Review Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 4
Impact of Transformative Leadership on Employee Performance In Mediation with Job Satisfaction
Prasad Kandi V.S., Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Kona Sri Kapardi, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Kavya Kobbarisetty, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation
Citation Information: Prasad Kandi., V.S., Sri kapardi, K. & Kavya, K. (2022). Impact of Transformative leadership on employee performance in mediation with job satisfaction. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(4), 1-7.
Abstract
Many Organizations look for employees to work for a longer period in their company. Employees look for various factors which make them decide whether to continue in the organization or change to a new company and also, analyze the scenarios of their performance and satisfaction levels. Does Transformational leadership affect employee job performance in a company? Does Transformational leadership show any impact on the decision-making of employees and does this improve the job performance of employees? This paper is to analyze the effects of leadership style – transformational towards employee performance in work, as mediated through job satisfaction. Design approach: Questionnaire method as survey is used as a tool for collecting the primary data. For managers looking to reduce training costs, leadership styles can make a difference. A manager who pays little attention to his subordinates is only when he does something wrong. You can reduce these costs by adopting a conversion style. This paper will help you expand your current work on leadership. Use a conceptual model developed to conceptualize employee performance to explore the relationship between leadership style and employee performance.
Keywords
Transformational, Leadership, Performance, Job satisfaction
Introduction
Transformative leadership is a leadership style that encourages, inspires, and motivates leaders to innovate and make changes that contribute to the growth that will shape the future success of the organization. Transformational leadership is defined as a leadership approach that transforms individuals and social systems. In this type of leadership, leaders work with teams to identify necessary changes and create visions that guide them through inspiration.
Job performance explains the work done by the employees of the organization each time. It deals with goals and deadlines & rate of submission of work in each amount of time. It includes allocation of work, development, testing, and release. All these in a financial year are considered in determining the performance to provide an appraisal rating. But there are factors affecting the job performance of employees and show the impact on the satisfaction levels of employees in an organization. In such scenarios, the Transformational Leadership style helps in identifying the needed change to improve performance and employee satisfaction levels.
Literature Review
According to Pearce & Sims (2002), transactional leadership is based on three theories. It derives from the expectation theory of using rewards to achieve maximum motivation, with a focus on clarifying the relationship between effort and rewards. It is based on exchange/equity theory and explains that higher rewards can generate higher efforts. And finally, a reinforcement theory assumes that the outcome of the action determines whether the action is repeated (Pearce & Sims, 2002). The authors suggest that transactional leadership works by enhancing (rewarding) desirable behavior.
According to Abdul Raziq and Raheela (2014) Maulabakhsh published in May 2016, the main challenge for businesses is keeping their employees happy to cope with the ever-changing and evolving environment, prosper and compete. To increase employee efficiency, effectiveness, productivity, and involvement in work, companies need to meet their needs by providing good working conditions Riordan et al. (2005). There is a lot of impact of working conditions on job performance and job satisfaction. Flexible working hours, low workloads, teamwork approaches, and supportive top management have a positive impact on employee performance in these work environments where employees are involved throughout the decision-making process. This leads to high employee satisfaction with the work Mustofa & Muafi (2021).
According to Wasif Inayat & Muhammad Jahanzeb Khan, better performance of employees depends on Job satisfaction. Job satisfaction is the positive and negative feelings an employee has towards their job or its level of job-related happiness. Thus, job satisfaction is one of the most trending research topics in the field of organizational psychology Doeleman (2021).
Dziuba, (2020) Manuela Ingaldi, dockage Zhuravskaya that staff is a necessary think about the implementation of the company’s mission and vision, particularly within the field of manufacturing. staff should meet performance criteria established by the organization to confirm the amount and quality of their work to fulfill structure standards, employees would like a piece setting that permits them to figure freely simply which may forestall them from reaching their full potential.
Transformational leadership has become prominent in leadership theory in recent years. Transformational leadership cares about the extent to which the leader fosters an inspiring vision for the longer term, seeking to create relationships with followers and develop them as individuals, thought-provoking freedom, and set a private example. supported charismatic leadership theory, transformational leadership is predicated on the view that leaders motivate followers to “perform beyond expectations.” instead of simply monitoring employee performance, managing rewards accordingly, and managing an existing system, transformation leaders seek to determine a transparent and optimistic view of what is happening. They strive to make a solidarity where individuals are willing to line aside individual considerations for the great of the collective. To try to this, they were willing, among other things, to form personal sacrifices and set an example. The utilization of the word "transformation" is vital - leaders taking this approach aim to vary mindsets, enhance, and harness employee thinking and creativity, and lift expectations of the collective about what are often achieved and stimulate innovation in how this will be achieved.
Studies have looked at the relationship between leadership style and absenteeism. Regarding the direct association, half of the studies found a negative relationship (Richardson and Vandenberg, 2005; Walumbwa and Lawler, 2003; Zhuet et al., 2005), while the other half found no relationship. Significantly (Gakovic, 2002; Walumbwa et al., 2004; Wang and Walumbwa, 2007). However, two studies looking for an intermediate relationship have been successful. Both show that transformational leadership is negatively correlated with absenteeism, which is moderated by the presence of a highly participatory work system (Richardson and Vandenberg, 2005) and by Human resource management practices that improve human capital (Zhu et al., 2005). Continuing from these last two studies, our study also models the negative relationship between switching styles and absenteeism, and we hypothesize that it is mediated by satisfaction enthusiasm at work.
Employees feel more satisfied at work with leaders who focus on supporting, providing feedback and empowering their followers (Rafferty & Griffin, 2006; Walumbwa & Lawler, 2003). Personalized consideration and employee engagement reflect what he defines as "growth orientation" and "supportive leadership," which he considers essential to satisfaction. in employee work.
Problem Statement
The research investigates transformative leadership’s impact on the job performance of employees & determining employees’ satisfaction in an organization.
Objectives
1. To explore the direct repercussions of transformational leadership on employee performance.
2. To investigate the supremacy of Transformative leadership on employees’ performance through job satisfaction as a mediating factor.
Scope
To know how the transformative leaders will control the employee dissatisfaction, thereby improving job performance and its importance from the perspective of employee morale. There is a clear correlation between employee attitudes & performance. Employee performance is related to job satisfaction. The discussion in the organizations about the performance is a major issue. Through the motivation and good leadership from the management, the employee gets job satisfaction, which results in a good performance.
Through this study, we can identify the various variables which affect employee absenteeism in an organization and can understand how Transformative Leadership enhances job satisfaction and improves performance.
It outlines the research methodology. It deals with hypothesis formulation, research design including sampling design, data collection, survey tools, and planned analysis methods Manoppo (2020).
Research Design: A design is a blueprint for collecting, measuring, and analyzing data. At the main stage, an exploratory study was performed and this type of research is used to discover the results of the research objectives by generating hypotheses and uncovering the gaps Purwana et al. (2020).
Sample Design: A sample design serves as a basis for sample selection. The sample for the study was respondents or the employees of various IT companies in Hyderabad.
Sampling technique: Simple random sampling technique is used here to collect data for analysis.
Sample Size: The sample size for this research is 380 which is taken as the population is very large. This research is done on various IT companies in Hyderabad. Hence 95% confidence & margin for error of 5% is possible with the sample size of 380. It gives an exact fit to +/- 0.10.
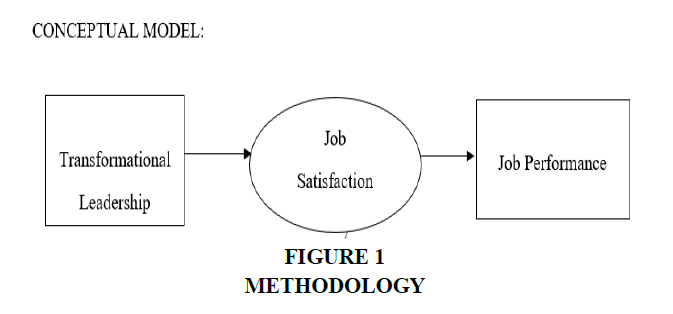
Tool development: Collected data was analyzed by questionnaire Figure 1.
Tools for hypotheses testing: Linear regression, Kruska006C Wallis test.
Analysis and Interpretation
Hypothesis Testing
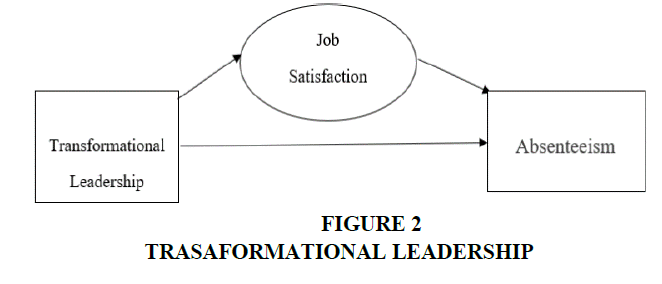
Our research paper discusses the employees’ job performance is influenced by Transformative leadership with job satisfaction as a mediating factor. The proposed conceptual model has two objectives Figure 2.
Objective 1: The direct repercussions of Transformative leadership on employees’ performance.
Objective 2: The arbitrate effect of Job satisfaction on the impact of transformative leadership on employees’ performance.
Hence the hypothesis testing has to be done for both the objectives and verify the mediating effect of the job satisfaction variable on the leadership variable and job performance variable and also compare it with the direct repercussions of Transformative leadership on the employees’ performance.
Hypothesis Testing for Objective 1
The first objective is the direct repercussions of Transformative leadership on job performance. So we consider the below hypothesis.
H1: Transformational leadership will impact/ has a direct impact on employees’ JP (job performance).
H2: Transformational Leadership will not impact/ has an indirect impact on JP (job performance).
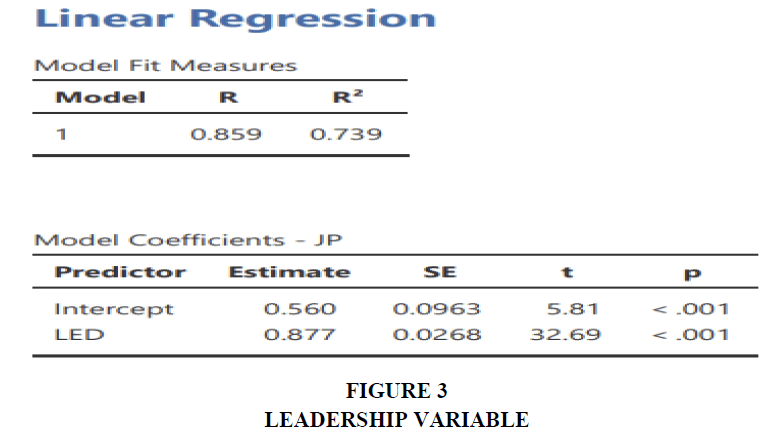
Testing is done by Linear Regression.
*LED – Leadership variable.
*JP – Job Performance Variable.
The above figure 3 represents the linear regression analysis of the two variables (leadership and job performance). LED represents the Leadership variables and the model coefficient is job performance. The model fit measures R and R^2 are less than 1 and their percentage is 73%. The linear regression between the LED and JP indicates p < 0.001, which indicates there is direct impact of Transformative Leadership on Employees’ performance. Hence H1 is accepted Figure 3.
Hypothesis Testing for Objective 2
The second objective of the research is analyzing the repercussions of Transformative leadership on employees’ performance with job satisfaction as mediating factor. Hence the following hypothesis should be considered.
H1: Job satisfaction variable has zero mediating effect on LED and JP variables.
H2: Job satisfaction variable has partial mediating effect on LED and JP variables.
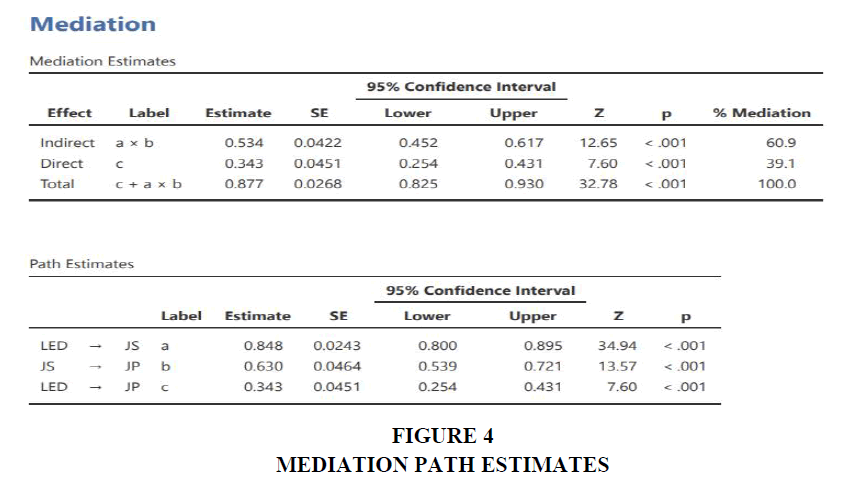
H3: Job satisfaction variable has high mediating effect on LED and JP variables Figure 4.
From the mediation figure we can interpret mediating impact of JS variable on the LED variable and JP variable
*LED – Leadership Variable
* JS – Job Satisfaction Variable
*JP – Job Performance Variable
The analysis is done at 95% confidence level with 380 sample size to estimate the accurate effect of the job satisfaction variable. From figure 4 the following observations are drawn:
1. The indirect effect a*b has the mediation percent of 60.9 with p< 0.001. This indicates that there is impact of job satisfaction variable on leadership variable and job performance variable since P < 0.001 is significant.
2. The direct effect c has a mediation percent of 39.1 with p < 0.001 indicates: leadership variable has direct impact on job performance variable.
3. As a whole from above two observations p< 0.001 is significant in both cases and a*b mediation percent is higher than c’s mediation percent but together the whole mediation percent is 100 with p<0.001 which is also significant.
From path estimates we can draw the following conclusions:
1. LED – JS (a) has p < 0.001, which is significant.
2. JS – JP (b) has p <0.001, which is significant.
3. LED – JP (c) has p < 0.001, which is also significant.
Hence if the JS mediation is positive and direct impact is negative, we can say that H3 is accepted as the mediating effect is high. If the JS impact is null and direct impact is positive, we can say H1 is accepted as there is zero mediating effect. But in this case, we have direct impact as well as mediating effect of JS on LED and JP with 60.9>39.1 i.e. % mediation of (a*b)>%mediation of (c). Hence, we can say there is partial mediating impact of Job satisfaction on transformational leadership variable and job performance variable. So H2 is accepted.
Conclusion
It is observed that satisfaction levels of employees increased through transformational leadership which promoted increase in performance of the employees. The transformative leadership style has been shown positive association towards performance of employees in work place. The present study has provided some insight on the processes by which transformational leadership can potentially influence employee job performance with job satisfaction as a mediating factor. Finally, present research assessed the role of leadership style and its impact on performance in the workplace. However further studies need to be undertaken in this direction on a larger scale.
References
Dziuba, S. T., Ingaldi, M., & Zhuravskaya, M. (2020). Employees' job satisfaction and their work performance as elements influencing work safety.System Safety: Human-Technical Facility-Environment,2(1).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Doeleman, H. J., van Dun, D. H., & Wilderom, C. P. (2021). Leading open strategizing practices for effective strategy implementation.Journal of Strategy and Management. .
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Han, S. H., Seo, G., Yoon, S. W., & Yoon, D. Y. (2016). Transformational leadership and knowledge sharing: Mediating roles of employee’s empowerment, commitment, and citizenship behaviors.Journal of Workplace Learning.
Inayat, Wasaf & Khan, Muhammad. (2021). A Study of Job Satisfaction and Its Effect on the Performance of Employees Working in Private Sector Organizations, Peshawar. Education Research International. 2021.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Maharani, V., Troena, E. A., & Noermijati, N. (2013).Organizational citizenship behavior role in mediating the effect of transformational leadership, job satisfaction on employee performance: Studies in PT bank Syariah Mandiri Malang east Java.International Journal of Business and Management,8(17), 1-12.
Manoppo, V. P. (2020). Transformational leadership as a factor that decreases turnover intention: a mediation of work stress and organizational citizenship behavior.The TQM Journal.
Mustofa, A., & Muafi, M. (2021). The influence of situational leadership on employee performance mediated by job satisfaction and Islamic organizational citizenship behavior.International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478),10(1), 95-106.
Pearce, C. L., & Sims Jr., H.P. (2002). Vertical versus Shared Leadership as Predictors of the Effectiveness of Change Management Teams: An Examination of Aversive, Directive, Transactional, Transformational, and Empowering Leader Behaviors. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 6, 172-197.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Purwana, D., Ahmad, A., & Saptono, A. (2020). The Influence of Leadership and Work Environment toward Organziational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) through Work Satisfaction.International Journal on Advanced Science, Education, and Religion,3(2), 57-71.
Raziq, Abdul & maula-bakhsh, Raheela. (2014). The Impact of Working Environment on Job Satisfaction. Procedia Economics and Finance. 23.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Riordan, C. M., Vandenberg, R. J., & Richardson, H. A. (2005). Employee involvement climate and organizational effectiveness.Human Resource Management, 44(4), 471–488.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Walumbwa, F. O., & Lawler, J. J. (2003). Building effective organizations: Transformational leadership, collectivist orientation, work-related attitudes and withdrawal behaviours in three emerging economies.The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 14(7), 1083–1101.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zhu, Weichun & Chew, Irene & Spangler, William. (2005). CEO Transformational Leadership and organizational Outcomes: The Mediating Role of Human-Capital-Enhancing Human Resource Management. The Leadership Quarterly. 16. 39-52.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 10-May-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11995; Editor assigned: 11-May-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-11995(PQ); Reviewed: 25-May-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-11995; Revised: 27-May-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11995(R); Published: 29-May-2022