Review Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 6
Evaluation of Non−Fungible Tokens (NFTs) Investor′s Attention in Relation to Cryptocurrency Pricing
Priyanka Budania, Manipal University Jaipur, Jaipur
Gaurav Lodha, Manipal University Jaipur, Jaipur
Garvita, Manipal University Jaipur, Jaipur
Citation Information: Budania, P., Lodha, G., & Garvita. (2023). Evaluation of non-fungible tokens (nfts) investor’s attention in relation to cryptocurrency pricing. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(6), 1-7.
Abstract
The recent era is adopting innovative techniques very rapidly, in the Finance sector the usage of Blockchain technology is growing very well because of its benefits like security and efficiency. Blockchain is part of artificial intelligence, which can be used in different areas and fields; it is also used in finance, accounting, and auditing for the removal of errors and big data analysis. Non-fungible tokens have gotten the enormous attention of investors, especially those dealing in cryptocurrencies. Non-Fungible tokens are the digital tokens that have a unique id, and ownership of particular digital art, collectibles, audios, videos, etc., and all the trading in NFTs is recorded on the Blockchain ledger. This paper is going to examine why Non-Fungible Tokens got the attention of Crypto Investors and if there is any relationship between cryptocurrency pricing and the Non-Fungible Tokens market. Secondary data is used for the analysis and is collected from sites like Trends.google.com and correlation method is used for analysing the relation between cryptocurrency and non-fungible tokens. This paper is going to examine why changing in Crypto pricing affects NFTs investor is Attention by using, relevant statistical tools to see the relationship between cryptocurrency pricing and NFT market.
Keywords
Non-fungible tokens (E31), Blockchain (O3), Cryptocurrency (O3), Investor’s attention.
Introduction
Block Chain
Blockchain is a type of distributed database that keeps an ever-expanding list of data entries verified by the network nodes that make up the system. Blockchain may appear like a suitable option for carrying out transactions involving digital currencies, but there are still certain technical issues and restrictions that need to be looked at and resolved. To prevent attacks and efforts to manipulate with blockchain transactions, high levels of transaction integrity, anonymity, and node privacy are required. The blockchain, which powers the Bitcoin cryptocurrency, is a digital ledger system that safeguards the veracity of transaction data. The blockchain, which serves as a "trust less" verification method for all transactions on the network, is regarded as the key technological advancement of Bitcoin. Instead of needing to build and maintain confidence with the transactional counterparties (another person) or a third-party middleman, users may rely on the reliability of the public ledger that is held globally on several decentralised nodes maintained by "miner-accountants" (like a bank). The main innovation is the use of the blockchain as the foundation for a new, decentralised, trust less transaction system. The blockchain enables the worldwide disintermediation and decentralisation of all types of transactions between all participants. (Swan, 2015). The system is built to maintain characteristics like easy and constant control by the content owner.
In comparison to the traditional centre-operated rights management system, the concept Blockchain is completely different. This implies that the owner has complete control over his transactions. Simple and uncomplicated operation would be needed to implement this idea. Secondary It is possible to achieve reasonable simplicity and security. It takes few minutes to generate the hash value for the computation. The calculations as quickly as possible in order to evade pirates. These prolonged mining times will interfere with the delivery of digital material. (Junichi, Fujimura, & et al., 2015).
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
On a blockchain, a non-fungible token is a sort of digital asset that, by definition, cannot be traded for all other digital assets (non-fungible). Anything that may be traded for yet another identical or equal object is said to be "fungible," a phrase that originates from the accounting and economic literature. Traditional forms of currency are fungible, which helps them work as means of exchange since they are seen as having the same value whether they are similar amounts of paper money or precious metals. Since both currencies are fungible, a five dollar bill and five one dollar notes can be used interchangeably. NFTs are viewed as a fad by some and as the future of digital art by others. A variety of NFT types have drawn interest from investors, with just some buying and selling for several million dollars despite only being made up of code. Despite reservations about the code's relative lack as a digital item, a buyer has assigned "value" to it. (Chohan, 2021).
Major works of art are naturally thought of as exclusive items for which purchasers pay enormous prices to retain them due to their rarity. Digital art has opened up a comparable path for value assignation. The current rise in popularity of NFTs is mostly due to the acquisition of digital artwork.
Cryptocurrencies
A digital payment system based on blockchain technology that does not require financial institutions to verify transactions is represented by cryptocurrency. Transactions using cryptocurrencies may be used to make micropayments in almost real-time. The usage of credit cards for a one-cent cost, like when downloading a service or product from the internet, is not what they are designed for. Cryptocurrency-based systems have the potential to simplify micropayments and allow businesses to deal immediate pay-per-use consumption of their supplies, including audio visual, mobile phone service, conveniences, and other services. (H¨ardle & Harvey, 2020).
Link between NFTs, Blockchain, and Cryptocurrencies
NFTs, are token kept on a blockchain system, may be utilised to characterize the rights to digital goods like as artwork, music, records, virtual houses, and pets. Online specialty shops like OpenSea, Axie Marketplace, and Rarible provide NFTs for sale. On these platforms, investors can also swap ownership stakes in the assets supporting NFTs. Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are exchangeable, or convertible; they all have the same value, which is the main contrast between them and NFTs. However, NFTs are non-fungible, which implies that since they are all unique, they cannot be exchanged for one another. High-level decentralised apps with high levels of verification, fraud protection, accessibility, atomicity, and traceability are therefore NFTs.
Literature Review
This study offers brand-new proof of the elements that interest investors in the NFT industry. Early in 2021, the NFT market began to draw attention from the general public at the same time as all major cryptocurrencies saw price increases. Utilizing a variety of time-series econometric approaches, from wavelet coherence analysis to vector autoregressive (VAR) regressions, test the hypothesis. (Pinto-Gutiérrez, Gaitán, & et al.,, 2022).
Researchers look into several facets of the NFT ecosystems in this technical paper. gives a general overview of cutting-edge NFT solutions before describing their technical elements, protocols, standards, and desirable properties. Gives a security progression after then, with talks on the opportunities, difficulties, and perspectives of their design approaches. The contemporary NFT ecosystems have never been thoroughly studied before. (Wang, Li, & Wang, 2021).
In particular, Non-Fungible tokens, often known as "crypto collectibles," are the focus of this paper's technical study of cryptocurrencies and blockchain, as well as the potential effects these technologies might have on the global art market and creative sectors. A resource-based analysis of the creative fields, their value - chain, and the agents' various negotiating positions and revenue-sharing agreements forms the basis of the study. This paper concluded that the creative industries are largely based on the rights management, licencing, and data management of digital and digitizable information goods, which blockchain architecture can help manage in a decentralised, automated manner, it is possible that blockchain technology can bring about significant evolution in the creative industries. (CHEVET, 2017).
NFTs are rights that may be transferred to digital objects like music, art, collectibles, or in-game goods. Since the beginning of 2021, the phenomena and its marketplaces have expanded dramatically. Researcher look at the connections between NFT sales, NFT customers (individual active blockchain wallets), and the prices of Bitcoin and Ether. Demonstrate that a shock in the price of Bitcoin causes an increase in NFT sales using daily data from January 2018 to April 2021. The quantity of active NFT wallets is also decreased by ethereum price shocks. The findings imply that (bigger) cryptocurrency markets influence the (smaller) NFT market's growth and development, but there is no apparent opposite effect. (Ante, 2021).
Developed in late 2017, A brand-new category of unique and undivided blockchain-based assets is known as NFTs. Regardless of the fact that fungible tokens have made it possible for unique use applications like initial coin offerings, the potential of NFTs as a valued component is yet unknown. The usefulness of NFTs in the field of event tickets is demonstrated in this study, which bridges the information gap between research and practice. Develop a working prototype of an NFT-based events ticketing system, design it, thoroughly test it, and then refine it. By doing so, it exemplifies the value of NFTs in tokenizing digital products, reducing fraud, and enhancing control over secondary market transactions. (Regner, Schweizer, & Urbach, 2019).
Objectives Of The Study
• To explain the concept of Non-fungible tokens.
• To explain the link between Non-fungible tokens and Blockchain Technology.
• To examine the NFTs investor’s attentions based on Crypto pricing.
• To study the relationship between NFTs sales of specific blockchain and relevant cryptocurrency pricing.
Hypothesis Of The Study
• H01 - There is no significant variation in NFTs investor’s attentions based on Crypto pricing.
• H02 - There is no significant relationship between NFTs sales of specific Blockchain and relevant Cryptocurrency Pricing.
Research Methodology
This Study is based on Secondary data collection. Secondary data is collected from the websites, National and international journal & Articles, Newspapers and Publications. NFTs investors’ attention is measured on the basis of number of NFT buyers and total number of NFT sales. The data is taken from cryptoslam.io for NFT buyers and NFT sales.
Specific blockchain is selected as the top blockchain platform, which have their own crypto coins for measuring the relationship between NFTs sales of specific blockchain and relevant cryptocurrency pricing. The data is taken from cryptoslam.io for NFTs sales of specific blockchain and from finance.yahoo.com for cryptocurrency pricing.
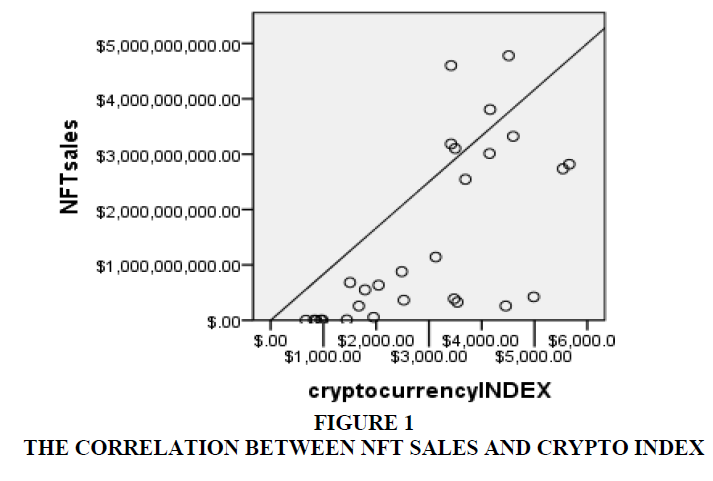
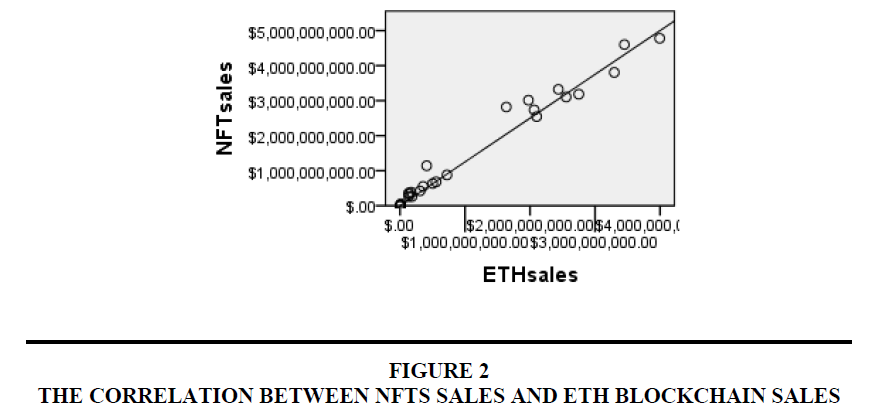
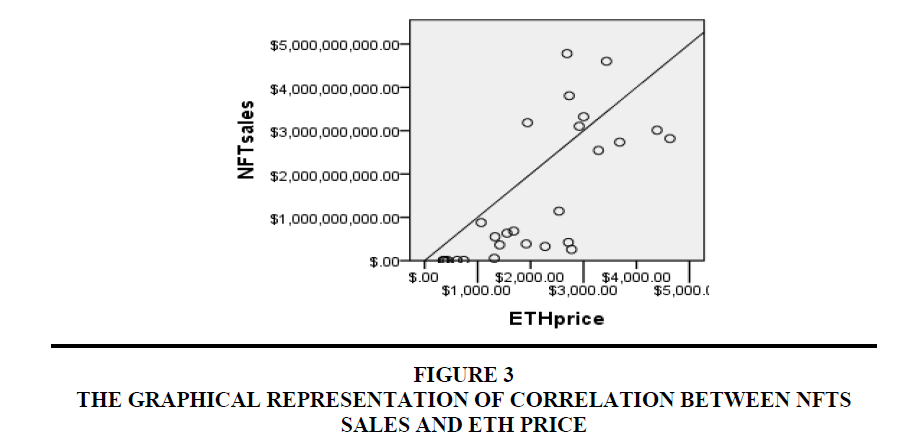
Data is taken for the period, July 2020 to September 2022 on monthly basis as per the availability of data Figures 1-3.
Pearson’s correlation method is used to prove both the hypothesis Tables 1-4.
Data Analysis
Data is analysed as Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
| Table 1 Correlation Between Nft Sales And Cryptocurrency Index |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| NFT sales | Cryto index |
||
| NFT sales | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .661** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
| Cryptocurrency INDEX | Pearson Correlation | .661** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
Interpretation
• Relationship – Suggests a strong association between NFT sales and Cryptocurrency. Index.
• Degree – 0.6 shows a high degree of correlation.
• Direction – Slop upward shows positive correlation.
| Table 2 Correlation Between Nfts Buyers And Cryptocurrency Index |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| NFTs Buyers | Cryptocurrency INDEX |
||
| NFTs Buyers | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .733** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
| Cryptocurrency Index | Pearson Correlation | .733** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
Interpretation
• Relationship – Suggests a strong association between NFT Buyers and Cryptocurrency. Index.
• Degree – 0.7 shows a high degree of correlation.
• Direction – Slop upward shows positive correlation.
| Table 3 Correlation Between Nft Sales And Eth Blockchain Sales |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| NFT sales | ETH sales | ||
| NFT sales | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .988** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
| ETH sales (Blockchain) |
Pearson Correlation | .988** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 28 | |
Interpretation
• Relationship – Suggests a strong association between NFTs Sales and ETH sales on Blockchain.
•Degree – 0.9 shows a high degree of correlation.
•Direction – Slop upward shows positive correlation.
| Table 4 Correlation Between Nfts Sales And Eth Price As Crypto Coin |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| NFT sales | ETH price | ||
| NFT sales | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .726** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 28 | 27 | |
| ETH price | Pearson Correlation | .726** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 27 | 28 | |
Interpretation
• Relationship – Suggests a strong association between NFTs Sales and ETH crypto coin price.
•Degree – 0.7 shows a high degree of correlation.
• Direction – Slop upward shows positive correlation between both the variables.
Results and Conclusion
All figures and tables represents that there is positive and strong relationship exists between NFTs sales and other given variables (ETH cryptocurrency price, ETH blockchain sales, Cryptocurrency Index and NFTs Unique Buyers). So both the null hypotheses are rejected. As they perojected that there is no significant relationship between NFTs investor’s Attention in relation to Cryptocurrency pricing. It can be said that changes in the cryptocurrency pricing drives the attention of NFTs investors whether it is in positive way or vice-versa. Further data shows that more investments were made when the prices of cryptocurrencies were increasing, high prices fluctuations were recorded in the period of 2021 and this period is also witnesses the high popularity and development in NFT market.
The study's findings have practical ramifications for institutions, governments, and investors who are expected to comprehend this developing sector as a component of the new digitalized economy where the cryptocurrency market is on growing phase.
References
Ante, L. (2021). The non-fungible token (NFT) market and its relationship with Bitcoin and Ethereum. Google Scholar, CrossRef
CHEVET, S. (2017). Blockchain Technology and Non-Fungible Tokens: Reshaping Value Chains in Creative Industries.
Chohan, U. W. (2021). Non-Fungible Tokens: Blockchains, Scarcity, and Value. Critical Blockchain Research Initiative (CBRI) Working Papers.
H¨ardle, W. K., & Harvey, C. (2020). Understanding Cryptocurrencies. Journal of Financial Econometrics, 181-208.
Junichi, K., Fujimura, S., & et al. (2015). The blockchain-based digital content distribution system. IEEE fifth international conference on big data and cloud computing, (pp. 187-190).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, CrossRef
Pinto-Gutiérrez, C., Gaitán, S., & et al.,. (2022). The NFT Hype: What Draws Attention to Non-Fungible Tokens? Mathematics.
Regner, F., Schweizer, A., & Urbach, N. (2019). NFTs in Practice - Non-Fungible Tokens as Core Component of a Blockchain-based Event Ticketing Application. Fortieth International Conference on Information Systems, Munich 2019.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, CrossRef
Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain Blueprint for a New Economy. O’Reilly Media.
Wang, Q., Li, R., & Wang, Q. (2021). Non-Fungible Token (NFT): Overview, Evaluation, Opportunities and Challenges.
Received: 15-May-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13597; Editor assigned: 16-May-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13597(PQ); Reviewed: 26-Jun-2023, QC No. AMSJ-22-13597; Revised: 25-Aug-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13597(R); Published:21-Sep-2023