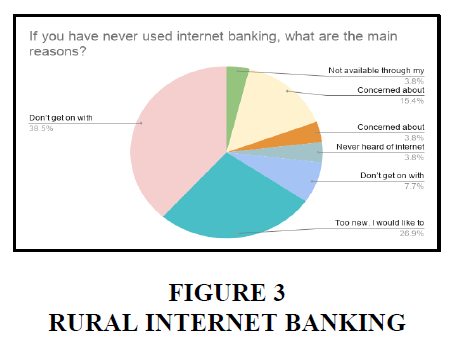
Rural
3. 38.5% of people in rural areas responded they don’t get on with on technology. 15.4% of people responded about concerned about security. 26.9% of the people felt that they are too new to the technology and they would like to try internet banking. 3.8% of the people never heard of the internet banking in rural areas.
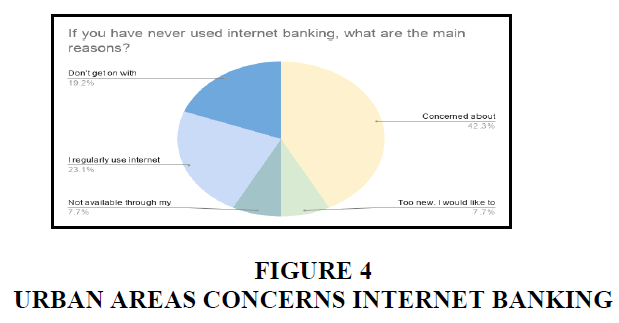
Urban
In urban areas, 42.3% of the people are concerned about security and 23.1% of the people uses the digital payments every day. 7.7% of the people want to use the digital payments but they are too new. 19% of the people don’t get on with the technology
Tatineni & Balaji, (2020)
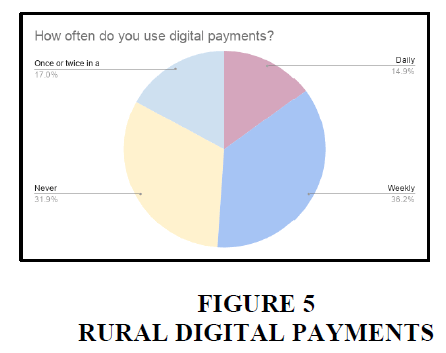
Rural
In rural areas, only 14% of the people are using digital payments daily. And 36% of the people are using weekly. 17% of the people uses digital payments once or twice in a month. And 31.9% of people in rural areas never uses digital payments.
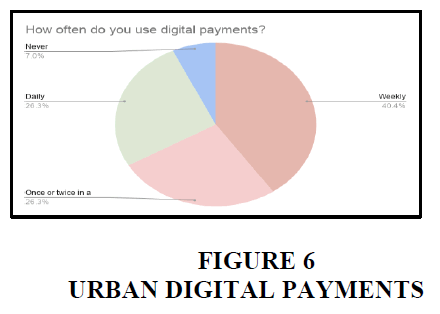
Urban
In urban areas, 26.3% of the people uses digital payments daily and 40.4% of the people uses it weekly. 26.3% of the people uses once or twice in a month. Only 7% of the people never uses digital payments in urban areas.
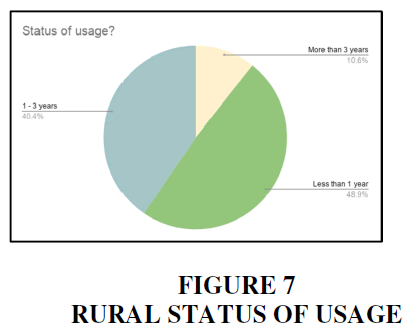
Rural
In rural areas, 48.9% of the people are using it since last one year only. 10.6% of the people in rural areas are using it since more than 3 years. And 40.4% of the people are using in between from 1 to 3 years.
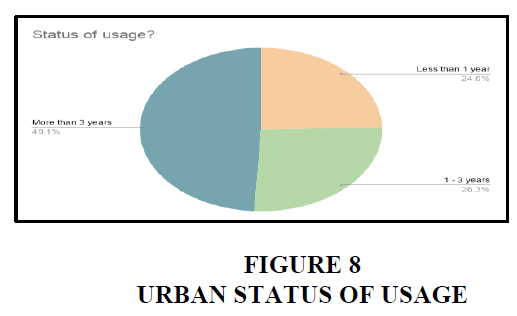
Urban
In urban areas, 49% of the people are using it since more than 3 years. 26.3% of the people are using in between from 1 to 3 years. 24.6% of people are using since less than a year only.
Rural
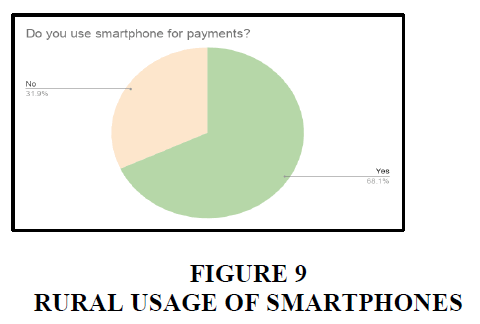
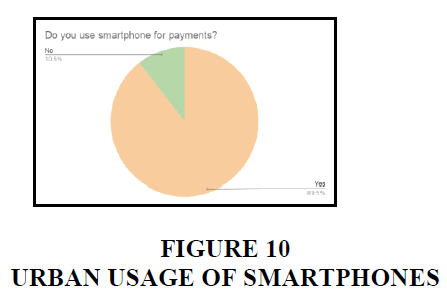
In rural areas, 32% of the people are not using smart phones Figures 1-5.
Urban
In urban areas, 89% of the people uses smart phone.
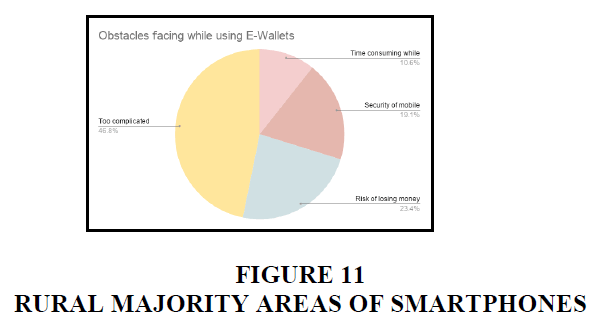
Rural
In rural areas, majority of the responded that it is too complicated to use digital payments. 23.4% of the people are afraid of losing money. 19.1% of people are concerned with the security of mobile. 10.6% of the people felt that it is time consuming.
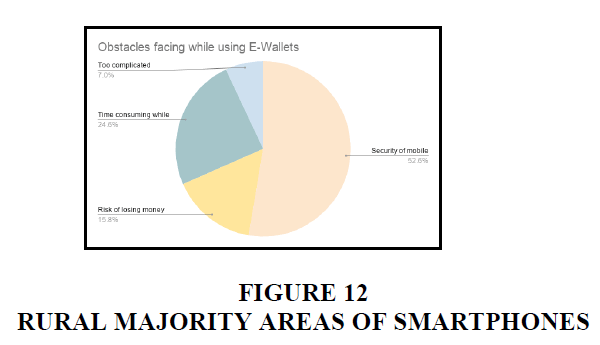
Urban
In urban areas, majority of the people are concerned about the security of mobile while using digital payments. 24.6% of the people felt that it is time consuming. 15.8% are afraid of losing money. And 7% of the people felt that it is too complicated Figures 6-14.
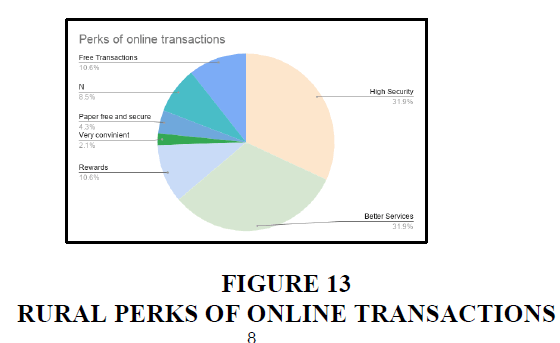
Rural
In rural areas, 32% of the people responded that they use mobile wallets because of the better services and high security. 10.6% of the people uses it because of free transactions. 4.3% of people feel that they are secure. And 10.6% of the people uses it for rewards.
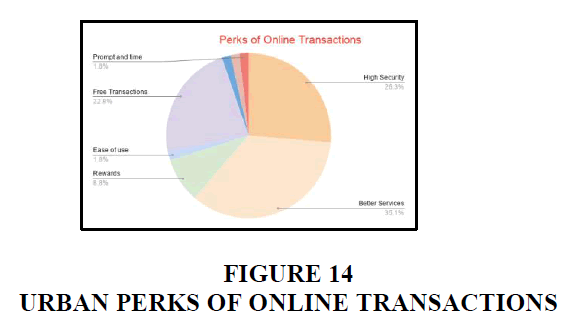
Urban
In urban areas, majority of the people uses online transactions because of better services, free transactions and high security. 8.8% of the people uses it for rewards. And only 1.8% of people uses because of its ease in payments.
Results and Discussion
4. 63.8% of the people in rural areas are using internet banking.
5. 87.7% of the people are using internet banking. 12.3% people of the people do not use internet banking.
6. 38.5% of people in rural areas responded they don’t get on with on technology. 15.4% of people responded about concerned about security.
7. In urban areas, 42.3% of the people are concerned about security and 23.1% of the people uses the digital payments every day. 7.7% of the people want to use the digital payments but they are too new.
8. In rural areas, only 14% of the people are using digital payments daily. And 36% of the people are using weekly.
9. In urban areas, 26.3% of the people uses digital payments daily and 40.4% of the people uses it weekly.
Findings
In Urban Areas
1. There is a rise of use in digital payments after demonetization.
2. 87.7% of people uses internet banking and the remaining are not using mainly because of the concern about security.
3. Uses for money transfer, bills payment, food, travelling.
4. Majority are concerned about security of mobile and too much time taken to process.
In Rural Areas
1. In rural areas, there is a rise in use of digital payments from past 1 – 3 years.
2. Uses for money transfers.
3. Don’t get on with technology.
4. Most of the Indian people buying goods and services only for cash based transaction habits in rural area; they need not go digital payments system either through using debit card or credit card or ETGS or any other.
5. Awareness programme would be conducted in rural area about using the digital payments like Smartphone based transactions.
6. The other important issue of digital payments is the lack of technology used in the rural people and also reach of technology to various locations.
7. Service providers will have to constantly invest in technology in order to improve security and ease of transaction. People will only shift when it’s easier, certain and safe to make cashless transactions.
Conclusion
From the above analysis it also appears that many people actually agree with the government on the usefulness of cashless economy as it helps to fight against terrorism, corruption, money laundering but one biggest problem in the working of cashless economy in India is cybercrime and illegal access to primary data. Therefore it’s important to strengthen Internet Security from protection against online fraud. Large number of population is still below literacy rate living in rural areas. For smooth implementation of cash less system in India, the following measures are recommended Government have to bring transparency and efficiency in payment system, strategies used by government and RBI to encourage cashless transactions by licensing payment banks, promoting mobile wallets and withdrawing service charge on cards and digital payments. A financial literacy campaign should be conducted by government time to time to make population aware of benefits of electronic payments.
References
Babu, P. R., Rao, P. V. D., & Balaji, C. H. Performance evaluation and its sustainability of flipkart start-up company in india.
Balaji, C., Venkateswara Kumar, K. S., Lalitha Devi, G., Pravallika, S., & Harika, K. (2019). Impact of acquisitions on financial performance of selected softwarecompanies in India. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(9), 2415-2419.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Balaji, C., Srikanth, A., & Babu, P. R. A Behavioural Study on Impact of FII and DII on Indian Stock Market.
Balaji, C., Rao, P. D., Rekha, Y. C., & Basheerunisa, S. (2019). Technological relationship between banknifty and other selected sectorial indices of NSE. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(3), 2314-2318.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Murali Krishna, N. (2006). Business process reengineering case of MPLS VPN service in BSNL.
Palani, M., & Kamaraju, S. (2017). The impact of service quality on customer satisfaction with mobile phone services of bsnl, thanjavur district of tamilnadu.
Patnaik, P. K. R., Balaji, C., & Narayana, MS (2019). Technological relationship between capital structure and financial efficiency in ACC Ltd. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(11), 2009-2013.
Tatineni, M. S. R., & Balaji, C. (2020). Mergers, acquisition and the strategies along with case studies of India. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 17(9), 1250-1257.
Received: 08-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12156; Editor assigned: 13-Jun-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-12156(PQ); Reviewed: 27-Jun-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-12156; Revised: 04-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12156(R); Published: 11-Jul-2022