Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 4
Impact of Digitization on Social Economic Transformation Of Indian Economy
Dr Roop Lal Sharma, Assistant Professor, School of Economics, Shri Mata
Vaishno Devi University, Katra, Jammu &Kashmir, India
Ajay Kumar Sharma, Research Scholar, School of Economics, Shri Mata
Vaishno Devi University, Katra, Jammu
Abstract
It is a well-known fact that digital India is the outcome of many innovations and technological advancements. These transform the lives of people in many ways and will empower the society in a better manner. The motive behind the concept is to build participative, transparent, and responsive system. The Digital India drive is a dream project of the Indian Government to remodel India into a knowledgeable economy and digitally empowered society, with good governance for citizens by bringing synchronization and co-ordination in public accountability, digitally connecting, and delivering the government programs and services to mobilize the capability of information technology across government departments. Hence, an attempt has been made in this paper to understand Digital India – as a campaign where technologies and connectivity will come together to make an impact on all aspects of governance and improve the quality of life of citizens.
Keywords
Digital India, Digital Technology, E-Kranti, E-Governance.
Introduction
The digital world that we live in today is that where every civilian has a bright prospect to transform the lives in many ways that were hard to envision just a couple of years ago. It is the outcome of several innovations and technology advances. Today, every nation wants to be fully digitalized that will empower society in a better manner. The 'Digital India' programme, an initiative of honorable Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi, will emerge new progressions in every sector and generates innovative endeavors for geNext. The motive behind the concept is to build participative, transparent and responsive system. All educational institutions and government services will soon be able to provide I-ways round the clock. Digital India will provide all services electronically and promote digital literacy. Digital Technologies which include the concept of cloud computing and mobile applications have emerged as the catalysts for express economic growth and citizen empowerment. Companies all over the world desire to invest in Digital India- the 21st century India, as a growth opportunity. Hence, an attempt has been made in this paper to understand Digital India – as a campaign where technologies and connectivity will come together to make an impact on all aspects of governance and improve the quality of life of citizens. Global investors like Sundar Pichai, Satya Nadella, Elon Musk have supported Modi's Digital India initiative.
Objectives
1. To know how the technologies and connectivity will come together to make an impact on all aspects of governance and improve the quality of life of citizens.
2. To find out how the government services can work effectively with practical solutions and innovative ideas to accomplish the vision of a digital India-a reality.
Data Collection
The secondary data has been collected. For this purpose, various magazines and journals have been used as it is a conceptual paper. Thus, the focus is to know more about the concept, its application, and the impact on economy via other parameters. Therefore, qualitative and quantitative data have been used.
Digital India
The programme contains tasks that target to make sure that govt. services are available to people digitally and people get advantage of the newest information and connections technological innovation. Gandhiji felt that 'India resides in its villages,' and technology will help the villages to grow and prosper. Digital libraries, online magazines, e-books can be made available for free which will further help in knowledge sharing. PM Modi rightly said in his speech in San Jose, "I see technology as a means to empower and as a tool that bridges the distance between hope and opportunity. Social media is reducing social barriers. It connects people on the strength of human values, not identities." Technology is a bridge indeed, a bridge that connects the hope that India's villages will be educated and aware to the opportunity of internet and access to information from across the world. 'Digital India' is not just an initiative but a need for this country, where majority of population still does not have access to the world of internet. The Digital India initiative seeks to lay emphasis on egovernance and transform India into a digitally empowered society. It is to ensure that government services are available to citizens electronically. Digital India also aims to transform ease of doing business in the country. The Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DEIT) anticipates that this program will have a huge impact on the Ministry of Communication and IT. The program is projected at Rs 1, 13,000 crore which will prepare the country for knowledge-based transformation.
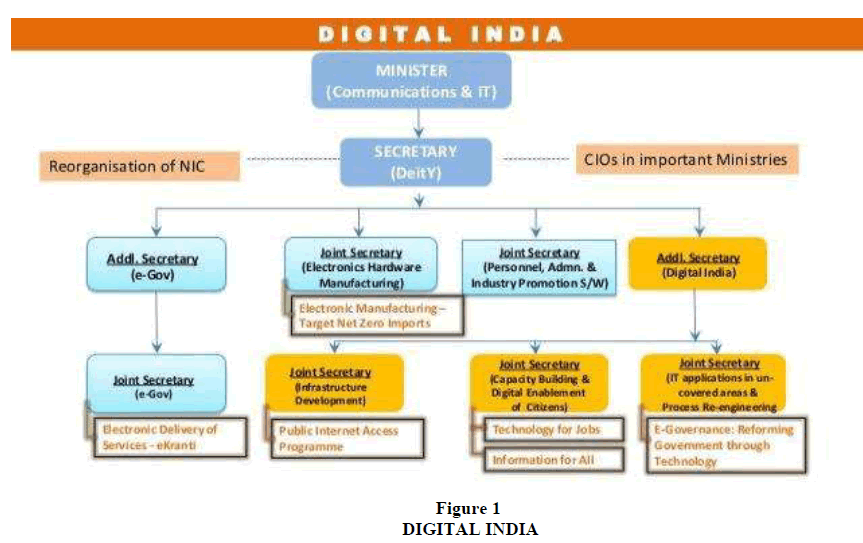
It will focus on providing high speed internet services to its citizens and make services available in real time for both online and mobile platform. Modi's government is focusing on providing broadband services in all villages of the country, tele-medicine and mobile healthcare services and making the governance more participative in Figure 1.
Major Projects under the Initiatives
Digital India comprises of various initiatives under the single programme each targeted to prepare India for becoming a knowledge economy and for bringing good governance to citizens through synchronized and coordinated engagement of the entire Government. Nine projects have been undertaken. These are as follows.
1. Highways to have broadband services: Government aims to lay national optical fiber network in all 2.5 lakh gram panchayats. Broadband for the rural will be laid by December 2016 and broadband for all urban will mandate communication infrastructure in new urban development and buildings. By March 2017, the government aims to provide nationwide information infrastructure.
2. Easy access to mobile connectivity: The government is taking steps to ensure that by 2018 all villages are covered through mobile connectivity. The aim is to increase network penetration and cover gaps in all 44,000 villages.
3. IT Training for Jobs: This initiative seeks to train 10 million people in towns and villages for IT sector jobs in five years. It also aims to train 0.3 million agents to run viable businesses delivering IT services. Additionally, the project involves training of 0.5 million rural IT workforce in five years and setting up of BPOs in each North-eastern state.
4. Manufacturing of electronics: The government is focusing on zero imports of electronics. In order to achieve this, the government aims to put up smart energy meters, micro-ATMs, mobile, consumer and medical electronics.
5. Provide public access to internet: The government aims to provide internet services to 2.5 lakh villages which comprises of one in every panchayat by March 2017 and 1.5 lakh post offices in the next two years. These post offices will become multi-Service centers for the people.
6. E-Governance: The government aims to improve processes and delivery of services through e- Governance with UIDAI, payment gateway, EDI and mobile platforms. School certificates, voter ID cards will be provided online. This aims for a faster examination of data.
7. E-Kranti: This service aims to deliver electronic services to people which deals with health, education, farmers, justice, security and financial inclusion.
8. Global Information: Hosting data online and engaging social media platforms for governance is the aim of the government. Information is also easily available for the citizens.
9. MyGov.in is a website launched by the government for a 2-way communication between citizens and the government. People can send in their suggestions and comment on various issues raised by the government, like net neutrality.
10. Early harvest programs: Government plans to set up Wi-Fi facilities in all universities across the country. Email will be made the primary mode of communication. Aadhar Enabled Biometric Attendance System will be deployed in all central government offices where recording of attendance will be made online.
Is India Digitally Ready
There is no doubt in it. India is ready for this. Immediately with the introduction of this campaign, many organizations came forward to lend their hands for achieving India a digitally equipped country. Organizations like BSNL, Reliance Ltd. are coming forward to spread digitalization among rural areas. And over 42000 villages all over India will be having seamless mobile connectivity by 2018. The Internet Saathi initiative aims to cover 4,500 villages over the next 18 months, starting with Gujarat, Rajasthan and Jharkhand. India is aiming to achieve universal digital literacy across the country. The prime importance is to make sure every individual can be able to leverage the potential of Digital India. The focus is at least one person in a household should transform into an e-literate. This can be achieved by BBNL which is planning to connect 2, 50,000 panchayats under the scheme. This will ensure the digitization and connectivity of local institutions like panchayats offices, schools, other government offices and libraries etc. India is reforming its government through technology in the name of E-Governance with the advancement of technology and digitalization. Under the e-governance programme, out of 252 schemes planned, 222 services have been provided in short span of time. The nine pillars of Digital India programme clearly confirms that India as a nation is at its nascent stage. One can easily assure that India will be digitally ready in the next three years.
Impact
India’s economy has witnessed a significant economic growth in the recent past by growing 7.3 per cent in 2015 as against 6.9 per cent in 2014. The steps taken by the government in recent times have shown positive results as India’s gross domestic product (GDP) at factor cost at constant (2011-12) prices 2014-15 is Rs 106.4 trillion (US$ 1.596 trillion), as against Rs 99.21 trillion (US$ 1.488 trillion) in 2013-14, registering a growth rate of 7.3 per cent. This clearly shows that the Digital India initiative introduced by Indian government has contributed a lot to boost the economy of the country. The Digital India project itself will create employment opportunities for 17 million people directly or indirectly which will help in fighting against unemployment problems in India. Government has planned to give IT training to 100 million students in smaller towns and villages as employment opportunity in IT sector is very high in India. In the next 5 years, India will emerge to be a leader in using IT in sectors like health, defence, education, agriculture and banking. Also, the service sectors will be digitally empowered. In the field of education, it also assures broadband connectivity in all panchayats, schools, libraries and other public places. Apart from Broadband connectivity, every village is provided with universal phone connectivity across the country. Mobile and internet banking can improve the financial inclusion in the country and can create win-win situation for all parties in the value-chain by creating an interoperable ecosystem and revenue sharing business models.
Telecom operators get additional revenue streams while the banks can reach new customer groups incurring lowest possible costs. The digital inclusion among the country ensures the ma nufacturing sector to revive the electronics manufacturing.
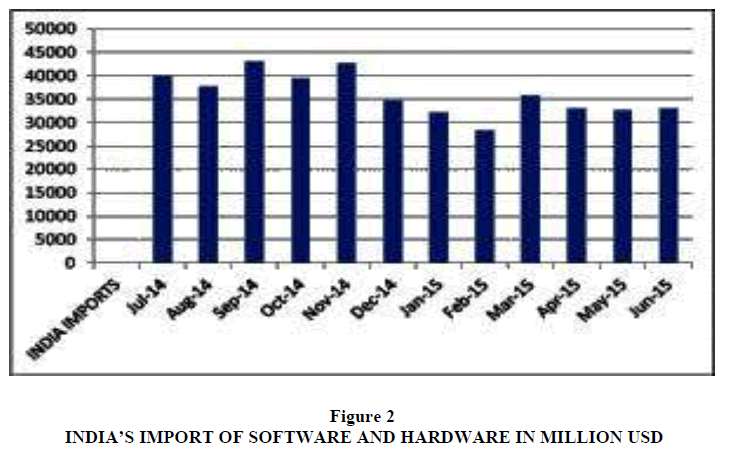
With the Make in India campaign and Digital India, the nation is planning to achieve net zero imports by 2020. This ensures the exports will be equal to the imports and this helps in the economic development of the nation. With the introduction of mobile connectivity in all villages, unique single portal can be maintained for all government related services. This ensures that all databases and information should be in electronic form and not manual. Next to crude oil, Electronics hardware comprises major parts of imports in India. Since India is a service-based country and till now we have focused only on software development, with the advent of Digital India, with its stress on making India a manufacturing hub will change the trend in Figure 2.
World’s leading research firm McKinsey has commented that the adoption of new technologies and innovative ideas across sectors by the Digital India programme will help India boost its GDP by $550 billion to $1 trillion by 2025.
Thus, the estimated impact of Digital India by 2020 would be cross cutting, ranging from broadband connectivity in all Panchayats, Wi-Fi in schools and universities and Public Wi-Fihotspots. The programme will generate huge number of IT, Telecom and Electronics jobs, both directly and indirectly. Success of this programme will make India Digitally empowered and the leader in usage of IT in delivery of services related to various domains such as health, education, agriculture, banking, etc.
The Digital India program is just the beginning of a digital revolution, once implemented properly it will open various new opportunities for the citizens.
References
- http://deity.gov.in/sites/upload_files/dit/files/Digital%20India.pdf.
- http://www.bgr.in/news/google-ready-to-help-in-digital-india-project/#more-338552
- http://www.bgr.in/news/fujitsu-to-bring-social-apps-to-boost-digital-india-drive/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_India