Review Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
A Study on the Impact of Human Resource Management Practices on Employee Performance
Sailaja VN, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation Deemed to be University
Vaishnavi M, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation Deemed to be University
Sai Krishna T, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation Deemed to be University
Citation Information: Sailaja, V.N Vaishnavi, M., Sai Krishna T., (2022). A study on the impact of human resource management practices on employee performance. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(5), 1-14.
Abstract
Human resources will be forced to labor under more stressful situations unless and until the organization delivers the best HRMP to its employees, resulting in poor performance and job satisfaction. This research investigates the impact of human resource management practices on employee performance and job satisfaction. A standardized questionnaire was used to interview 229 volunteers from various organizations. The topic is investigated using correlation and linear regression in this research. The results demonstrate that a variety of dependent factors, such as age, education, and current work experience, have a significant moderating effect on the relationship between HRM practices and employee performance. When mediation is employed, job satisfaction is unrelated to HR management practices.
Keywords
Career Planning, Compensation, Employee Performance, Job Satisfaction, Performance Appraisal, Selection, Training.
Introduction
Businesses must continually seek out fresh ideas to be competitive in today's fast-paced, ever-changing economy. Because of its capacity to give the company with a competitive edge, HR has become a more important component of the business than any other organization has ever seen. As a result of globalization and new technology, the shift to an information-based economy and the quick entry of new competitors into well-established markets are becoming more essential. This highlights the need of good HRM in accomplishing organizational objectives. Furthermore, since the quality of government workers' work has a considerable influence on the government's capacity to operate, the issue of how officers near government authorities do their duties has overtaken the question of how well neighboring authorities perform their tasks. As a consequence, the government has devised criteria for assessing a company's success based on its employees' performance. Furthermore, directors and academics will put a higher value on job performance. Being able to efficiently manage an organization's human resources is crucial in today's business world. HRM practices have an impact on a company's ability to gain a long-term competitive edge. Human resources are managed effectively and efficiently.
Review of Literature
Esmael et al. (2016) Evaluated the impact of HRM policies on organisational commitment and employee performance. In this model, the Chi-square concept was applied. There is a link between human resource management and employee performance, according to study. Furthermore, the research discovered that organizational commitment has a bigger indirect impact on HRM than it has a direct one.
Wahidha Begum, F. Dr. M. Shiek Mohamed, and others looked at how HRM practises in the industry affect employee happiness and performance in 2016. The goal of the research was to evaluate how HR practises in Tiruchirappalli BPO (Company Process Outsourcing) companies affect employee satisfaction and business success. According to data, HRM practises, employee happiness, and an organization's success are all linked Begum (2016).
What role does high-performance human resources play in ensuring employee satisfaction at work? Gurbuz Sait is a fictional character created by Gurbuz (2009). The goal of this study is to determine how effective HR (human resources) activities may boost people's job satisfaction. This model used stepwise multiple regression analysis using standard deviations. The study's flaws are emphasised, as well as recommendations for further research. We look at what this means in terms of a high-performing HR strategy and staff retention.
Satisfy Yousef alsafadi, Shadi Altahat, The impact of Human Resource Management Practices (HRMP) on Employee Performance (EP) is investigated using Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). IBM, SPSS, and AMOS are examples of statistical techniques. This study's results highlight the significance of job satisfaction and employee engagement in human resource performance.
Mustafa Fedai AVU, Turgay Saracoglu, Murat KO (2014). Organizational Commitment, Human Resource Management Practices, and Job Satisfaction The goal of this study is to determine how HRM practises, job satisfaction, and intentions to stay with a company affect employees in private Turkish enterprises. Coefficients, means, standard deviations, and correlations are all used in multiple regression analysis. Employee happiness and loyalty are boosted by HRM practices such as hiring and firing, training and development, wage and benefits, and performance assessments, according to the research.
Mira et al. (2019) Employee performance is influenced by employee satisfaction and HR management practises. The goal of this research is to find out how human resource practises including training and development, incentives, job analysis, social support, recruiting and selection, employee connection and empowerment, and employee happiness affect employee performance. A measurement model is used to examine the data's validity and reliability. The purpose of this study was to see how the Saudi Arabia Port Authority's human resource policies affect worker happiness and performance.
Shabbir Malik, Shahzad, a year ago how human resources are managed in Pakistan's pharmaceutical business has an impact on employees' opinions of their own performance. The goal of this study is to evaluate how these three human resource management practices effect employee job satisfaction. According to the results of each regression analysis, compensation has a considerable influence on how people see their own performance.
Amer Abehantash (2019). A Case Study of Bank of Texas Human Resource Management Practices and Job Performances The goal of this research is to create a conceptual framework that incorporates five Human Resources Management (HRM) practises, such as supervision, job training, and pay practices, job satisfaction, and turnover absenteeism, as well as to explain and relate the relationships between these variables. The goal of this study is to find out how human resource management practices in the Texas private banking sector influence job satisfaction and how to measure it.
Kamran Ahmad is a Pakistani Muslim who now resides in the United States.
Mumtaz, Rizwan Jawaid, and Khurram Umar Mehtab (Umar Mehtab) are among Mumtaz's friends (2005) HR practises are influenced by how well individuals do their jobs. The goal of this study is to see whether there is a link between employee opinions of their own performance and how promotions are handled in the banking industry in Pakistan. This research will assist bank executives in adopting or altering rules and practises that will help their employees perform their jobs more efficiently.
Purohit et al. (2014). HR practises in textile divisions have an impact on managers' job satisfaction. The goal of this study is to show that good human resource management is a crucial strategy for textile companies in Haryana, India, to keep its managers pleased. A five-point Likert scale was used to analyse the data. Tehmina Sattar, Khalil Ahmad, Syeda Mahnaz Hassan, and Khalil Ahmad address a critical gap in the literature by concentrating on more localised outcomes that have a major influence on the link between HR practices and employee satisfaction (2015). Employee engagement reduces the negative effects of HR practices on employee productivity and pleasure at work. The goal of this study is to explore how employee engagement influences employee satisfaction and performance. Employee training and empowerment, rather than rewards and incentives, have a higher influence on how well they perform and how happy they are at work, according to the conclusions of this study Ali (2019).
Evidence on HR Policies and Practices' Effects on Employee Job Satisfaction, Amir Ali Khushk, Pakistan Telecommunications Ltd. (PTCL), Hyderabad (2015). The goal of the research was to evaluate how HR policies and procedures affect employee job satisfaction in terms of compensation and performance. This research will address a gap in the literature by giving information on how the pay and performance functions of human resources work. Management should adopt fair and equitable pay regulations, as well as a performance assessment system that decreases bias at all levels, according to the conclusions of this study Sattar et al. (2015).
Objectives
1. Consider how employee productivity is affected by human resource management.
2. The purpose of this research is to see how demographic characteristics influence the link between HRM and employee performance by using moderating effect.
3. The purpose of this research is to see how work happiness influences the link between HR and employee performance by using mediating effect.
4. The goal of this study is to find out how demographics and work satisfaction affect the relationship between HRM practices and employee performance by using mediating and moderating effect Figures 1 and 2.
Ho1: Techniques used in HRM have no statistically significant impact on employee performance.
Ho2: Demographic characteristics have little bearing on the link between HR management practices and
employee performance.
Ho3: The relationship between HRM and employee performance is unaffected by job contentment.
Ho4: The association between HRM practices and employee performance is unaffected by demographic
characteristics or job happiness.
Data analysis and interpretations
Ho1: Human resource management techniques have no statistically meaningful effect on employee
performance.
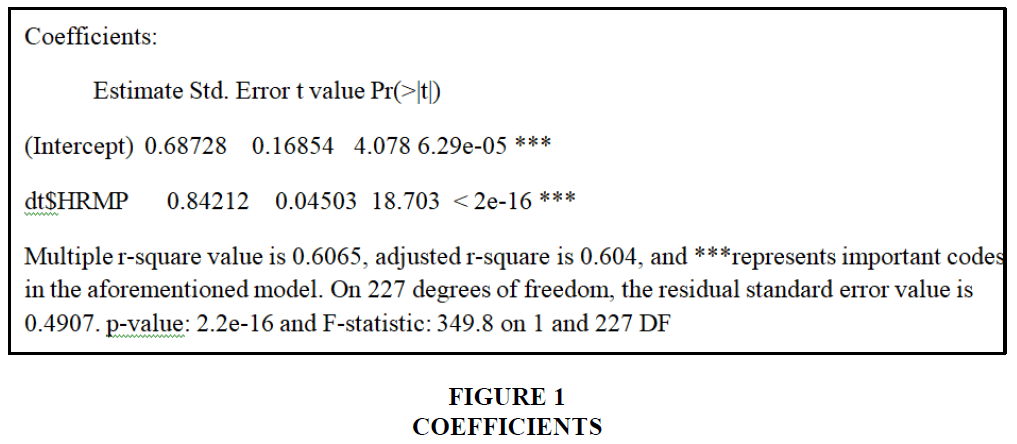
HR, according to the study's findings, have an influence on how well employees do their professions. The data is analyzed using linear regression since the p-value is less than 0.05. As a consequence, HRM has no statistically meaningful influence on how well employees do their jobs Figures 3 and 4.
Ho2: Demographic considerations have little bearing on the relationship between HRM and employee
performance.
Using Moderation Method for Following Dependent Variables
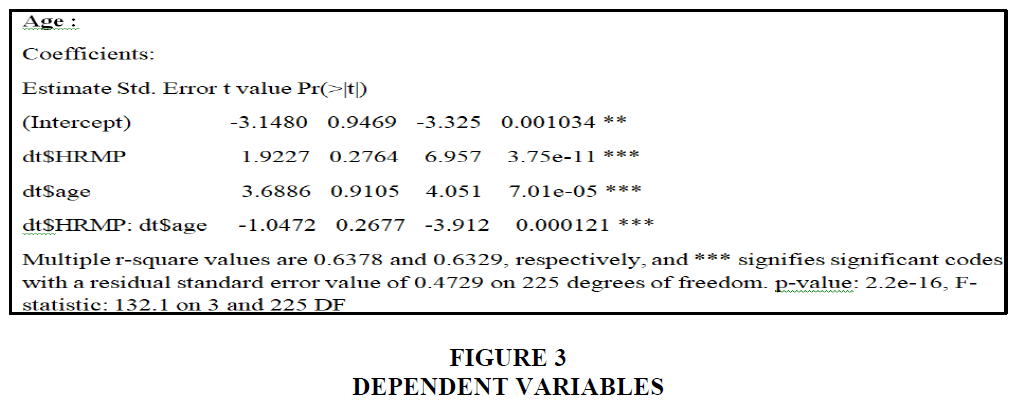
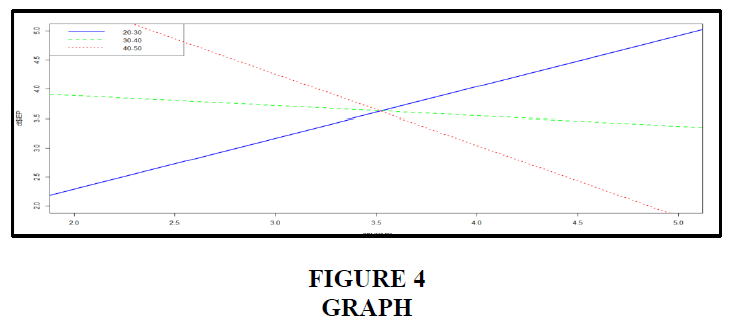
The bulk of individuals who replied, according to the graph above, are between the ages of 20 and 30, accounting for 86.5 percent of the total. The second-largest age group, 30–40, represents 9.6% of the population, while the third-largest, 40–50, represents 3.5 percent. The blue line represents the age group 20–30, the green line represents the age group 30–40, and the red line represents the age group 40–50, all having a p-value of 0.001, or 0.001034. In this case, the house is valued $3.75. In this example, the p-value is 0.01. Age is a significant mediator in the relationship between hrmp and employee performance Figures 5 and 6.
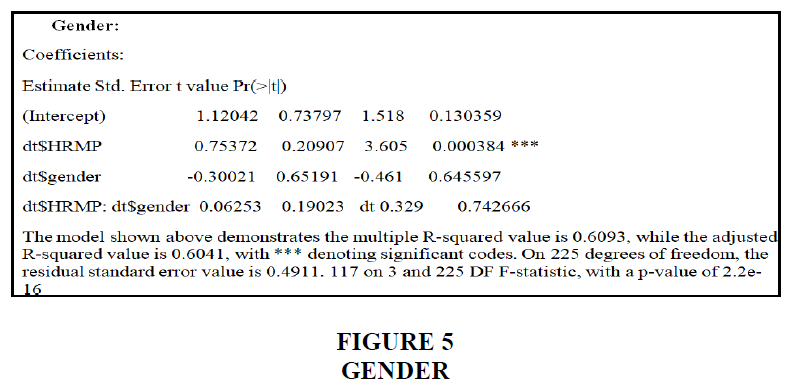
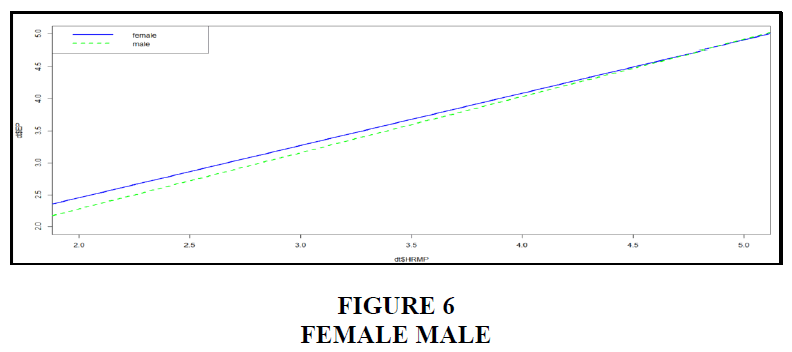
As seen in the graph above, men make up the majority of the responses (57.6%). Female workers make up the second biggest group of responders, accounting for 42.4% of all replies, due to the fact that there are more males than women working at the organization. As a consequence, males have responded in greater numbers. The lady is represented by the blue line, while the guy is represented by the green line. Because the p-value is more than 0.05, the result is null. Gender isn't a moderator in this case. It has nothing to do with employee productivity or HR management. Because the p-value is bigger than 0.742666, it has no effect Figures 7 and 8.
Graph
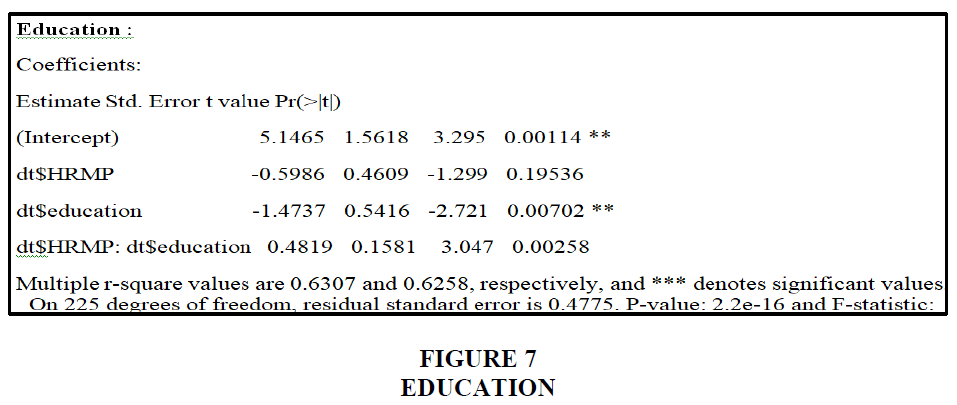
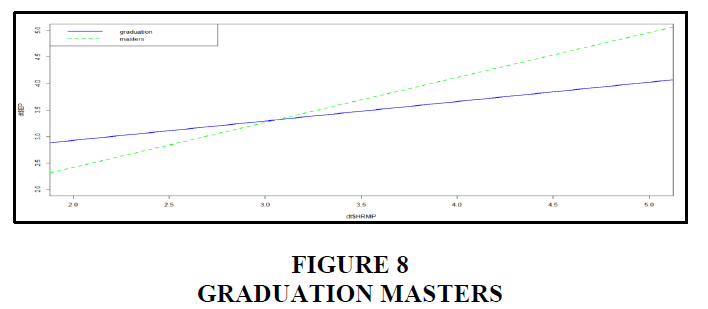
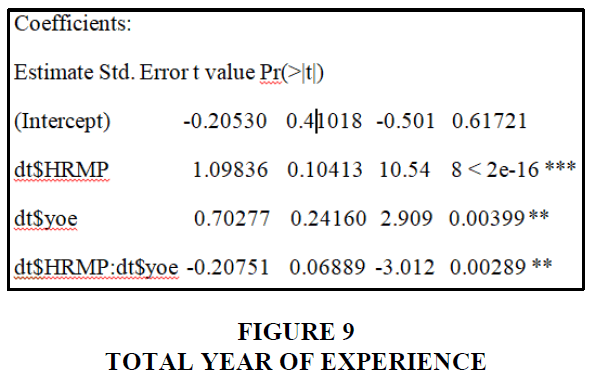
The majority of people who answered held both a master's and a bachelor's degree, as seen in the graph above. In reality, 59% have a master's degree and 41% have a bachelor's degree. A blue line represents someone with a bachelor's degree, while a green line represents someone with a master's degree. With a p-value of 0.01 for 225 degrees of freedom, education is a mediator of the relationship between HR management practices and employee performance Figure 9.
Total Year of Experience
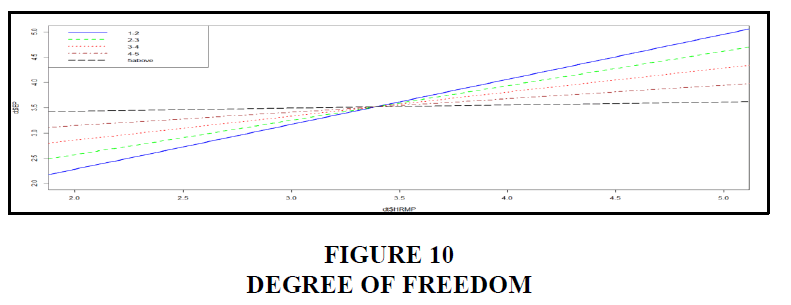
The model has multiple r square values of 0.6221 and 0.6171, with *** denoting significant codes and a residual standard error of 0.483 on the 225 degrees of freedom. P-value: 2.2e-16 and F-statistic: 123.5 on 3 and 225 DF Figure 10.
Graph
The bulk of individuals who replied (29.3%) had only worked for a year or less, as seen in the graph above. The second most common answer, accounting for 28.8% of all responses, is someone with 3–4 years of experience. The third group of responders is those who have worked for at least two years. They make up 26.6 percent of the total population. Those with 3-5 years of experience make up the fourth largest group of responders (12.7 percent). Because there are more people with less experience, employees with less than 5 years of experience make up the majority of responses 2.6 percent Figures 11 and 12.
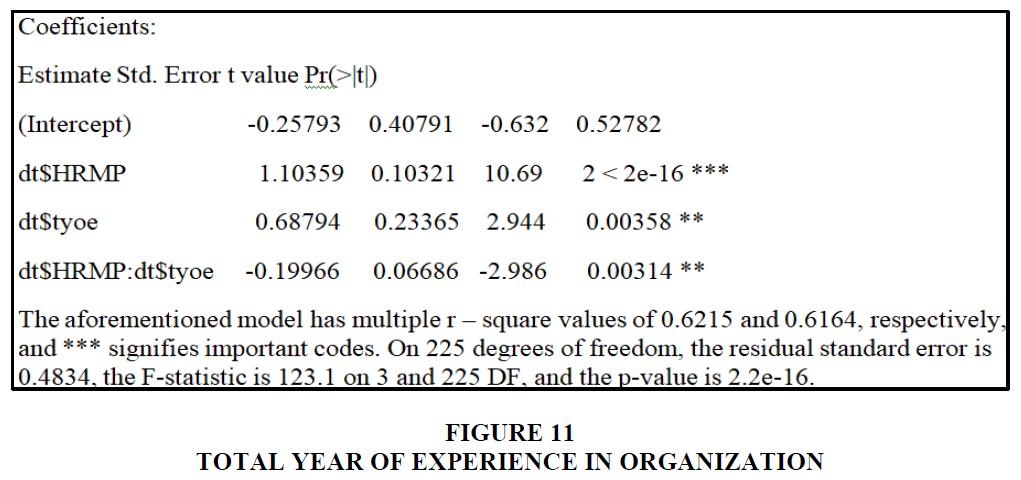
Total year of experience in organization
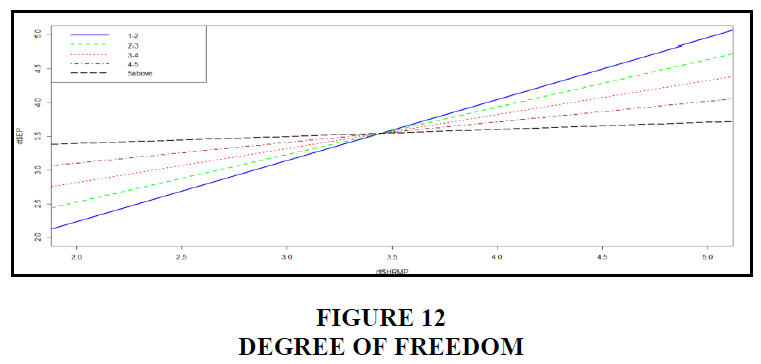
According to the graph, the majority of those who responded, 32.8 percent of the workers, had been with the organization for one to two years. People who had previously worked for a corporation accounted for the second-largest group of respondents. Employees who have been with the organisation for two to three years make up 26.6 percent of the total workforce. The third-largest group of respondents has previously worked for a business. Employees having a three- to four-year tenure with the firm (24%). The vast majority of those who responded had previously worked for a company. Only 2.6% of workers had been with the company for five years or more, while 13% had been there for four to five years. The p-value in this case is more than 0.05. Because it is null, the total number of years an employee has worked for the firm has no impact on hrmp or employee performance Figure 13.
Ho3: Job satisfaction has a little influence on the relationship between HR and employee performance.
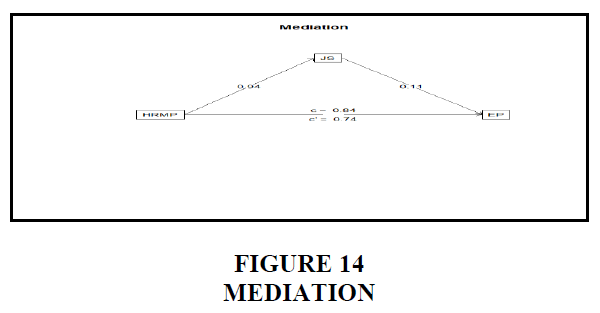
The graph depicts the responses of 229 poll participants: scale, strongly agree, agree, neutral, disagree, and strongly disagree. I use a five-point scale that goes from very high to very low (of 5, 4, and 3,2,1). The great majority of responses Gürbüz (2009) are undecided, with just a small percentage expressing strong agreement. In the mediation research, job satisfaction was shown to be a poor mediator, meaning that no mediation was necessary a resolution reached Figures 14 and 15.
Ho4: Employee happiness and productivity are two dependent variables on which human resource management practises have a little impact.
Variable: Moderator: Age, Mediator: Job Satisfaction
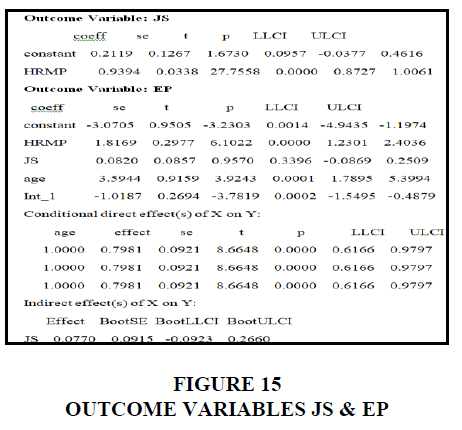
Age is a key modulator of human resource management practices, employee performance, and workplace satisfaction, according to the statistics. X has a direct influence on Y's age of 0.7981 and an indirect effect on Y's work satisfaction of 0.0770. Both the moderating and mediating impacts of human resource management practices on employee performance and job satisfaction are influenced by employee age Figure 16.
Variables Moderator Gender, Mediator Job Satisfaction
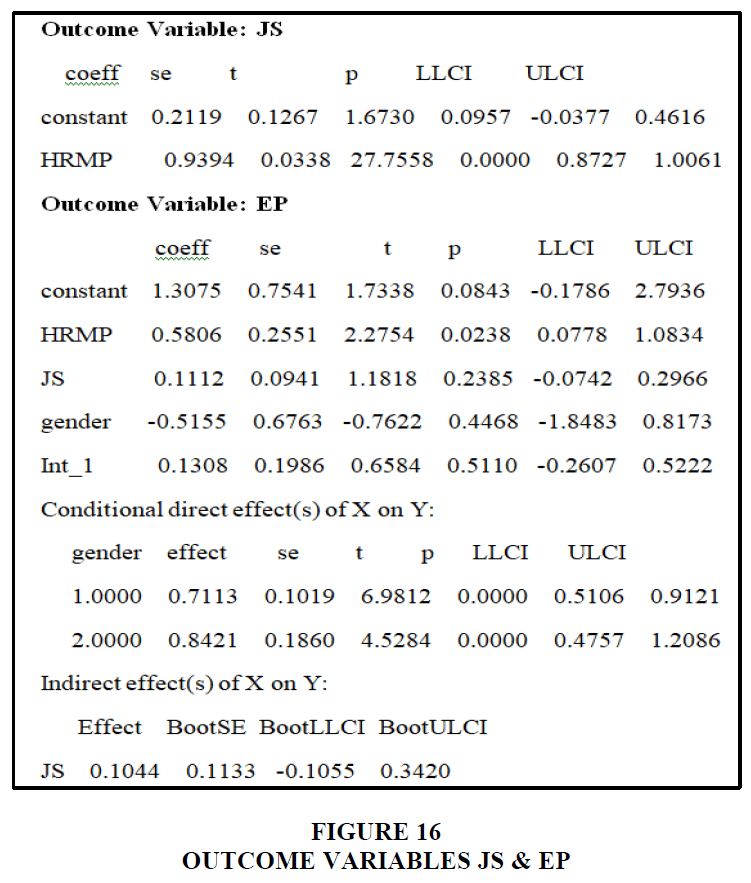
We may deduce from the data that age is a significant modulator of human resource management practices, employee performance, and workplace satisfaction. X has a 0.7981 direct impact on Y's age and a 0.0770 indirect effect on Y's job satisfaction. Employee age influences both the moderating and mediating effects of human resource management practices on employee performance and job satisfaction Figure 17.
Variables Moderator: Education, Mediator: Job Satisfaction
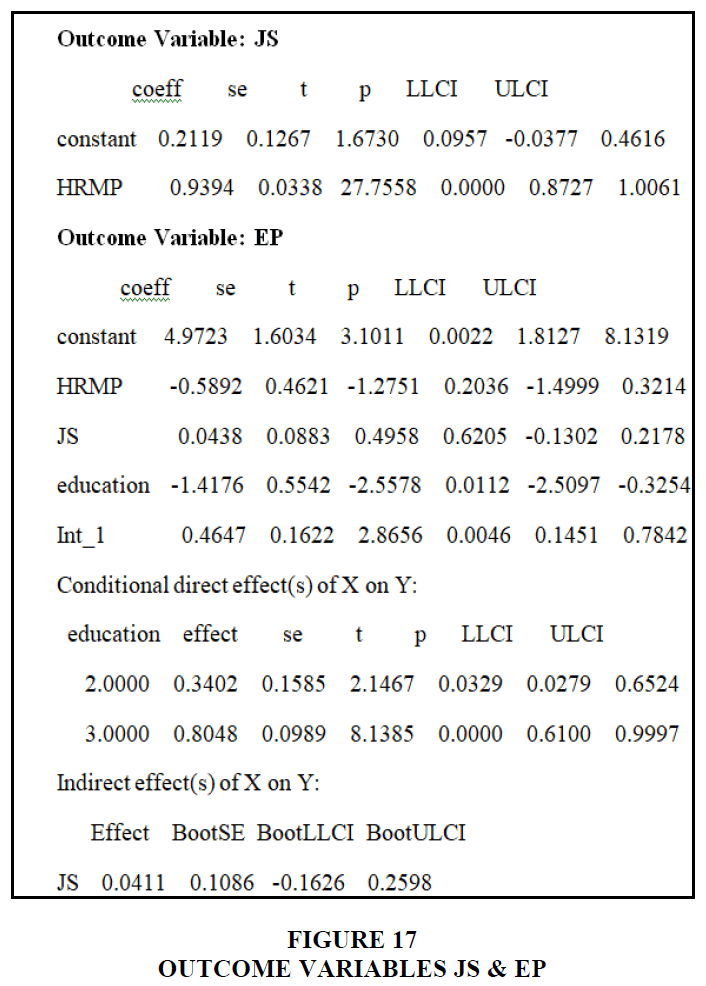
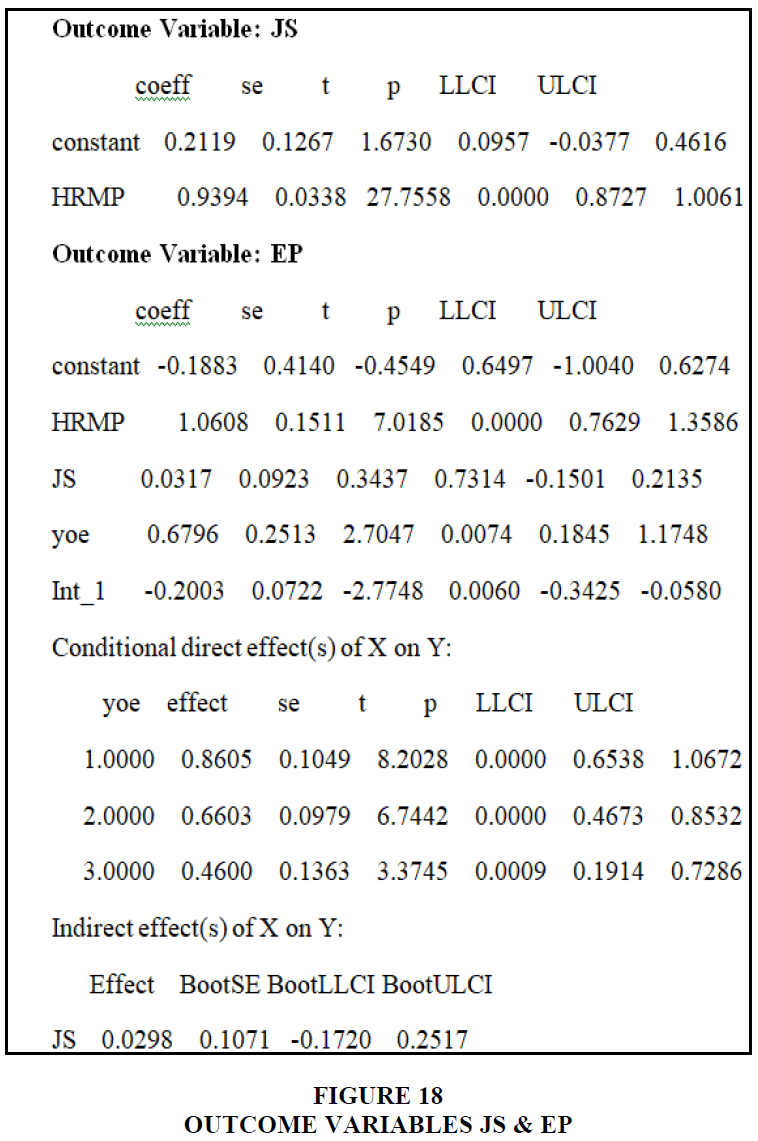
In the aforementioned data, education has a value of -0.3254, hemp has a value of 0.3214, and job happiness has a value of 0.2178, showing that education does not serve as a moderator in signaling job satisfaction of HRM practices on employee performance. On the bootstrapping process, education has a direct impact of 0.3402, 0.8048, and job satisfaction has an indirect effect of 0.0411. The moderator and mediator's effect on human resource management techniques on employee performance and job satisfaction was shown to be insignificant in this research Cherif (2020) Figure 18.
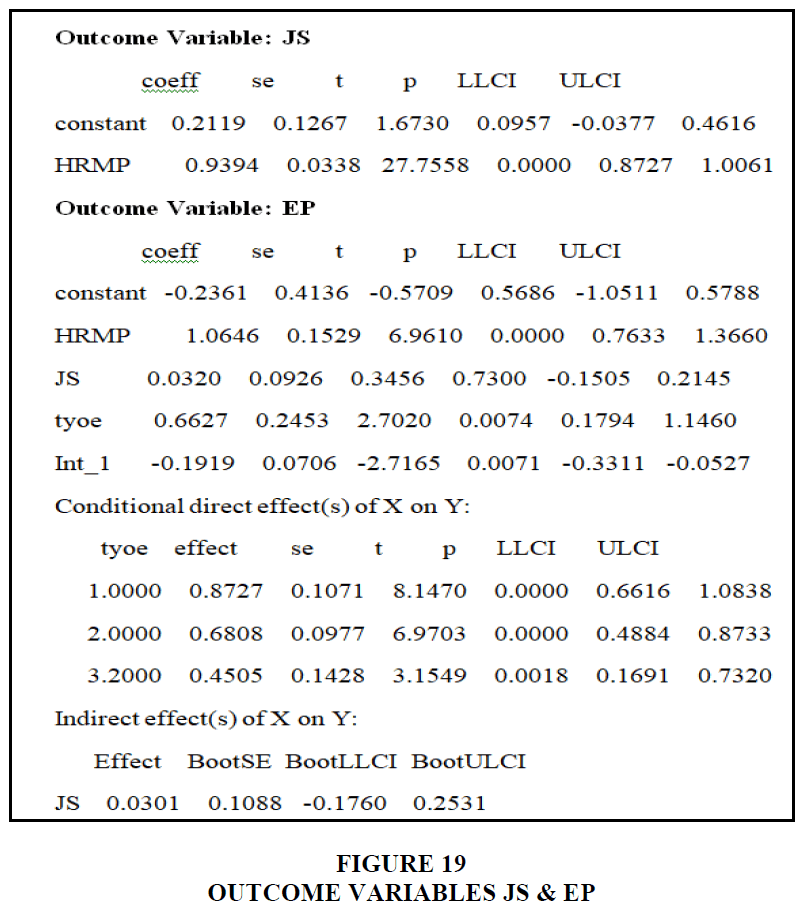
The total year of coffee experience is 1.1748, the value of human resources management techniques is 1.3586, and the value of work satisfaction is 0.0317 in the aforementioned result. When it comes to job satisfaction, the complete year of experience acts as a moderator. The total year of experience direct impact of the X and Y effect is 0.8605, 0.6603, 0.4600, and the work satisfaction indirect effect of X and Y is 0.0298, according to the bootstrap value. Employee performance is influenced by the moderators' and mediators' combined years of experience in human resource management practices Koc et al. (2014) Figure 19.
Variable Moderator Total Year of Experience in Organization, the Mediator Job Satisfaction
The total year of experience in the organization is 0.6627, HRM practices are 1.0646, and work satisfaction is 0.0320, according to the findings. This is influenced by the length of time the moderator has worked for the organization. It's crucial to the moderator. The total year of experience in the company has a direct influence on X and Y, with values of 0.8727, 0.6808, and 0.4505, respectively, in terms of bootstrap values. 0.0301 is the indirect impact of X and Y on work satisfaction. We may deduce that their total year of work experience has a moderating and mediating influence on human resource management strategies, as well as employee performance and job satisfaction.
Findings
When the technique of moderation is used in the study of HRM approaches and employee performance, the dependent variables improve (age, gender, and work experience).
When the mediation strategy is used, work happiness has a negative impact on the link between HR practices and employee performance.
Conclusion
Finally, this study has aided in the analysis of the relationship between HRM practices and employee engagement in the workplace. The relevance of HRM practices in increasing employee performance was also highlighted in this study. Employee performance is influenced by a variety of variables, including training and development, remuneration, job stability, and promotion. Employee involvement will also assist government management, which is under pressure to improve employee performance by concentrating on human resource management practices.
References
Ali, A. (2019). Impact of HR Policies and Practices on Employee Job Satisfaction: Evidence from Pakistan Telecommunication Ltd.(PTCL) Hyderabad, Pakistan. SEISENSE Journal of Management, 2(2), 48-57.
Begum, F. W., & Mohamed, D. M. S. (2016). A Study on HRM Practices and its Impact on Job Satisfaction and Organization Performance in BPO Sector, Tiruchirappalli. International Journal of Advanced Research in Management, 7(3), 1-9.
Cherif, F. (2020). The role of human resource management practices and employee job satisfaction in predicting organizational commitment in Saudi Arabian banking sector. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy, 40(7/8), 529-541.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross ref
Esmael M.A.Tabouli, Nasser Ahmed Habtoor &Mohammad Nashief S, The Impact of Human Resources Management on Employee Performance: Organizational Commitment Mediator Variable, Jo: Asian Social Science,
Gürbüz, S. (2009). The effect of high performance HR practices on employees’ job satisfaction. İstanbul Üniversitesi İşletme Fakültesi Dergisi, 38(2), 110-123.
Kamran AhmadUmar MehtabRizwan MumtazKhurram Jawaid, Impact on Hr practices of employee performance, Jo: International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences,
Koç, M., Cavus, M. F., & Saraçoglu, T. (2014). Human resource management practices, job satisfaction and organizational commitment. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 4(9), 178.
Mira, M., Choong, Y., & Thim, C. (2019). The effect of HRM practices and employees’ job satisfaction on employee performance. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 771-786.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross ref
Nurun Nabi, Md., Syduzzaman, Md., Shaykh Munir, Md., and The Impact of Human Resource Management Practices on Job Performances: A Case Study of Dhaka Bank Pvt. Ltd., Bangladesh, Jo:
Purohit, H., Malik, P., & Malik, S. C. (2014). Impact of HR Practices on Job Satisfaction Level of Managerial Employees in Textile Units. International Journal of Statistics and Reliability Engineering, 1(2), 140-152.
Sattar, T., Ahmad, K., & Hassan, S. M. (2015). Role of human resource practices in employee performance and job satisfaction with mediating effect of employee engagement. Pakistan Economic and Social Review, 81-96.
Yousef alsafadi, Shadi Altahat Human Resource Management Practices and Employee Performance: The Role of Job Satisfaction, Jo: Journal of Asian Finance Economics and Business
Received: 04-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12125; Editor assigned: 08-Jun-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-12125(PQ); Reviewed: 20-Jun-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-12125; Revised: 20-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12125(R); Published: 27-Jul-2022