Research Article: 2019 Vol: 23 Issue: 3
Determinants of Social Media Marketing Adoption among Smes: A Conceptual Framework
Bhabesh Kumar, Ab Bank Limited
Ahmed Al Asheq, World University of Bangladesh
Munmun Rahaman, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University
Md. Mobarak Karim, World University of Bangladesh
Abstract
In recent times, many small and medium-sized business firms have embraced different avenues of social networking sites precisely in their business communication model, which has triggered an intensive transformation in business firms’ marketing dynamics. Acceptance, adoption, and leverage of social media (SM) marketing has become a common marketing practice tool for business firms and this new model of marketing tool extends an unexplored and new opportunity for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to integrate social media platform into their daily marketing activities. This scenario calls for an in-depth research study towards the marketing researchers to examine the impact of SM marketing on the business and marketing performance of SME firms. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to review relevant literature to determine what group of factors might have an impact on the SMEs’ decision to accept and adopt SM marketing into their organizational process. The proposed topic of this current paper offers future research studies a holistic conceptual framework of SM marketing adoption among SMEs, which is still not fully established in the existing literature. Moreover, the paper also extends a useful means to investigate the types of researches which need to be studied and investigated to facilitate empirical evidence based on additional research advancement in the domain of SM marketing.
Keywords
Social media marketing, Technology adoption, e-commerce platform, SMEs.
Introduction
The information technology (IT) has the capability to revolutionize the overall marketing aspects of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) firms, such as accelerating new customer acquisition, access to a new market, and enhancing firm’s efficiency (Alford & Page, 2015). Undoubtedly, the electronic platform has transformed the traditional buying and selling mechanism in the market. Due to the emergence of IT, business firms tend to integrate social media into their marketing activities. Lamberton & Stephen (2016) argued that the unprecedented growth of social media usage has widened up new windows for business organizations to get in touch with their customers. Social media offers an innovative method of reaching out to more customers. Recently, a noteworthy level of attention is particularly given in the field of social media marketing (Tafesse & Wien, 2018). With the help of SM channels, communications between business firms and individuals have been augmented and enhanced at a rapid pace (Berthon et al., 2005). In particular, social media are viewed as an essential tool for facilitating and enhancing the degree of customer interaction and that’s why SM marketing has become an indispensable tool for customer relationship approach in the business firms (Galati et al., 2017). Although plenty of literature focused on the strategic attributes of social media marketing, how the business firms adopt and implement social media in their marketing mix, is still overlooked. Meanwhile, SMEs are regarded as one of the salient modes of contribution to the economic growth of a nation. According to Asheq & Hossain (2019) and Hossain & Asheq (2019), SMEs work as a driver of economic development of a country. In spite of SME’s contributory in economic development, SMEs is experiencing adoption barrier in accepting new technologies (Dahnil et al., 2014). It can be argued that adopting and integrating social media into SMEs’ marketing process will not only widen new avenues of opportunities but also modify its business operational processes. The current research trend of e-commerce offers a new option for researchers to study social media (SM) marketing. Hence, it has become a research requirement to investigate the determining factors of adoption of social media marketing among SME firms. Unfortunately, a scarce study has been conducted in the context of SMEs’ acceptance of social media platform as their marketing strategy. Furthermore, a theoretical framework of SMEs’ adoption of social media marketing is missing in the existing literature. Therefore, the study has facilitated a conceptual framework for identifying determinant variables of SMEs social media (SM) marketing adoption.
Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
The concept of ‘Social Media’ can be defined as
“A group of Internet-based applications that build on the ideological and technological foundations of web 2.0, and that allow the creation and exchange of user-generated content” (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010).
Effing and Spil (2016) coined social media as
“A goal-directed planning process for creating user-generated content, driven by a group of internet applications, to create a unique and valuable competitive position”.
The initial aim of a social media strategy is to integrate SM platform with a business organization’s strategic marketing objectives and offers a practical route towards attaining those objectives (McCann & Barlow, 2015). Social media (SM) triggers a novel marketing approach (Eagleman, 2013). Social media marketing may be observed as a relatively new commerce platform that is integrated with promotional and marketing activities of different goods, and services, through IT-enabled online platform which is followed by social media (Dahnil et al., 2014). Social media marketing concept can be defined as leveraging social media features to attain marketing goals in line with other marketing approaches.
The authors of this paper scrutinized the existing literature by identifying the primary data sources which can be regarded as the salient publications in the domain of electronic marketing, online marketing, and social media marketing. Also, some of the related domain of publications were also searched such as electronic and online marketing in SME firms as a part of the literature review. Based on these, the following factors were identified as the determining variables of SMEs’ adoption of social media marketing.
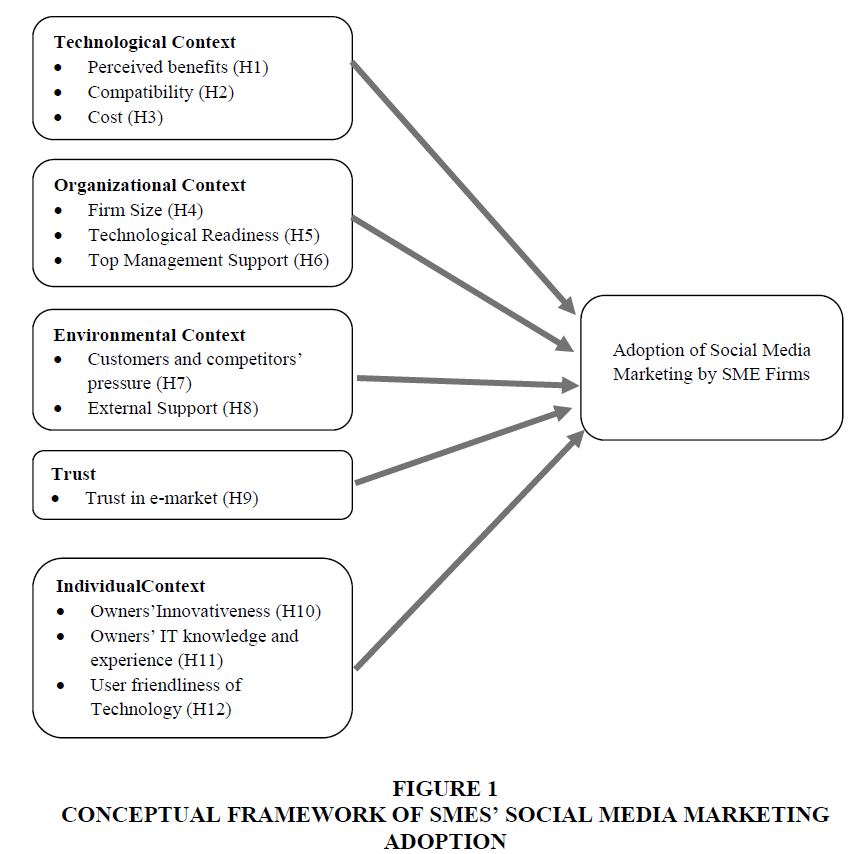
Technological context assesses the diversified advantages of adopting social media marketing in SME firms. Roger (2003) suggests that technological adoption by a business firm is positively correlated with perceived benefits offered by technology. Perceived benefit indicates the realizable benefits which can be provided by e-commerce technology to a business organization (Rahayu & Day, 2015). In an organizational set-up, technological advancement can smoothly be accepted if it is compatible with organizational culture and values (Morteza et al., 2011). Premkumar & Roberts (1999) indicate that the more expensive a specific technology will be, the less likely it will be adopted by a firm. The cost has been examined as a determining variable to influence electronic marketing adoption in previous studies (El-Gohary, 2012; Gilmore et al., 2007). These discussions guide to the following proposed hypotheses:
H1: Perceived benefits will positively influence SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H2: Compatibility will positively influence SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H3: Cost will negatively influence SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
Organizational dimension offers the internal factors of a business organization that would influence a firm’s choice to adopt any technology (Qashou & Saleh, 2018). Organizational context reflects what kind of organizational characteristics induce the adoption of technology by SMEs. The size of a business firm is likely to impact technology adoption (Roger, 2003). It can be perceived that bigger business firms are characterized with more technical and economic resources to adopt technology than those of the firms which are relatively small in size (Duan et al., 2012). Another factor that would determine SMEs’ technology adoption is technology readiness, which comprises of IT infrastructure and technologically sound human resources (Zhu & Kraemer, 2005). Rahayu & Day (2015) found a positive interdependent relationship between e-commerce adoption and readiness of technology. From the organization point of view, support from the top management plays a critical role in supporting social media marketing adoption in the SME context. SME firms will be more likely to accept and implement new technology when top management will provide a substantial level of support. Furthermore, in the state of resources limitation in SMEs, top management assistance ensures resource allocation for technology adoption (Ramdani et al., 2009). Based on these discussions, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H4: Size of the firms will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H5: Technology readiness will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H6: Management support will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
The environmental context reflects the pressure from the competing rivals and trading partners for an SME firm (Chwelos et al., 2001). In some cases, customers hold some degree of power to make an SME firm adopt a specific technology (Rahayu & Day, 2015). Research suggests that competitor’s pressure is most likely to influence individual business firm’s decision to adopt technology and the pressure from the different government organizations possess greater degree of effect on SMEs’ choice to accept technology as they are financially reliant on Govt. organizational support for their existence (Duan et al., 2012). Zhu & Kraemer (2005) argued that when business rival parties involve in adopting the electronic business platform, then business firms are more likely to adopt electronic commerce platform within the industry. Hence, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H7: Customers and competitors’ pressure will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H8: External support (i.e. Govt.) will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
Trust dimension reflects the trustworthiness in the context of online transaction and security system in an e-commerce platform. Trust has been considered as a potential variable to affect the degree of technological acceptance (Pavlou & Gefen, 2004). Moreover, SMEs’ adoption of e-marketing is positively triggered by the trust in e-business platform (Duan et al., 2012). Hence, the arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H9: Trust in the electronic business platform will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
In terms of technology adoption individual context referes to the firm owner’s experience in IT and innovatinevess (Rahayu & Day, 2015). Because, SME firm owner or business managers hold the power to accept a new technology. Cloete et al. (2002) evidenced in their study that acceptance of e-commerce is heavily dependent on the willingness of the business firm owner. In figure 1 justifibale since SMEs ought to centralize from the structural perspective, thus SME owner/managers play a potential role in making any important strategic decision for business (Nguyen & Waring, 2013).
In this currentpaper, SME firm owner’s innovatinevess reflects the extent to which an individual accepts aninnovation more rapidly thsn other individuals in same environment (Marcati et al., 2008). Furthermore, Ghobakhloo & Tang (2013) argued that those SME owners who are more innovative, they are more intended to adopt e-coomerce platform. It is not unfamiliar that lack of IT skills has remained a problem for SMEs (Rahayu & Day, 2015). If SME owners or managers possess greater degree of IT skills or IT related experience, then they will be more likely to accept new IT technology and this exposure to IT skills will reduce the uncertainity of accepting social media technology. Morteza et al. (2011) conclded that user’s IT knowledge and skills would facilitate the speed of new technology acceptance. It can also be surmised that if the new technology offers more user friendly functions for SME owners, they would be more likelyto adopt technology. Hence, based on these discussion, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H10: SME firm owners/managers’ innovatieness will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H11: SME firm owners/managers IT knowledge and experience will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
H12: Technological user friendliness for SME firm owners/managers will positively impact SM marketing adoption among SMEs.
Conclusion
The current paper seeks to discuss the relationship between technological, organizational, environmental context and SMEs’ adoption of social media marketing through proposing a conceptual framework for further research investigation. The proposed framework of SM marketing puts forward a unique ground for the researchers to examine and validate by empirical research studies in the future. The paper significantly identifies the supporting which would stimulate SM marketing adoption among SMEs. Since a lot of SMEs are experiencing several hindrances in leveraging new technology, SM marketing can be deemed as an advantageous mode of interactive communication (Dahnil et al., 2014). Nonetheless, with SMEs’ resource constraint, a dearth of deep understanding of social media would exert a strong negative impact on small firms. Based on the literature review, it can be surmised that SM marketing has a deepening connection with e-marketing. According to Kaplan & Haenlein (2010), social media can be referred to as an online based application. Hence, it would be relevant to classify SM marketing as a subset of a broader range of e-marketing.
References
- Alford, P., & Page, S.J. (2015). Marketing technology for adoption by small business. The Service Industries Journal, 35(11-12), 655-669.
- Asheq, A.A., & Hossain, M.U. (2019). SME PERFORMANCE: IMPACT OF MARKET, CUSTOMER AND BRAND ORIENTATION. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 23(1), 1-9.
- Berthon, P., MacHulbert, J., & Pitt, L. (2005). Consuming technology: Why marketers sometimes get it wrong. California Management Review, 48(1), 110-128.
- Chwelos, P., Benbasat, I., & Dexter, A.S. (2001). Empirical test of an EDI adoption model. Information Systems Research, 12(3), 304-321.
- Cloete, E., Courtney, S., & Fintz, J. (2002). Small Businesses’ Acceptance and Adoption of e‐Commerce in the Western‐Cape Province of South‐Africa. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 10(1), 1-13.
- Dahnil, M.I., Marzuki, K.M., Langgat, J., & Fabeil, N.F. (2014). Factors influencing SMEs adoption of social media marketing. Procedia-social and behavioral sciences, 148, 119-126.
- Duan, X., Deng, H., & Corbitt, B. (2012). Evaluating the critical determinants for adopting e-market in Australian small-and-medium sized enterprises. Management Research Review, 35(3/4), 289-308.
- Eagleman, A.N. (2013). Acceptance, motivations, and usage of social media as a marketing communications tool amongst employees of sport national governing bodies. Sport Management Review, 16(4), 488-497.
- Effing, R., & Spil, A. A. M. (2016). The social strategy cone: Towards a framework for evaluating social media strategies. International Journal of Information Management, 36(1), 1-8.
- El-Gohary, H. (2012). Factors affecting E-Marketing adoption and implementation in tourism firms: An empirical investigation of Egyptian small tourism organisations. Tourism Management, 33(5), 1256-1269.
- Galati, A., Crescimanno, M., Tinervia, S., & Fagnani, F. (2017). Social media as a strategic marketing tool in the Sicilian wine industry: evidence from Facebook. Wine Economics and Policy, 6(1), 40-47.
- Ghobakhloo, M., & Hong Tang, S. (2013). The role of owner/manager in adoption of electronic commerce in small businesses: The case of developing countries. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 20(4), 754-787.
- Gilmore, A., Gallagher, D., & Henry, S. (2007). E-marketing and SMEs: operational lessons for the future. European Business Review, 19(3), 234-247.
- Hossain, M.U., & Al Asheq, A. (2019). The Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation to SME Performance in Bangladesh. International Journal of Entrepreneurship. 23(1), 1-6.
- Kaplan, A.M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Business horizons, 53(1), 59-68.
- Lamberton, C., & Stephen, A.T. (2016). A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing: Research evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future inquiry. Journal of Marketing, 80(6), 146-172.
- Marcati, A., Guido, G., & Peluso, A.M. (2008). The role of SME entrepreneurs’ innovativeness and personality in the adoption of innovations. Research Policy, 37(9), 1579-1590.
- McCann, M., & Barlow, A. (2015). Use and measurement of social media for SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 22(2), 273-287.
- Morteza, G., Daniel, A.A., & Jose, B.A. (2011). Adoption of e-commerce applications in SMEs. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 111(8), 1238-1269.
- Nguyen, H.T., & S. Waring, T. (2013). The adoption of customer relationship management (CRM) technology in SMEs: An empirical study. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 20(4), 824-848.
- Pavlou, P.A., & Gefen, D. (2004). Building effective online marketplaces with institution-based trust. Information systems research, 15(1), 37-59.
- Premkumar, G., & Roberts, M. (1999). Adoption of new information technologies in rural small businesses. Omega, 27(4), 467-484.
- Qashou, A., & Saleh, Y. (2018). E-marketing implementation in small and medium-sized restaurants in Palestine. Arab Economic and Business Journal, 13(2), 93-110.
- Rahayu, R., & Day, J. (2015). Determinant factors of e-commerce adoption by SMEs in developing country: evidence from Indonesia. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, 142-150.
- Ramdani, B., Kawalek, P., & Lorenzo, O. (2009). Predicting SMEs' adoption of enterprise systems. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 22(1/2), 10-24.
- Rogers, E.M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations. Free Press. New York, 551.
- Tafesse, W., & Wien, A. (2018). Implementing social media marketing strategically: an empirical assessment. Journal of Marketing Management, 34(9-10), 732-749.
- Zhu, K., & Kraemer, K.L. (2005). Post-adoption variations in usage and value of e-business by organizations: cross-country evidence from the retail industry. Information Systems Research, 16(1), 61-84.