Review Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 1
Bibliometric Analysis of Social Media as a Marketing Tool: A Co-authorship and Co-occurrence analysis
Barkha, Maharshi Dayanand University
Seema Rathee, Maharshi Dayanand University
Citation Information: Barkha, & Rathee, S. (2023). Bibliometric analysis of social media as a marketing tool: a co-authorship and co occurrence analysis. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(1), 1-11.
Abstract
Purpose: Customers increasingly devote a lot of time on social as well as digital media for a number of reasons, from obtaining information to make final product purchasing. Consequently, small companies devote a significant amount of time on social media to engage with their audience in order to promote their brand, improve sales, improve relationship with their customers and boost a number of visitors on their website. The importance of social media is continuously growing that’s why the objective of this study is to present a bibliometric analysis of social media as a marketing tool based on Scopus database literature for a certain time period. Research Methodology: During the period 2010 to 2022, 640 publications related to social media and social media marketing were identified for bibliometric study. Bibliometric analysis is carried out with the help of VOS Viewer software. Co-authorship and Co-occurrence analysis technique were used to identify the trend of publications, most cited research articles, authors and keywords. Result: Galati A. was the author who contributed most to social media as a marketing tool publication. USA and United Kingdom were the most influential countries in social media research areas. Additionally, four themes of co-word analysis were identified in the study which are Communication Tool, Evolvement of Social Media Marketing, Social Media Adoption, and Consumer Behaviour. Implications: This study will be helpful for the various researchers in providing directions for future research.
Keywords
Bibliometric Analysis, Social Media, Marketing Tool, Social Media Marketing.
Introduction
People can use social media platforms to promote their content, share images and videos, and communicate with each other. The term "social media," invented in the late 1990s, has gained popularity to the point that there are currently over 4 billion active users worldwide (Number, 2016). Therefore, social media refers to technologies aided by computers which enable individuals to create and exchange information, views, and other forms of expression with the use of virtual networks and communities (Obar and Wildman, 2015).
The use of social media platforms for marketing objectives is referred to as "social media marketing." Alves et al. (2016) The process of creating content for social media platforms with the goal of advertising products and services, forming a community with the target audience, and driving potential consumers to a company's website is known as social media marketing. Social media marketing is always evolving, with new highlights and applications being introduced consistently.
Businesses have been encouraging to utilize social media as a marketing tool by growth of digital marketing and the emergence of social media. Micro, small, and medium-sized businesses commonly use social media to advertise, sell, and build brand awareness because it is an inexpensive tool. They create profiles on various social media platforms and share information by way of photographs and videos on different platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, so that their current and potential customers can stay up to speed on their business Amrita & Mohan (2016).
With the growing relevance of social media, a slew of studies on its use in marketing has arisen in the recent era Leung et al. (2017); Zeng and Gerritsen, 2014; Leung et al., 2021). As per a new concept, it is beneficial for academic scholars to analyse previous relevant research on a regular basis in order to gain a wide grasp of the intellectual structure of the topic and foresee how it will progress. (De Bakker et al., 2005; Line and Runyan, 2012; Leung et al. (2021) Csordás et al. (2014).
A widespread and thorough method for identifying and analysing vast amounts of scientific data is known as bibliometric analysis. It allows us to look into the nuances of a given discipline's evolution while also providing information on the field's emerging areas. Donthu et al. (2021) Bibliometrics is a scientific area of research that has gained a lot of attention from mainstream scholars. (Alvarez-Betancourt & Garcia-Silvente, 2014; Donthu et al. (2021). Bibliometric analysis has been used in various study disciplines over the past ten years since it is a technique for assessing the advantages of a specific topic area (Sweileh, 2020; Donthu et al. (2021); Shang et al., 2015; Donthu et al. (2021). According to Ellegaard & Wallin (2015), “bibliometric analysis is a form of evaluation that defines the quality and impact of scientific papers in a specific area”. It examines academic aspects of the papers under consideration, such as keywords, authors, nations, and publishing patterns. (Aydin and Senel, 2019; Donthu et al. (2021).
Review of Literature
(Siddiqui, 2016) in his paper defined social media as computer technologies make enable individuals to share or exchange information, opinions, snapshots, videos, and other material with one another over a network. The key benefits of social media marketing are greater brand exposure and relationship management, enhanced targeted traffic and SEO, word-of-mouth and lead generation, and market data pertaining to target demographics and competitors. Social media refers to internet-based applications and basic ideas that are based on (but not limited to) web 2.0 and enable individuals to produce, change, and share information, ideas, thoughts, visions, media, associations, and links with one another (all created by the users) (Montoya, 2011; Johnston, 2011; Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010; Nair, 2011; CSORDAS et al. 2014). Social Media has become increasingly in communication and marketing strategies Bansal et al. (2014). Social media will only be useful as a marketing tool if firms create a social media presence and offer consumers relevant information at the right time. Bashar et al. (2012).
The way businesses market their products and services is changing due to the advent of social media which possess different problems additionally opportunities for them (Arora and Sanni, 2019; Dwivedi et al., 2015, 2017; Hossain et al., 2019; Nisar et al., 2018; Wang and Herrando, 2019). If digital marketing and social media marketing are utilized wrongly or by untrained managers, it can harm companies (Aswani et al., 2018). Small businesses essentially learn how to utilise social media effectively to protect themselves from this harm. (Braojos-Gomez et al., 2015) Ahmad et al. (2018). To develop digital marketing strategies that complement the company's objectives, businesses must link their social media marketing tactics with their corporate goals. (Tafesse and Wien, 2018; Thorpe, 2018) When used effectively, social media marketing may result in increased customer satisfaction and perceived value, as well as co-creation, brand loyalty, and a positive attitude. (Laroche et al., 2013). Social media marketing allows the marketers to research online user-generated content, e-wom conversations, and consumer reviews on websites and online communities which have opened up new ways for them for gaining customer experience. (Chang et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2017). Because customers as well as potential customers spend so much time on social media platforms, marketers have started to develop approaches and strategies to reach out to them through social media presence Faruk et al. (2021). As a result, several studies have been conducted on “digital marketing,” “search engine optimization,” “online marketing,” “social media marketing” and many more (Jimnez, 2020). The present study provides an intensive analysis of previous studies published by researchers from different countries on the topic of "social media as a marketing tool" between 2010 to 2021 Bhanot (2012).
Bibliometric analysis is valuable for interpreting and planning the combined logical information and developmental subtleties of deeply grounded fields by sorting out huge volumes of unstructured information in thorough ways Donthu et al. (2021). The term “bibliometric” was first introduced by Pritchard (1959). He described bibliometric analysis as the use of mathematical and statistical methods in a variety of publications, such as books, articles, reviews, and conference papers, in understanding the evolution of a certain study topic. Thus, various researchers use the bibliometric analysis method Jones et al. (2015) of published literature to recognize various themes. Based on the data utilised in the study, the bibliometric analysis uses a number of methodologies, including performance analysis, scientific mapping, and network analysis, to show the intellectual structure of a certain field of study. (Cobo et al. 2011; Donthu et al. (2021). The traditional bibliometric analysis is citation and content analysis. The most popular analysis methods are “co-authorship analysis, co-word analysis, or co-occurrence analysis, and citation analysis” Bajaj (2016).
“Co-authorship analysis” provides the co-author's network-based map which represents the most contributing authors in a particular research area -based on countries, authors, and organization Donthu et al. (2021). “Co-word analysis” is a method which looks at how words that come together frequently have a theme in common and establish a future relationship among topics Donthu et al. (2021). Citation analysis examines the most significant articles in a study area in order to acquire a better grasp of the topic's intellectual dynamics. Researchers used several other bibliometric analysis like co-citation analysis and bibliographic coupling (two publications with a shared reference also have comparable content) along with co-authorship analysis, co-word analysis, and citation analysis to assess the importance and prominence of research dynamics for example: most contributing nations, authors, organisations, sources, and keywords Van Eck & Waltman (2010). In emerging bibliometric research, network mapping is used to construct clusters or themes using various analytical approaches such as co-authorship analysis, bibliographic coupling method, and co-occurrence analysis. Van Eck & Waltman (2010). Therefore, this study applied co-authorship analysis based on authors and countries, and keyword co-occurrence analysis methods to evaluate the previously published articles on the topic “social media as a marketing tool”.
Methodology
Data Collection
This study used a screening method in the Scopus database to find and retrieve appropriate research papers for inclusion. Because Scopus is a high-quality database that comprises top journals, subject areas, type of studies, the language of studies, keyword selection, published articles or articles in the press, year of publication, and many more, we were able to choose the best research papers Ghorbani et al. (2022). Therefore, this study extracted the bibliographic data from the Scopus database instead of other databases like Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO), and Research Gate. Words such as “Social Media Platforms, Social Media, Social Media Tools, Social Media Networks and Marketing Tool, Marketing Communication Tool, Communication Tool, Advertising Tool” were used to search in the titles, keywords, and abstracts of the publications. Following the loading of the dataset, it is discovered that it contains a total of 1112 items earliest known to 1993. The authors, on the other hand, used the "publication year" filtering approach to save data covering the period from 2010 to 2021. This time period is selected because of the use of social media for marketing activities initiated in 21st century. This study selected only articles from two subject areas that are “Business, Management and Accounting” and “Economics, Econometrics, and Finance” in the English language Kim et al. (2021). Articles in the English language were selected for the study while articles in other languages were ignored. A list of keywords for the articles search in the database, including social media, social media marketing, marketing, social networking websites, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, advertising, SMEs, small business, consumer behaviour, customer engagement, web 2.0, user-generated content, e-wom and many more was generated based on existing studies on social media as a marketing tool. Since 2010, research on social media marketing has received a lot of attention due to the rapid expansion of the internet and social media that’s why this study examined the studies associated with social media as a marketing tool by searching specified keywords for the period starting from 2010 to 2021. While other forms of publications were omitted from the study, including conference papers, reviews, books, comments, and notes, simply research articles are included in the study. At first, 11 articles related to “social media as a marketing tool” were derived but 207 articles were retained as these are relevant to “social media as a marketing tool” articles, and irrelevant articles were removed from the study. At last, this study extracted 207 articles in a CSV excel file containing valuable information such as author's names, titles, keywords, publication year, paper id, etc Chaudhary (2017).
Data Analysis
To evaluate bibliographic data, VOSviewer software has been frequently utilised. In comparison to other bibliographic software tools, VOSviewer has been extensively utilized for carrying out bibliographic data analysis in several study domains. VOSviewer is a software program that carefully creates and visualizes the bibliographic network Chatterjee & Kar (2020).
The VOSviewer analysis visualises a large quantity of data in a single graphical map based on similarity visualisation. Noor et al. (2020). As a result, the map created in VOSviewer using the text mining approach is made up of connected phrases, resulting in a single theme or cluster Van Eck & Waterman (2010) Lorenzo-Romero & Constantinides (2014).
VOSviewer analysis shows a significant amount of information in a single graphical map based on the depiction of similarities Noor et al. (2020). As an outcome, the map created in VOSviewer using text mining approach is made up of connected terms, forming one theme or cluster Van Eck & Waterman (2010). Several clusters or themes of nations, journals, institutions, sources, and keywords were used in the title and abstract of published works as a result of citation analysis, bibliographic coupling, and co-occurrence analysis. These clusters are coloured differently to show the proximity of distinct keywords, authors, journals, organizations, and countries in specific research streams Table 1.
| Table 1 Summary Statistics |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Results |
| Documents | 207 |
| Keywords | 852 |
| Period | 2010-2021 |
| Authors | 535 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc) | 153 |
| Average citation per document | 4.86 |
| References | 10306 |
Summary Statistics
Yearly Growth Output
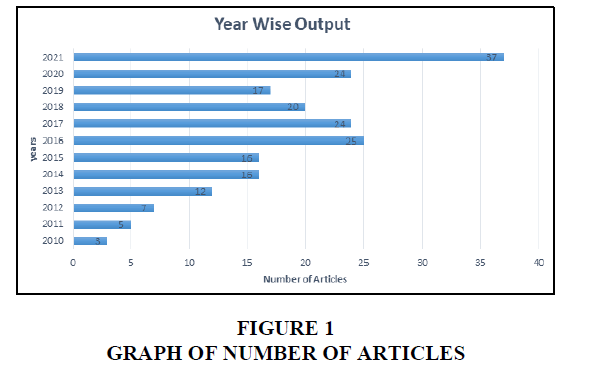
Figure 1 depicts the 207 annual publications on the topic “social media as a marketing tool”. In the year 2010, the utilization of social media as a marketing tool for small businesses began to rise. From 2010 to 2012, there were just a few articles every year. From 2010 to 2014, it shows a rise in the use of social media. In both the years 2014 and 2015, an equal number of papers were published. In 2016, however, the yearly growth of social media publications as a marketing tool was 9 articles. However, from 2016 to 2019, it exhibited a downward trend, going from 25 to 17 articles. It demonstrated growing behaviour over time, with several publications increasing by twofold from 17 to 34 in a short period Divya & Regi (2014) Figure 1.
Contribution of Countries in Social Media Research Area
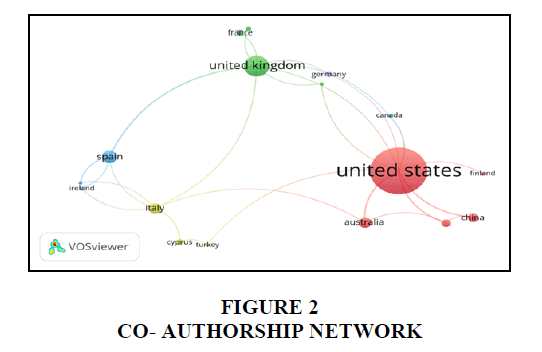
Collaboration between countries in different research areas is one of the issues emphasized in recent years. This analysis of the study represents the most contributing countries in social media as a marketing tool research Gan & Wang (2014) area through co-authorship links. Co-authorship data were used in co-author analysis method to assess the collaboration among countries (Zupic & Cater, 2015; Noor et al. (2020). As per data retrieved from the Scopus database, this study identified 207 publications from 65 countries in the social media area. In VOSviewer, this study chose "co-authorship analysis" as the kind of analysis and "countries" as the unit of analysis. Furthermore, in a VOSviewer, this study picked a minimum number of documents for each nation of 3 and a minimum number of citations for each country of 3 to identify the most contributing country and the countries that collaborated. Table 2 shows the top ten nations with the greatest number of publications. The highest contributing nation, according to the co-authorship network study, was the United States, which had 52 papers and 1583 citations with 17 co-author linkages. Particularly, researchers from the USA have conducted research together with a researcher from many different countries. The United Kingdom is the next contributing country having 21 publications with 1391 citations and 10 total link strengths. India is the 3rd country following 17 publications. As per cluster 1, researchers from the USA, Australia, China, and Hong Kong collaborated mostly together. France, Greece, Lebanon, and United Kingdom were seen in the second cluster. Ireland, Netherland, and Spain are the countries that contribute to the social media research area with each other falling in the 3rd cluster. Cyprus, Italy, and Turkey were the countries were in the 4th cluster indicates that these countries work together on social media related research studies. Germany and Canada fall in the 5th and 6th cluster, these countries indicate that they didn’t collaborate with any other country Iblasi et al. (2016) Öztamur & Karakad?lar (2014) Table 2 and Figure 2.
| Table 2 Countries That Contribute To The Social Media Research Area |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Documents | Citations | Total Link Strength |
| USA | 52 | 1583 | 17 |
| United Kingdom | 21 | 1391 | 10 |
| India | 17 | 174 | 0 |
| Spain | 12 | 289 | 7 |
| Italy | 10 | 315 | 7 |
| Australia | 10 | 260 | 5 |
| Malaysia | 10 | 112 | 1 |
| South Africa | 10 | 294 | 5 |
| China | 8 | 276 | 4 |
| Czech Republic | 8 | 32 | 3 |
| Hong Kong | 7 | 139 | 2 |
A Total of 207 Articles Related To “Social Media as Marketing Tool” in The “Business”,
Management and Accounting” and “Economics, Econometrics, and Finance” are included. 14 Most cited journals or sources in both the areas are demonstrated in table 3. In a VOSviewer, this study used citation analysis as a type of analysis and "sources" as a unit of analysis. Additionally, this study determined a 2 minimum number of articles and 2 minimum number of citation occurrences in a threshold level. Table 3 shows that the “Industrial Marketing Management” journal had the highest citation in this study area. This journal has been cited by different researchers 1581 times in a definite period. Following the “Industrial Marketing Management”, second journal “Public Relation Review” has 531 citations and contributed 6 paper published. And all the remaining journals don’t have highest citations and articles published but they are contributing significantly in the study area Thaha et al. (2021) Table 3.
| Table 3 Most Cited Sources In Social Media Search |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr. No. | Sources | Documents | Citations | Citation per Document |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. |
Industrial Marketing Management Public Relation Review Current Issues in Tourism International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management International Journal of Retail and Distribution Management Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing Publishing research quarterly European Journal of Marketing Journal of Promotion Management Indian Journal of Marketing Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure |
3 6 4 3 3 3 3 4 3 3 3 3 3 3 |
815 531 479 201 91 83 58 57 49 30 28 27 9 6 |
271.66 88.5 119.75 67 30.33 27.6 19.33 14.25 16.33 10 9.3 9 3 2 |
As per data retrieved from the Scopus database, this study identified 207 publications from 65 countries in the social media area. In VOSviewer, this study chose "citation analysis" as the kind of analysis and "authors" as the unit of analysis. Furthermore, in a VOSviewer, this study picked a minimum number of documents per author of 2 and a minimum number of citations per country of 3 to identify the most contributing author and highly cited author. Table 4 shows the top 14 authors with the greatest number of citation. The most cited authors, according to the citation analysis technique, were the Christodoulides G. and Michaelidou N., which had 2 papers and 662 citations with 331 per document citations. The Munar A.M is the next most cited author having 2 publications with 191 citations. Table 5 demonstrates the top 10 cited documents in “Social Media as a Marketing Tool” research. “Usage, Barriers and Measurement of Social Media Marketing: an exploratory investigation of Small and Medium B2B Brand’ is the highest cited document published in the year 2011, followed by “Social Media as a Destination Marketing Tool: Its use by National Tourism Organisations” published in the year 2013 with 414 citations. The citations analysis technique measures number of times other authors mention the document in their research study. The citation received by a document shows the role of the paper in other studies (Donthu et al. 2021) Table 4 and Table 5.
| Table 4 Most Cited Authors |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr. No. | Authors | Documents | Citations | Citation per Documents |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. |
Christodoulides G. Michaelidou N. Munar A.M Constantinides E. Chen H.-T. Lim W.M. Galati A. Alarcon-Del-Amo M.-D.-C. Vrontis D. Leung X.Y. Jibril A.B. Kumar P. Kaur K. Amoah J. |
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 |
662 662 191 114 83 50 43 37 23 17 6 5 3 2 |
331 331 95.5 57 41.5 25 21.5 18.5 11.5 8.5 2 1.66 1.5 1 |
| Table 5 Most Cited Documents |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sr. No. | Authors | Documents | Citations |
| 1. | Michaelidou n. (2011) | Usage, Barriers and Measurement of Social Media Marketing: an exploratory investigation of Small and Medium B2B Brands | 495 |
| 2. | Hays s. (2013) | Social Media as a Destination Marketing Tool: Its use by National Tourism Organisations | 414 |
| 3. | Lovejoy k. (2012) | Engaging Stakeholders through twitter: how nonprofit organizations are getting more out of 140 characters or less | 393 |
| 4. | Mariani m.m. (2016) | Facebook as a Destination Marketing Tool: Evidence from Italian Regional Destination Management Organizations | 167 |
| 5. | Siamagka n. t. (2015) | Determinants of Social Media Adoption by B2B Organizations | 167 |
| 6. | Swani k. (2014) | Should Tweets: Differ for B2B and B2C? An Analysis of Future 500 Companies’ Twitter Communications | 153 |
| 7. | Zhao x.(2015) | The Influence of Online Reviews to Online Hotel Booking Intentions | 147 |
| 8. | Geruin-eagleman a.n. (2016) | Communicating via Photographs: a gendered analysis of Olympic Atheletes’ Visual Self-Presentation on Instagram | 116 |
| 9. | Constantinides e. (2011) | Potential of the Social Media as Instruments of Higher Education Marketing: A Segmentation Study | 111 |
| 10. | Kudeshia c. (2017) | Social EWOM: It Affect the Brand Attitude and Purchase Intention of Brands? | 109 |
Co-occurrence Analysis
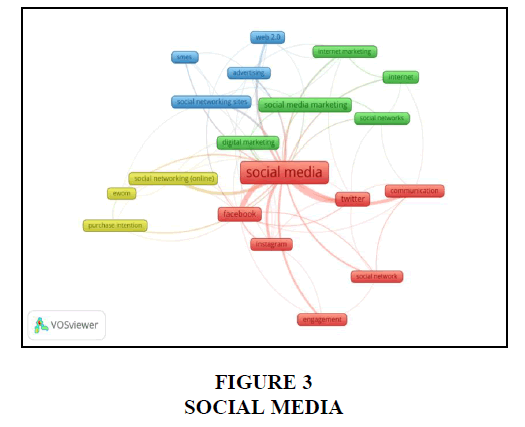
This study used thematic analysis of published papers to uncover research topics and hotspots in social media marketing research from 2010 to 2021, based on the co-occurrence of keywords detected in the article's title, keywords, and abstract. Crucial learning areas where the articles connected to social media as a marketing tool had an important role in deciding how they may be classified systematically can be identified with the aid of this analysis. In a VOSviewer, this study used co-occurrence analysis as a type of analysis and "All Keywords" as a unit of analysis. Additionally, this study determined a 6 minimum number of keyword occurrences in a threshold level. As shown in figure 1, the keyword network visualisation map was created using the co-occurrence frequencies of the top 19 keywords out of a total of 852 terms Figure 3.
To highlight the link between keywords in a certain cluster or subject, visualised co-word networks were created. The four clusters of keywords were recognized as Communication Tool, Evolvement of Social Media Marketing, Social Media Adoption, and Consumer Behaviour. A first cluster “Communication Tool” refers to various social media platforms such as in the network are Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter that are employed to communicate with their customers or clients, or staff. The second cluster “Evolvement of Social Media Marketing” comprises 5 keywords as internet, internet marketing, digital marketing, social networks or social media platforms, and social media marketing which shows the growth of social media marketing over time. The third theme “Managerial Application” consists of 4 keywords that are Web 2.0, social networking sites, SMEs, and advertising which indicates small and medium enterprises started using the social networking sites for advertising and promoting their product. The last and fourth cluster is “consumer behaviour” and how e-wom (electronic word of mouth) on social networking platforms influences the customer’s intention to purchase the products and services Figure 4.
Co-authorship Analysis
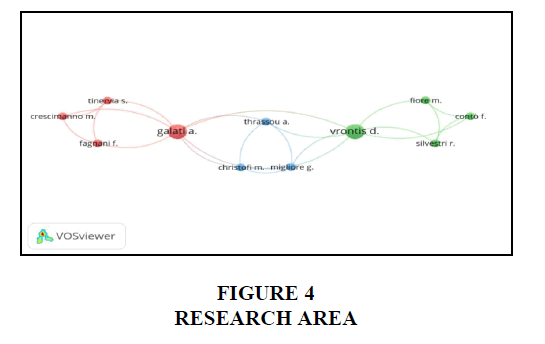
To assess the collaboration trends and identify leading authors in the research area for the period 2010 to 2021, this study conducted a co-authorship analysis of the publication’s authors of social media research. This study selected a form of analysis as co-authorship analysis and a unit of analysis as “Authors” in a VOSviewer. Furthermore, this study chose authors who have at least one study in the social media research area. With co-authorship analysis, the authors are categorized into 3 clusters; as demonstrated in figure 2, 23 links were identified. 11 authors out of 535 authors with a minimum of one study in social media as a marketing tool research area. The first cluster includes crescimanno m., fagnani f., galati a., and tinerva s. which indicates that these 4 authors are connected. They collaborate into research area with each other. Second cluster contains conto f., fiore m., silvestri r., and vrontis d., these authors collaborate. And thrassou a., christofi m., and mighore g. are the authors lied in the 3rd cluster which shows the contributions from these 3 authors.
Conclusion
The bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive perspective of certain research domains, allowing researchers to focus on specific areas in order to add new results and information to the literature. This bibliometric research study summarises Scopus publications on social media as a marketing strategy. As per the search results, from 2010 to 2021, the usage of social media as a marketing tool in small businesses has expanded rapidly, according to the search results. The majority of the studies utilize the terms social media and social media marketing as per the analysis. “Advertising, social networks, purchase intention, multiple social media platforms, digital marketing, social media marketing, web 2.0, branding, and many more” were explored in addition to social media and social media marketing. Second, the study demonstrates that, since 2010, research on social media marketing has received a lot of attention due to the rapid expansion of the internet and social media. Author linked nations such as the United States and the United Kingdom contribute significantly to the number of published articles and citations. India ranks third in terms of research contributions. Through co-authorship analysis, the authors were grouped into three clusters, each with two linkages. There are 11 authors out of 535 who have published at least one study in the area of social media as a marketing tool. Galati A. is the author who contributed the most to the social media marketing. According to the outcome of co-occurrence anlysis, four clusters of keywords were identified: communication tool, the evolution of social media marketing, social media acceptance in MSMEs, and social media influence.
Scope and Limitations
This study suffers from two limitations. At first, it is based on a small list of keywords that are utilized to find research articles. Second, even if this report makes use of bibliographic analysis applications, errors might still arise because of the author's subjective view. This study offers the direction for future research, such as expanding the keywords used in subsequent research to allow for greater sample sizes, such as using social media sites and databases apart from Scopus. Furthermore, future studies can compare the outcome of bibliometric analysis by using different bibliometric analysis software.
References
Ahmad, S.Z., Bakar, A.R.A., & Ahmad, N. (2018). Social media adoption and its impact on firm performance: the case of the UAE. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alves, H., Fernandes, C., & Raposo, M. (2016). Social media marketing: a literature review and implications. Psychology & Marketing, 33(12), 1029-1038.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Amrita, S.M., & Mohan, R. (2016). Application of social media as a marketing promotion tool—A review. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Bajaj, R.A. (2016) A Study of Social Media Marketing Strategies Used by Micro Small Medium Enterprises MSME_S for Customer Acquisition and Retention.
Bansal, R., Masood, R., & Dadhich, V. (2014). Social media marketing-a tool of innovative marketing. Journal of Organizational Management, 3(1), 1-7.
Bashar, A., Ahmad, I., & Wasiq, M. (2012). Effectiveness of social media as a marketing tool: An empirical study. International Journal of Marketing, Financial Services & Management Research, 1(11), 88-99.
Bhanot, S. (2012). Use of social media by companies to reach their customers. SIES Journal of Management, 8(1).
Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A.K. (2020). Why do small and medium enterprises use social media marketing and what is the impact: Empirical insights from India. International Journal of Information Management, 53, 102103.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chaudhary, P., Sahahi, A. (2017). “Role of Social Media in Marketing and Business Growth,” International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 8, Issue 10, ISSN 2229-5518.
Csordás, T., Markos-Kujbus, É., & Gáti, M. (2014). The attributes of social media as a strategic marketing communication tool. Journalism and Mass Communication, 4(1), 48-71.
Divya, S., & Regi, B. (2014). An empirical study on effectiveness of social media as a marketing tool. International Journal of current research and academic review, 2(3), 163-168.
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W.M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Faruk, M., Rahman, M., & Hasan, S. (2021). How digital marketing evolved over time: A bibliometric analysis on scopus database. Heliyon, e08603.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gan, C., & Wang, W. (2014). A bibliometric analysis of social media research from the perspective of library and information science. In Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society (pp. 23-32). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Ghorbani, Z., Kargaran, S., Saberi, A., Haghighinasab, M., Jamali, S. M., & Ale Ebrahim, N. (2022). Trends and patterns in digital marketing research: bibliometric analysis. Journal of Marketing Analytics, 10(2), 158-172.
Iblasi, W.N., Bader, D.M., & Al-Qreini, S. A. (2016). The impact of social media as a marketing tool on purchasing decisions (Case study on SAMSUNG for electrical home appliances). International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research, 4(1), 14-28.
Jones, N., Borgman, R., & Ulusoy, E. (2015). Impact of social media on small businesses. Journal of small business and enterprise development.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kim, J., Kang, S., & Lee, K.H. (2021). Evolution of digital marketing communication: Bibliometric analysis and network visualization from key articles. Journal of Business Research, 130, 552-563.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Leung, X.Y., Sun, J., & Bai, B. (2017). Bibliometrics of social media research: A co-citation and co-word analysis. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 66, 35-45.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lorenzo-Romero, C., & Constantinides, E. (2014). Social Media as Marketing Strategy: An Explorative Study on Adoption and Use by Retailers? This study is framed within Research Project with reference number ECO2009-08708 (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Gobierno de España, 2009–2013). In Social media in strategic management. Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Noor, S., Guo, Y., Shah, S.H.H., Nawaz, M.S., & Butt, A.S. (2020). Bibliometric analysis of social media as a platform for knowledge management. International Journal of Knowledge Management (IJKM), 16(3), 33-51.
Öztamur, D., & Karakad?lar, ?.S. (2014). Exploring the role of social media for SMEs: as a new marketing strategy tool for the firm performance perspective. Procedia-Social and behavioral sciences, 150, 511-520.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Thaha, A.R., Maulina, E., Muftiadi, R.A., & Alexandri, M.B. (2021). Research Trends and Mapping on Social Media in SMEs: A Bibliometric Analysis.
Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. scientometrics, 84(2), 523-538.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 11-Sep-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12539; Editor assigned: 14-Sep-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-12539(PQ); Reviewed: 05-Oct-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-12539; Revised: 28-Oct-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12539(R); Published: 08-Nov-2022