Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 6S
Intellectual Knowledge-base of Influencer Marketing: A Systematic Literature Review Approach
Divyashree M, St. Aloysius (Deemed to be University), Mangaluru, Karnataka
Subin MK, Nitte (Deemed to be) University, Mangalore, Karnataka
Citation Information: Divyashree, M., & Subin, M.K. (2025). Intellectual knowledge-base of influencer marketing: a systematic literature review approach. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(S6), 1-17.
Abstract
Influencer marketing is popular for its attention driving action and bridging the gap between the brands and audiences in a technology led era. However, there exists a substantial void in presenting the spectrum of the past literatures concerning influencer marketing. The review made use of a combination of bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review method as an effective tool of Scientific Procedures and Rationales for Systematic Literature Reviews (“SPAR-4-SLR”)approach to synthesize the earlier works in the field of influencer marketing and to showcase the intellectual knowledge base of the same. The analysis was applied to serve multiple objectives of uncovering the current trends, reach and growing potentials for research in influencer marketing domain. In order to meet the study objectives, bibliographic data of 1012 documents between the period 2000 to 2025, were retrieved from Scopus database.The study reveals the influential articles, impactful authors, prominent sources, contributing countries and most relevant themes. The themes found by the analysis comprise of service quality, customer experience, online reviews, brand management, social marketing, trustworthiness, marketing strategy, social media influencers, attractiveness and internet marketing. The findings of the study suggest for an intensive research exploration in the field and it will create value to various stakeholders such as researchers, academicians, marketers, consumers and business delegates in their strategy formulation and policy implementation.
Keywords
Social Media Influencers, Online Reviews, Systematic Literature Review Method, Bibliometric Analysis, Science Mapping, Internet Marketing.
Introduction
The popularity of digital media goes far beyond expectations as it enables getting a wide reach, providing information, selling products, and delivering services to consumers(Lamberton & Stephen, 2016). The era of digitalization and marketing analytics opens a world for marketers to frame advanced marketing strategies(Rosário & Dias, 2023).Marketers nowadays explore the scope of social media for developing brand awareness, sales of products and services, and dealing with consumers based on the rapid growth and popularity of social media networking (Hazari & Sethna, 2023).The marketing world is witnessing various novel practices such as QR code-enabled interactive packaging, social media contests, dynamic pricing, and personalized advertising (Purchase & Volery, 2020).The digital environment makes people not only the customers of a particular brand or product, but also promoters of the same (Lamberton & Stephen, 2016). Social media platforms flourish these days in the shadow of technological and internet advancements, which opens a huge space for firms to capitalize on for marketing(Jun Myers et al., 2011).
For marginalizing the sales and generating high revenues, firms all over the world, regardless of the industries and countries, are preferring influencer marketing strategies over traditional marketing techniques(Iswanto et al., 2024).Now a days, artificial intelligence opens new opportunities for firms to conduct marketing practices(Marvi et al., 2024).Exploring the scope of artificial intelligence for gathering and processing market data will be beneficial for influencer marketers(Bansal et al., 2024).The growth of influencer-basedmarketing has been rapid in recent years(Tanwar et al., 2022). Influencer marketing is a novel method of promoting the product by capturing data related to the targeted audience (rohitbansal). A marketing strategy in which some influential personalities on digital platforms promote and share the product information to their followers and the general public is generally referred to as influencer marketing(Tanwar et al., 2021). The independent persons who have the power to become third-party endorsers who can influence the attitude and behavior of a mob through various social media techniques are referred to as social media influencers(Freberg et al., 2011). They are the people with strong connection with a group of people over social media platforms, who can influence them by creating content, can easily promote brands(Araujo et al., 2017). The content delivery of influencers attracts marketers who want to spread the reach of their products, and by offering heavy sponsorship and rewards, they can demand that the influencers deploy their product information in social media content, which will be viewed by millions of followers (Hudders & Lou, 2023). Thus, it enables marketers to interact with their customers by sharing content and messages online (Tanwar et al., 2022).
The increased fame of social media and digital platforms induced the customers to trust, admire, and become loyal to the content creators (Chen et al., 2024).Influencers can receive appraisal, admiration, and affection from millions of people for engaging them and introducing something new to them(Hudders& Lou, 2023). Thus, consumers’ taste, selection, choice, decision-making, attitudes, and point of view are shaped by these social media influencers(Joshi et al., 2025).In the case of influencer-based brand advertisements, all the people and socializers pay higher attention and interest regardless of the gender or other characteristics of the influencers (Hazari & Sethna, 2023).Because,the youngsters and children are devoting time on social media to follow their influential personalities playing video games, unboxing products, introducing and reviewing new products, and making their daily vlogs (De Veirman et al., 2019).The so-called influencers are developing networks and collaborating with certain brands for promoting their products or services to a community or mob following them by creating contents, which have a global reach (Chen et al., 2024). Platforms such as Instagram help marketers to advertise and organize marketing campaigns for their products using certain algorithms which is generated based on the psychographic and behavioral aspects of the users (Hazari & Sethna, 2023).
Marketing decisions and strategies are developed by marketers and organisations based on consumer and marketing data, highlighting the importance of data-driven marketing and communication(Rosário & Dias, 2023). The scope of marketing is endless in the dynamic world, and thus, it requires a wide range of abilities and skills for individuals involved in marketing activities(Hartley et al., 2019). Aligning with these, the effectiveness of influencer-based marketing differs according to the trust of followers in influencers, the authenticity of content delivery, and the transparency they possess (Migkos et al., 2025).
This paper undertakes a systematic examination of scholarly literature concerning the influencer marketing domain. Through a structured bibliometric analysis, the study seeks to identify influential contributions, prominent researchers, key publication outlets, prevailing publication trends, and recurring thematic concerns within the field. By mapping the intellectual landscape of existing research, the analysis aims to illuminate the evolution and current state of knowledge surrounding influencer marketing field and to highlight areas for future investigation.
Literature Review
Marketing and innovation are the two basic functions through which firms can create a customer base in the long run(Grossberg, 2016).The conventional method of marketing is aligned with attracting new customers and maintaining the relationship with them(Lee & Scott, 2015). Whereas, digital marketing is becoming an easy way for all the firms to interact with their consumers worldwide, as it solves most of the issues that arise from conventional marketing techniques (Diez-Martin et al., 2019). The adoption of digital marketing tools makes a crucial positive impact on the venture performance of many enterprises(Deku et al., 2024). Organizations are now adopting digital technologies for marketing promotions by exploring the wonders of technology (Grossberg, 2016). Because, digitalization enables firms to interact with customers cost-effectively(Andersson et al., 2024). Blending entrepreneurial marketing with sophisticated technologies and sustainable marketing practices guarantees long-term business success to the firms (Nyquist et al., 2025). Innovation plays a critical role in marketing activities(Purchase & Volery, 2020). Influencer marketing is one of the novel and innovative marketing strategies adopted by majority of the enterprises these days (Bansal et al., 2024; Tanwar et al., 2022).
Influencer marketing has a substantial effect on consumer behavior and decision-making, as influencer communication and characteristics greatly affect purchasing behavior (Pan et al., 2024).The influencer marketing practice involves identifying a suitable person to demonstrate the products or services on the social media domain by various means and thereby canvassing people towards a particular brand or firm(Tanwar et al., 2022). People who have social media accounts on various platforms and share some content regularly with a group of people following them are called influencers (Bansal et al., 2024). The celebrities, who share their glamorous and friendly lifestyle over social media, interacting with their followers through messages on interactive platforms, develop a positive belief regarding the messages in the minds of their followers (Quesada Baena et al., 2024).The high level of admiration and affection given to the vloggers and influencers by the people captivates many marketers and brands to approach them for including their brand promotions by making them huge payments(De Veirman et al., 2019).Influencer marketing has become an ever-growing segment nowadays as numerous people want to pursue a career in social media content creation, want to follow some other content creators, and want to make collaborations(Joshi et al., 2025). The current situations enable digital consumers and followers to express their opinions and views about a product or service that are visible to a huge crowd, which affects consumers ' purchase decisions(Vrontis et al., 2021).
Initially, people enter into the social media domain as a hobby or time pass, which is converted into a full-time career when they start to get a wide reach among their target audience (Joshi et al., 2025). Their content delivery can attract the attention of millions of followers and high reach among others (De Veirman et al., 2019). The scope of influencer marketing also expanded to live video game streaming platforms, as most of the youngsters watch their gaming influencers playing video games and interacting with them, which eventually becomes an opportunity for marketers to promote their products and brands(Evans et al., 2023).Even though,in order to engage the consumer for a long time, the businesses have to make the best decision with regard to the selection of a strategic influencer for marketing and plan for data-driven methods(Migkos et al., 2025).Ensuring the authenticity of social media influencers is pivotal for the growth and success of influencer marketing practices(Mai et al., 2025).The social media influencers will also have a darker side as they can damage the mental and physical health by smear campaigns on their glamorous lifestyle, unhealthy food recommendations, and idealized images(Hudders& Lou, 2023). Food and beverages promoted by celebrity stars and influencers may not always have nutritional value, and they can create dietary issues, especially for youngsters and children(Packer et al., 2022).
The data regarding consumer behavior generated through social media platforms assists marketers in finding out the influencing consumers and developing strategies accordingly(Araujo et al., 2017). While researching through consumer data, the companies are able to make new initiatives in connection with customer-centric marketing, which develops brand loyalty and satisfaction among customers(Rosário & Dias, 2023). Certain social media domains facilitate marketers to analyze the taste and preference, and behavior of the consumers by tracking the consumers' interactions and messages(Araujo et al., 2017). When the products are customized or personalized based on such data-driven, customer satisfaction will be high, as there may be fewer complaints regarding the products(Chandra et al., 2022). That is why the fashion industries predominantly use the scope of influencer marketing to convey messages and interact with large digital audience, which helps them to create a brand image(Tanwar et al., 2021).For some exceptional cases, some of the enterprises are reluctant to explore the opportunities of digital marketing using interactive platforms(Nazir et al., 2025).Cultural change, restricted access to funds and resources, high cost, and technology and expertise requirements are restricting small enterprises from exploring the novel digital marketing platforms(Peter & Dalla Vecchia, 2021).
Research Methodology
The current paper which intends to explore the theoretical foundations of influencer marketing adopted a combination of systematic literature review method and bibliometric analysis. The former analysis approach seeks to evaluate the past literatures in the field so as to set a foundation for future exploration in the area and the latter unravels the bibliographic data in influencer marketing domain with the thought of presenting the entire spectrum of research initiatives in the concerned area. The study also made use of modified version of “Scientific Procedures and Rationales for Systematic Literature Reviews” (“SPAR-4-SLR”) protocol in presenting the trends and aspects of past literatures in a scientific manner through an established pattern of analysis. The procedure and mechanism used in synthesizing the existing literatures in the domain are as follows Table 1.
| Table 1 Spar-4-SLR of Influencer Marketing |
Assembling  Keyword Search and Data Retrieval Keyword Search and Data Retrieval |
| Database Used: Scopus |
| Keywords Applied: “Influencer marketing” OR “Creator marketing” OR “Endorsement marketing” |
Arranging Sorting and Groping Sorting and Groping |
| Publication Year: 2000 – 2024 |
| Subject Area: “Business, management and accounting” |
| Type of Dcouments: Article |
| Source Type: Journal |
Assessing Evaluation and Interpretation Evaluation and Interpretation |
| Unit of Analysis:Abstracts and keywords |
| Analysis Tools: A) Performance Analysis – covers trends in publication, influential works, impactful authors, prominent sources B) Science Mapping – covers network analysis, thematic analysis, factorial analysis and temporal analysis |
| Reporting Strategy: Tables and figures followed by interpretations |
Keyword Search and Data Retrieval
The researcher has undertaken an intensive evaluation of the past literatures in the field of influencer marketing so as to proceed with the study objectives. A combination of several keywords has been adopted for this purpose. The initial search of the keyword “influencer marketing” without any filter strategy generated 3379 documents. However, a set of different other keywords such as “ambassador marketing”, “creator marketing” and “content creator marketing” are employed for the search resulting different outcomes. The search was done on 25-06-2025 with specific focus on the keywords and abstracts of the documents. Adoption of Scopus as the database gives access to scholarly research articles in the domain of influencer marketing.
Sorting and Groping
The arrangement of the bibliographic data was done by adopting certain sorting and grouping mechanism. Various filters used for the review comprise of “year”, “document type”, “subject area” and “source type”. Year of publication being one of the filter strategy was chosen between 2000 to 2024, that is for 25 years. The subject area was confined to “business, management and accounting”. Similarly, the retrieval of the data concerning influencer marketing limited to article type and the source type to journal. The search employing these sorting strategies generated 1012 research articles with the keyoword “influencer marketing”. Hence, bibliographic data on 1012 documents formed the part of the analysis.
Evaluation and Interpretation
The bibliographic data extracted from Scopus database is evaluated in terms of bibliometric analysis with the objective of quantifying the qualitative data to synthesize the past works in the field of influencer marketing. The study also made use of systematic literature review method to add value to the knowledge base of influencer marketing. The paper had employed “Biblioshiny R package” and “VOSviewer”for performing performance analysis and science mapping as part of bibliometric analysis, where the former is used to ascertain trends in publication, influential works, impactful authors, prominent sources and major contributing countries and collaborators, and the latter is adopted to give the significant themes and terms forming part of influencer marketing on account of term co-occurrence analysis.
Analysis and Interpretations
Analysis is presented in two parts. First part deals with performance analysis and the second depict the science mapping. A conjunction of different analysis approaches is adopted under two broad heads of analysis
Performance Analysis
The performance analysis in this review shows the relevance and excellence of past literatures in the domain of influencer marketing. It unravels the trend in publication, significant research contributions and major contributors as well as reveals the prominent source of journals. Further, it uncovers country collaborations in the selected area of study.
Trends in Publication
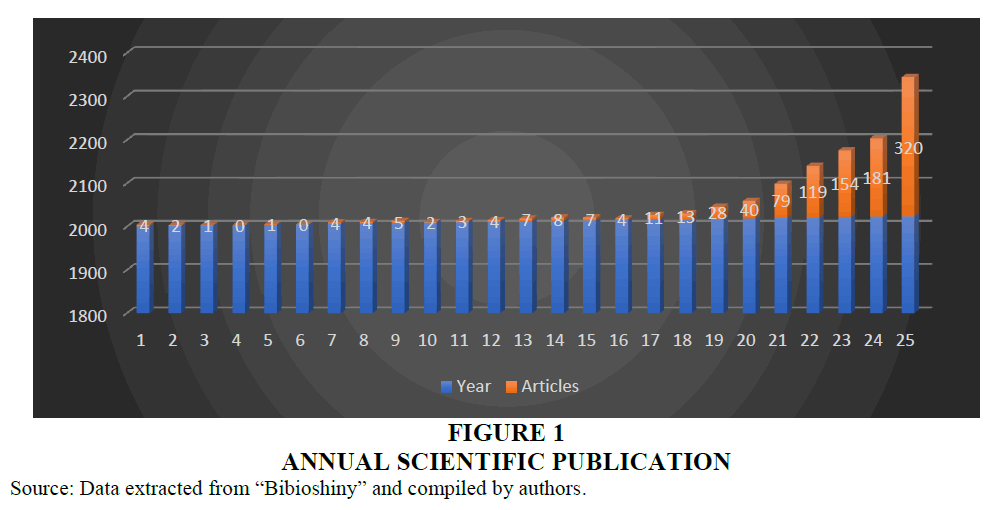
The review covered the research articles published for a period of 25 years from 2000 to 2024 in the field of influencer marketing. There is an evident increasing trend in the publication and the highest number of publications are accounted for 320 in the year 2024. The increase in publications depicts the rising significance of this domain. However, there is a negative annual growth rate in publication accounted for -5.39 %. The average citation per document stands at 42.56%, and international co-authorship rate accounts for 25.88% Figures 1-7.
Figure 1 Annual Scientific Publication
Source: Data extracted from “Bibioshiny” and compiled by authors.
Most Influential Articles
The analysis reveals the most significant works in the area of influencer marketing on the basis of total citations received by the same. The analysis reveals that the article entitled “Influencer Marketing: How message value and credibility affect consumer trust of branded content on social media” of Lou and Yuvan is the most prominent article in influencer marketing with 1447 total citations, followed by the article titled “Marketing through Instagram influencers: the impact of number of followers and product divergence on brand attitude” of Veirman et al., 2017 with 1382 total citations. The works highlights the fundamental aspects of influencer marketing and role of Instagram as an effective tool for influencer marketing Table 2.
| Table 2 Most Influential Articles | |||||
| Author | Year | Title of the Article | Source | Total Citations | Total Citations Per Year |
| Lou and Yuan | 2019 | “Influencer Marketing: How message value and credibility affect consumer trust of branded content on social media” | Journal of interactive advertising | 1447 | 206.71 |
| Veirman et al., | 2017 | “Marketing through Instagram influencers: the impact of number of followers and product divergence on brand attitude” | International Journal of Advertising | 1382 | 153.56 |
| Kumar et al., | 2010 | “Undervalued or Overvalued Customers: Capturing Total Customer Engagement Value” | Journal of Service Research | 987 | 61.69 |
| Schouten et al., | 2020 | “Celebrity Vs.Influenecer endorsements in advertising: the role of identification, credibility, and product endorser fit | Leveraged marketing communications | 918 | 153.00 |
| Sokolova and Kefi | 2020 | “Instagram and YouTube bloggers promote it, why should I buy? How credibility and parasocial interaction influence purchase intentions” | Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services | 832 | 138.67 |
| Audrezet et al., | 2020 | “Authenticity under threat: When social media influencers need to go beyond self-presentation” | Journal of Business Research | 583 | 97.17 |
| Jin et al., | 2019 | “Instafamous and social media influencer marketing” | Marketing Intelligence and Planning | 572 | 81.71 |
| Campbell and Farrell | 2020 | “More than meets the eye: The functional components underlying influencer marketing” | Business Horizons | 539 | 89.83 |
| Hughes et al., | 2019 | “Driving Brand Engagement Through Online Social Influencers: An Empirical Investigation of Sponsored Blogging Campaigns” | Journal of Marketing | 478 | 68.29 |
| CWC and Kim | 2019 | “The mechanism by which social media influencers persuade consumers: The role of consumers’ desire to mimic” | Psychology and Marketing | 444 | 63.43 |
Most Impactful Sources
Table 3 and presents the most prominent sources in publishing research articles in the field of influencer marketing. The two top most significant journals in the domain includes “Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services” and “Journal of Business Research” with 46 and 40 articles respectively. These sources known for their scholarly articles in the selected area.
| Table 3 Top Contributing Sources | |
| Sources | Articles |
| Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services | 46 |
| Journal of Business Research | 40 |
| International Journal of Advertising | 34 |
| Journal Of Digital and Social Media Marketing | 27 |
| Psychology and Marketing | 26 |
| Journal of Interactive Advertising | 23 |
| Journal Of Research in Interactive Marketing | 23 |
| Journal of Marketing Management | 19 |
| European Journal of Marketing | 16 |
| Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics | 15 |
| Innovative Marketing | 14 |
| Journal of Promotion Management | 14 |
| Marketing Intelligence and Planning | 13 |
| Journal of Marketing | 12 |
| Current Issues in Tourism | 11 |
Most Prominent Authors
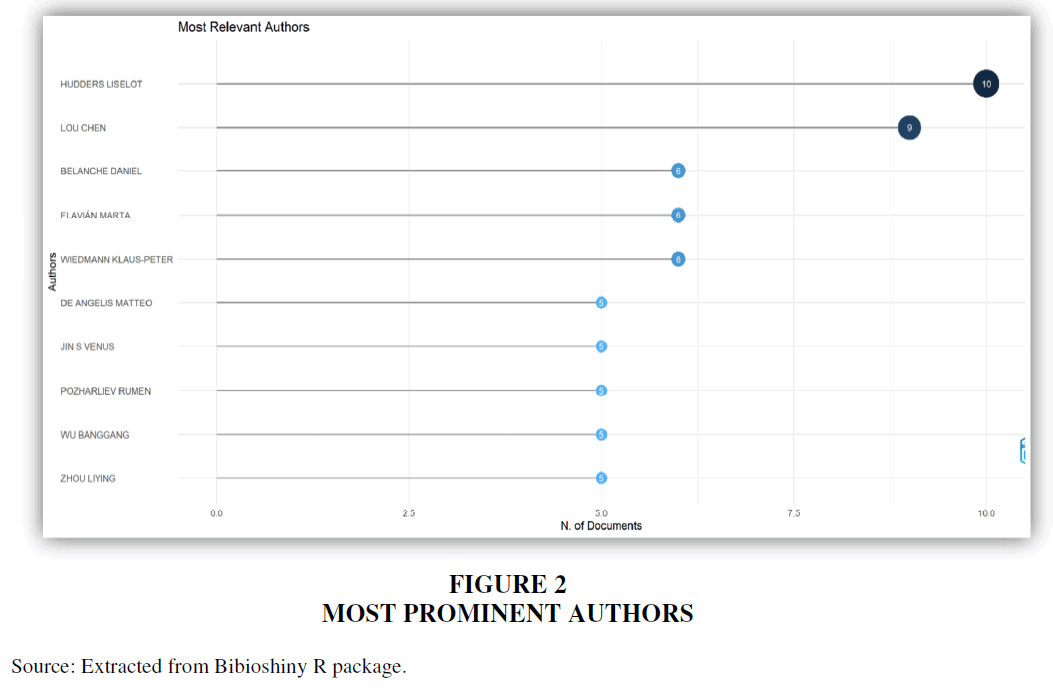
Table 4 and Figure 2 deals with the prolific authors in the research area of influencer marketing. It is found that, HuddersLiselot, Lou Chen and Belanche Daniel are the prominent authors in the field of influencer marketing with 10, 9 and 6 publications respectively with 2774, 2109 and 798 citations respectively. Along with their publications and citations, respective h-index of authors validate their contributions to the field.
Figure 1 Annual Scientific Publication
Source: Data extracted from “Bibioshiny” and compiled by authors.
| Table 4 Most Prominent Authors | |||
| Author | Number of Publications | Total Citations | h-index |
| HuddersLiselot | 10 | 2774 | 10 |
| Lou Chen | 9 | 2109 | 8 |
| Belanche Daniel | 6 | 798 | 6 |
| Flavián Marta | 6 | 798 | 6 |
| Wiedmann Klaus-Peter | 6 | 355 | 5 |
| De Angelis Matteo | 5 | 175 | 4 |
| Jin S Venus | 5 | 1112 | 5 |
| Pozharliev Rumen | 5 | 175 | 4 |
| Wu Banggang | 5 | 186 | 5 |
| Zhou Liying | 5 | 186 | 5 |
Science Mapping
The existing body of knowledge in influencer marketing is showcased through graphical representations which is done through science mapping. It is composed of several analysis techniques such as thematic analysis, factorial analysis, temporal analysis and network analysis. The most emphasized themes are extracted by the thematic analysis, while unravelling of the spectrum of past literatures is done by factorial analysis. On the other hand, temporal analysis put forward the topics and words focused by the earlier researchers in the influencer marketing, while network analysis gives the list of noteworthy terms based on their number of occurrences.
Thematic Analysis
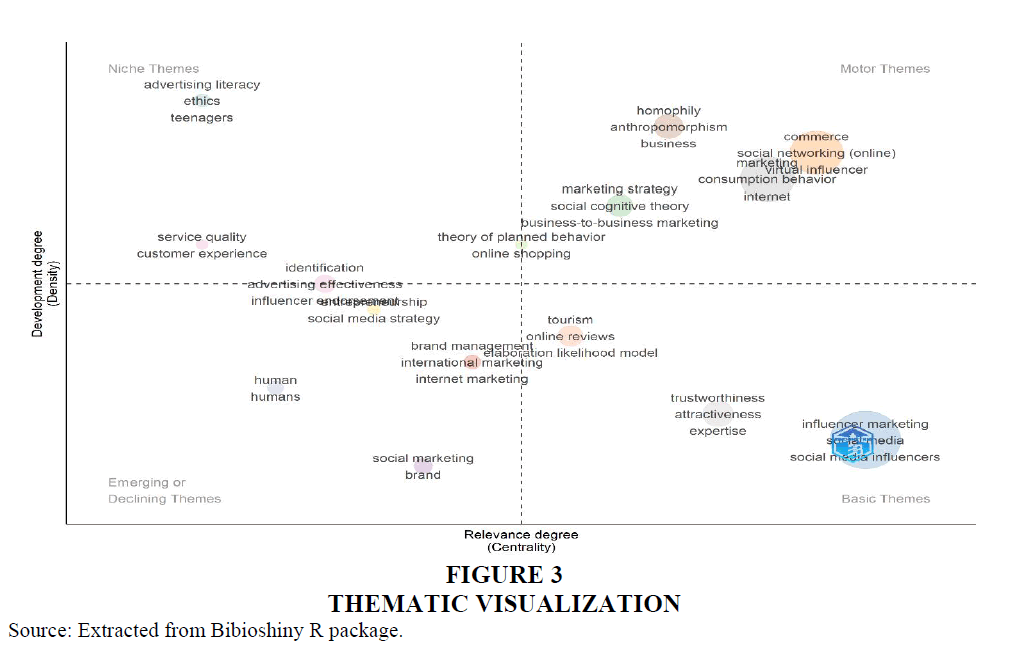
The analysis was performed using Biblioshiny software with author keywords combination. Figure 3 depicts the thematic visualization where in the vertical axis are concerned with the density of the themes and horizontal axis deals with the centrality of the themes. The map is split into quadrants, each having certain themes based on their significance. The left upper side of the quadrant shows niche themes characterized by high impact and low centrality and the themes cover “advertising literacy”, “ethics”, “teenagers”, “service quality”, and “customer experience”. The upper right-side quadrant is known for motor themes marked by high impact and high centrality. It comprises of the themes such as “homophily”, “anthropomorphism business”, “social networking”, “commerce”, “virtual influencer”, “consumer behaviour”, “internet”, “marketing strategy”, “social cognitive theory”, and “business marketing strategy”. The lower left quadrant deals with emerging or declining themes characterized by low impact and low centrality covers the themes such as “social marketing”, “brand management”, “international marketing”, “internet marketing” “humans”, “influencer entrepreneurship” and “social media strategy”. The lower right quadrant marked by high centrality and low impact is known for basic themes, consists of the themes such as “tourism”, “online reviews”, “trustworthiness”, “attractiveness”, “expertise”, “influencer marketing”, “social media” and “social media influencers”. The analysis shows that one of the themes “advertising effectiveness” falls in mid-way between niche themes and emerging themes. Similarly, another theme “theory of planned behaviour” falls between niche themes and motor themes. Spread of influencer marketing themes under different heads highlights the rising relevance of this domain and denotes the scope for intense research in the future.
Factorial Analysis
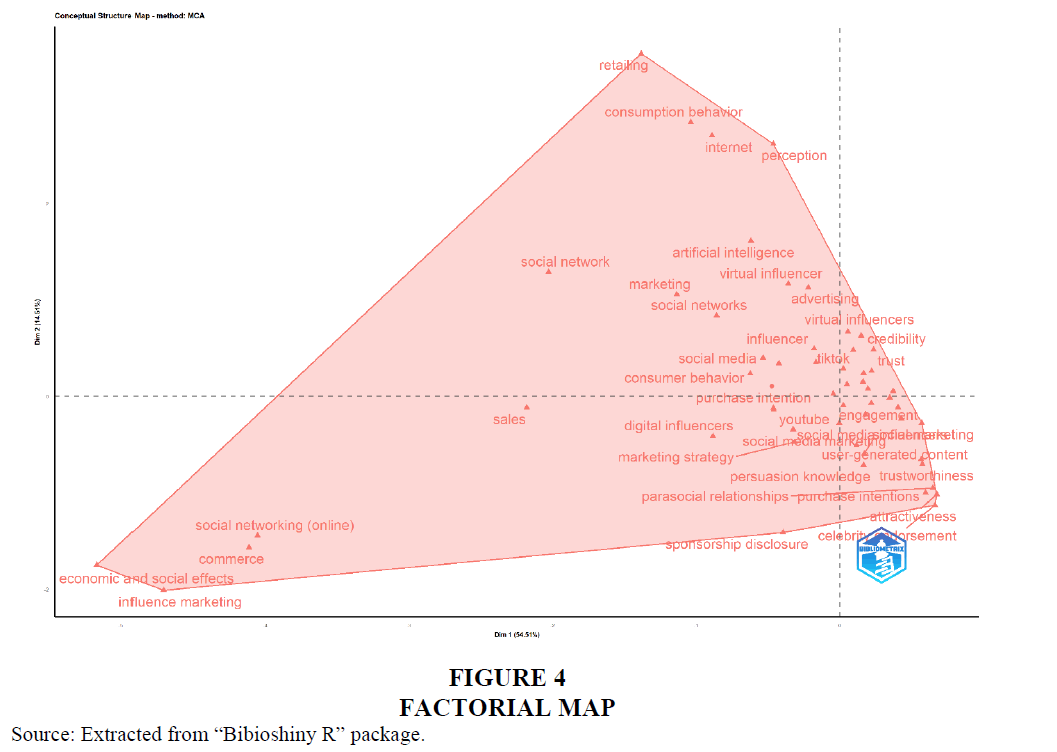
The analysis is carried out unravel the structure of research articles in a particular domain. It gives segregates and groups the topics in a research field based on their relevance. The analysis performed in “Bibioshiny R” package produced one cluster and denotes the topics focused. The cluster gives an overview of the themes highlighted according to the common words used by the researchers. Figure 4 showcasing the factorial map covers more than 30 key elements related influencer marketing. It includes the elements such as artificial intelligence, social networks, advertising, consumer behaviour, digital influencers, parasocial relationships, tiktok, virtual influencer, marketing strategy etc.
Temporal Analysis
A corpus of articles in the area of influencer marketing is presented using temporal analysis. The word cloud analysis made use of author keywords as unit of analysis. The word cloud map given in the figure 5 shows the word cloud where “influencer marketing”, “social media”, “social media influencers”, “marketing”, “Instagram”, “social media marketing” etc. are the prominent author keywords employed in the research domain of influencer marketing.
Network Analysis
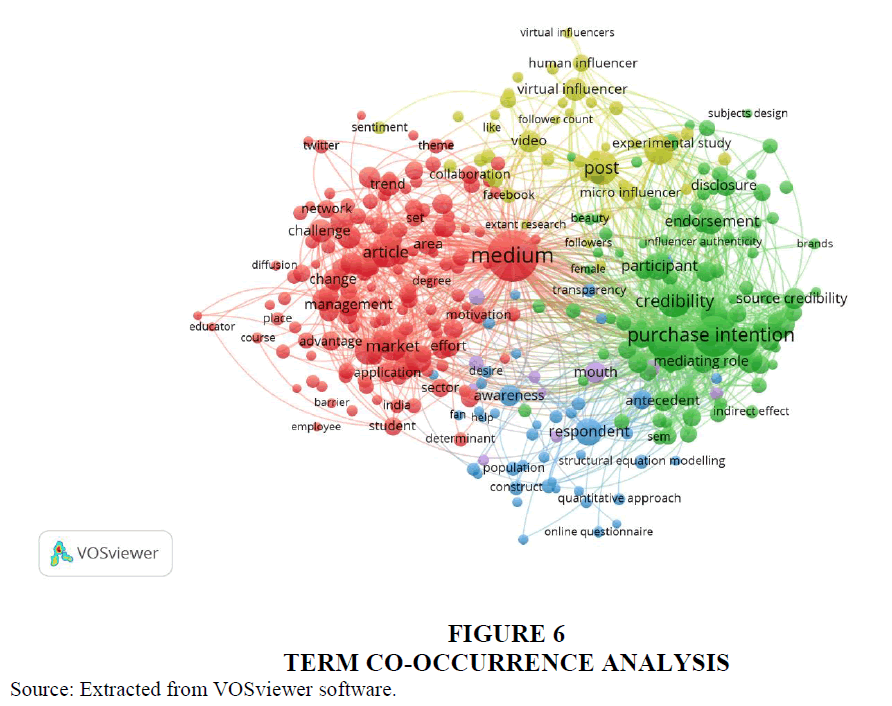
Keyword co-occurrence analysis was performed through VOSviewer software so as to present the effective term usage in terms of influencer marketing research. Network analysis is an effective tool to visualize the frequently occurring terms in the research field. The network analysis in this review reveals four clusters, firstly red (cluster 1) deals with 148 items highlighting the background of research in influencer marketing; secondly, green (cluster 2) are related to purchase intentions and consumer attitude covering 102 items; thirdly, blue (cluster 3) deals with content marketing and digital platforms including 42 items; fourthly, yellow (cluster 4) are connected to social media handles and followers comprised of 41 items; finally purple (cluster 5) represent 11 items deals with marketing practice and significance of word of mouth Table 5.
| Table 5 Summary of Clusters | |||
| Keywords | Total Occurrence | Links | Total Link Strength |
| Cluster 1: Background of Research in Influencer Marketing | |||
| Medium | 294 | 342 | 2771 |
| Article | 111 | 291 | 978 |
| Market | 96 | 281 | 858 |
| Business | 85 | 272 | 912 |
| Development | 80 | 269 | 803 |
| Challenge | 61 | 232 | 668 |
| Time | 60 | 234 | 670 |
| Management | 59 | 281 | 601 |
| Trend | 56 | 228 | 576 |
| Change | 51 | 226 | 527 |
| Cluster 2: Purchase Intentions and Consumer Attitude | |||
| Purchase Intention | 185 | 307 | 1967 |
| Intention | 179 | 313 | 1892 |
| Credibility | 120 | 302 | 1285 |
| Trustworthiness | 87 | 252 | 1005 |
| Participant | 86 | 282 | 889 |
| SMI | 81 | 252 | 834 |
| Endorsement | 75 | 253 | 779 |
| Attractiveness | 73 | 248 | 863 |
| Mediating Role | 55 | 222 | 617 |
| Source Credibility | 52 | 203 | 631 |
| Cluster 3: Awareness and Content Marketing | |||
| Respondent | 87 | 281 | 997 |
| Awareness | 53 | 241 | 590 |
| Mediator | 43 | 214 | 480 |
| Research Model | 25 | 176 | 318 |
| Population | 24 | 164 | 291 |
| Generation Z | 20 | 155 | 256 |
| Scale | 20 | 152 | 259 |
| Food | 20 | 152 | 251 |
| Purchasing Decision | 15 | 117 | 170 |
| Content Marketing | 11 | 100 | 122 |
| Cluster 4: Social Media Handles and Engagement | |||
| Post | 131 | 304 | 1208 |
| Experiment | 94 | 243 | 812 |
| Virtual Influencer | 63 | 198 | 566 |
| Video | 56 | 224 | 555 |
| Micro Influencer | 34 | 184 | 349 |
| Human Influencer | 34 | 143 | 313 |
| Comment | 32 | 144 | 278 |
| 26 | 147 | 247 | |
| Instagram Post | 24 | 135 | 240 |
| Influencer Type | 21 | 114 | 206 |
| Cluster 5: Marketing Practice and Word of Mouth | |||
| Mouth | 51 | 223 | 561 |
| Electronic Word | 31 | 172 | 368 |
| Destination | 31 | 165 | 336 |
| Tourist | 28 | 172 | 318 |
| EWOM | 19 | 123 | 234 |
| Travel | 17 | 108 | 148 |
| Usefulness | 15 | 118 | 166 |
| Marketing Practice | 10 | 112 | 132 |
| Hotel | 8 | 80 | 96 |
| WOM | 8 | 75 | 83 |
Source: Authors’ compilation based on keyword occurrence map from VOSviewer.
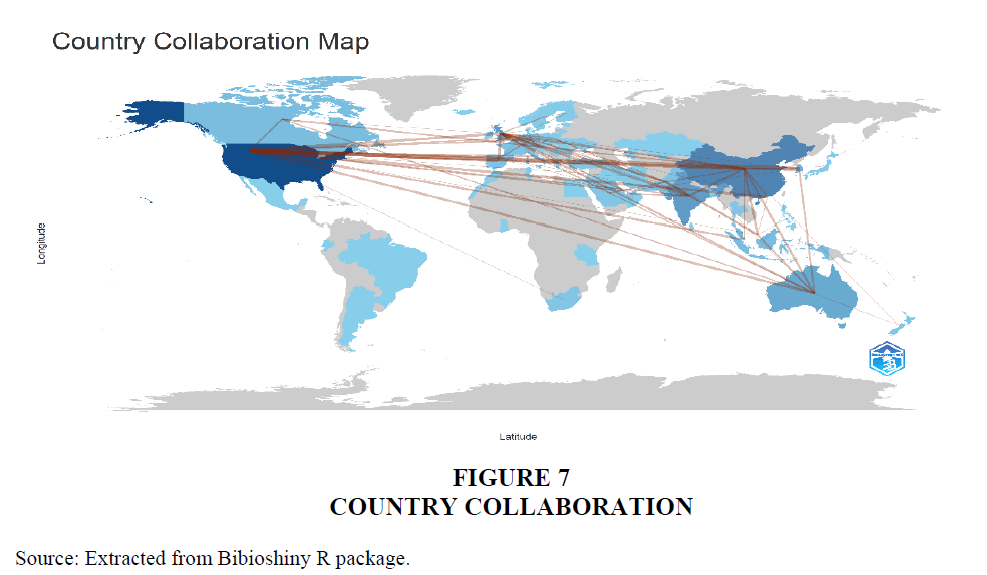
Country Collaboration Trend
The country collaboration for research in the area of influencer marketing are given in this analysis. Collaboration of countries were extensively seen between Australia and Malaysia and Australia and Korea. Other Collaborators with Australia includes Canada, Bangladesh, Austria, New Zealand and so on. High amount of partnership is observed among the nations in terms of research initiatives in the domain of influencer marketing.
Findings
The current study adopted a global approach to the past literatures in the influencer marketing research was employing bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review method. It provided an insight into the current trends in the influencer marketing research as well a possibility for future research in this field. The outcomes of the study paves way for an in-depth exploration in the domain so as to address the gap in the literatures. The application of performance analysis and science mapping approach resulted in valuable outputs with regard to the selected study area. Since the study period covered 25 years from 2000 to 2024, was effective in getting the intellectual structure of the research articles published during this period. The year of 2024 accounted for highest number of publications (320 publications) in the field is an eye opener to the potential researchers to understand the rising scope of the subject area opening novel research opportunities in the same.
The review shows “Influencer Marketing: How message value and credibility affect consumer trust of branded content on social media” as a most influential publication in the field with 1447 total citations followed by “Marketing through Instagram influencers: the impact of number of followers and product divergence on brand attitude” with 1382 total citations. The analysis on impactful sources reveals that “journal of retailing and consumer services” is the top contributing source of journal with 46 publications in the area, followed by “journal of business research” with 40 publications connected to influencer marketing. HuddersLiselot is the most prominent author in the domain of influencer marketing with 10 publications, 2774 total citations and 10 h-index, followed by Lou Chen with 9 publications, 2109 total citations and 8 h-index. USA (380) tops the list in terms of publications in the area of influencer marketing, followed by China (213), India (133), UK (132), Australia (88) and so on.
The thematic analysis gives a list of themes acting as guiding light for the prospective researchers in the field. The density and centrality concepts list “advertising literacy”, “ethics”, “teenagers”, “service quality” etc. as niche themes, “homophily”, “anthropomorphism business”, “social networking” etc. as motor themes, “social marketing”, “brand management”, “international marketing”, “internet marketing” etc., as emerging themes and “tourism”, “online reviews”, “trustworthiness”, “attractiveness” etc. as basic themes. The factorial analysis reveals the closely knitted key elements that has to be given emphasis in the research in influencer marketing covering “artificial intelligence”, “social networks”, “advertising”, “consumer behaviour” etc. In addition to this the temporal analysis reveals the prominent author keywords in the domain including “influencer marketing”, “social media”, “social media influencers”, “marketing”, “Instagram” etc. Further the network analysis reveals five different clusters of keywords having relevance in influencer marketing research. The clusters include, “background of research in influencer marketing” “purchase intentions and consumer attitude”, “awareness and content marketing” “social media handles and engagement” and“marketing practice and word of mouth”. Australia and Malysia as well as Australia and Korea are found to be the major collaborators in the research initiatives associated with influencer marketing.
Conclusion
The review paper was successful in showcasing the trends in publication and potential for future prospects in the area of influencer marketing. The analysis approach of bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review method were effective in meeting the study objectives. The analysis which accounted bibliographic data of 25 years between 2000 to 2024 reveals the flow of research publications in the domain of influencer marketing for more than two decades. Further, the increasing trend in terms of publication is a guiding light to the potential researchers in the field to decide the pace of their research journey. The influential works, impactful authors and prominent sources depict the increase in scholarly interest to the area selected. The approach followed is a significant step to synthesize the past literatures in this area of study. The outcomes of the science mapping analysis mainly determine the themes, key aspects and the terms that are to be focused in the collective research efforts to be undertaken in the future. Each tools provide a scientific justification to put forward the key aspects.
The study results are an added advantage to the various stakeholders such as academicians, researchers, policy makers, marketers, consumers and business delegates in their strategy formulation concerned to their area of operation. The collaboration between different nations in the research area paves way for several other strategic partnerships which will aid the countries involved in terms of economic and social benefits. The ultimate aim of the study to uncover the intellectual knowledge base of influencer marketing, hence satisfied with several other added values.
However, apart from the significance of the study, it also suffers from certain limitations. First of all, the bibliographic data for the study is extracted from the Scopus database and the study results are exclusively based on the same. The correctness and quality of the results solely dependent on the quality of the data retrieved. The data falling outside the purview of the Scopus database is not accounted for analysis under the study. It is highly advisable to adopt a conjunction of the qualitative and quantitative tools and techniques for the evaluation of the earlier works in any field of research.
References
Andersson, S., Aagerup, U., Svensson, L., & Eriksson, S. (2024). Challenges and opportunities in the digitalization of the B2B customer journey. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 39(13), 160–174.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Araujo, T., Neijens, P., &Vliegenthart, R. (2017). Getting the word out on Twitter: The role of influentials, information brokers and strong ties in building word-of-mouth for brands. International Journal of Advertising, 36(3), 496–513.
Bansal, R., Saini, S., Ngah, A. H., & Durga Prasad, T. (2024). Proselytizing the potential of influencer marketing via artificial intelligence: mapping the research trends through bibliometric analysis. In Cogent Business and Management (Vol. 11, Issue 1). Cogent OA.
Chandra, S., Verma, S., Lim, W. M., Kumar, S., &Donthu, N. (2022). Personalization in personalized marketing: Trends and ways forward. In Psychology and Marketing (Vol. 39, Issue 8, pp. 1529–1562). John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Cai, H., Liu, L., Liao, M., & Fang, J. (2024). A Comprehensive Overview of Micro-Influencer Marketing: Decoding the Current Landscape, Impacts, and Trends. In Behavioral Sciences (Vol. 14, Issue 3). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI).
Deku, W. A., Wang, J., &Preko, A. K. (2024). Digital marketing and small and medium-sized enterprises’ business performance in emerging markets. Asia Pacific Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 18(3), 251–269.
De Veirman, M., Hudders, L., & Nelson, M. R. (2019). What Is Influencer Marketing and How Does It Target Children? A Review and Direction for Future Research. In Frontiers in Psychology (Vol. 10). Frontiers Media S.A.
Diez-Martin, F., Blanco-Gonzalez, A., & Prado-Roman, C. (2019). Research challenges in digital marketing: Sustainability. Sustainability (Switzerland), 11(10).
Evans, R. K., Christiansen, P., Finlay, A., Jones, A., Maden, M., & Boyland, E. (2023). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of digital game-based or influencer food and non-alcoholic beverage marketing on children and adolescents: Exploring hierarchy of effects outcomes. In Obesity Reviews (Vol. 24, Issue 12). John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Freberg, K., Graham, K., McGaughey, K., & Freberg, L. A. (2011). Who are the social media influencers? A study of public perceptions of personality. Public Relations Review, 37(1), 90–92.
Grossberg, K. A. (2016). The new marketing solutions that will drive strategy implementation. In Strategy and Leadership (Vol. 44, Issue 3, pp. 20–26). Emerald Group Publishing Ltd.
Hartley, P., Routon, P. W., & Torres, L. (2019). The Skills Marketing Majors Believe They Acquire: Evidence From a National Survey. Journal of Marketing Education, 41(3), 202–214.
Hazari, S., & Sethna, B. N. (2023). A Comparison of Lifestyle Marketing and Brand Influencer Advertising for Generation Z Instagram Users. In Journal of Promotion Management (Vol. 29, Issue 4, pp. 491–534). Routledge.
Hudders, L., & Lou, C. (2023). The rosy world of influencer marketing? Its bright and dark sides, and future research recommendations. International Journal of Advertising, 42(1), 151–161.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Iswanto, D., Handriana, T., NazwinRony, A. H., &Sangadji, S. S. (2024). Influencers in Tourism Digital Marketing: A Comprehensive Literature Review. In International Journal of Sustainable Development and Planning (Vol. 19, Issue 2, pp. 739–749). International Information and Engineering Technology Association.
Joshi, Y., Lim, W. M., Jagani, K., & Kumar, S. (2025). Social media influencer marketing: foundations, trends, and ways forward. Electronic Commerce Research, 25(2), 1199–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-023-09719-z
Jun Myers, Helena Czepiec, Juanita Roxas, & Debbora Whitson. (2011). Teaching Students Self-Advertising/Marketing Skills in the Age of Social Media: Designing an Experiential Exercise.
Lamberton, C., & Stephen, A. T. (2016). A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing: Research evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future inquiry. Journal of Marketing, 80(6), 146–172.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lee, H. W., & Scott, C. J. (2015). Marketing or sales: the executive decision. Journal of Business Strategy, 36(5), 43–49.
Mai, N. Q., Nguyen, L. T. Van, Thuan, N. H., & Ngo, L. V. (2025). Decoding influencer authenticity: the CueSphere model of extrinsic cues. Journal of Services Marketing, 39(10), 32–51
Marvi, R., Foroudi, P., & Cuomo, M. T. (2024). Past, present and future of AI in marketing and knowledge management. Journal of Knowledge Management, 29(11), 1–31.
Migkos, S. P., Giannakopoulos, N. T., & Sakas, D. P. (2025). Impact of Influencer Marketing on Consumer Behavior and Online Shopping Preferences. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 20(2), 111.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nazir, M. A., Rizwan, H., & Zhu, X. (2025). A thematic analysis of factors influencing small and medium enterprise adoption of social media marketing: a TOE framework perspective. Qualitative Market Research, 28(1), 178–204.
Nyquist, A. M., Farshid, M., & Brown, T. (2025). Employing digital twin technology in the pursuit to avert sustainable marketing myopia. Journal of Research in Marketing and Entrepreneurship, 27(2), 277–293.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Packer, J., Russell, S. J., Siovolgyi, G., McLaren, K., Stansfield, C., Viner, R. M., & Croker, H. (2022). The Impact on Dietary Outcomes of Celebrities and Influencers in Marketing Unhealthy Foods to Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. In Nutrients (Vol. 14, Issue 3). MDPI.
Pan, M., Blut, M., Ghiassaleh, A., & Lee, Z. W. Y. (2024). Influencer marketing effectiveness: A meta-analytic review. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science.
Peter, M. K., & Dalla Vecchia, M. (2021). The Digital Marketing Toolkit: A Literature Review for the Identification of Digital Marketing Channels and Platforms. In Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (Vol. 294, pp. 251–265). Springer.
Purchase, S., & Volery, T. (2020). Marketing innovation: a systematic review. Journal of Marketing Management, 36(9–10), 763–793.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Quesada Baena, L., Binder, A., Neureiter, A., Saumer, M., &Matthes, J. (2024). “Do you practice what you preach?” The effects of celebrities’ pro-environmental messages on social media on young adults’ pro-environmental behavior. Young Consumers, 26(7), 22–37.
Rosário, A. T., & Dias, J. C. (2023). How has data-driven marketing evolved: Challenges and opportunities with emerging technologies. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 3(2).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Tanwar, A. S., Chaudhry, H., & Srivastava, M. K. (2021). Influencer marketing as a tool of digital consumer engagement: A systematic literature review. In Indian Journal of Marketing (Vol. 51, Issue 10, pp. 27–42). Associated Management Consultants Pvt. Ltd.
Tanwar, A. S., Chaudhry, H., & Srivastava, M. K. (2022). Trends in Influencer Marketing: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Interactive Advertising, 22(1), 1–27.
Vrontis, D., Makrides, A., Christofi, M., &Thrassou, A. (2021). Social media influencer marketing: A systematic review, integrative framework and future research agenda. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 45(4), 617–644.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 21-Jul-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-16099; Editor assigned: 22-Jul-2025, PreQC No. AMSJ-25-16099(PQ); Reviewed: 18-Aug-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-16099; Revised: 19-Aug-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-16099(R); Published: 29-Aug-2025