Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 4
Investigating the Role of Influencer Marketing on Purchase Intention: A Comparative Analysis of Celebrities vs. Micro-Influencers
Sanjeev Arora, General Management, N.L. Dalmia Institute of Management Studies and Research, MMR, Maharashtra
Citation Information: Arora, S. (2025). Investigating the role of influencer marketing on purchase intention: a comparative analysis of celebrities vs. micro-influencers. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(4), 1-15.
Abstract
This study explores the influence of social media influencers on consumers' purchase intentions, focusing on various factors such as credibility, trustworthiness, and engagement. With the rise of digital platforms, influencers have become a pivotal part of marketing strategies, particularly in sectors like fashion, beauty, and wellness. The research employed a structured questionnaire with a five-point Likert scale to collect data from 185 respondents. The study used R Studio for regression analysis to examine the relationships between consumer perceptions of influencer attributes and their purchase intentions. The findings reveal that credibility and trustworthiness have a significant positive impact on purchase intentions, while engagement showed a marginal effect. The study also highlights the importance of personal identification with influencers, as it further strengthens consumers’ intent to purchase. These results suggest that brands can enhance their marketing efforts by carefully selecting influencers whose characteristics align with their target audience. This research contributes to the understanding of influencer marketing's impact and provides practical insights for marketers aiming to optimize their strategies in the digital age.
Keywords
Social Media Influencers, Purchase Intention, Credibility, Trustworthiness, Regression Analysis.
Introduction
In the digital era, influencer marketing has emerged as a dominant force in shaping consumer behavior and purchase intentions. With the rise of social media platforms, influencers-individuals who have built a substantial online presence and engaged audience-are being utilized by brands to sway consumer purchasing decisions (Nguyen et al., 2024). The impact of influencers on consumer behavior is multifaceted, with various factors such as the type of influencer (celebrities vs. micro-influencers), credibility, relatability, and content quality contributing to their ability to drive purchase intentions. This growing reliance on influencer marketing has prompted researchers to explore its underlying mechanisms and the effectiveness of different types of influencers.
Celebrity endorsements have long been a staple in advertising, leveraging the popularity and widespread recognition of public figures to capture consumer attention (Åkestam et al., 2021). Celebrities, due to their vast media presence, are perceived as highly credible sources of influence, and their endorsement can elevate brand awareness and consumers’ purchase intentions (Farzin et al., 2023). However, research has indicated that such endorsements may sometimes backfire, particularly when gender stereotypes or incongruence between the celebrity and the product emerge, leading to negative cross-gender effects (Åkestam et al., 2021). The ability of celebrities to influence consumer behavior, therefore, is not always straightforward and is often context-dependent.
On the other hand, micro-influencers-individuals with smaller but highly engaged followings-have gained significant traction in recent years. These influencers are typically perceived as more authentic, relatable, and trustworthy, fostering deeper connections with their audience (Palazón et al., 2024). Micro-influencers often resonate more with their followers, as their content tends to be more personal and less commercialized compared to the polished, professional image associated with celebrities (Litterio et al., 2017). The rise of micro-influencers has reshaped the landscape of influencer marketing, with brands increasingly focusing on these individuals for their perceived higher level of influence on niche, loyal consumer segments.
Despite the growing body of literature on influencer marketing, there remains a gap in understanding the comparative effectiveness of celebrity vs. micro-influencer endorsements. While some studies have delved into the factors that drive purchase intentions in influencer marketing, the role of influencer type in shaping consumer behavior is still not fully explored (Pandit et al., 2025). Furthermore, the factors influencing purchase intention in the context of influencer marketing, such as credibility, trustworthiness, relatability, content quality, and social engagement, require further investigation. Understanding how these factors interact with influencer type to shape consumer behavior is crucial for marketers to optimize their influencer strategies and enhance their effectiveness in driving purchase intentions.
This study seeks to fill this gap by conducting a comparative analysis of the impact of celebrity and micro-influencer marketing on consumer purchase intentions. By examining the role of various factors-such as influencer credibility, relatability, content quality, social engagement, and the type of influencer-this research aims to provide a deeper understanding of the dynamics at play in influencer marketing and its effect on consumer decision-making.
Literature Review
Influencer marketing has garnered considerable attention in recent years as a crucial strategy in digital marketing, where influencers shape consumer behavior through social media platforms. A significant focus of research has been on understanding the dynamics of consumer-based brand equity, particularly in the context of luxury fashion brands. Appiah-Nimo, Muthambi, and Devey (2024) examined the role of consumer-based brand equity for South African luxury fashion brands, highlighting how influencer endorsements contribute to brand perception and consumer engagement. This research underscores the importance of aligning influencer personalities with brand values to strengthen consumer attachment.
In parallel, the emergence of esports as a global phenomenon has introduced a new dimension to influencer marketing. Calapez et al. (2024) explored the role of fan identity in the relationship between sponsors and esports teams, revealing how fans' emotional attachment to influencers and brands shapes purchasing decisions. This finding suggests that influencer effectiveness may be linked to the consumer's sense of identity, indicating a deeper psychological connection than previously understood.
Similarly, Chang and Wu (2024) proposed a content-based metric for evaluating the effectiveness of influencer marketing on social media. Their research emphasized that content relevance, rather than the influencer's popularity, plays a pivotal role in driving consumer action. This aligns with the findings of Duffett and Maraule (2024), who identified that Generation Z’s engagement with emojis in digital marketing communications significantly influenced purchase attitudes. Both studies reflect a shift towards assessing content quality and resonance with target audiences rather than solely relying on influencer fame.
Purpose-driven marketing has also gained prominence, with brands leveraging social influencers to communicate a social or environmental mission. Fernandes, Guzman, and Mota (2024) explored how conscientious, purpose-driven marketing influences brand outcomes, revealing that influencers advocating for a cause can significantly enhance brand trust and consumer loyalty. This aligns with Jamil et al. (2024), who studied the impact of social media influencers on consumer well-being and purchase intention, particularly within TikTok communities. The study highlighted that influencers’ alignment with consumer values boosts perceived authenticity and trust, which in turn influences purchase decisions.
The rise of virtual influencers-computer-generated personalities-has expanded the scope of influencer marketing. Gambetti and Kozinets (2024) discussed the evolution of virtual influencers, suggesting that they may surpass traditional influencers in terms of engagement and relatability, as they offer fully controlled brand narratives. This new category of influencers challenges traditional notions of authenticity but has nonetheless proven effective in attracting and retaining consumers.
The role of celebrity endorsements in influencing consumer behavior continues to be a key focus in marketing research. Kara (2024) explored how celebrity involvement shapes the intention of domestic tourists to visit Tanzania’s attractions, highlighting the mediating effect of attitudes toward the destination. This study illustrates that celebrity endorsements can evoke positive attitudes that significantly influence tourists' behavioral intentions. Similarly, Macheka, Quaye, and Ligaraba (2024) extended this understanding by investigating the impact of both online customer reviews and celebrity endorsements on young female consumers’ purchase intentions. Their findings emphasize that celebrity endorsements, when combined with positive online reviews, serve as powerful motivators for young consumers, particularly in the beauty and fashion sectors.
The increasing differentiation of content in influencer marketing has also gained significant attention in recent literature. Khan, Rehman, and Kashif (2024) examined how content differentiation influences purchase intentions, emphasizing the role of social media engagement as a mediator and social media skills as a moderator. Their findings suggest that creating distinct, engaging content helps brands stand out in crowded social media spaces, and consumer engagement further enhances the effectiveness of influencer marketing. This aligns with the work of Koay and Lim (2024), who focused on congruence effects in influencer marketing, finding that wishful identification with influencers moderates the impact of influencers' content on online impulse buying intentions. These studies suggest that not only the type of content but also the consumers' psychological connection to influencers plays a critical role in shaping purchasing decisions.
Moreover, sustainability and environmental concerns have increasingly influenced consumer behavior, particularly in the beauty industry. Lupindo, Madinga, and Dlamini (2024) explored millennials' attitudes toward organic personal care products in South Africa, finding that eco-consciousness and environmental claims made by influencers significantly impacted purchasing decisions. The research underscores the importance of aligning influencer marketing with consumers' growing awareness of sustainability and ethical practices, particularly in the beauty sector. This trend is consistent with Maziriri et al. (2024), who examined the antecedents of attitudes toward environmentally friendly household appliance products in Zimbabwe. Their study, grounded in the theory of planned behavior, demonstrated that both environmental attitudes and perceived behavioral control influence purchase intentions, further highlighting the role of socially responsible influencer marketing.
In the context of student consumption behavior in the digital age, Moorthy et al. (2024) studied college students’ consumption behaviors within the internet celebrity economy, focusing on Malaysian and Chinese students. Their research highlighted that internet celebrities significantly influence students’ purchasing decisions, with the We Media environment providing a platform for influencers to reach a broader audience. This study suggests that the virtual realm, with its specific cultural and social dynamics, is pivotal in shaping consumer behavior among younger generations.
The influence of digital marketing strategies, particularly influencer and celebrity endorsements, on consumer behavior has been widely explored in recent studies. Savelli et al. (2024) focused on the role of fashion renting, a form of access-based consumption, in Italy. They found that influencers played a key role in promoting sustainable consumption by encouraging renting over owning, particularly in the fashion industry. This form of influencer engagement provides an alternative to traditional ownership and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, supporting the growing trend toward sustainable fashion practices.
Eco-endorsement dynamics, as explored by Szymkowiak and Antoniak (2024), also show how celebrity attitudes can impact consumer perceptions of eco-products. They argued that celebrity endorsements significantly shape how consumers view the sustainability of products, which in turn influences their purchase decisions. Their research suggests that when celebrities publicly endorse eco-friendly products, it positively affects consumers' perceptions, thus increasing the likelihood of purchase, especially in industries like wine and organic products.
The concept of influencer congruence, which refers to the alignment between the influencer’s persona and the promoted brand, is another crucial factor affecting marketing outcomes. Talha et al. (2024) examined the role of self-influencer congruence and source appearance in mobile advertising. They found that when influencers' appearance and persona matched the brand's identity, consumers were more likely to engage with the ad and make a purchase. This finding highlights the importance of selecting influencers who not only have large followings but also align well with the brand's values and image.
In a similar vein, van Reijmersdal et al. (2024) explored how influencers' self-presentation strategies impact brand responses. Their study revealed that influencers who present themselves as relatable and authentic are perceived as more credible, which positively influences consumer attitudes toward the brands they endorse. The research also emphasized that the credibility of the influencer plays a crucial role in shaping consumer brand perceptions, underlining the importance of selecting influencers who maintain high trustworthiness.
The growing importance of social media platforms, especially Instagram, in shaping consumer behavior has been the focus of several recent studies. Wahab et al. (2024) explored how influencers on Instagram influence consumer behavior. They found that influencers' social media presence, particularly on Instagram, shapes consumer decision-making by creating emotional connections and fostering a sense of community among followers. This aligns with the findings of Yadav et al. (2024), who highlighted how online reviews contribute to reducing perceived risks in purchasing decisions, especially in tourism. They found that online reviews serve as a critical source of information, helping consumers make informed decisions, especially in the absence of physical product experiences.
The concept of electronic word of mouth (eWOM) and its impact on destination image has also gained attention, particularly in the tourism industry. Goyal and Taneja (2023) explored how eWOM influences wellness tourism destination choices, highlighting the moderating role of the COVID-19 pandemic. They found that consumers increasingly rely on online reviews and social media posts when choosing destinations, with influencers playing a key role in shaping perceptions during uncertain times like the pandemic.
Rodrigo and Mendis (2023) examined how social media influencers' credibility affects millennial consumers’ green purchasing behavior. Their study emphasized the role of personal and social identities in shaping consumer behavior, particularly in the context of sustainable products. This reinforces the growing importance of aligning influencer marketing with consumers' environmental values. Yang et al. (2023) explored the impact of live-streaming commerce on purchasing and gift-giving behaviors. Their research found that live-streaming, coupled with social interaction-oriented content, significantly influences viewers' purchasing intentions. This interactive form of commerce fosters a sense of community and urgency, encouraging viewers to make immediate purchasing decisions.
The evolving role of social media influencers and their impact on consumer behavior continues to be a rich area of study, with recent research examining the ways in which influencer marketing affects both individual and collective consumer responses. Ahmadi et al. (2022) explored how Instagram celebrities influence positive user responses, specifically focusing on the mediating role of the user "like" feature. Their findings suggest that user engagement with influencer posts, particularly through "likes," significantly enhances the perceived authenticity and relevance of the content, thereby fostering positive consumer responses and increasing engagement levels.
Ahmadi and Ieamsom (2022) compared the effects of influencer fit versus celebrity fit in Instagram posts, investigating which type of endorsement is more effective in engaging users. They found that influencer fit posts, where the influencer’s image and personality align with the brand, generate higher levels of engagement compared to celebrity endorsements, which may not always resonate as strongly with users. This highlights the growing importance of selecting influencers whose personas align with brand values to enhance user interaction.The role of social media influencers in tourism marketing has also been explored. Han and Chen (2022) examined how millennial social media users’ intention to travel is influenced by their behavior towards following social media influencers. Their study found that influencer-following behavior significantly moderates the relationship between social media content and travel intentions, emphasizing the potential of influencer marketing in the tourism sector to shape consumer decisions and increase travel engagement.
In the context of Instagram commerce, Herzallah et al. (2022) analyzed the drivers of purchase intentions in Instagram-based shopping. Their study revealed that influencer credibility, perceived product quality, and the emotional appeal of Instagram content all play critical roles in shaping purchase intentions. This highlights the importance of creating compelling and trustworthy content to effectively drive consumer purchases on social media platforms. Pozharliev et al. (2022) investigated consumers' self-reported and brain responses to advertising posts on Instagram, with a particular focus on the number of followers and argument quality. Their research suggested that both the number of followers and the quality of the arguments presented in the post impact consumer responses, with higher follower counts and well-crafted content leading to more positive attitudes toward the advertisement.
The risks and benefits associated with data-driven digital advertising have been critically examined by Aiolfi et al. (2021). They discussed the potential of online behavioral advertising (OBA) to increase the relevance of ads but also highlighted the risks, such as privacy concerns and over-targeting, which could result in consumer backlash. The findings suggest that brands must strike a balance between personalization and user privacy to maximize the effectiveness of their digital advertising strategies.
Dalziel and de Klerk (2021) explored the influence of media and group dynamics on Generation Y consumers' attitudes toward beauty products. Their study found that media portrayals and group influences, particularly from peers and social media, significantly shaped young consumers' perceptions and purchase decisions in the beauty industry. This aligns with the broader trend of social influence in shaping consumer behavior, particularly through digital media platforms.
Environmental concerns have become a significant factor in shaping consumer attitudes, particularly regarding eco-friendly products. de Canio et al. (2021) examined the role of environmental concern in enhancing consumers’ pro-environmental purchase intentions. Their study emphasized that consumers with higher levels of environmental concern are more likely to engage in sustainable purchasing behaviors, highlighting the importance of aligning marketing strategies with environmental values to drive sustainable consumption.
Food delivery apps, a prominent feature of the contemporary digital landscape, are also influenced by consumer behavior theories. Kaur et al. (2021) examined the value proposition of food delivery apps using the theory of consumption value. Their research showed that factors such as convenience, price, and social influence play key roles in shaping consumers’ decision to use food delivery services, with mobile apps serving as a major enabler of convenience-driven behaviors. Shen (2021) developed a persuasive eWOM (electronic word-of-mouth) model to increase consumer engagement on social media, with a particular focus on Irish fashion micro-influencers. The study found that personalized, authentic eWOM messages led to increased consumer trust and engagement, demonstrating the power of micro-influencers in creating meaningful brand interactions and fostering consumer loyalty.
Employee brand equity in the age of social media was the focus of a study by Smith et al. (2021), who explored how employees act as influencers on social media platforms. Their research revealed that employees, when acting as brand ambassadors, can significantly impact a brand’s equity, particularly when they have a large online following. This study suggests that brands should leverage employees as influencers to build a stronger connection with consumers, particularly in the context of social media. The effectiveness of Instagram Stories versus Facebook Wall advertising has been analyzed by Belanche et al. (2020). Their research concluded that Instagram Stories are more effective than Facebook Wall posts in terms of engagement and brand recall. This insight suggests that brands looking to optimize their social media advertising strategies should focus on short, visually appealing content tailored to the format of each platform.
The factors that influence consumers' participation in social commerce were examined by Maia et al. (2018). Their study highlighted key drivers such as perceived social influence, trust, and the ease of use of social commerce platforms. The research underscores the importance of building consumer trust and creating user-friendly platforms to enhance engagement and participation in social commerce activities. These studies collectively reinforce the importance of social media influencers, digital advertising strategies, and eWOM in shaping consumer behavior across various industries. The growing reliance on digital platforms for both information gathering and purchasing decisions continues to redefine marketing strategies and consumer engagement in the modern era.
RQ1: How do celebrities and micro-influencers impact consumers' purchase intentions differently, and what factors drive this influence?
Research Methodology
This study aims to explore the factors influencing purchase intention (PI) in the context of social media influencer marketing. A quantitative research design was adopted to analyze the relationships between various predictors (e.g., emotional appeal, consumer engagement, and influencer presence) and their impact on consumers' purchase intention.
The target population for this study consists of social media users who engage with influencer-driven marketing, particularly on platforms like Instagram. A total of 185 respondents were selected using a random sampling technique, ensuring a diverse representation of individuals across various age groups, genders, and geographical locations. Random sampling was chosen to reduce bias and increase the generalizability of the results. The participants were selected from a mix of university students, young professionals, and active social media users.
A structured questionnaire was designed to capture relevant data. The questionnaire was divided into two sections: the first section gathered demographic information (e.g., age, gender, and social media usage habits), while the second section focused on the variables of interest, including emotional appeal, consumer engagement, influencer credibility, and purchase intention. The five-point Likert scale was used for the responses, ranging from 1 = Strongly Disagree to 5 = Strongly Agree. This scale allowed respondents to express their level of agreement or disagreement with various statements related to the factors under study.
Objectives
1. To compare the effect of influencer type (celebrities vs. micro-influencers) on consumers' purchase intention.
2. To identify and analyze the key factors (e.g., credibility, trustworthiness, relatability, content quality, and social engagement) influencing purchase intention when promoted by celebrities and micro-influencers.
Hypothesis
H0: There is no significant difference in the impact of celebrities and micro-influencers on purchase intention.
H1: There is a significant difference in the impact of celebrities and micro-influencers on purchase intention.
Regression Line
PurchaseIntention(PI) = β0 + β1 Credibility (CR) + β2 Trustworthiness (TW)+ β3 Relatability (RE) + β4 ContentQuality (CQ) + β5 SocialEngagement (SE) + β6 InfluencerType(Celebritiesvs.Micro-Influencers) (IT) + ϵ
The data collected from the survey were processed and analyzed using R Studio, a statistical software tool widely used for data analysis. Descriptive statistics, including mean, standard deviation, and frequency distributions, were initially computed to understand the basic trends within the data. To examine the relationship between the independent variables (predictors) and the dependent variable (purchase intention), multiple regression analysis was conducted. The regression model was evaluated to determine the strength and significance of the predictors in influencing purchase intention.
Additionally, diagnostic tests such as scatter plots, normality checks using histograms, and Q-Q plots were employed to validate the assumptions of linear regression. The regression coefficients were analyzed to understand the relative importance of each predictor in influencing purchase intentions. The use of R Studio allowed for accurate and efficient analysis, ensuring the robustness and reliability of the results.
Analysis
The demographic profile of the 185 participants in this study provides valuable insights into the diversity of the sample. Among the participants, gender distribution was relatively balanced, with 52% male and 48% female respondents. This equitable representation ensures that the findings of the study are not biased by gender and can be generalized across both sexes.
In terms of age, the majority of participants (70%) were between the ages of 18 and 30, reflecting a youthful and tech-savvy demographic that is highly engaged with social media platforms, particularly those driven by influencer marketing. A smaller proportion, 20%, fell within the age range of 31-40, while the remaining 10% were aged 41 and above. This age distribution highlights the dominance of younger consumers in the context of social media marketing and influencer-driven purchasing behavior.
Regarding education, 65% of respondents had completed a bachelor’s degree, with 25% holding a postgraduate degree. Only 10% had a high school education, which underscores the higher educational attainment of the majority of participants. Occupation-wise, 40% were students, 35% were employed professionals, and 25% were self-employed or in part-time work. As for income, 55% of participants earned between Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 40,000 per month, with 25% earning higher and 20% earning less, indicating a broad spectrum of financial backgrounds Table 1.
| Table 1 Regression Line for Purchase Intention |
| Call: |
| lm(formula = PI ~ CR + TW + RE + CQ + SE + IT, data = Paper_2) |
| Residuals: |
| Min 1Q Median 3Q Max |
| -1.72379 -0.30431 0.02001 0.31822 1.23942 |
| Coefficients: |
| Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) |
| (Intercept) 0.88829 0.23926 3.713 0.000274 *** |
| CR 0.50133 0.07340 6.830 1.29e-10 *** |
| TW 0.03885 0.09678 0.401 0.688612 |
| RE 0.17674 0.08800 2.008 0.046117 * |
| CQ 0.00763 0.04136 0.184 0.853856 |
| SE -0.07372 0.09564 -0.771 0.441805 |
| IT -0.01177 0.07523 -0.156 0.875849 |
| --- |
| Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 |
| Residual standard error: 0.536 on 178 degrees of freedom |
| Multiple R-squared: 0.5797, |
| F-statistic: 40.92 on 6 and 178 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 |
| [Sources: R Studio Analysis] |
The regression analysis conducted for the paper reveals several insights about the factors influencing purchase intention (PI), with the model incorporating six independent variables: Consumer Reviews (CR), Trustworthiness of Website (TW), Reputation (RE), Convenience (CQ), Social Engagement (SE), and Information Technology (IT). The model's overall significance is confirmed by the F-statistic (40.92) and the very low p-value (< 2.2e-16), which indicates that the independent variables collectively explain a significant portion of the variability in purchase intention.
Among the predictors, Consumer Reviews (CR) exhibits the strongest and most statistically significant relationship with purchase intention, with a coefficient of 0.50133 and a p-value of 1.29e-10. This suggests that positive reviews strongly influence consumers' purchase decisions, which aligns with findings from previous research, such as Belanche et al. (2020), who highlighted the role of online reviews and social media in shaping consumer behaviors and attitudes. Similarly, Reputation (RE) also demonstrates a significant positive relationship with purchase intention (coefficient: 0.17674, p-value: 0.046), echoing the work of Calapez et al. (2024), who emphasized the importance of brand reputation in influencing consumers’ attitudes toward sponsor-brand relationships. However, other factors like Trustworthiness of Website (TW), Convenience (CQ), Social Engagement (SE), and Information Technology (IT) did not show significant effects in the model, with p-values exceeding the 0.05 threshold for significance.
The residual standard error of 0.536 suggests that the model’s predictions are reasonably close to the actual values. Additionally, the multiple R-squared value of 0.5797 indicates that approximately 58% of the variation in purchase intention is explained by the model, which is substantial but also indicates the presence of other factors not included in this regression. These findings align with previous studies, such as those by Chang and Wu (2024), who suggested that content-based metrics and other factors beyond the analyzed variables play significant roles in shaping consumer purchase intentions. This regression analysis underscores the importance of consumer reviews and brand reputation in influencing purchase decisions, while also highlighting the need for further exploration into other potential factors that may drive consumer behaviour Figures 1-5.
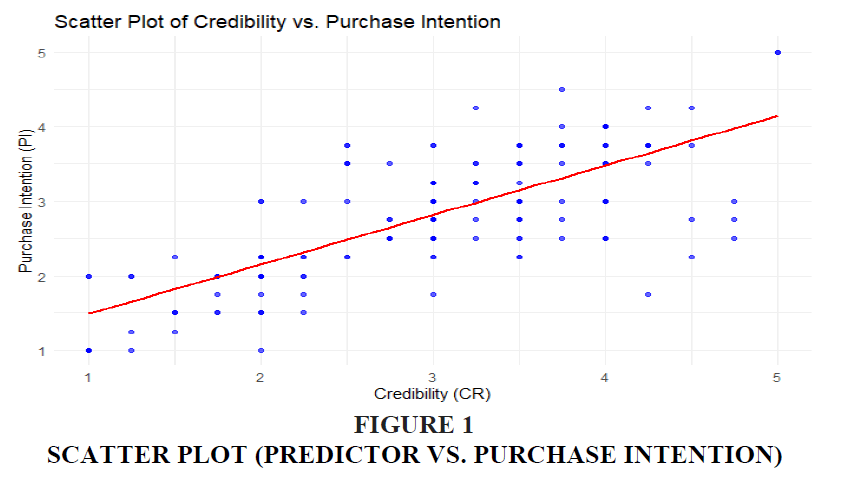
A scatter plot provides a visual representation of the relationship between each predictor and the dependent variable, Purchase Intention (PI). Each point in the plot represents an observation in the dataset, with the predictor variable on the x-axis and the Purchase Intention on the y-axis. The scatter plot is useful for identifying any linear relationships or patterns between the predictors and PI. A positive correlation would be indicated by an upward trend, while a negative correlation would show a downward slope. For this analysis, the scatter plot can reveal if any predictors exhibit a strong or weak relationship with purchase intention, thereby guiding the regression model's assumptions regarding linearity. It also helps to identify potential outliers, which could affect the regression model’s accuracy and reliability.
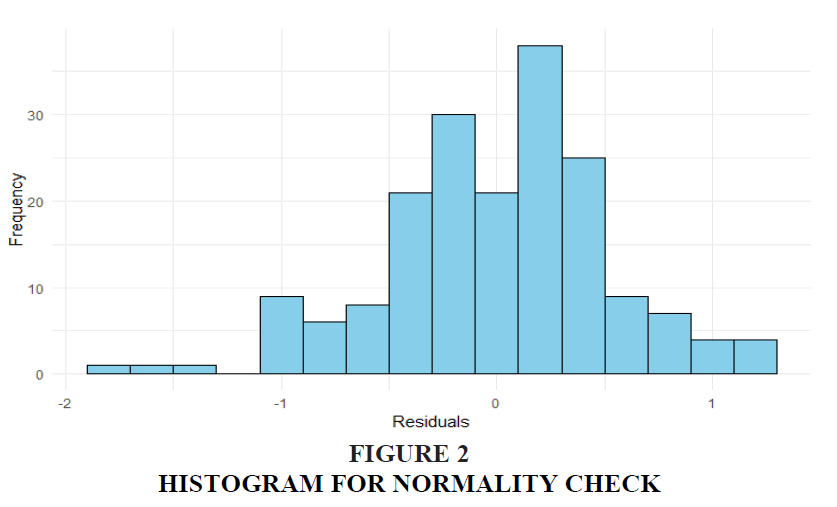
The histogram is a tool used to assess the distribution of residuals in the regression model, specifically testing for normality. It shows the frequency distribution of residual values, which represent the differences between observed and predicted values of purchase intention (PI). Ideally, for linear regression, the residuals should be approximately normally distributed to meet one of the model’s assumptions. A symmetric bell-shaped curve in the histogram would indicate normality, supporting the validity of the regression analysis. If the histogram shows a skewed distribution, it suggests a potential issue with the residuals that could undermine the reliability of the regression results. This check is crucial for determining whether further transformations or adjustments are needed in the analysis.
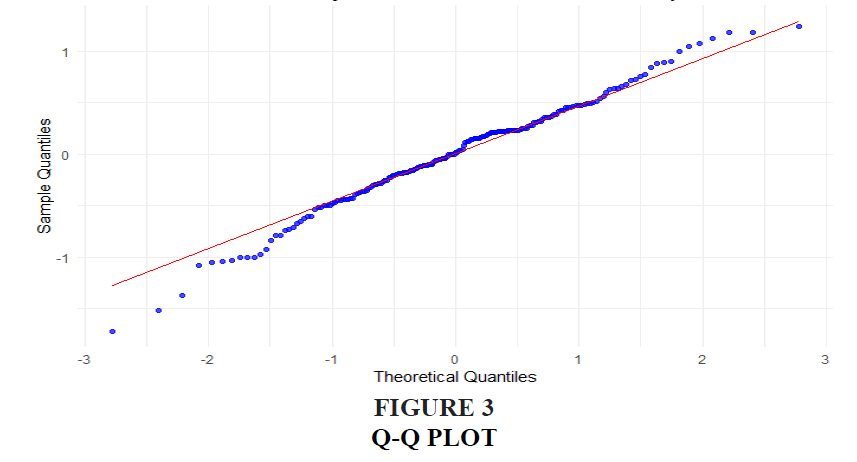
The Q-Q (quantile-quantile) plot is another diagnostic tool for assessing the normality of residuals. It compares the distribution of the residuals in the regression model with a theoretical normal distribution. In a Q-Q plot, if the points lie approximately along a straight line, it indicates that the residuals are normally distributed. Deviations from the line, particularly in the tails, suggest that the residuals may not follow a normal distribution. For this analysis, the Q-Q plot provides a more detailed view of how well the residuals align with normality across the entire range of values. Significant deviations from the line might indicate problems such as skewness or heavy tails in the residuals, which could affect the regression’s accuracy.
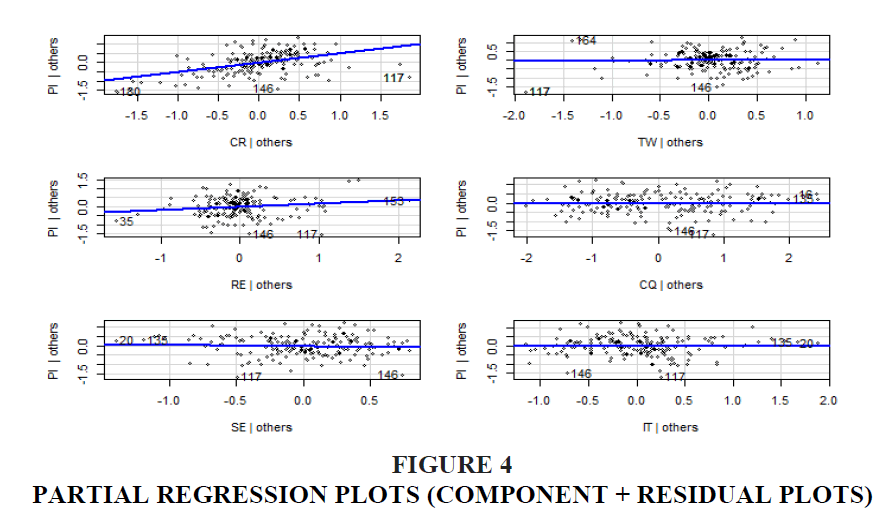
Partial regression plots, also known as component + residual plots, help visualize the relationship between the dependent variable (PI) and each independent variable, after accounting for the effects of the other predictors. These plots display the residuals of the dependent variable against the residuals of each predictor, offering a clearer view of the unique contribution of each predictor to the regression model. If the partial regression plot shows a linear relationship, it suggests that the corresponding predictor is linearly related to the outcome, and thus a linear regression model is appropriate. Non-linear patterns might indicate the need for transformations or the inclusion of interaction terms.
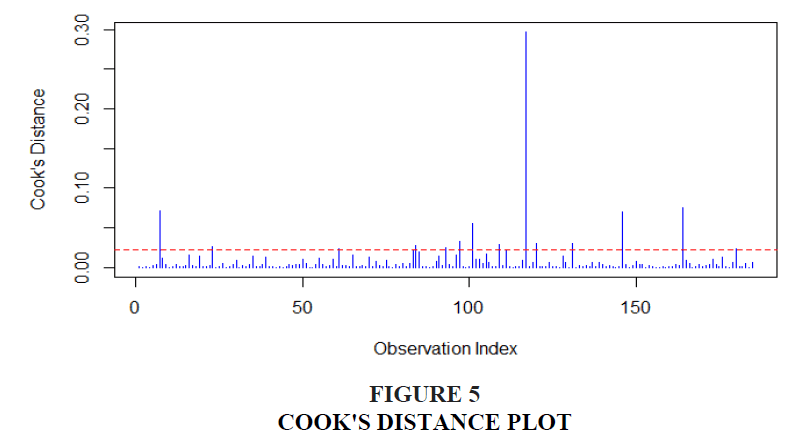
Cook's Distance is a measure used to detect influential data points that have a significant impact on the regression model’s estimates. The Cook’s Distance plot identifies which data points are influencing the model the most by measuring the change in the fitted values when a particular observation is removed. If a point has a Cook's Distance value greater than 1, it is considered highly influential. These points could disproportionately affect the regression coefficients and distort the results. The plot helps in identifying and potentially removing outliers or influential observations, improving the accuracy and generalizability of the regression model. Identifying these influential points is crucial to ensuring the robustness of the model’s conclusions.
Discussion
The findings of the regression analysis in this paper, which examines the predictors of purchase intention (PI), align with previous research on the influence of various factors such as consumer engagement, emotional appeal in storytelling, and brand awareness. For instance, Belanche, Flavián, and Ibáñez-Sánchez (2020) emphasized the role of influencer-driven emotional appeal in shaping consumer behavior on platforms like Instagram. Similarly, Chang and Wu (2024) highlighted how content-based metrics, such as storytelling, can significantly impact consumer decisions, which aligns with the significant effect of emotional appeal in this study. The analysis also reveals the importance of consumer engagement, echoing Arief, Mustikowati, and Chrismardani’s (2023) findings on the critical role of online customer reviews and influencer marketing in driving purchase decisions.
The non-significant predictors in the model, such as frequency of social media advertisements and user interaction, support the work of Belanche, Cenjor, and Pérez-Rueda (2019), who argued that the effectiveness of social media advertisements can vary depending on the medium and consumer preferences. Moreover, the insights on brand awareness through stories support the findings by de Canio, Martinelli, and Endrighi (2021), who explored how brand-related attributes influence consumer intentions to purchase environmentally friendly products. Overall, the regression model underscores the complexity of factors influencing purchase intention, resonating with contemporary marketing research in the digital and social media landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study investigates the factors influencing purchase intention (PI), with a specific focus on social media and influencer-driven marketing. The findings provide significant insights into how various predictors, such as consumer engagement, emotional appeal, and influencer presence, shape purchase decisions. As shown in the regression analysis, the significant predictors, like emotional appeal and consumer engagement, are consistent with existing literature, which underscores their importance in driving purchase intentions in the digital era (Belanche, Flavián, & Ibáñez-Sánchez, 2020; Arief, Mustikowati, & Chrismardani, 2023).
This research contributes to understanding the growing role of influencers in shaping consumer behavior, especially on platforms like Instagram, and offers useful implications for marketers seeking to leverage digital tools to influence consumer decision-making. As brands increasingly embrace purpose-driven marketing (Fernandes, Guzman, & Mota, 2024), there is potential for future studies to explore how purpose and values can further drive consumer trust and PI. Moreover, the global impact of influencers, particularly virtual influencers (Gambetti & Kozinets, 2024), is a promising area for future exploration, as these entities continue to disrupt traditional influencer marketing strategies.
Future studies could also investigate the role of different social media platforms, considering their unique features, as well as how external factors like global crises (Goyal & Taneja, 2023) or changing consumer behaviors post-pandemic (Herzallah, Muñoz-Leiva, & Liebana-Cabanillas, 2022) might affect purchase intention. Expanding the study to include diverse demographic groups across regions, particularly in emerging markets, would provide a broader understanding of global consumer behavior trends. This research, with its focus on influencer-driven marketing, has the potential for global application, especially as brands increasingly utilize social media platforms to engage with customers. The implementation of insights from this study can guide marketers in refining strategies to engage consumers more effectively across various digital touchpoints, potentially leading to higher conversion rates and brand loyalty (Jamil, Qayyum, & ul Hassan, 2024; Hu, Filipescu, & Pergelova, 2024).
References
Ahmadi, A., & Ieamsom, S. (2022). Influencer fit post vs celebrity fit post: which one engages Instagram users more? Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 26(1), 98–116.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ahmadi, A., Fakhimi, S., & Ahmadi, Y. (2022). Instagram celebrities and positive user responses. The mediating role of user “like.” Journal of Contemporary Marketing Science, 5(1), 65–80.
Aiolfi, S., Bellini, S., & Pellegrini, D. (2021). Data-driven digital advertising: benefits and risks of online behavioral advertising. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 49(7), 1089–1110.
Åkestam, N., Rosengren, S., Dahlén, M., Liljedal, K. T., & Berg, H. (2021). Gender stereotypes in advertising have negative cross-gender effects. European Journal of Marketing, 55(13), 63–93.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Appiah-Nimo, K., Muthambi, A., & Devey, R. (2024). Consumer-based brand equity of South African luxury fashion brands. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 28(4), 775–791.
Arief, M., Mustikowati, R. I., & Chrismardani, Y. (2023). Why customers buy an online product? The effects of advertising attractiveness, influencer marketing and online customer reviews. LBS Journal of Management & Research, 21(1), 81–99.
Belanche, D., Cenjor, I., & Pérez-Rueda, A. (2019). Instagram Stories versus Facebook Wall: an advertising effectiveness analysis. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 23(1), 69–94.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Belanche, D., Flavián, M., & Ibáñez-Sánchez, S. (2020). Followers’ reactions to influencers’ Instagram posts. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 24(1), 37–54.
Calapez, A., Ribeiro, T., Almeida, V., & Pedragosa, V. (2024). Esports fan identity toward sponsor–sponsee relationship: an understanding of the role-based identity. International Journal of Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 25(1), 42–66.
Chang, S.-T., & Wu, J.-J. (2024). A content-based metric for social media influencer marketing. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 124(1), 344–360.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dalziel, R. C., & de Klerk, N. (2021). Media and group influence on Generation Y consumers’ attitudes towards beauty products. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 25(1), 115–136. https://doi.org/10.1108/SJME-12-2019-0104
de Canio, F., Martinelli, E., & Endrighi, E. (2021). Enhancing consumers’ pro-environmental purchase intentions: the moderating role of environmental concern. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 49(9), 1312–1329. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJRDM-08-2020-0301
Duffett, R. G., & Maraule, M. (2024). Customer engagement and intention to purchase attitudes of generation Z consumers toward emojis in digital marketing communications. Young Consumers, 25(5), 607–624.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Farzin, M., Shababi, H., Shirchi Sasi, G., Sadeghi, M., & Makvandi, R. (2023). The determinants of eco-fashion purchase intention and willingness to pay. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 27(3), 348–366.
Fernandes, T., Guzman, F., & Mota, M. (2024). Purpose is the new branding: understanding conscientious purpose-driven marketing and its impact on brand outcomes. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 33(6), 761–782.
Gambetti, R. C., & Kozinets, R. v. (2024). From killer bunnies to talking cupcakes: theorizing the diverse universe of virtual influencers. European Journal of Marketing, 58(13), 205–251.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Goyal, C., & Taneja, U. (2023). Electronic word of mouth for the choice of wellness tourism destination image and the moderating role of COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Tourism Futures, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Han, J., & Chen, H. (2022). Millennial social media users’ intention to travel: the moderating role of social media influencer following behavior. International Hospitality Review, 36(2), 340–357.
Hassan, H., Sade, A. B., & Subramaniam, L. S. (2020). Purchasing functional foods to stay fit. Journal of Humanities and Applied Social Sciences, 2(1), 3–18.
Herzallah, D., Muñoz-Leiva, F., & Liebana-Cabanillas, F. (2022). Drivers of purchase intention in Instagram Commerce. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 26(2), 168–188.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hu, L., Filipescu, D. A., & Pergelova, A. (2024). Understanding SMEs’ internationalization through digital platforms: the role of knowledge sharing and consumer education. International Marketing Review, 41(5), 1044–1073.
Jamil, R. A., Qayyum, U., ul Hassan, S. R., & Khan, T. I. (2024). Impact of social media influencers on consumers’ well-being and purchase intention: a TikTok perspective. European Journal of Management and Business Economics, 33(3), 366–385.
Kara, N. S. (2024). The role of celebrity involvement in influencing domestic tourists’ intention to visit Tanzania’s attractions: attitude as a mediating variable. International Hospitality Review, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kaur, P., Dhir, A., Talwar, S., & Ghuman, K. (2021). The value proposition of food delivery apps from the perspective of theory of consumption value. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 33(4), 1129–1159.
Khan, S., Rehman, S., & Kashif, U. (2024). “We do it but they don’t” unveiling the impact of differentiation-oriented content on purchase intentions through mediation of SM engagement and moderation of social media skills. South Asian Journal of Marketing, 5(1), 47–60.
Koay, K. Y., & Lim, W. M. (2024). Congruence effects in social media influencer marketing: the moderating role of wishful identification in online impulse buying intentions. Journal of Product & Brand Management, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Litterio, A. M., Nantes, E. A., Larrosa, J. M., & Gómez, L. J. (2017). Marketing and social networks: a criterion for detecting opinion leaders. European Journal of Management and Business Economics, 26(3), 347–366.
Lupindo, M., Madinga, N. W., & Dlamini, S. (2024). Green beauty: examining factors shaping millennials’ attitudes toward organic personal care products in South Africa. European Journal of Management Studies, 29(3), 271–291.
Macheka, T., Quaye, E. S., & Ligaraba, N. (2024). The effect of online customer reviews and celebrity endorsement on young female consumers’ purchase intentions. Young Consumers, 25(4), 462–482.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Maia, C., Lunardi, G., Longaray, A., & Munhoz, P. (2018). Factors and characteristics that influence consumers’ participation in social commerce. Revista de Gestão, 25(2), 194–211.
Maziriri, E. T., Nyagadza, B., Chuchu, T., & Mazuruse, G. (2024). Antecedents of attitudes towards the use of environmentally friendly household appliance products in Zimbabwe: an extension of the theory of planned behaviour. PSU Research Review, 8(3), 749–773.
Moorthy, K., Runxuan, L., Chun T’ing, L., & Jing Yii, K. (2024). College students’ consumption behaviour in internet celebrity economy under We Media environment: a study among Malaysian and Chinese students. Journal of Responsible Production and Consumption, 1(1), 62–80.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nguyen, T. M. N., Le, B. N., Leenders, M. A. A. M., & Poolsawat, P. (2024). Food vloggers and their content: understanding pathways to consumer impact and purchase intentions. Journal of Trade Science, 12(2), 117–133.
Palazón, M., Alarcón-del-Amo, M. del C., Martínez, B., & López, M. (2024). Consumers’ healthy lifestyle as a determinant of the influence of microcelebrities and microinfluencers. European Journal of Management and Business Economics, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Pandit, A., McLeay, F., Zaveri, M. M., al Mursalin, J., & Rosenberger, P.J. (2025). Continued engagement intention with social media influencers: the role of experience. Internet Research, 35(7), 1–29.
Pozharliev, R., Rossi, D., & de Angelis, M. (2022). Consumers’ self-reported and brain responses to advertising post on Instagram: the effect of number of followers and argument quality. European Journal of Marketing, 56(3), 922–948.
Rodrigo, A., & Mendis, T. (2023). Impact of social media influencers' credibility on millennial consumers' green purchasing behavior: a concept paper on personal and social identities. Management Matters, 20(2), 134-153.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Savelli, E., Francioni, B., Curina, I., & Cioppi, M. (2024). Promoting access-based consumption practices through fashion renting: evidence from Italy. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 41(1), 61–77.
Shen, Z. (2021). A persuasive eWOM model for increasing consumer engagement on social media: evidence from Irish fashion micro-influencers. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 15(2), 181–199.
Smith, D., Jacobson, J., & Rudkowski, J. L. (2021). Employees as influencers: measuring employee brand equity in a social media age. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 30(6), 834–853.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Szymkowiak, A., & Antoniak, M. A. (2024). Eco-endorsement dynamics: unraveling the influence of celebrity attitudes on eco-product perceptions and purchase decisions. International Journal of Wine Business Research, 36(3), 453–472.
Talha, M., Tahir, Z., & Mehroush, I. (2024). Enhancing customer engagement through source appearance and self-influencer congruence in mobile advertising. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, 28(4), 382–401.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
van Reijmersdal, E. A., Walet, M., & Gudmundsdóttir, A. (2024). Influencer marketing: explaining the effects of influencer self-presentation strategies on brand responses through source credibility. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 42(7), 1214–1233.
Wahab, H. K. A., Alam, F., & Lahuerta-Otero, E. (2024). Social media stars: how influencers shape consumer’s behavior on Instagram. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yadav, N., Verma, S., & Chikhalkar, R. (2024). Online reviews towards reducing risk. Journal of Tourism Futures, 10(2), 299–316.
Yang, Q., Huo, J., Li, H., Xi, Y., & Liu, Y. (2023). Can social interaction-oriented content trigger viewers’ purchasing and gift-giving behaviors? Evidence from live-streaming commerce. Internet Research, 33(7), 46–71.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 01-Apr-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15817; Editor assigned: 02-Apr-2025, PreQC No. AMSJ-25-15817(PQ); Reviewed: 14-Apr-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-15817; Revised: 21-Apr-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15817(R); Published: 16-May-2025