Review Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 4S
Influence of Human Resource Management Practices on Employee Job Satisfaction with Special Reference to Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises
Shital Deshmukh, Prin. N. G. Naralkar Institute of Career Development and Research, Pune
Pavan Kumar Balivada, Institute of Management Technology, Hyderabad
Vibhuti Tyagi, Raj Kumar Goel Institute of Technology, Ghaziabad (U.P)
Indira Singh, Chetana's Institute of Management and Research, Bandra East, Mumbai
Krishan Kumar Garg, Lingayas Lalita Devi institute of Management and Sciences Mandi road, New Delhi
Shikha Gupta, Lingayas Lalita Devi Institute of Management and Sciences Mandi Road, New Delhi
Citation Information: Deshmukh, S., Kumar Balivada, P., Tyagi, V., Singh, I., Kumar Garg, K., & Gupta, S. (2024). Customer journey and experience in the banking sector: a comprehensive analysis and future scope. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(S4), 1-9.
Abstract
An important topic of study in organisational studies is the link between Human Resource Management (HRM) practises and how happy employees are with their jobs. It's important for companies, especially Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises (SSMEs), to know how HRM practises affect employee satisfaction as the modern workplace changes all the time. To be satisfied with your job, you need to feel good about your physical, mental, and emotional responses to your workplace. How well HRM practises work has a big impact on these responses, which in turn affects employees' general health and productivity. Small and medium-sized businesses (SSMEs) may have a more flexible organisational structure and a close-knit work culture. This means that HRM practises can have a big impact on job happiness. As a result, it is important to understand how HRM practises affect not only job satisfaction but also the culture and success of small and medium-sized businesses as a whole. When it comes to small and medium-sized businesses (SSMEs), HRM practises have a more complex effect on job happiness because these businesses have limited resources, unique operational challenges, and a close-knit work environment. This study will help both academics and business people by shedding light on best practises that can improve the working conditions of small and medium-sized businesses (SSMEs), leading to a more efficient and happy workforce. HRM practises and employee job satisfaction in the specific context of small-scale manufacturing enterprises is what this study tries to look into.
Keywords
Human Resource Management Practices (HRMP), Employee, Job Satisfaction, Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises (SSMEs).
Introduction
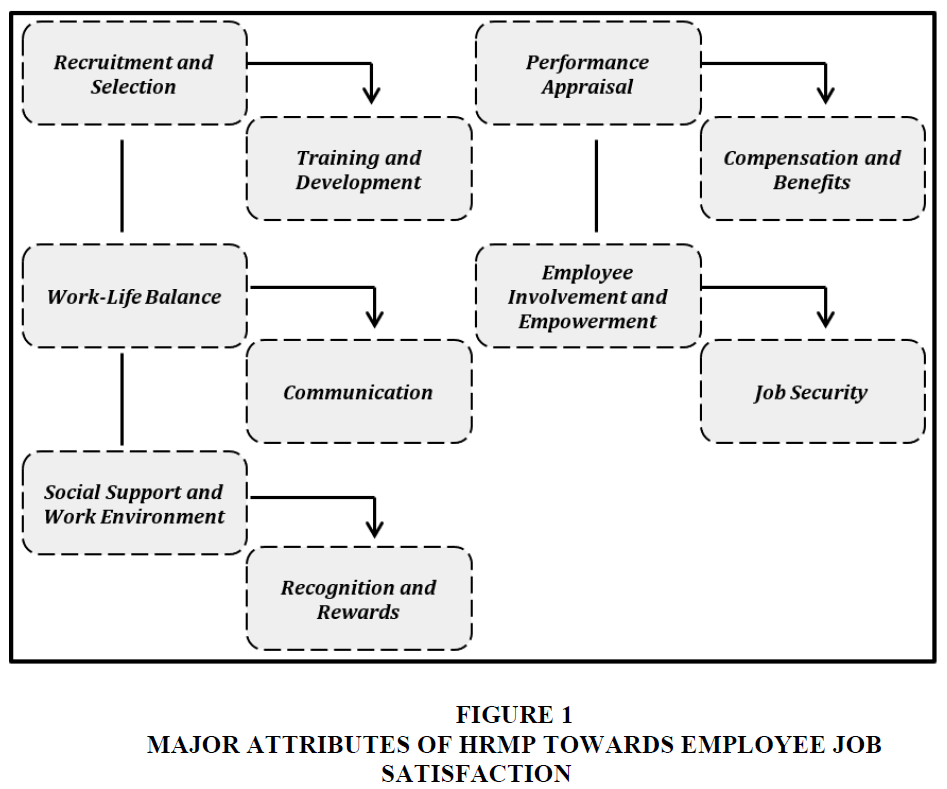
The fundamental principle of Human Resource Management (HRM) is rooted in its capacity to effectively synchronise the objectives of an organisation with the desires and ambitions of its employees. Human resource management (HRM) practises have a significant impact on the overall employee experience, encompassing several aspects such as recruiting, selection, training, performance review, and remuneration. In the context of small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs), where the organisational structure tends to be more flexible and the work culture characterised by close-knit relationships, the impact of human resource management (HRM) practises on employees' job satisfaction can be significant. The purpose of this research is to ascertain the primary “human resource management (HRM) practises and their influence on employee job satisfaction” inside the distinctive confines of small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs). Through a comprehensive analysis of recruitment strategies, training programmes, performance evaluation systems, remuneration frameworks, and the overall work environment, our objective is to elucidate the complex dynamics that either enhance or diminish job satisfaction within smaller-scale manufacturing contexts (Kumawat & Meena, 2022). The study of HRM practises and their impact on job satisfaction in Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises (SSMEs) is of utmost importance due to the distinct problems and possibilities faced by these enterprises Figure 1.
Here are Some Key Features to Consider
1. The implementation of efficient recruiting and selection procedures within small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) can result in the acquisition of highly competent and driven personnel (Jain, R., 2022).
2. Employees that possess appropriate abilities and align well with the organisational culture make valuable contributions to fostering a healthy work environment, hence augmenting job happiness.
3. The provision of training and development opportunities facilitates the acquisition of novel skills by employees, hence fostering their professional growth and advancement within the organisation.
4. Employees who hold the perception that their employer allocates resources towards their professional development are inclined to have higher levels of job satisfaction.
5. The implementation of equitable and transparent performance evaluation methods within small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) has a positive impact on employee work satisfaction.
6. Providing constructive feedback and acknowledging exemplary work can contribute to the enhancement of employees' sense of achievement and job happiness.
7. Ensuring competitive and equitable remuneration packages is crucial for fostering employee happiness.
8. In the context of small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs), when there may be constraints on resources, it is noteworthy that non-monetary bonuses and perks can exert a substantial influence on job satisfaction, hence contributing to overall employee well-being.
9. small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) frequently have time constraints and budget limitations, hence presenting difficulties in achieving a harmonious equilibrium between work and personal life (M., K., & ABDULLAH, M. R. T. L., 2023).
10. The implementation of policies aimed at promoting work-life balance, such as the provision of flexible work schedules or the ability to work remotely, has been found to have a beneficial effect on job satisfaction.
11. The cultivation of open and transparent communication inside small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) contributes to the establishment of a favourable work environment.
12. The level of employee satisfaction is positively correlated with their level of knowledge regarding corporate objectives, organisational changes, and their individual responsibilities within the company.
13. The inclusion of employees in decision-making processes and the delegation of duties can have a positive impact on job satisfaction.
14. Organisations that foster a sense of ownership among their employees may potentially observe elevated levels of job satisfaction.
15. In the context of small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs), where there may be inherent uncertainties, the provision of job security and stability can have a positive influence on employee happiness (Supriyanto., et.al., 2018).
16. The presence of a good and supportive work environment has a substantial impact on the level of job satisfaction experienced by employees.
17. Small scale manufacturing enterprises (SMEs) ought to prioritise the establishment of robust social networks among their workforce and the cultivation of a workplace environment that fosters collaboration and mutual assistance.
18. The recognition and awarding of employees for their contributions, especially within smaller organisational contexts, holds significant importance in fostering job happiness.
19. Possible types of acknowledgment in the workplace may encompass verbal recognition, employee of the month awards, or similar means of expressing appreciation (Srivastava., et.al., 2022).
Review Literature
The research conducted by Absar et al. (2010) examines the influence of human resources practises on job satisfaction within manufacturing companies located in Bangladesh. This study examines the correlation between human resource practises and work satisfaction among employees, utilising data obtained from a representative sample of manufacturing organisations. The results indicate a noteworthy and favourable association, implying that the implementation of efficient human resource practises, including recruitment, training, and performance evaluation, has a direct impact on increasing the overall job satisfaction of employees within the manufacturing industry of Bangladesh. In their research, Ahmad and Jasimuddin (2021) look into the connection between "commitment, person-organization fit, human resource management practises, communication satisfaction", and the Malaysian context. The study looks at how these characteristics are related to each other. The results indicate that in Malaysian organisational contexts, employees' commitment can be strengthened by effective communication satisfaction, in combination with strong HR practises and a favourable person-organization fit.
In their meta-analysis study, Alsaiari et al. (2020) set out to determine whether and how demographic factors impacted the relationship between HRM practises and employee loyalty. The research looks into the possibility that demographic variables like age and gender affect the form and strength of the relationship between HRM practises and employee loyalty. The study's findings shed light on the interplay between demographics and the effect of HRM strategies on staff loyalty, which is an important area for further research. Basnyat and Clarence Lao (2020) conduct a qualitative investigation in 2020 to look at how workers feel about the link between HRM practises and employee turnover. This research delves into the qualitative aspects of HRM practises and their impact on employee retention and turnover decisions. This study sheds light on the complex processes that affect employee turnover within the context of HRM practises by looking at it from the employees' perspectives. In the setting of nonprofit organisations, Bastida, et al. (2018) set out to investigate whether there is a connection between HRM practises and employee job satisfaction. The purpose of this study is to examine how HRM practises in nonprofits affect employee happiness on the workplace. This study's findings throw light on the complexities of HRM in the nonprofit sector and how it affects employee satisfaction.
Maimako and Bambale (2016) present a theoretical framework. The purpose of this research is to examine the relationship between HRM practises and employee job satisfaction at Kano State's state-owned universities. This study aims to provide light on the unique context of state-owned institutions by investigating the effect of certain HRM practises on employee job satisfaction. Understanding the relationship between HRM practises and employee happiness in the setting of Kano State's universities requires a conceptual model, which the article provides, and a framework, which the research provides. The study conducted by Ray and Ray (2011) examines the effects of Human Resource Management (HRM) practises on work satisfaction among employees in a specific group of small and medium-sized iron and steel companies in India. The findings of this research were published in the journal Public Policy and Administration Research. This study examines the HRM practises employed by these organisations and their impact on employee job satisfaction. This study provides valuable insights into the impact of HRM practises on job satisfaction within the small and medium-sized firms functioning in the iron and steel industry in India.
Research Methodology
This study employed a combination of both primary & secondary data collection approaches to gain relevant information. The primary focus of the researchers was on utilising primary data gathering methods, specifically through collaboration with private small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) located in the Delhi-NCR region. In the context of the National Capital Region (NCR), our study focused exclusively on privately-owned small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs). The sample size for our study comprised 165 individuals who held positions as working executives and managers inside the small scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) under investigation. As researchers, we employed a methodology known as stratified random selection to carefully choose the participants, so guaranteeing a balanced and unbiased representation. A well designed questionnaire was produced and subsequently given to a cohort of working executives and managers, following their explicit consent. The data obtained from these questionnaires was subsequently subjected to meticulous analysis employing a range of tools and procedures for our research.
Objective of the Study
1. To study the influence of various dimensions that affects the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees with special reference to SSMEs.
2. To evaluate the influence of the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees with special reference to SSMEs.
3. To suggest findings & conclusion.
Hypothesis of the Study
H1: There is no strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSMEs.
H2: There is a strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSMEs.
H3: There is no strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and encouragement of personal growth & skill development by SSMEs.
H4: There is a strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and encouragement of personal growth & skill development by SSMEs.
Opportunities for Progress and Skill Development are Fostered by SSME
Table 1 shows descriptive statistics represents the mean values & std. deviation values of the variables. As per table 1, S.D. & mean values of HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees 12.463 and 57.8921 & similarly S.D. & mean values of opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSME is 23.121 and 96.1865.
| Table 1 Descriptive Statistics | |||
| Mean | Std. Deviation (S.D.) | Frequency (N) | |
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | 57.8921 | 12.463 | 165 |
| Opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSME | 96.1865 | 23.121 | 165 |
| Where: HRMP (Human Resource Management Practices) & SSME (Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises) | |||
The correlations between variables are shown in Table 2, which is called the Correlations table. Table 2 shows that there is a strong link between HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSME . This is because the significant value is 0.000, which is less than 0.05. Hence, the alternate hypothesis, ‘there is a strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSMEs’ is accepted & null hypothesis rejected.
| Table 2 Correlations | |||
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | Opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSME | ||
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .816** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 165 | 165 | |
| Opportunities for progress and skill development are fostered by SSME | Pearson Correlation | .816** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 165 | 165 | |
| **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) | |||
Encouragement of Personal Growth & Skill Development by SSME
Table 3 shows descriptive statistics represents the mean values & std. deviation values of the variables. As per table 1, S.D. & mean values of HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees 29.981 and 68.8765 & similarly S.D. & mean values of encouragement of personal growth & development by SSME is 48.762 and 121.2316.
| Table 3 Descriptive Statistics | |||
| Mean | Std. Deviation (S.D.) | Frequency (N) | |
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | 68.8765 | 29.981 | 165 |
| Encouragement of personal growth & development by SSME | 121.2316 | 48.762 | 165 |
| Where: HRMP (Human Resource Management Practices) & SSME (Small Scale Manufacturing Enterprises) | |||
The correlations between variables are shown in Table 4, which is called the Correlations table. Table 4 shows that there is a strong link between HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and encouragement of personal growth & development by SSME. This is because the significant value is 0.000, which is less than 0.05. Hence, the alternate hypothesis, ‘there is a strong relationship between the HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees and encouragement of personal growth & skill development by SSMEs’ is accepted & null hypothesis rejected.
| Table 4 Correlations | |||
| Correlations | |||
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | Encouragement of personal growth & development by SSME | ||
| HRMP takes care of the job satisfaction & well-being of employees | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .799** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 165 | 165 | |
| Encouragement of personal growth & development by SSME | Pearson Correlation | .799** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | ||
| N | 165 | 165 | |
| **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) | |||
Findings of the Study
1. Staff happiness and contentment in small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) are positively affected by efficient selection and recruitment procedures. Establishing a good match between personnel and the organisation is of utmost importance.
2. Enhancement of job satisfaction and well-being is a direct result of investments in training and development. Staff members of SSMEs benefit from possibilities for ongoing education.
3. Workers in small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) report more happiness and contentment in their jobs when their performance reviews are fair and open.
4. In small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs), a competitive and equitable remuneration package, which includes non-monetary perks, is a major factor in determining job satisfaction and overall well-being.
5. Given the frequently difficult nature of the work environment at SSMEs, policies that encourage a balance between work and personal life have a good impact on job satisfaction and overall well-being.
6. For small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs), creating a healthy work environment through open and honest communication practises is essential for employee happiness and satisfaction on the job.
7. Job satisfaction and well-being are positively impacted by employee involvement in decision-making processes and empowerment programmes, especially in the unique setting of SSMEs.
8. Employees in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), where risks are higher, are more likely to be satisfied with their work and healthier overall if they feel their jobs are secure.
9. small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSME) workers report higher levels of job satisfaction and general well-being when they work in an encouraging and supportive workplace.
10. Staff morale and productivity at small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) are boosted when workers are acknowledged and compensated for their efforts.
Conclusion
Thorough study of the specific dynamics and challenges inherent in small-scale manufacturing enterprises is necessary for research projects to gain a comprehensive understanding of these characteristics. Furthermore, it is crucial to consider various factors, such as leadership styles, organisational culture, and the particular industrial context, when analysing the influence of human resource management (HRM) practises on employee job satisfaction within small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs). The study's findings indicate that the successful application of Human Resource Management Practises across multiple dimensions has a substantial impact on the job satisfaction and well-being of employees in small scale manufacturing enterprises. The study highlights the significance of customised human resource management practises (HRMP) in addressing the distinct difficulties and possibilities faced by small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs). It emphasises the role of personalised HRMP in fostering a favourable work atmosphere, improving employee contentment, and promoting overall organisational well-being in SSMEs. The conclusions may further emphasise the importance of continued research and strategic human resource management (HRM) efforts in addressing the unique dynamics of small-scale manufacturing enterprises (SSMEs) and promoting long-term employee satisfaction and well-being.
References
Absar, M. M. N., Azim, M. T., Balasundaram, N., & Akhter, S. (2010). Impact of human resources practices on job satisfaction: Evidence from manufacturing firms in Bangladesh. Economic sciences series, 62(2), 31-42.
Ahmad, K. Z. B., & Jasimuddin, S. M. (2021). The linkage between communication satisfaction, human resources management practices, person-organization fit, and commitment: evidence from Malaysia. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 64(1), 23-37.
Alsaiari, A., Puteh, F., & Ali, A. J. M. (2020). Could demographic variables impacting the relationship between HRM practices and Employee Loyalty? A meta-analysis review. databases, 4(1).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Basnyat, S., & Clarence Lao, C. S. (2020). Employees’ perceptions on the relationship between human resource management practices and employee turnover: A qualitative study. Employee Relations: The International Journal, 42(2), 453-470.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bastida, R., Marimon, F., & Carreras, L. (2018). Human resource management practices and employee job satisfaction in nonprofit organizations. Annals of Public and Cooperative Economics, 89(2), 323-338.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ileana Petrescu, A. and Simmons, R. (2008), "Human resource management practices and workers' job satisfaction", International Journal of Manpower, 29(7), 651-667.
Jain, R. (2022). Review Paper on Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 9(2), 11-16.
Kumawat, D., & Meena, R. P. (2022). A Study on the Effectiveness of Start-Up India Scheme for Youth Entrepreneurs: A way of Economic Growth in India. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 9(3), 7-12.
Ling, F. Y. Y., Ning, Y., Chang, Y. H., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Human resource management practices to improve project managers’ job satisfaction. Engineering, construction and architectural management, 25(5), 654-669.
M., K., & Abdullah, M. R. T. L. (2023). Creating Economic Resilience of Rural Economy in Facing the Potential Storm Clouds of Global Recession. Kaav International Journal of Economics , Commerce & Business Management, 10(1), 1-10.
Maimako, L. B., & Bambale, A. J. A. (2016). Human Resource Management Practices and Employee Job Satisfaction in Kano Stateowned Universities: A Conceptual Model. Journal of Marketing & Management, 7(2).
Ray, S., & Ray, I. A. (2011). Human Resource Management Practices and Its Effect on Employees’ Job Satisfaction: A Study on Selected Small and Medium Sized Iron &Steel Firms in India. Public Policy and Administration Research, 1(1).
Rodjam, C., Thanasrisuebwong, A., Suphuan, T., & Charoenboon, P. (2020). Effect of human resource management practices on employee performance mediating by employee job satisfaction. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(3), 37-47.
Srivastava, D. A., Chaudhary, D. N., & Srivastava, M. P. (2022). An Exploratory Impact of Social Media Influencer Marketing on Consumer. Kaav International Journal of Arts, Humanities & Social Science, 9(1), 1-7.
Supriyanto, A. S., Ekowati, V. M., Alim, S. Y. A. H. I. R. U. L., & Waluyo, A. P. (2018). Transformational leadership role in mediating the effect of emotional intelligence on manager performance moderated by innovative work behavior. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 5(4), 100-106.
Received: 24-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14205; Editor assigned: 27-Nov-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-14205(PQ); Reviewed: 29-Dec-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-14205; Revised: 29-Mar-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14205(R); Published: 04-Apr-2024