Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 6S
Measuring Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Selected Companies of Telecommunication and Automobile Sector in India
Pavithra J, SRM Institute of Science and Technology
Gunjan Sharma, Department of Management Prestige institute of Management and Research Bhopal
Jyotika Bahl, Gargi College, University of Delhi
Swati Ojha, Department of Management Prestige Institute of Management and Research Bhopal
Prasanta Chatterjee Biswas, CDOE Parul University Vadodra
Citation Information: Pavithra, J., Sharma, G., Ojha, S., & Chatterjee Biswas, P. (2025). Measuring fundamental and technical analysis of selected companies with reference to telecommunication and automobile industry in india. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(S6), 1-15.
Abstract
This study explores the organizational structure and financial analysis of Motilal Oswal Financial Services Ltd., with a practical application through two sectoral case studies: Vodafone Idea Ltd. (telecommunications) and Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. (automobile). The research focuses on understanding the internal functioning of Motilal Oswal’s advisory services, emphasizing the role of departmental coordination and communication in delivering efficient client solutions. The study uses both fundamental and technical analysis to evaluate the financial performance of the selected companies. Vodafone Idea Ltd. shows significant financial stress, with negative shareholder funds, high debt-to-equity ratio, and continuous net losses. Despite improved operating margins, the company’s liabilities outweigh assets, indicating potential insolvency risks. On the other hand, Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. reflects strong financial health, marked by consistent sales growth, improved operating margins, and a solid asset base. Its lower debt levels and increasing reserves signal sound financial management and investor confidence. From a technical standpoint, Vodafone Idea shows short-term uptrend potential, while Mahindra & Mahindra displays bullish reversal patterns, supporting long-term investment prospects. The findings highlight the impact of internal organizational effectiveness on financial advisory services and portfolio strategy. For Motilal Oswal, maintaining a client-centric structure supported by strong interdepartmental communication enhances strategic agility. The internship offered valuable insights into real-world financial evaluation and organizational dynamics, contributing to practical understanding and career preparedness in financial services.
Keywords
Vodafone Idea, Mahindra & Mahindra, Financial Analysis, Technical Analysis, Debt-to-Equity, Client Advisory, Shareholder Funds, Investment Strategy, Indian Financial Sector, Sectoral Comparison, Fundamental Ratios.
Introduction
The advisor role at Motilal Oswal Financial Services is central to the company’s mission of providing comprehensive wealth management and financial solutions to its clients. Advisors at Motilal Oswal act as trusted financial consultants, guiding clients through a range of investment options, market trends, and portfolio strategies Acharya & Roy (2020).
Key Responsibilities
• Client Relationship Management: Advisors build and maintain strong relationships with clients, understanding their financial goals and tailoring personalized investment strategies to meet those objectives.
• Investment Advisory: They offer expert advice on various financial products such as equities, mutual funds, fixed income instruments, and alternative investments, ensuring clients’ portfolios are optimized for growth, income, or risk
• Market Research & Insights: Advisors stay updated with the latest market trends, financial news, and research reports, leveraging Motilal Oswal’s in-house research expertise to provide clients with informed guidance.
Objective of the Study
Following are the objectives of the study:
• To understand the organisation structure at Motilal Oswal Financial Services Ltd
• To understand the working of the central advisory department
Importance of the Study
Understanding the organizational structure of Motilal Oswal Financial Services Ltd. is essential for gaining insights into how the company operates and makes strategic decisions. This study will help in understanding the internal dynamics and coordination between departments, which is critical for delivering effective advisory services. Additionally, analyzing the structure can reveal areas for improvement, contributing to better client service and operational efficiency. For an intern, this study enhances personal growth by providing a deeper understanding of corporate governance and the financial services industry's functioning Geels, (2012).
Scope of the Study
The scope of this study focuses on understanding the organizational framework of Motilal Oswal Financial Services Ltd., including its hierarchy, departmental functions, and inter-departmental coordination. It will explore how different teams, such as research, operations, and client servicing, interact to achieve the company’s objectives. The study will also cover the reporting structures and decision-making processes within the organization Kumaraswamy et al. (2012).
The study will also consider how the structure supports the company’s overall efficiency and ability to adapt to changing market conditions. While the focus is on understanding internal organizational dynamics, the study will not delve into external factors like market competition or industry analysis.
By examining these elements, the study aims to provide insights into how the current structure supports the company’s growth, efficiency, and ability to respond to market dynamics. The scope is limited to internal organizational aspects without delving into external factors like market positioning or competitor analysis.
Period of the Study
The study was conducted for a brief period of 45 days ranging between 4th June,2024 to 19th July,2024.
Literature Review
An important area of focus for assessing effectiveness and customer satisfaction in financial institutions has been the study of organizational structures. Flatter structures improve agility, according to Kumar and Sharma's (2015) analysis of the effects of hierarchical coordination on strategic decision-making in Indian financial services. In a similar vein, Rao (2016) highlighted how departmental integration helps consulting firms maintain customer engagement Lall, (1980).
In the context of stock performance and fundamental analysis, Mehta and Bansal (2017) highlighted the relevance of key financial ratios such as P/E, ROE, and current ratio in predicting long-term stock performance in India’s telecom sector. Patel and Singh (2018) elaborated on this by performing sector-wise comparative ratio research, which demonstrated that debt-to-equity ratios are especially important in highly leveraged businesses like telecom.
The ramifications of diminishing promoter ownership were examined by Verma (2019), who claimed that a smaller stake frequently indicates low insider confidence, which has a detrimental effect on investor behavior. The findings of Raghavan and D'Souza (2020) that promoter behavior frequently comes before changes in market sentiment, especially during restructuring events or FPOs, are consistent with this Mytelka, (2000).
Nair (2021) used methods such as Fibonacci retracements and moving averages to examine the significance of technical analysis in stock advice responsibilities. According to his research, combining technical indicators offer superior entry and exit strategies when compared to separate instruments. In the meantime, Roy and Banerjee (2022) confirmed the predictive reliability of trend patterns like rounded bottoms and double tops in the Indian auto industry by testing their efficacy.
The contribution of internal organizational frameworks to advising effectiveness was discussed by Saxena and Thomas (2023). The advantages of effective interdepartmental communication in producing consistent customer outcomes were highlighted by their study on mid-sized financial advising businesses. Narayan et al. (2023) echoed these findings by linking internal structure to adaptability in volatile markets, particularly during periods of digital transition.
The post-pandemic strategy changes in Indian financial services were the subject of recent research like Menon and Joshi (2024). They underlined that in order to keep customers and maintain growth, digitization and agile decision-making procedures are increasingly essential. In order to match organizational goals with changing market needs, their work also emphasized the necessity of consistent personnel training and a strong feedback loop Pandey et al. (2013).
Finally, there has been ongoing interest in sectoral financial performance. Deshmukh and Pillai (2024) provided a comparative study between automobile and telecom companies in India, revealing that while large-cap automobile firms show strong asset utilization and positive EPS, telecom companies face financial instability due to high debt and low ROCE. These results validate the current study's interpretation of the balance sheet.
Research Methodology
The study is based on secondary data that is collected from the company’s website as well as other prominent financial sites like moneycontrol, screener and trading view was used for technical analysis.The data analysis made is based on fundamental and technical analysis. The tools used for fundamental analysis include:
• Balance sheet analysis
• Quarterly results analysis
• Ratio analysis
• P/E Ratio
• Price to Book value
• Debt to Equity
• Current Ratio
• Promoters holding
• Book value
• ROCE and ROE
The tools used for technical analysis includes:
• Moving average
• Relative Strength Index
• Fibonacci retracements
• Trend analysis
• Support and resistance levels
Data Analysis
Tele-Communications Sector Stock Under Study: Vodafone Idea Limited about the Company
Vodafone Idea or VI is an Indian mobile network operator with its headquarters based in Mumbai and Gandhinagar. It is an all-India GSM operator offering 2G,3G,4G LTE Advanced, 5G,VoLTE and VoWiFi services. It is the third largest mobile telecommunications network in India and the 12th largest mobile telecommunications network in the world. Vodafone Idea limited was created on 31 August 2018 by the merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular. In 2020, the two separate brands were rebranded as Vi. On February 2023, the Government of India ordered the company to convert its interest dues worth 161.33 billion Indian rupees to equity at the rate of 10 rupees per share face value when the market value was about 8.5 rupees per share, thus making the government the single biggest shareholder in the company Tables 1-4.
| Table 1 Quarterly Results | ||||
| PARTICULARS | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| Sales | 10,656 | 10,716 | 10,673 | 10,607 |
| Expenses | 6,499 | 6,435 | 6,324 | 6,274 |
| Operating profit | 4,156 | 4,282 | 4,349 | 4,333 |
| Operation profit margin | 39% | 40% | 41% | 41% |
| Net profit | -7,840 | -8,738 | -6,986 | -7,666 |
| Increase in sales | 1.18% | 0.56% | -0.40% | -0.62% |
| Increase in expense | 2.80% | -0.98% | -1.72% | -0.79% |
| increase in net profit | -22.14% | -11.45% | 20.05% | -9.73% |
| Table 2 Balance Sheet of Vodafone Idea(in RS. CR.) | ||
| BALANCE SHEET ANALYSIS | 24-Mar | 23-Mar |
| EQUITIES AND LIABILITIES | ||
| SHAREHOLDER'S FUNDS | ||
| Equity Share Capital | 50,119.80 | 48,679.70 |
| TOTAL SHARE CAPITAL | 50,119.80 | 48,679.70 |
| Reserves and Surplus | -153,763.80 | -122,522.30 |
| TOTAL RESERVES AND SURPLUS | -153,763.80 | -122,522.30 |
| TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS FUNDS | -103,644.00 | -73,838.80 |
| NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||
| Long Term Borrowings | 202,896.20 | 189,290.10 |
| Deferred Tax Liabilities [Net] | 0 | 0 |
| Other Long Term Liabilities | 31,733.80 | 31,885.40 |
| Long Term Provisions | 3.9 | 7.1 |
| TOTAL NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES | 234,633.90 | 221,182.60 |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||
| Short Term Borrowings | 4,989.20 | 12,530.40 |
| Trade Payables | 13,921.60 | 13,711.20 |
| Other Current Liabilities | 35,067.40 | 33,676.30 |
| Short Term Provisions | 33.3 | 11.4 |
| TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES | 54,011.50 | 59,929.30 |
| TOTAL CAPITAL AND LIABILITIES | 185,001.40 | 207,273.10 |
| ASSETS | ||
| NON-CURRENT ASSETS | ||
| Tangible Assets | 154,429.30 | 55,548.20 |
| Intangible Assets | 0 | 96,432.90 |
| Capital Work-In-Progress | 0 | 241.7 |
| Other Assets | 0 | 0 |
| FIXED ASSETS | 154,429.30 | 169,798.90 |
| Non-Current Investments | 162.6 | 162.6 |
| Deferred Tax Assets [Net] | 0 | 0 |
| Long Term Loans And Advances | 0 | 0 |
| Other Non-Current Assets | 13,780.50 | 19,143.30 |
| TOTAL NON-CURRENT ASSETS | 168,372.40 | 189,104.80 |
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||
| Current Investments | 0.2 | 0 |
| Inventories | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Trade Receivables | 2,122.20 | 2,124.50 |
| Cash And Cash Equivalents | 453.9 | 771.6 |
| Short Term Loans And Advances | 235.6 | 279.1 |
| Other Current Assets | 13,816.90 | 14,992.70 |
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS | 16,629.00 | 18,168.30 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 185,001.40 | 207,273.10 |
| Table 3 Quarterly Results | ||||
| PARTICULARS | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| Sales | 33,892 | 34,436 | 35,299 | 35,452 |
| Expenses | 27,642 | 28,706 | 29,075 | 28,848 |
| Operating profit | 6,249 | 5,730 | 6,224 | 6,604 |
| Operation profit margin | 18% | 17% | 18% | 19% |
| Net profit | 3,684 | 2,484 | 2,977 | 3,125 |
| Increase in sales | 4.42% | 1.61% | 2.51% | 0.43% |
| Increase in expense | 3.15% | 3.85% | 1.29% | -0.78% |
| increase in net profit | 22.88% | -32.57% | 19.85% | 4.97% |
| Table 4 Balance Sheet of Mahindra & Mahindra | ||
| BALANCE SHEET OF MAHINDRA AND MAHINDRA (in Rs. Cr.) | 24-Mar | 23-Mar |
| EQUITIES AND LIABILITIES | ||
| SHAREHOLDER'S FUNDS | ||
| Equity Share Capital | 599.62 | 599.05 |
| TOTAL SHARE CAPITAL | 599.62 | 599.05 |
| Reserves and Surplus | 51,676.94 | 42,497.35 |
| TOTAL RESERVES AND SURPLUS | 51,676.94 | 42,497.35 |
| TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS FUNDS | 52,276.56 | 43,356.73 |
| NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||
| Long Term Borrowings | 1,134.86 | 2,331.56 |
| Deferred Tax Liabilities [Net] | 1,555.06 | 1,470.29 |
| Other Long Term Liabilities | 1,678.92 | 1,374.15 |
| Long Term Provisions | 1,187.23 | 1,207.09 |
| TOTAL NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES | 5,556.07 | 6,383.09 |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||
| Short Term Borrowings | 450.03 | 2,312.17 |
| Trade Payables | 18,591.95 | 17,145.62 |
| Other Current Liabilities | 6,252.60 | 5,975.37 |
| Short Term Provisions | 684.17 | 606.83 |
| TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES | 25,978.75 | 26,039.99 |
| TOTAL CAPITAL AND LIABILITIES | 83,811.38 | 75,779.81 |
| ASSETS | ||
| NON-CURRENT ASSETS | ||
| Tangible Assets | 21,283.83 | 13,050.12 |
| Intangible Assets | 0 | 3,926.08 |
| Capital Work-In-Progress | 0 | 950.27 |
| Other Assets | 0 | 0 |
| FIXED ASSETS | 21,283.83 | 19,760.82 |
| Non-Current Investments | 21,548.74 | 17,539.06 |
| Deferred Tax Assets [Net] | 926.74 | 0 |
| Long Term Loans And Advances | 93.09 | 177.45 |
| Other Non-Current Assets | 4,853.18 | 3,658.85 |
| TOTAL NON-CURRENT ASSETS | 48,705.58 | 41,136.18 |
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||
| Current Investments | 8,446.66 | 9,548.01 |
| Inventories | 9,504.82 | 8,881.35 |
| Trade Receivables | 4,549.46 | 4,041.73 |
| Cash And Cash Equivalents | 5,525.92 | 4,481.75 |
| Short Term Loans And Advances | 2,378.92 | 2,176.96 |
| Other Current Assets | 4,700.02 | 5,513.83 |
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS | 35,105.80 | 34,643.63 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 83,811.38 | 75,779.81 |
Fundamental Analysis
Market capitalization: Rs. 1,25,712 Cr (Large Cap)
Market capitalization is defined as the total market value of the outstanding shares of the company. It is calculated as a product of number of shares outstanding and its current market price.
Following points can be interpreted from the above quarterly results analysis of Vodafone Idea ltd
• Sales figures have not seen any significant change over the four quarters
• On the other hand, expenses have been decreasing from the second quarter even though the decrease in expense is very nominal and not significant
• The operating profit margin of the company has increased in the last financial year. It is a positive point for the company
• Inspite of the positive operating profit made by the company, the net profit remains as a negative figure indicating a net loss of a very huge amount. This is due to two factors
• Depreciation charged
• Interest payments
The company has to focus on settling its debts to reduce its interest payments and to improve the profitability position.
Analysis and Interpretation of Key Ratios
• P/E Ratio: -4.0245
The company’s earnings are negative indicating a net loss.It may be due to poor financial performance , industry challenges or structural issues. However, a negative P/E ratio doesn’t necessarily mean that a company is a bad investment. The company maybe in its turnaround phase and earnings might be temporarily negative
• ROCE and ROE
ROCE and ROE of Vodafone Idea ltd are negative indicating a poor utilization of assets and a lack of profitability.
• Debt to Equity: -2.733
It indicates that debt portion of the company is higher than its equity. A higher debt level would indicate that the company has a huge amount of fixed interest obligations thereby, reducing the returns to equity shareholders.
• Current Ratio: 32
Current ratio represents the ratio of current assets to current liabilities. Current ratio of 0.32 is very much below the ideal ratio of 1.5 times. A lower current ratio indicates that the company doesn’t have sufficient current assets to cover its short term obligations.
• Promoters holding: 17%
The promoters shareholding has decreased from 48.91 % to 38.17%. This reflects poor or low confidence of promoters in the company’s future prospects. Also, the Government has reduced its holdings from 32.23% to 23.80%.
• Book value: -12.73
Book value refers to the amount that shareholders will receive against each one share after netting of the assets and liabilities. It means that the company’s net asset value is negative. It indicates that company’s liabilities are higher than its assets.
• Price to Book value: -0.87
It indicates that the company is trading at a discount to its book value, suggesting that the market has a negative view on Vodafone Idea’s financial health and its future prospects Shah & Ajmera, (2022).
• EPS: -Rs6.7
It indicates that the company is reporting a loss of Rs.6.71 per share.
Negative Total Shareholders Funds
• Total shareholders funds of Vodafone Idea ltd is at –Rs.1,03,644 crores, an increase by Rs.29806 crores
• It means that if the company were to liquidate all its assets and pay off its liabilities, it would still not have enough funds to cover its debts and shareholders would be left with a deficit
• Following are the reasons for the negative value in the total shareholders funds
• Accumulated losses: The company has reported net loss in a huge amount for the past 4 quarters
• High debt levels: The company is facing a significant debt burden and is losing out all its profts by making interest payments
• A negative shareholders fund situation is a red flag situation for both investors and lenders indicating a high level of financial risk and potential insolvency
Increase in Equity Shareholders Funds
Vodafone Idea went for an FPO in April 2024, resulting in an increase in the equity shareholders funds compared to that of previous year Figures 1-4.
Increase in Borrowings
Vodafone idea has increased it long term borrowings which indicates that it has to shell extra amount from its profits to meet the interest obligations on its borrowings and this would further reduce the returns of equity shareholders.
Other key observations from the balance sheet
• Increase in tangible assets
It indicates that the company has invested funds in increasing the level of tangible assets held by the company. This could possibly indicate that the company is on plans to expand its operations and improve its production. However, there is a significant reduction in intangible assets from 96,432.90 crores to nil
• Noncurrent investments remains unchanged and current investments have increased by Rs.0.20crores
• Cash and cash equivalents have reduced from Rs.771.60 crore in 2023 to Rs.453.90 crores in 2024
Technical Analysis
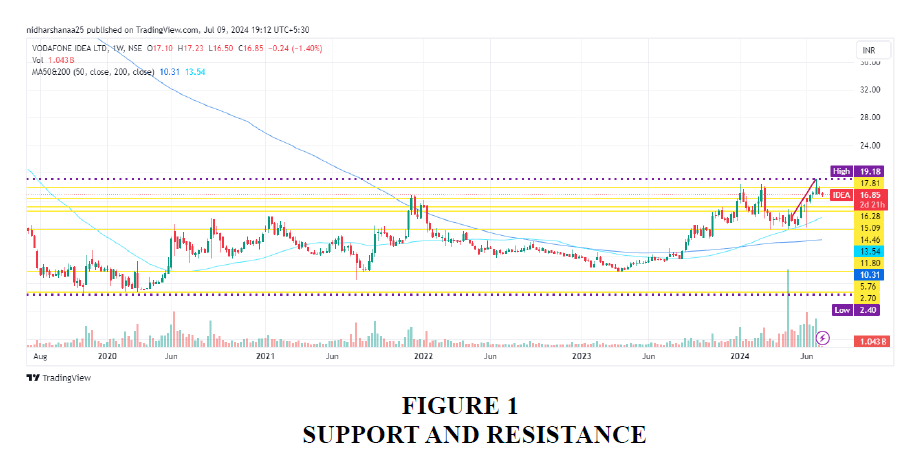
OPEN 16.99
CLOSE 17.89
HIGH 19.18
LOW 16.86
Support is the level below which the market doesn’t fall and market goes up. Resistance level is the price point above which the market doesn’t rise. In the above chart various support and resistance levels are marked . If the stock breaks its support and goes up, a new resistance level will be established and the previous resistance level will now act as a support to the new resistance level.
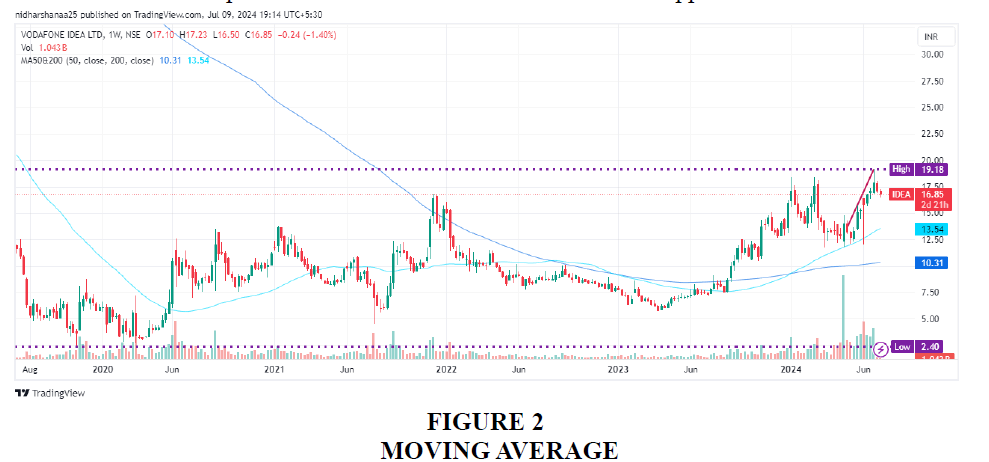
The stock is trading above its 50D and 200D Moving Average. In the above chart, dark blue or the lower lying line is the 200D moving average and the higher lying line or the light blue line is its 50D Moving Average. If the stock is trading above its 50D moving average, it would represent a short-term uptrend in its price and if the price is above its 200D moving average, it would indicate a long term bullish trend. When the price crosses above or below a moving average, it would signal a potential trend reversal. When the shorter-term MA crosses above the longer-term MA, it is considered as a buy signal and it indicates that the trend is up. If the shorter-term MA crossed below the longer-term MA , it is considered as a sell signal and indicates that the trend is moving down. In the above chart, 50D MA crosses 200D MA from above indicating an uptrend and a potential buying opportunity.
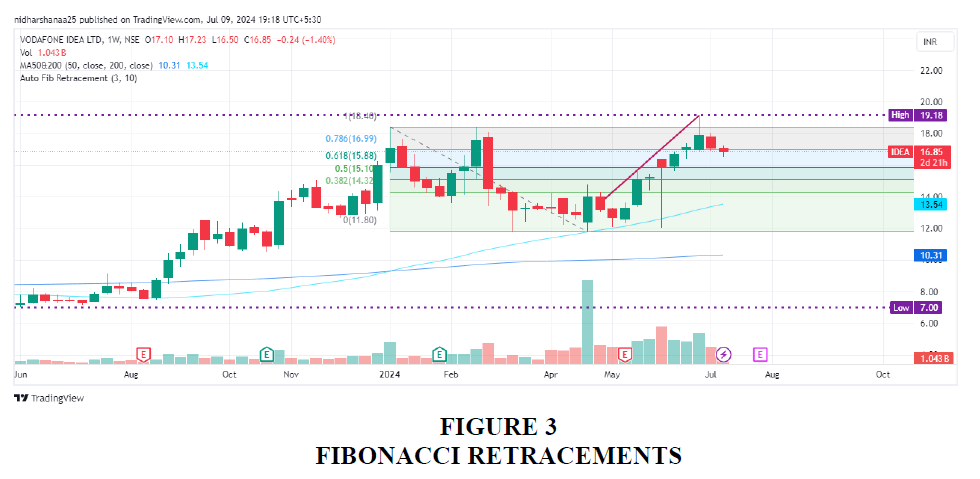
Fibonacci retracements are horizontal lines on a stock chart that indicate where support and resistance levels are likely to occur. Prominent retracements levels are 38.2,50,61.8 and 78.6. The last time the market fell, it retraced at 38.2 level and now if it breaks the support level at 38.2 retracement level, it would further fall Shende, (2014).
Auto Mobile Sector: Stock Under Study: Mahindra & Mahindra
About The Company
Mahindra & Mahindra is an Indian automobile manufacturing company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It is a core unit of conglomerate Mahindra Group. It is a major producer of sports utility vehicles, trucks and farm tractors. It was established in 1945 as Mahindra & Mohammed and later renamed Mahindra & Mahindra. Its unit, Mahindra Tractors, is the largest manufacturer of tractors in the world by volume. Its major competitors in the Indian market include Maruti Suzuki India and Tata Motors. Its products include
• Automobiles
• Commercial vehicles
• Tractors
• Motorcycles
The company is active in domestic and international markets. It is the flagship company of the Mahindra Group, also it is a diversified business company. It has its presence in major industries such as
→ Aerospace
→ Agri-business
→ Components
→ Consulting
→ Financial services
→ Real estate etc
Fundamentals
Market capitalization: Rs.3,58,006 Crores (Large Cap)
Market capitalization is defined as the total market value of the outstanding shares of the company. It is calculated as a product of number of shares outstanding and its current market price. Large cap companies are well-established businesses with a significant market share. These companies dominate the industry and are very stable. They hold themselves well in times of recession or during any other adverse event. Investors prefer large cap companies for stability. They are also called ‘Blue-chip’ stocks.
Analysis and Interpretation of the Quarterly Results
• Sales for the four quarters are in an uptrend. Even though the rate of increase in sales isn’t consistent, the company has managed to show at least a nominal rate of increase in its sales over the past four quarters.
• Expenses have increased in the first three quarters of the financial year and during the last quarter, the expenses fell by 0.78% as compared to the expenses incurred in the third quarter Vinutha, & Goud, (2018).
• Company has managed to increase the operating margin in the last two quarters despite the 1% fall in the second quarter. Increasing operating profit margin is a positive point for the company and when it is along with an increase in sale and corresponding decrease in expenses, it shows that the core operations of the business are being effective and efficient Swain, (2022).
• The net profit of the company has improved and is quite promising. After a drastic 32% fall in net profits in the second quarter, the company managed to put it back on track with a 20% increase in net profits in the third quarter followed by a less than proportionate increase in the fourth quarter.
Analysis and Interpretation of Balance Sheet Items
• Shareholder’s funds
• The equity shareholdings in the company increases by 0.55 crores, even though it is not a nominal increase, it would lead to dilution in the rights of existing shareholders.
• The reserves and surplus increased by 21.6%. This can be interpreted in two ways
• The company’s profitability has increased leading to increase in the reserves
• Too much of funds are idle. It must be effectively utilized to ensure there is no loss in the opportunity cost.
• Overall, the total shareholder funds increased by 20.5%
• Non-current and current liabilities
• Long term borrowings fell by 51.8%. It is a positive sign because decreasing levels of debt would lead to reduced interest payments which would eventually increase the earnings of the equity shareholders.
• Long term provisions also witnessed a decrease.
• Short term borrowings fell drastically by 80% indicating that company has settled 80% of its short term borrowings
• However, there was an increase in other current liabilities and short term provisions.
Assets
• Tangible assets have increased by Rs.8,000 crore which indicated that the company has invested in its tangible assets. Its intangible assets and capital WIP were brought down to nil.
• Current investments fell by a little over Rs.1,100 crore
• Trade receivables increased by Rs.500 crores
• Cash and cash equivalents increased by Rs.1,100 crore. This can be interpreted in two different ways
• The company’s profitability has increased leading to increase in the cash holdings
• Too much of funds are idle. It must be effectively utilized to ensure there is no loss in the opportunity cost.
Overall, the balance sheet figure have improved from what it was in the previous year and are providing a positive sign and looks promising.
Analysis and interpretation of key ratios
• P/E Ratio: 8
The P/E ratio of the company is a little high compared to the industry P/E of 30 times. It might indicate that the stock is over valued or investors have so much confidence on the performance of the stock. P/E of the stock is falling and EPS of the stock is increasing, which is a positive sign. Also, when compared with competitors, the P/E is a little high as that of competitors is well within the industry P/E.
• ROCE and ROE
ROCE: 13.7%
ROE: 18.4%
Though ROCE is positive, it is very low when compared to its competitors, which can be improved.
ROE is in line with that of its competitors, it is positive for the company.
• Debt to Equity: 61
It indicates that debt portion of the company is more than the equity. The ideal debt equity ratio is 2:1 and the debt equity ratio of the company is below the ideal ratio, which is a positive sign . Among its competitors, Mahindra & Mahindra has the highest debt equity ratio, which is now a point to be focused.
• Current Ratio: 30
Current ratio represents the ratio of current assets to current liabilities. Current ratio of 1.30 is a little below the ideal ratio of 1.5 times. This indicates that the company has to improve its current asset position and reduce its current liabilities.
• Promoters holding: 6%
Promoters holdings has been reducing over the period. This would indicate lack of promoters confidence in the performance and financial health of the company.
• Book value: 532
Book value refers to the amount that shareholders will receive against each one share after netting of the assets and liabilities. On liquidation, each shareholders would receive Rs.532 against each share held by them. Book value is less than the current value, indicating that the share is over valued.
• Price to Book value: 40
It indicates that the company is trading at a premium to its book value, suggesting that the market has a positive view on the company’s financial health and its future prospects. The share is trading at 2.36x its book value. It signals that the shares are over valued.
• EPS: 90.6
It indicates that the company is reporting a profit of Rs.90.6 per share. Higher EPS indicates that the company is giving great returns to its shareholders and it is a positive point for the company to attract shareholders and investors.
Technical Analysis
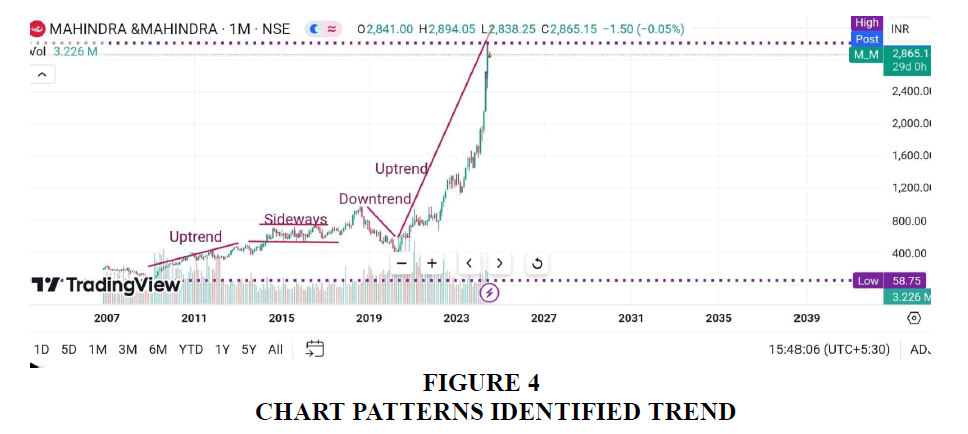
With a monthly timeframe, it can be seen that
2011 to 2015 àUptrend
2015 to 2019 àSideways trend
2019 to 2021à Downtrend
2022 to presentà uptrend
• The patterns marked in yellow ink represent a double top pattern which is a bullish reversal sign
It can be seen from the above chart that market declined post the double top pattern
The above chart is set at a hourly time frame
• The patterns marked in purple are rounding bottom and rounding top patterns
Rounding bottom is a bullish reversal sign
It can be seen that the market goes up after the rounding bottom pattern
Rounding top is a bearish reversal sign
It can be seen that the market falls post the formation of rounding top
• Apart from the patterns identified above, various accumulation and distribution zones can also be spotted
Mahindra and Mahindra Todays Performance
Outlook: Bullish
Decision: Buy
Open: Rs.2841
High: Rs. 2894.05
Low: Rs.2838.25
Close: Rs.2875.85
Current price: Rs.2875.85
Patterns like head and shoulder and rounding bottom are spotted on a monthly time frame
Rounding bottom is a bullish reversal sign
Head and shoulder is a bearish reversal sign
Findings
• Clear Organizational Structure: The company's structure is well-defined, with clear roles and responsibilities, which helps in maintaining operational efficiency and accountability.
• Effective Communication: Communication across departments is generally well-organized, ensuring that tasks are coordinated smoothly and information flows effectively.
• Client Focus: The organizational setup emphasizes a client-centric approach, with departments aligned to support overall client service and satisfaction.
Suggestions
• Simplify Decision-Making: Streamlining decision-making processes could improve the company’s ability to respond quickly to market changes and client needs.
• Focus on Training: Regular training and development programs could help employees stay updated with industry trends and improve their performance.
• Strengthen Client Feedback: Implementing a stronger client feedback mechanism could help the company better align its services with evolving client needs and expectations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of the organizational structure at Motilal Oswal Financial Services Ltd. reveals a well-defined and client-focused framework that supports the company's operations and strategic goals. The clear roles, effective communication, and flexible approach to market changes enable the organization to provide strong advisory services and adapt to evolving industry trends. However, there are opportunities for improvement, particularly in enhancing cross-departmental collaboration, streamlining decision-making processes, and leveraging digital tools for greater efficiency. By focusing on these areas, the company can further strengthen its competitive position and continue to deliver high-quality services to its clients.
This research has provided valuable insights into the functioning of a leading financial services firm and offered practical learning opportunities in analyzing and understanding organizational structures. The experience gained will be instrumental in contributing to future professional growth in the financial services industry.
References
Acharya, N., & Roy, M. S. (2020). A Study on Fundamental Analysis of Indian Telecom Companies. International Journal of Technology and Management, 5, 28-34.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Geels, F. W. (2012). A socio-technical analysis of low-carbon transitions: introducing the multi-level perspective into transport studies. Journal of transport geography, 24, 471-482.
Kumaraswamy, A., Mudambi, R., Saranga, H., & Tripathy, A. (2012). Catch-up strategies in the Indian auto components industry: Domestic firms’ responses to market liberalization. Journal of International Business Studies, 43(4), 368-395.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lall, S. (1980). Vertical inter‐firm linkages in LDCs: an empirical study. Oxford bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 42(3), 203-226.
Mytelka, L. K. (2000). Local systems of innovation in a globalized world economy. Industry and innovation, 7(1), 15-32.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Pandey, S., Bilaspur, C. G., Verma, I. V., & Jain, I. V. (2013). Measuring financial soundness of Indian telecom companies. A comparative analysis. Int J Manage, 2, 1-13.
Shah, S., & Ajmera, A. (2022). Fundamental & Technical Analysis On Selected Sectors. International Journal of Management, Public Policy and Research, 1(1), 62-67.
Shende, V. (2014). Analysis of research in consumer behavior of automobile passenger car customer. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 4(2), 1-8.
Swain, S. (2022). A Study on Technical Analysis of Selected Stocks of NSE Fifty with refers to FinSkool (Doctoral dissertation, BIITM, Bhubaneswar).
Vinutha, J., & Goud, G. V. (2018). A Study on Technical Analysis of Selected stocks of Nifty Fifty Bangalore.
Received: 27-Jun-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15996; Editor assigned: 28-Jun-2025, PreQC No. AMSJ-25-15996(PQ); Reviewed: 10-Jul-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-15996; Revised: 29-Jul-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15996(R); Published: 01-Aug-2025