Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 5
Impact Of Digitalization On Marketing Of Insurance Products
Rajesh Verma, ASIBAS, Amity University
Stuti Gupta, ASIBAS, Amity University
Kunal Goyal, Amity University
Vernika Sahni, Amity University
Citation Information: Verma., R. Gupta., S, Goyal, K., & Sahni, V. (2021). Impact of digitalization on marketing of insurance products. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 25(5), 1-8.
Abstract
Keywords
Insurance, Marketing, Digitalization.
Introduction
Insurance Business in India
The insurance industry in India is undergoing a major transformation. Increased awareness, accessibility, accessibility, regulatory reform, and economic growth are some of the key factors affecting the industry. For some insurers, it is a phase of re-establishment and self-preservation for others, dealing with these disruptors is crucial to their survival. The government's decision to allow a direct investment of more than 74% has made the Indian insurance industry profitable for foreign investors and empowered insurers to operate aggressive programs related to expansion and innovation. Digital transformation in India has disrupted the business environment in all industries and the insurance industry is affected. The increase in Internet access (with the number of users in India expected to increase from 429 million in 2017 to 829 million by 2021 at a rate of 17.9%) will continue to influence the insurance business and other industries. Currently, Investors are still investing in computerized business processes to achieve efficiency and reduce costs. As per industry estimates, digital production can reduce by approximately 20-30% of the cost of non-life insurance products and 15-20% of the cost of life insurance. In addition to the cost benefits, digital transformation also creates opportunities for collaboration between them.
Distribution of General Insurance in India
Without mediators, there would be only a direct channel, where customers could go to an insurance company branch and purchase insurance.
It is hard to imagine that if this were the only channel, how the growth of the sector would grow. Price is one of the many ways consumers think about deciding on insurance. Other important factors are the scope of the spread offered by competing insurance providers, access and availability of inaccessible coverage, distributor and insurance company arrangements, risk management services offered, insurers and the reputation of the mediators involved in the payment of claims and the ability to make decisions. The various distribution channels are Insurance Agent, Insurance Brokers, Bancassurance channel, Telephone sales, Internet and Digital marketing, Workplace Marketing, Post Offices, Insurance marketing firm and others.
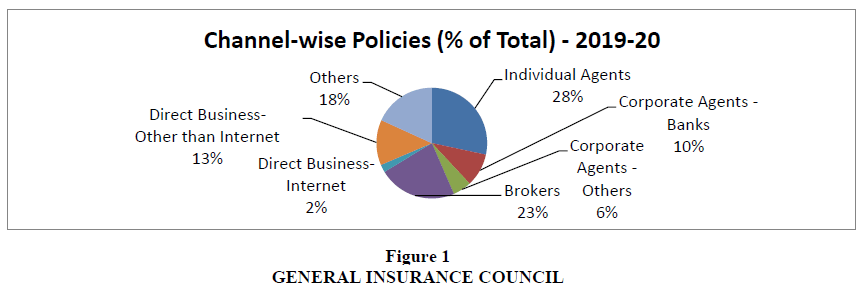
According to above Figure 1 Individuals – Agents is leading distribution channel on basis of percentage of policies sold in FY 2019-20 with 6,85,75,429 policies sold in that year, it is being followed by Brokers who sold 5,51,17,989 policies, direct business – other than internet sold 3,19,67,775 policies , corporate agents – banks sold 2,33,78,453 policies, others sold 4,39,61,777 policies ,corporate agents – other sold 1,31,45,352 policies and direct business – internet sold 55,01,608 policies.
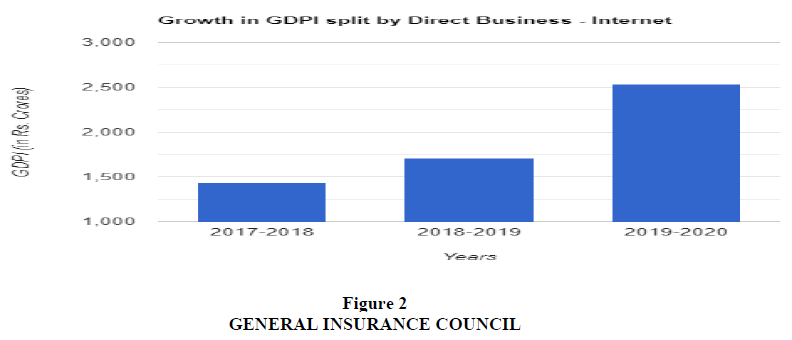
Above Figure 2 represents the growth in Gross Direct Premium Income, by direct business through internet made by general insurance companies in past three financial years and from the table we can say that it has been taking a significant growth year by year, in 2017-2018 GDPI was Rs.1433 Crores, in 2018-2019 GDPI was Rs.1707 crores and in 2019-2020 GDPI was Rs.2530 crores which is a significant increase.
Entry of Web Aggregators in Distribution
The online insurance journey began with the emergence of comparative and research platforms. At the same time, the idea of consolidating insurance arose in 2005 with players like Apnainurance and Bimadeal entering the market. About 20 other players such as Policybazaar, Zibika, Fintact, Myinsuranceclub and Insuring India as well as several others have established their own venues. After examining the consolidation model, the paid start-ups led to insurance companies and received commissions on all earnings conversions. Web aggregators have emerged as a new distribution channel in the insurance price list. Following the adoption of regulation by web aggregators in 2013, the number of registered web aggregators increased from 11 in 2013 to 22 March 2021. IRDAI issued guidelines for web-aggregators in 2011, 2013 and 2015, and the business is regulated under these guidelines and the webmasters have been granted a valid operating license. They now operate as insurance product platforms from multiple insurance providers and provide information about product features, benefits, price, settlement claim and inclusion, etc., and comparisons of insurance products.
New Practices Adopted By Insurers to Meet Customer Expectations
1) Simplification - When developing a consumer awareness strategy, insurers should consider customer categories, census, preferred languages, communication method, duration of attention of key customer groups and the level of financial literacy. For example, videos and product information can be edited in local languages for better understanding and must be shared with authorization from agents and customers to avoid any form of inappropriate communication.
2) Customer Centricity - Insurance providers need to raise the standard of customer engagement procedures to prevent conditions such as interactive voice response (IVR) loops, network communication, and viewing customer submissions, transactions, and requests, etc. Creating a living environment around customers through bonding with solidarity devices, social media communications, compatible offer suggestions, financial dashboards, digital storage, and health monitoring will generate more communication points and can promote better customer relationships.
3) Personalization - The future insurance market is designed to be professionally driven and customized. To develop a personalized approach, insurers must use the information available to customers. In addition, the integration of customer information has the potential to lead to a deeper understanding of customer behavior. It will ensure that the interaction is customized and customer friendly. Improving contact points can lead to more meaningful and customized interactions.
4) Digitization - For insurers, the digitalization of marketing processes has always been a priority. The provision of the Internet, easy communication channels, digital document acceptance, online claim processes and other applications and flexibility in account access are the basic services expected. In addition, the removal of paperwork with the introduction of business process strategies will provide greater relief for customers.
Review of Related Studies
According to Kishori, & Kumaran (2019) The digitalization of the insurance industry has many advantages and many challenges, where change must take place without interruption, the day-to-day running of the business. This new technology is forward-looking and creates a brighter future for customers and the insurance industry while these technologies provide security issues and data theft on a regular basis. Insurance providers will have more connections with existing customers and attract new customers with new sales, boost profits and individual growth. Digital inclusion will fundamentally change the business model and the insurance price list. Insurance companies need to develop their own computerized systems. Digital insurance varies from company to company. According to Vijay (2019) Overall the future of the digital marketing industry is bright. The banking and insurance industry is growing, and customers are satisfied with the digital marketing service in India. It will advance in the coming day with a digital marketing and digital marketing campaign in India. According to Ananda Ramaiah Shetty (2019), digital insurance marketing is one of the most effective ways for a domestic insurance company to compete with national insurers. Making ads on an online platform or digital platform, having a paid communication campaign helps many customers. And most importantly, insurance companies should incorporate this into their business which will help them grow their business output. And the main motivation must be to gather the attention of more and more people who can be easily influenced these days using an online platform only. According to Karthi (2012) insurance companies offer value to customers through online marketing. Unlike traditional marketing, Customers learn about product details, which are unique features, market conditions, competitive products, vision, purpose, company policy can be understood. The value added by customers should be made better by the company in online insurance advertising. E insurance stimulates customers to create demand and recognize those needs, seeking flexible information about insurance industry, to explore those alternatives from the digital information provided by insurance websites, making purchasing decisions and providing customer support posts. Companies should educate customers on the use of online insurance on effective communication methods. See should encourage customers to learn the use of online insurance and if possible national campaigns should organize by IRDA in all provinces and regions and encourages customers to use e-insurance fast and fast communication. Ultimately online insurance marketing creates a new path to companies to produce a large profit.
Objectives of the Study
1. To study Impact of digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
2. To study impact of use of mobile app/web portal and virtual assistance/chatbots for services related queries on digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
3. To study impact of use of mobile app/web portal and virtual assistance/chatbots for interaction for understanding the insurance terms/benefits/ limitations/cost on digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
Hypothesis of the Study
H1 – Information on insurance company’s website, does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H2 – Information from online aggregators does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H3 – For services related queries use of Mobile app/web portal platform does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H4 - For services related queries use of virtual assistance/chatbots platform does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H5 – For understanding the insurance terms/benefits/limitations/cost use of mobile app/web portal platform does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H6 – For understanding the insurance terms/benefits/limitations/cost use of virtual assistance/chatbots platform does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H7 – Purchasing insurance smoothly does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H8 – Consumer more reachable to insurer does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H9 – Availability of insurance products does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H10 – Making claim hassle free does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H11 – Customer services facilitate to higher level does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
H12 – More products options to consumer does impact digitalization on marketing of insurance products.
Population and Sample
A well-structured questionnaire was designed on google forms to collect the data. The Questionnaire contains all closed ended questions and was distributed to residents in Delhi NCR. The researcher was able to get 200 responses as questionnaire was sent through online mode due to Covid-19 situation. Both primary as well as secondary data is used for the research. The secondary data was collected from company websites, lounge books, referrals, internet browsing, Journals.
Statistical Techniques used In the Present Study
Multiple Regression analysis is used to analyse the data, it contains three tables, Model summary, ANOVA summary and Coefficient Table 1.
| Table 1 Represents Model Summary | ||||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the estimate | R Square change | F Change |
| 1 | .761 | .578 | .551 | .384 | .578 | 21.378 |
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Elements of this table is relevant for interpreting the result: -
1. The R value shows the correlation between the dependent variable (DFMIP) and independent variables (DMPO, VCIUI, DPIS, MWPIFS, OASOI, MWPIUI, DCMR, VCIFS, DCPHF, ICWSOI, DIAIP, DCSHL). A value more than 0.4 need to be analysed further but in this case, value is 0.761 which is good.
2. The R Square value represents the total variation for the dependent variable that could be explained by the independent variables. A value more that 0.5 is considered as good as it represents that the model is effective enough to determine the relationship and in this case the value of R Square is 0.578 which is good.
3. The Adjusted R square represents the generalization of the results which is the variation of the sample results from the population in multiple regression. It is appropriate to have a minimum difference between R square and Adjusted R square and in this case the value of adjusted R square is 0.551 which is not far from 0.578, value of R square.
Model summary table values are satisfactory so now we can proceed.
The items on this Table 2 that are relevant to interpreting the results are:
| Table 2 Represents Anova Summary | |||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sign. |
| 1 | 37.839 | 12 | 3.153 | 21.378 | .000 |
P- value/ Sig value: Generally, a confidence interval of 95% or a 5% level of significance value is selected for the study. Therefore, the significance value should be less than 0.05. In the table above, it is .000. Therefore, the result is significant.
F-ratio: It represents an improvement in variable prediction by inserting a model after looking at the inaccuracies in the model. The value is greater than 1 per efficient F production model. In the table above, the figure is 21.378, which is good.
The following results concludes that since the p value of the ANOVA Table 3 is below the tolerable value level, there is therefore a possibility of rejecting null hypothesis for further analysis.
| Table 3 Represents Coefficient Summary | |||||
| Model | B | Std. Error | Beta | T | Sig. |
| (constant) | .314 | .097 | 4.140 | .003 | |
| ICWSOI (Insurance Company's website provides most valuable source of information) | .321 | .067 | .302 | 4.308 | .002 |
| OASOI (Online aggregators provides most valuable source of information.) | .335 | .053 | .319 | 5.283 | .000 |
| MWPIFS (Mobile app/web portal is preferred platform for interaction for services related queries.) | .339 | .058 | .322 | 5.682 | .000 |
| VCIFS (Virtual assistance/chatbots is preferred platform for interaction for services related queries) | .370 | .053 | .356 | 5.339 | .000 |
| MWPIUI (Mobile app/web portal is preferred platform for interaction for understanding the insurance) | .334 | .051 | .325 | 4.085 | .001 |
| VCIUI (Virtual assistance/chatbots is preferred platform for interaction for understanding the insurance) | .345 | .050 | .329 | 5.901 | .000 |
| DPIS (Digitalization made the process of purchasing insurance smooth) | .349 | .069 | .309 | 5.045 | .000 |
| DCMR (Digitalization made consumer more reachable to insurer) | .303 | .077 | .280 | 3.753 | .004 |
| DIAIP (Digitalization increased the availability of insurance products) | .385 | .088 | .363 | 5.964 | .000 |
| DCPHF (Digitalization enabled insurance claim process hassle free) | .324 | .066 | .307 | 4.057 | .001 |
| DCSHL (Digitalization pushed customer service facilities to higher level) | .396 | .083 | .351 | 5.150 | .000 |
| DMPO (Digitalization enabled to give more product options to customer) | .365 | .068 | .333 | 5.366 | .000 |
Dependent variable: DFMIP (Digitalisation facilitates marketing of insurance products)
Predictors: (Constant), DMPO, VCIUI, MWPIUI, MWPIFS, VCIFS, OASOI, ICWSOI, DPIS, DCMR, DIAIP, DCSHL, DCPHF.
The items on this table that are relevant to interpreting the results are:
Sig. value – a confidence interval of 95% or a 5% level of significance value is selected for the study. Therefore, the significance value should be less than 0.05 and in the table all the predictors significance value is lower than 0.05, so all rejects the null hypothesis which concludes that all predictors have significant impact on the dependent variable i.e., DFMIP (Digitalization facilitates marketing of insurance products).
Suggestions
1. Traditional insurers are strongly needed to immediately begin to predict and measure the expected extent of the IoT impact on their business - and to plan for future changes accordingly.
2. Insurers need to opt for AI based technology for improving facilities of value-added services for the consumer.
3. In the way to grow in the market, insurers need to compete on price and on value added services while keeping pace with the changing business developments in the marketplace.
4. With the increase in number of distribution channels, insurers must focus on growing distribution channels like “Direct business – through Internet” which is increasing year by year.
Conclusion
The digitalization in insurance sector has altered the way companies communicate with customers, creates an environment in which marketing, information and technology should work together. Retailers and large industries have made great strides in digital acquisition platforms to bring a satisfactory customer experience. Like mobile and social networks increasing popularity, consumers rely on Smartphones and tablets in research, compare prices and buy products online - anytime, anywhere. Still, customers expect that the same accurate and easy experience from their insurance carriers as they do from their favourite program, search engine or online retailer. Digital inclusion has fundamentally changed the business model and the introduction of web aggregators in distribution channel has impacted the business of many insurers in a good as well as bad way, but consumers are happy to use web aggregator platforms for the information purpose. Consumers are also more inclined towards using mobile apps, chatbot, and company’s website for interaction purpose of any kind like service related or claim related ones. Digitalization has impacted on value added services which directly impacted the way by which insurers are now marketing their insurance products, engagement with customers and after sale services like how well and timely queries has been resolved, how smoothly and quickly claim has been approved etc. all these factors have now became important for marketer to market his insurance products in the competitive market.
References
- Arora, A. (2003). E-Insurance: Analysis of the Impact and Implications of E-commerce on the Insurance Industry. Masters Dissertation, 1-62.
- Chitkara, S. (2016). Perceptual Exploration of Factors and Issues Affecting Adoption of E-Insurance. Macrothink Institute, 99-112.
- R.Karthi. (2012). Influences of online marketing in the prospective Indian Insurance Industry. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 1-7.
- Goel, N. (2018). Business Today. Retrieved from Business Today Money Today: https://www.businesstoday.in/opinion/columns/money-today/naval-goel-founder-and-ceo-policyx-com/story/231834.html
- Hebbar, M.A. (2016). DIGITALIZATION OF INSURANCE SECTOR: ISSUES AND CHALLENGES TO AN INSURANCE ADVISOR. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Engineering and Technology(IJATET), 1-5.
- Kumaran, M. K. (2019). A STUDY ON DIGITALIZATION OF INSURANCE INDUSTRY: CUSTOMER’S OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES. Pramana Research Journal, 1-5.
- Lall, S. (2020). Financial express. Retrieved from Financial express: https://www.financialexpress.com/money/covid-19-necessitates-full-scale-digitization-of-the-insurance-industry/2029403/
- LUND, H.N. (1996). The Impact of Technology on the Distribution of Insurance and Financial Services. Marco Island Spring Meeting, 1-22.
- Mangal, D. (2019). Assisted Distribution:Changing the face of insurance sales. New Delhi: Confederation of Indian Industry.
- Millard, E. (2020, February 19). 321 web marketing. Retrieved from 321 web marketing: https://www.321webmarketing.com/digital-marketing-benefits-for-insurance-agencies/
- Mishra, A.K. (2018). Assessment of Effect of Globalization on Indian Insurance Industry . Journal of Advanced Research in Business Law and Technology Management, 1-4.
- Odoyo, D.F. (2011). E-Insurance: An Empirical Study of Perceived Benefits. International Journal of Business and Social Science , 1-6.
- P.Vijay. (2019). IMPACT OF DIGITAL MARKETING SERVICES ON BANKING AND INSURANCE SECTORS IN INDIA. International Conference On Winning the Marketing War - Challenges and Responses, 61-67.
- Shetty, A.R. (2019). Digital insurance marketing in respect to private insurance company in Bangalore. International Journal of Applied Research , 1-4.
- Singh, A. (2020). Distribution Channels in Life and General Insurance: A Conceptual Analysis. Studies in Indian Place Names, 1-22.