Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 6
Navigating the Digital Currency Ecosystem: A Bibliometric Analysis
Srijan Anant*, University of Allahabad, Prayagraj, India
Neha Sangwan, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India
Sumit Kumar Singh, United University, Prayagraj, India
Jevesh Nandan, Bareilly College, Bareilly, India
Shweta Vats, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India
Citation Information: Anant, S., Sangwan, N., Singh, S. K., Nandan, J., & Vats, S. (2025). Navigating the digital currency ecosystem: A bibliometric analysis. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(6), 1-26.
Abstract
Digital currencies are the currencies which exist solely in electronic form and encompass a wide range of instruments such as CBDC, bit coins, crypto currencies, etc. Due to rapid rise in usage of digital currencies majority of countries are planning to issue digital fiat currencies regulated by central banks. The objective of this study is to comprehensively identify and analyze the digital currencies research, its discern trends, growth patterns and evolutionary shifts within the Scopus database through bibliometric analysis. We find motor, niche, basic and emerging themes through thematic map. The findings show that electronic money has been transformed into digital currencies over the years and revealed various future trends and topic by using techniques such as co-author, co-word, bibliographic coupling and citation analysis. Finally, the study identifies the future agenda which can serve as a valuable foundation for future investigation, catering the needs of both academicians and practitioners.
Keywords
Digital Currencies, Virtual Currencies, Electronic Money, Bibliometric Analysis, Digital Cash.
Introduction
In the midst of the swift advancement of technologies like big data, blockchain and smart contracts, the global economy has undergone a period of rapid expansion (Agur et al., 2023; Luu et al., 2023). Comprehending the factors influencing this diversity holds significance as digital currencies may potentially assume a significant role in shaping the payment systems of the future (Horváth, 2023; Moro & Nispi Landi, 2024).
Worldwide, around 90% of central banks are investigating Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), which have been instrumental in preserving economic stability and market liquidity throughout the COVID-19 pandemic (Zhang et al., 2023). In 2020, the Bahamas unveiled the “Sand Dollar,” followed by Nigeria's introduction of the "e-Naira" in 2021, alongside the launch of the “DCASH” in the East Caribbean and the “E-CNY” in China (An et al., 2024). CBDCs are designed to optimize cross-border transactions and bolster financial stability, tackling issues such as prolonged transaction times and restricted operating hours (Cheng, 2023; Dunbar, 2023). Currently, the European Central Bank (ECB) is exploring the possibility of introducing a digital euro and has initiated a survey targeting individuals, experts and organizations to gauge stakeholders' views on the potential implementation of such a digital currency (Tronnier et al., 2023).
However, it is conceivable to devise Central bank digital currencies in a manner that mitigates money laundering risks while simultaneously preventing a depletion of bank deposits. In particular, setting the interest rate on CBDC at an adequate level can incentivize sellers who refrain from engaging in money laundering to accept CBDC (Le et al., 2023; Wang, 2023; Wu et al., 2024). Also, hedging behavior in futures markets minimizes CBDC uncertainty by affecting risk aversion, thereby influencing macroeconomic outcomes (Azzone & Barucci, 2023; Dunbar, 2023).
Bibliometric analysis serves as a crucial statistical method for comprehensively mapping the current state of knowledge within a specific scientific domain (Chaudhry & Al-Ansari, 2016). Given the extensive scope of the review and the large dataset size, the study employs bibliometric analysis as a means to yield comprehensive scientific insights, utilizing various critical approaches such as counting, citation analysis, co-citation analysis, bibliographic coupling, keyword occurrence analysis and thematic analysis to identify pertinent research trends (Bhaskar et al., 2022; Parlina et al., 2020). Historically, recording, storing and manually analyzing all existing research data has posed significant challenges, making bibliometric statistical tools indispensable in addressing these limitations (Farooq, 2024). Recent literature has showcased the utility of bibliometric analysis in various fields, including finance (Ingale & Paluri, 2022; Shao et al., 2019), finance and management (Nobanee & Ellili, 2023; Trotta et al., 2024) and managerial finance (Pattnaik et al., 2023).
The research endeavor aims to gain insights into digital currencies, employing practical guidelines and adopting bibliometric analysis techniques throughout the study (Bhaskar et al., 2022). Consequently, our investigation is centered on the utilization of bibliographic analysis to ascertain prevailing research trends and evolutionary patterns within the refined academic literature on digital currencies, encompassing theoretical, logical and statistical approaches. This bibliometric inquiry scrutinizes the development, contemporary trends and patterns within digital currencies research. Despite the significance of digital currencies influence and its impacts, previous research has seen limited quantitative analysis in this regard. Notably, the research emphasizes how digital currencies are the future of financial sector and its scope in research field.
The primary objective of this article is to consolidate scholarly research and address four key research inquiries. The principal contributions of this study include:
(1) Identifying critical areas of topic strengths and weaknesses;
(2) Revealing knowledge gaps and advancements among top researchers in digital currencies;
(3) Highlighting historical, current and emerging trends in research topics;
(4) Investigating the impact of research areas and offering quantitative analyses of academic literature.
The research paper has following section ahead, Section 2, delineates the research methodology., while Section 3 outlines the results and key findings of bibliometric analysis, employing co-word analysis, cartographic and thematic mapping. Section 4 offers discussions and findings and Section 5 conclusion and limitation of research. Finally, Section 6 proposes avenues for future research exploration.
Materials and Methods
This study employs a bibliometric analysis to systematically examine the prevailing research within the realm of Central Bank Digital Currencies. Bibliometric technique utilizes quantitative methodologies to evaluate characteristics of literatures, such as authors, citations, publications, co-citations and keywords (Costa et al., 2019). Among the array of scientific statistics, bibliometric occupied a distinguished position (Romanelli et al., 2021).
Throughout scientific literature, bibliometric serves a dual purpose: to quantify the impact of research and to delineate the structure of research domains through two methodologies: (i) performance analysis, which evaluates the effectiveness of scientific contributors (e.g., rankings of influential authors and publishers) by assessing productivity metrics (e.g., publication frequencies over time); (ii) bibliometric networks (also termed as science mapping or bibliometric mapping), which elucidate the underlying structure of scientific literature by examining interconnections among authors, institutions and keywords (Nakagawa et al., 2019; Öztürk et al., 2024; Romanelli et al., 2021). Despite its advantages, bibliometric analysis is still relatively novel in business research and in numerous cases, its implementation fails to harness its complete potential (Donthu et al., 2021).
Sample Selection Process
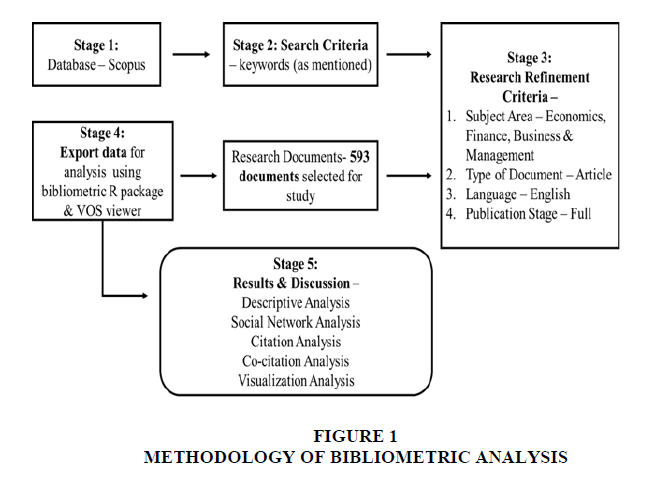
The sample has been selected by using a five step process (Figure 1). We select our sample of papers through searches conducted on the Elsevier Scopus database. A search query was performed in the "Scopus" database using a combination of keywords TITLE-ABS-KEY ("cbdc" OR "digital currency" OR "electronic money" OR "digital money" OR "electronic currency" OR "digital cash" OR "electronic cash" ) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, "BUSI") OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, "ECON")) AND (LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Digital Currency") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Central Bank Digital Currency") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "CBDC") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Digital Currencies") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Digital Money") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Central Bank Digital Currencies") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Electronic Cash") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "E-money") OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD , "Electronic Money")) AND ( LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE , "ar" )) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, "English")) AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBSTAGE, "final" )) to retrieve relevant results through 593 final documents. The Scopus database is particularly suitable for bibliometric research due to its comprehensive coverage across various publishers and fields of study (Ball & Tunger, 2007; Öztürk et al., 2024; Parlina et al., 2020).
Meta-analysis and bibliometric analysis, both quantitative in nature, may confuse scholars due to their similarities in handling extensive literature. Meta-analysis focuses on summarizing empirical evidence, analyzing effects and relationships among variables, beneficial for addressing research questions with substantial data. In contrast, bibliometric analysis examines the social and structural relationships within a field, summarizing its intellectual structure by analyzing various research constituents (Combs et al., 2011; Romanelli et al., 2021). To study the literature of Central Bank Digital Currencies, the best suited review method is bibliometric analysis as it analyzes overall social, intellectual and structural relationships of the topic.
Manuscripts meeting inclusion criteria were extracted to csv format and for precise outcomes, leverage the open-source R Package BIBLIOSHINNY to work with data frames in conjunction with VOSviewer software. Irrelevant data in the dataset were excluded using dimensionality-reduction techniques. VOSviewer and Biblioshiny software facilitated comprehensive network mapping of filtered data, aiding in visualizing data and constructing social structures through parameter filtering for a close fit (Costa et al., 2019; Donthu et al., 2021; Romanelli et al., 2021).
Meta-Literature Review
The study conducts the meta literature review by emphasizing on the quantitative dimension of the bibliometric analysis. Our analysis centers on the descriptive analysis, social network analysis, citation analysis, co-citation analysis and visualization analysis as presented in section 3.
Results and Discussion
Descriptive Analysis
The paper presents descriptive analyses concerning publication patterns, source dynamics, prominent authors and institutions, as well as future trends in topics. The descriptive examination illustrates the yearly progression of research, influential papers and authors, top journals, contributions from various countries and significant keywords. Part A outlines the analyzed findings, including document counts by year, author contributions, sources, countries and subject areas. And part B provides insights into research trends and academic collaboration networks through bibliometric analysis results, presented graphically to illustrate the annual growth of topic and overview using co-occurrence networks, thematic maps and social structures.
Furthermore, the research unveils the findings regarding authors’ with high productivity, authors' keywords and countries, which encompass the most commonly utilized words by authors, word dynamics, globally cited manuscripts, tree-map diagrams showing frequency, three-field plot diagrams and co-word analysis.
Main Information about Data
Table 1 presents the primary information of research papers published in the Scopus database within the selected dataset.
| TABLE 1 MAIN INFORMATION ABOUT DATA |
|
|---|---|
| DESCRIPTION | RESULTS |
| Main information about data | |
| Timespan | 1996:2024 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc) | 230 |
| Documents | 593 |
| Annual growth rate % | 13.54 |
| Document average age | 4 |
| Average citations per doc | 29.65 |
| References | 28375 |
| Document contents | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 1820 |
| Author's Keywords (DE) | 1641 |
| Authors | |
| Authors | 1400 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 131 |
| Authors collaboration | |
| Single-authored docs | 144 |
| Co-Authors per Doc | 2.66 |
| International co-authorships % | 31.53 |
| Document types | |
| article | 593 |
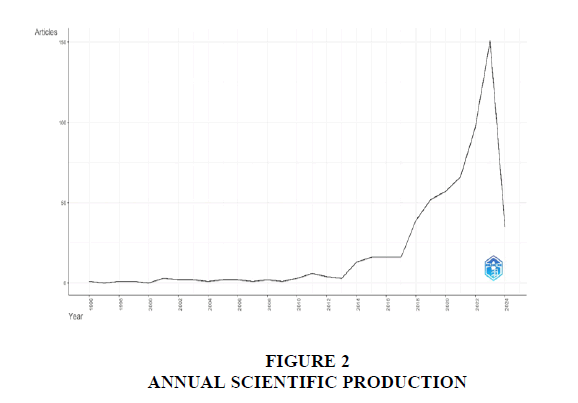
Table 1 briefly elaborate that the annual growth rate percentage of publication was 13.54% with the timespan presence from 1996-2024, sources 230, 593 documents, average citations per doc 29.65, single-authored docs 131 and international co-authorship 31.53%. The research analysis presented in this article comprises 593 documents spanning from 1996 to 2024. Figure 2 illustrates a data diagram depicting the search results for publication documents by year, showcasing trends in Central Bank Digital Currencies.
Over the 28-year period, there is a noticeable upward trend in article production on Central Bank Digital Currencies, particularly evident from 2013, but it slowdown between 2015 to 2017, followed by steady rise from 2017 to 2023. The highest number of articles, 151 documentations, is observed in 2023. Notably, the first research publication on CBDCs dates back to 1996, with the number of documents reaching 593 by 2024.
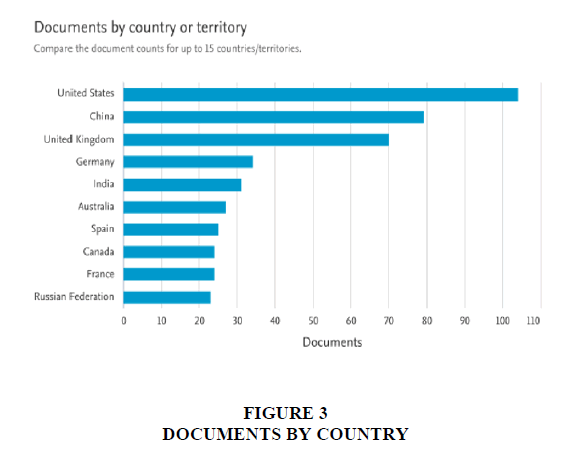
Figure 3 illustrates the annual publication of papers from various countries. In 2022, over 97 research papers were published, while in 2023, the number increased to over 151 articles. This suggests a growing interest among researchers in the subject area, with annual manuscript outputs showing worldwide encouragement. Figure 3 unveils top 10 countries out of 84 nations highly engaged in publishing the most articles. The highest number of articles are published by United states with 104 documents followed by China (79), United Kingdom (70), Germany (34) and India (31).
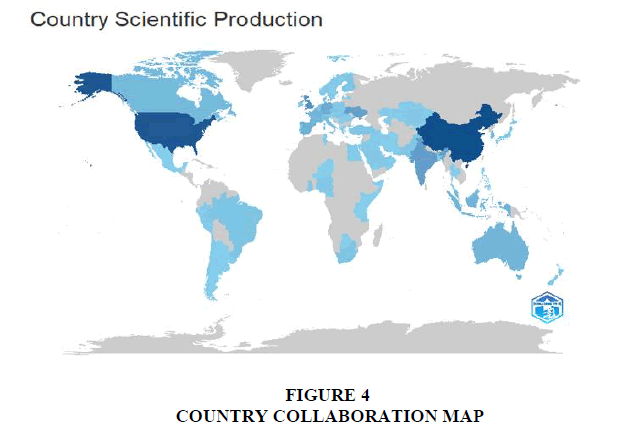
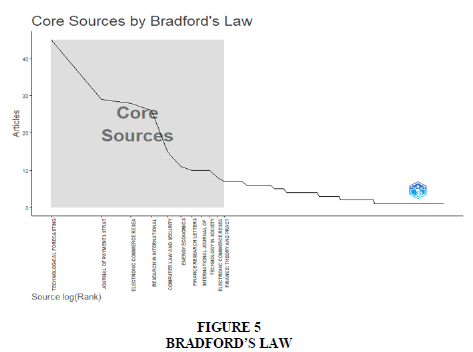
Figure 4 depicts a collaboration map showcasing countries involved in publishing articles, where darker shading indicates a higher frequency of article publications. Bradford’s law of scattering which is used to recognize the core journals related to Digital Currencies, by delineating in three hierarchical zones using a geometric series represented as 1: n: n2. The breakdown of these nucleus divisions is provided in Figure 5.
Table 2 below represents three zones (core, allied and alien journals), core journals consist of 11 journals that published 199 articles while zone 2 represents 50 journals with 199 published articles. A table 3 represent list the top 11 journals rank wise which is categorized within zone 1 category.
| TABLE 2 NUCLEUS OF BRADFORD’S LAW |
||
|---|---|---|
| Zones | Journals | Articles |
| Zone 1 (core) | 11 | 199 |
| Zone 2 (allied) | 50 | 199 |
| Zone 3 (alien) | 169 | 195 |
| Total | 230 | 593 |
| TABLE 3 ZONE 1 JOURNALS USING BRADFORD’S LAW |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Rank | Freq | cumFreq | Zone |
| Technological forecasting and social change | 1 | 45 | 45 | Zone 1 |
| Journal of payments strategy and systems | 2 | 29 | 74 | Zone 1 |
| Electronic commerce research and applications | 3 | 28 | 102 | Zone 1 |
| Research in international business and finance | 4 | 26 | 128 | Zone 1 |
| Computer law and security review | 5 | 15 | 143 | Zone 1 |
| Energy economics | 6 | 11 | 154 | Zone 1 |
| Finance research letters | 7 | 10 | 164 | Zone 1 |
| International journal of information management | 8 | 10 | 174 | Zone 1 |
| Technology in society | 9 | 9 | 183 | Zone 1 |
| Electronic commerce research | 10 | 9 | 192 | Zone 1 |
| Finance: theory and practice | 11 | 7 | 199 | Zone 1 |
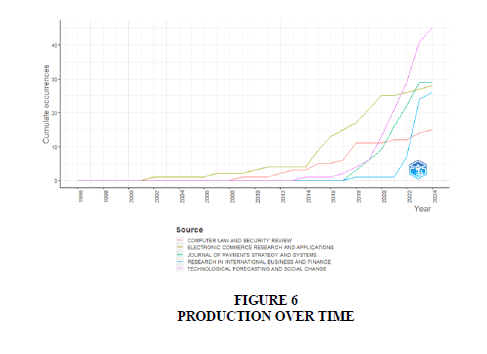
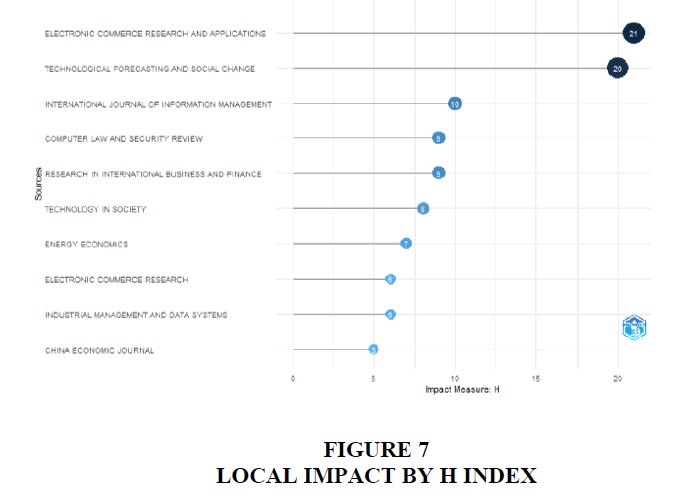
Figure 6 displays the analysis of documents published annually by source type. It indicates that the Computer Law and Security Review, Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, Journal of Payment Strategy and Systems, Research in International Business and Finance and Technological Forecasting and Social Change stand out as prominent journals in the field of Central Bank Digital Currencies. The h-index is a metric that indicates the productivity and impact of an author's publications (Figure 7). It quantifies both the number of publications and the citations received by those publications, means it measures the influence of the particular author rather than that of a journal.
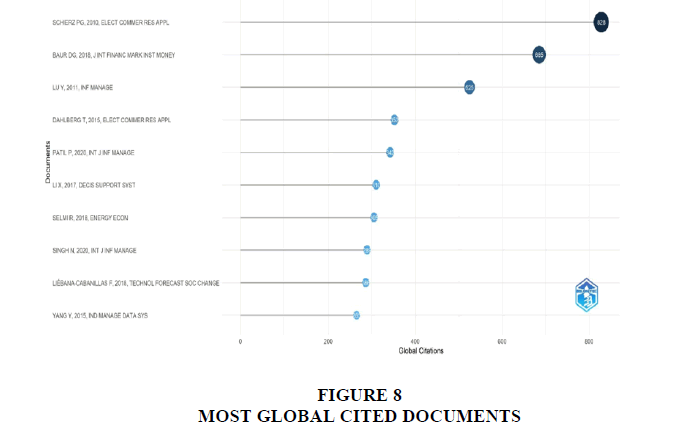
Schierz et al., 2010 is the most globally cited author followed by Baur et al., 2018, (Lu et al., 2011) and (Dahlberg et al., 2015). Figure 8 portrays the authors with the highest global citations. Table 4 indicates the authors' contributions in terms of both the quantity of papers and their fractionalized values while table 5 shows the top twenty-five authors, along with the titles of articles published in various journals and the total citations per year. (Li & Wang, 2017; Liébana-Cabanillas et al., 2018; Shao et al., 2019) emerge as the top three authors based on highest total citations of their publications.
| TABLE 4 AUTHORS' CONTRIBUTIONS |
||
|---|---|---|
| Authors | Articles | Articles Fractionalized |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 7 | 2.11666667 |
| LI X | 5 | 1.48333333 |
| ASONGU SA | 4 | 1.5 |
| GONG X | 4 | 0.93333333 |
| HAUSKEN K | 4 | 1.83333333 |
| OZILI PK | 4 | 3.5 |
| WANG Y | 4 | 1.16666667 |
| WANG Z | 4 | 2.08333333 |
| ALONSO SLN | 3 | 1.08333333 |
| BALASUBRAMANIAN K | 3 | 0.83333333 |
Cartographic Analysis or Social-Network Analysis
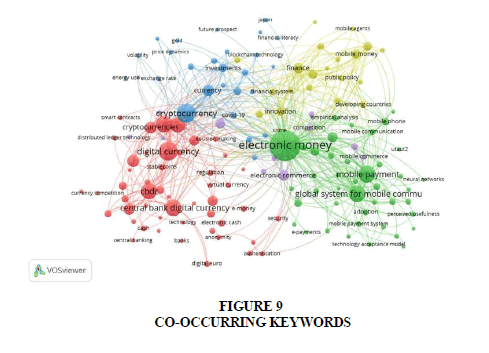
The cartographic analysis illustrates a map of keywords, reflecting their occurrence and relevance to central bank digital currencies. Articles sharing identical keywords are grouped together as these keywords signify content areas in cartographic report as in Figure 8. We used VOSviewer software to examine the co-occurrence of keywords. Figure 9 derived from a minimum of 5 co-occurring keywords out of 150 in total, the results depict the outcomes of cartographic analysis. Analysis comprises of five clusters, densest emphasizing ‘electronic money’ (red cluster), who’s connection intertwine with digital currencies, central bank digital currencies, cryptocurrency and mobile payments. In contrast, the cluster with less density (red) on topic ‘central bank digital currencies’ and other peripheral cluster (blue cluster) which target ‘cryptocurrency’.
Through cartographic keyword analysis, it becomes evident that there is limited work related to central bank digital currencies, with a predominant emphasis on cryptocurrencies or electronic money, particularly focusing on digital payment. Authors have ample opportunity to explore the efficiency, adoption and functionality of digital currencies.
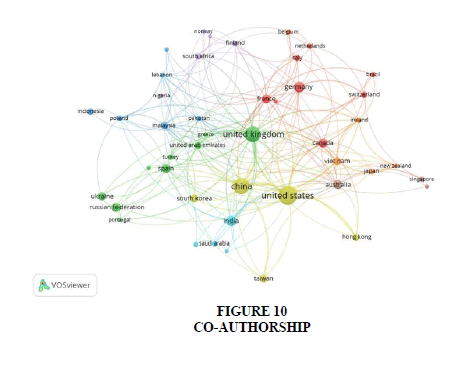
In terms of co-authorship occurrences over time, Figure 10 illustrates the progression of countries added to the pioneer US. The study employs “full-counting method”. Notably, countries such as US, UK, China, Germany and India have shown recent interest and investment in the topic.
From the dataset, out of 87 countries collaborating on research related to CBDC through co-authorship, the minimum number of articles from a single country considered was 5. Therefore, the threshold limit will be 45. The total link strength counts to be 349 as depicted by the figure.
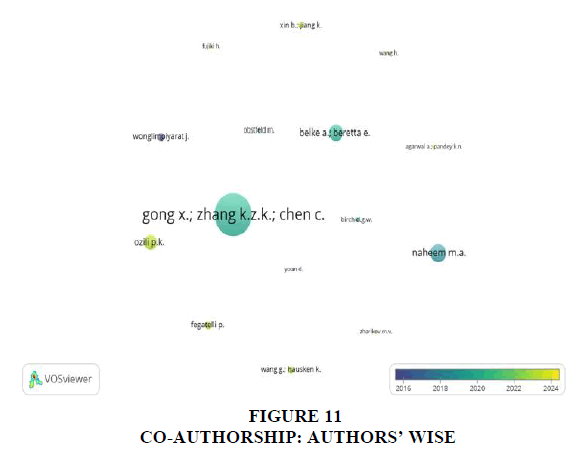
Figures 10 & 11 shows the co-author networks representing co-authorship analysis authors’ wise and citation network between authors respectively. Citation analysis aims to assess the impact of a specific article or author by identifying instances where other authors reference their work in their own papers. The impact or "quality" of an article is gauged by the frequency with which it is cited by other researchers in their research.
| TABLE 5 TOP TWENTY-FIVE AUTHOR’S NAMES, ARTICLE OF DIFFERENT JOURNAL AND RESPECTIVE CITATION |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Year | Title | Source | TC | TCPY |
| LIX | 2017 | The technology and economic determinants of cryptocurrency exchange rates: the case of bitcoin | Decision support systems | 310 | 38.75 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2018 | Predicting the determinants of mobile payment acceptance: a hybrid semi-neural network approach | Technological forecasting and social change | 286 | 40.85714 |
| LIX | 2019 | Antecedents of trust and continuance intention in mobile payment platforms: the moderating effect of gender | Electronic commerce research and applications | 245 | 40.83333 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2019 | Mobile payment is not all the same: the adoption of mobile payment systems depending on the technology applied | Technological forecasting and social change | 242 | 40.33333 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2014 | The moderating effect of experience in the adoption of mobile payment tools in virtual social networks: the m-payment acceptance model in virtual networks | International journal of information management | 200 | 18.18182 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2019 | To use or not to use, that is the question: analysis of the determining factors for using nfc mobile payment systems in public transportation | Technological forecasting and social change | 112 | 18.66667 |
| LIX | 2020 | What have we learnt from 10 years of fintech research? A scientometric analysis | Technological forecasting and social change | 81 | 19.2 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2017 | Extended and explanatory model of mobile payment adoption of mobile services | Technological forecasting and social change | 81 | 10.125 |
| LIÉBANA-CABANILLAS F | 2020 | Determinants of the intention to use mobile m-payment services | Telecommunications policy | 74 | 14.8 |
| WANG Y | 2020 | Transition from web to mobile e-government: The triple effects of information status quo inertia | International journal of information management | 60 | 12 |
| GONG X | 2020 | The effects of central bank digital currency news on financial markets | Technological forecasting and social change | 55 | 18.33333 |
| GONG X | 2020 | What drives trust transfer with web vendors? The dual model of perceived entitativity | Information and management | 51 | 12.75 |
| WANG Y | 2021 | A global perspective on central bank digital currency | China economic journal | 50 | 12.5 |
| LIX | 2021 | Blockchain technology for coordination of stakeholders in construction supply chain: A review | Journal of construction engineering and management | 49 | 12.25 |
| ALONSO SLN | 2021 | Central banks digital currency: detection of optimal countries for the implementation of a cbdc and the implication for payment industry innovation | Journal of open innovation: technology, market and complexity | 44 | 11 |
| ALONSO SLN | 2020 | Reasons fostering or discouraging the implementation of central bank-backed digital currency: a review | Economies | 39 | 7.8 |
| ASONGU SA | 2021 | On the diffusion of mobile phone innovations for financial inclusion | Technology in society | 35 | 8.75 |
| GONG X | 2020 | Self-disclosure in mobile payment applications: common and differential effects of personal and proxy control enhancing mechanisms | International journal of information management | 33 | 6.6 |
| HAUSKEN K | 2022 | Do national development factors affect cryptocurrency adoption? | Technological forecasting and social change | 28 | 9.333333 |
| WANG Z | 2022 | Green stocks, crypto asset, crude oil and covid19 pandemic: application of rolling window multiple correlation | Resources policy | 26 | 8.666667 |
| OZILI PK | 2023 | Cbdc, fintech and cryptocurrency for financial inclusion and financial stability | Digital policy, regulation and governance | 21 | 10.5 |
| ASONGU SA | 2021 | Law, mobile money drivers and mobile money innovations in developing countries | Technological forecasting and social change | 14 | 3.5 |
| GONG X | 2022 | A dedication-constraint model of consumer switching behavior in mobile payment applications | Information and management | 13 | 4.333333 |
| WANG Z | 2022 | Money laundering in a cbdc world: a game of cats and mice | Journal of financial crime | 8 | 2.666667 |
| HAUSKEN K | 2022 | A game between central banks and households involving central bank digital currencies, other digital currencies and negative interest rates | Cogent economics and finance | 7 | 2.333333 |
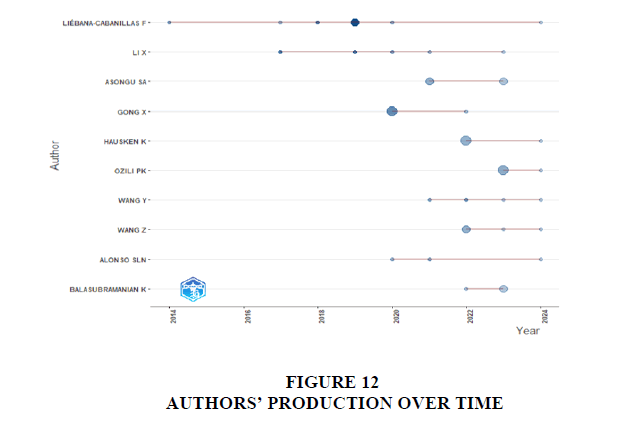
The Figure 12 below illustrates the output of distinguished authors over time. The size of each bubble corresponds to the number of papers authored, while displaying the combined sum of citations and published publications for each year. Additionally, the timeline taken by each author is depicted in the line chart.
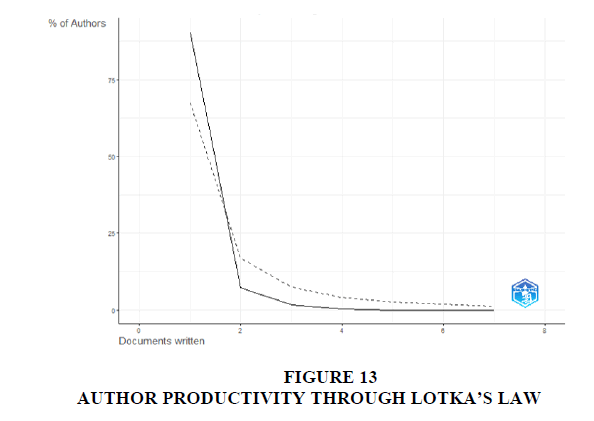
Lotka's Law, formulated by Alfred J. Lotka in the 1920s, is a principle in bibliometrics that describes the distribution of productivity among authors in scientific fields. According to Lotka's Law, the number of authors who have published a certain number of papers decreases exponentially as the number of papers increases. In other words, a few authors produce a large number of papers, while the majority of authors produce only a few papers. Figure 12 shows how papers related to topic also follow Lotka’s law related to authors’ productivity.
Bibliographic Coupling
Bibliographic coupling occurs when two articles reference the same sources. This approach enables researchers to recognize related or comparable works by analyzing their shared citations, offering insights into the intellectual associations and thematic parallels across various research pieces.
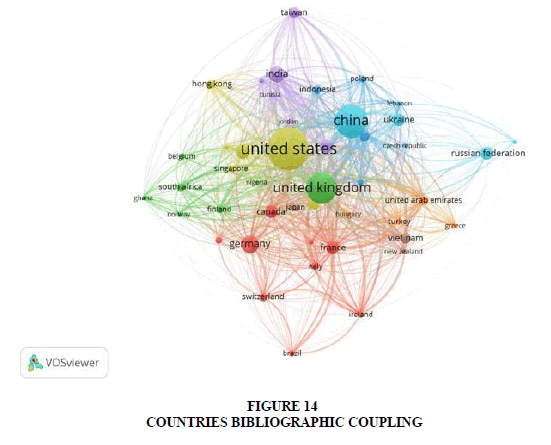
Figure 14 depicts the countries bibliographic coupling with minimum number of 5 documents from a country, 45 countries meet the threshold limit out of a total of 87 countries. United States, United Kingdom and China being the top most countries with maximum link strength.
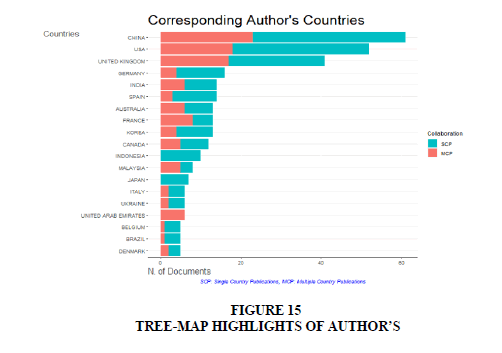
The list of most significant authors contributed by the countries of origin (Figure 15). This indicates publications categorized as Single Country Publications (SCP) and Multiple Country Publications (MCP). The China, USA and UK emerge as the top three nations with the highest number of articles written on the subject domain. From the graphical representation (Table 6), it is evident that the overall trend productivity growth rate for publications by Single Country Publications is higher.
Figure 15 showcases the Tree-Map representing the word dynamics of the most influential authors related to this research. The Word dynamics Tree-Map highlights the significant aspects or dynamic trends observed among authors. It is a valuable tool for investigating popular topics within the field of study. The Tree-Map comprises dimensions and measures, with the values in the dimensions defining the structure. The diagram below represents that keyword “electronic money” is 21% used highest among the data, while authentication is the least used keyword.
| TABLE 6 OVERALL TREND PRODUCTIVITY GROWTH RATE FOR PUBLICATIONS |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Articles | SCP | MCP | Freq | MCP_ratio |
| CHINA | 61 | 38 | 23 | 0.102 | 0.377 |
| USA | 52 | 34 | 18 | 0.0876 | 0.346 |
| UNITED KINGDOM | 41 | 24 | 17 | 0.069 | 0.414 |
| GERMANY | 16 | 12 | 4 | 0.0269 | 0.25 |
| INDIA | 14 | 8 | 6 | 0.0236 | 0.428 |
Trend Topics
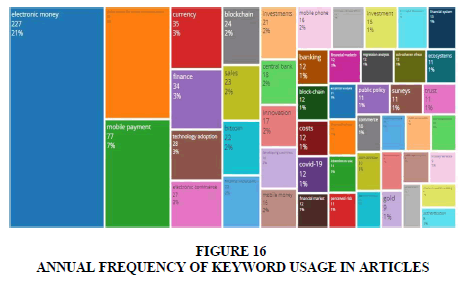
Table 7 displays the frequency of keyword usage by authors, indicating a temporary surge in popularity compared to previous studies. This table represents the most commonly used keywords on the social network during the specified period, reflecting the topics discussed by authors within the year. In 2023, the predominant keywords among authors included financial inclusion, central bank and mobile money, while in 2022 were currency, finance and investment. In Figure 16, the bubbles below signify the annual frequency of keyword usage in articles within the specified timeframe.
| TABLE 7 MOST FREQUENT AUTHORS KEYWORDS |
|
|---|---|
| Items | Frequency |
| Electronic money | 227 |
| Global system for mobile communications | 80 |
| Mobile payment | 77 |
| Currency | 35 |
| Finance | 34 |
| Electronic commerce | 27 |
| Sales | 23 |
| Bitcoin | 22 |
| Financial inclusions | 22 |
| Investments | 21 |
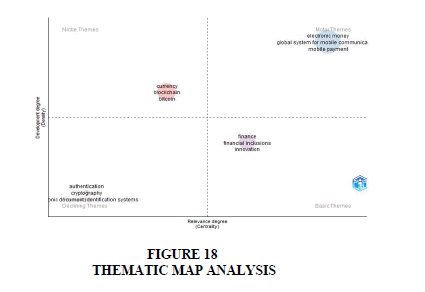
Thematic Map Analysis
The Thematic Map is generated from a co-occurrence keyword network to create a two-dimensional representation of typological themes within a domain. The clusters identified through the preceding co-word analysis represent the current hot themes or topics, categorized based on their density and centrality in a two-dimensional analysis diagram using Biblioshiny R language software. The arrangement of "themes" within each quadrant facilitates analysis. Initially, significant data segments are identified and summarized into keywords or key phrases. Subsequently, through an iterative process, these keywords or key phrases are utilized to derive underlying "themes," which represent recurring thought patterns or concepts in the data. These derived "themes" can be visualized in a mind map. The Thematic Map provides an intuitive plot for analyzing themes based on their quadrant placement: upper-right quadrant (Q1) represents motor-themes, lower-right quadrant (Q2) represents basic themes, lower-left quadrant (Q3) represents emerging or disappearing themes and upper-left quadrant (Q4) represents very.
The thematic map with four clusters is shown in Figure 18. The map was created by assessing the density and centrality rankings of keywords. Quadrant one themes or motor themes represents highly developed themes, which includes the role of electronic money in financial systems, global system for mobile communication developed all over the world, technological development, electronic commerce and usage of mobile payments and its adoption. Fourth quadrant or transverse themes are central to research but not developed include financial inclusion, innovation in finance, technology development in finance and mobile money. Second quadrants or niche themes are not central but highly developed to topic as central bank currency, bitcoins, investments, block chain and crypto-currencies. Third or declining/ emerging themes indicating low density and low centrality includes topic such as cryptography, electronic document identification systems, network security, electronic cash, electronic payment systems and payment protocol. The researchers should focus on these areas as there are emerging topics. The topics included in motor themes are highly isolated and a lot of work is already being done on these topics.
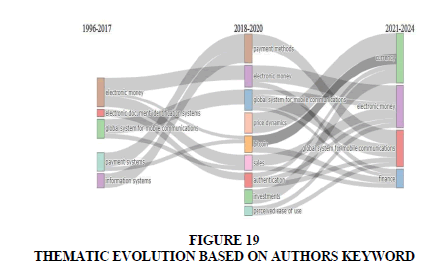
Thematic Evolution
Thematic Evolution" refers to the study of how research themes or topics change over time within a particular field or discipline. This analysis examines the emergence, evolution and disappearance of themes or topics in scholarly literature, tracking their development and prominence over different periods. Figure 19 highlights the papers contribution from 1996 to 2024 related to central currencies. As evident, electronic money has been a subject of research since 1996, with new areas emerging, such as currency and global system communication, since the 1990s. Authors can contribute to these emerging areas by concentrating on digital currency topics. Various topics, including bit coin, investments and price dynamics, have amalgamated into a single area known as currency. The data has been extracted by cutting the time into two slices to get better results, first time slice from 1996 to 2017 and another from 2018-2024.
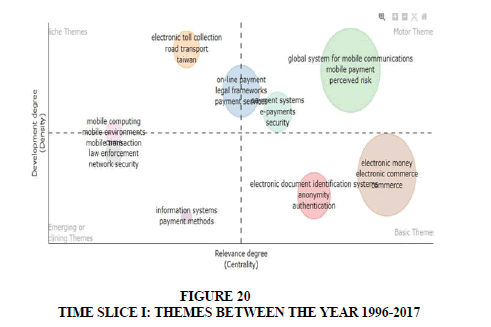
Time Slice I (1996-2017): In timelines between 1996 to 2017, authors have focused on mobile payments, mobile computing, online payments and electronic money. Majority of authors have contributed in basic themes such as electronic money and electronic commerce (Figure 20).
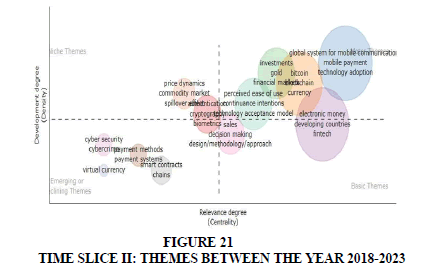
Time Slice II (2018-2023): Authors in second time-slice between 2018 & 2023 have contributed and focused on cyber security, cybercrime, payment methods, virtual currency; the following topics are the key essential emerging themes. Motor themes during these years are focusing on technology adoption, continuance intentions, mobile payments, block-chain and bit coins (Figure 21).
A comprehensive bibliometric literature review was conducted to gain insights into Central Bank Digital Currencies. The study commenced by extracting data using reverse keywords ("cbdc" OR "digital currency" OR "electronic money" OR "digital money" OR "electronic currency" OR "digital cash" OR "electronic cash" resulting in over 1829 articles from the Scopus database. A refined and focused approach reduced the corpus to 593 articles by systematically excluding irrelevant sources, taking into account subject areas. These articles were then imported into CSV format. The study period spanned from 1996 to 2024. Each article underwent review based on its abstract, research design and methodology employed. Utilizing Biblioshinny, bibliometric R-programming language and VOS-viewer software, the data from the articles were extracted and analyzed for visualization.
Table 1 summarizes the research, revealing a 13.54% annual publication growth rate spanning 1996 to 2024, with 593 documents analyzed. Notably, the average citation per document stands at 29.65, with 131 single-authored documents and 31.53% international co-authorship. The analysis focuses on Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) trends. Figure 2 tracks the evolution of CBDC publications over 28 years, witnessing a surge since 2013, peaking at 151 articles in 2023. Despite minor slowdowns between 2015 and 2017, the trajectory remains upward, reflecting the growing interest in CBDCs. The study underscores the continuous rise in CBDC research output.
Additionally, Figure 3 showcases the global interest in CBDC research, with over 97 papers published in 2022 and surpassing 151 in 2023. Among 84 nations, the United States leads with 104 documents, followed by China (79), the United Kingdom (70), Germany (34) and India (31), highlighting the widespread engagement in CBDC-related studies. Figure 4 displays a collaboration map of countries involved in Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) research, highlighting publication frequency. Bradford’s law categorizes core journals into three zones, with Table 2 detailing their distribution.
Notably, Table 3 lists top-ranked journals within zone 1. Additionally, Figure 5 illustrates annual document publication trends, emphasizing key journals like Computer Law and Security Review and Journal of Payment Strategy and Systems. Figure 6 introduces the h-index to measure authors' impact, with Schierz et al. (2010) leading in global citations, followed by Baur et al. (2018) and others, as depicted in Figure 7. Table 4 outlines authors' contributions, while Table 5 lists top authors and their publications' total citations per year, with Li & Wang (2017) and others emerging as top contributors.
The cartographic analysis conducted unveils distinct clusters of keywords related to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), indicating prevalent themes and areas of focus within the research domain. Notably, the analysis reveals a predominant emphasis on topics such as cryptocurrencies and electronic money, with limited attention directed towards CBDCs specifically. This highlights an opportunity for researchers to delve deeper into the efficiency, adoption and functionality of CBDCs, exploring uncharted territories within the field.
Furthermore, the co-authorship occurrences over time, as illustrated in Figure 10, elucidate the evolving landscape of collaborative research efforts, with countries like the US, UK, China, Germany and India demonstrating a recent surge in interest and investment in CBDC-related research. The utilization of the "full-counting method" facilitates a comprehensive evaluation of co-authorship dynamics, with the dataset revealing collaborations among 87 countries, each contributing a minimum of 5 articles and generating total link strength of 349, as depicted in the figure.
Additionally, Figures 10 and 11 present co-author networks and citation networks, respectively, offering insights into the impact and quality of articles within the CBDC research domain. Citation analysis serves to gauge the influence of specific articles or authors by identifying instances of their work being referenced by other researchers, providing valuable metrics for assessing scholarly impact and contribution. These findings collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the collaborative and citation dynamics shaping the landscape of CBDC research, while also underscoring potential areas for further exploration and investigation.
The graphical representations, such as Figure 12, effectively depict the output of distinguished authors over time, shedding light on their productivity and impact within the field. Furthermore, the application of Lotka's Law and bibliographic coupling principles, as illustrated in Figures 12 and 13, respectively, offers valuable perspectives on the distribution of author productivity and intellectual associations across research articles.
Moreover, the analysis delves into thematic trends and keyword dynamics, as demonstrated in Figures 14, 15, 16 and 17, uncovering significant themes and emerging topics within the CBDC research domain. Additionally, the thematic evolution analysis depicted in Figure 18 provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of research themes over time, highlighting the emergence of key areas such as electronic money and global system communication.
Overall, these findings not only provide a nuanced understanding of the current state of CBDC research but also offer valuable directions for future exploration, including potential areas of focus and emerging research trends. Through a multifaceted analysis encompassing author productivity, thematic trends and keyword dynamics, this research contributes to the ongoing discourse on CBDCs and lays the groundwork for further scholarly inquiry in this dynamic and evolving field.
Practical Implication
The practical implication of this review is that CBDC represents a key innovative non-regulatory monetary measure available to central banks over countries which seeks to offer an alternative virtual currency to private crypto-currencies and helps in leveraging its inherent price stability. Central banks can effectively use digital currency to improve the efficiency of domestic payments and financial stability. Regulatory agencies must ensure that issuance of CDBC do not cause shocks or sudden disruptions to the money market; thus to avoid such shocks they should carefully design the currency. Further, the policymakers should also evaluate the adoption of electronic money and cryptocurrencies as it would indirectly encourage the use of digital currency by the users. The use of central bank digital currency as a monetary policy would help to combat the financial crimes in the economy. In order to encourage the use of digital currency by users, it is important to allocate resources for programs focusing on financial literacy by government. These initiatives would educate users on the benefits, cost and consequences of central bank digital currency. Through clear communication about digital currency and their intended purposes, we can empower individuals to make well-informed decisions. Government should assess how digital currency adoption would enhance financial inclusion in the economy.
Conclusion
This study has meticulously examined and depicted global scientific endeavors in the realms of Digital Currencies, aiming to offer an exhaustive overview of the research disseminated in scholarly literature. The primary limitation of the study lies in the fact that all the articles included are predominantly in English and stem from industrialized nations. Thematic analysis reveals that the research topic has a substantial yet relatively undeveloped field of study, characterized by a mixture of cross-cutting and overarching fundamental themes. It's noteworthy that the database solely relied on "SCOPUS" without considering other prominent journal data sources such as WOS, Google Scholar, Elsevier, among others. A combined analysis of data from diverse sources could potentially yield even more robust results.
Findings
The findings of this study offer valuable guidance to both emerging and seasoned researchers, aiding them in identifying new research focal points, pertinent sources and collaborative opportunities to make well-informed decisions. Through an exploratory bibliometric analysis of publications on digital currencies, topics such as "Mobile Banking" and "Electronic money" were discussed in 2019 and 2022. However, due to space constraints, many published articles were not comprehensively examined in this review, which may be considered a limitation of the study. Nevertheless, the study unveiled a significant relationship between international scientific collaborations and the efficacy of digital currencies research, indicating that research conducted through international partnerships tends to garner greater citation impact. This insight informs future researchers about emerging themes, contexts and collaboration prospects in these domains, shedding light on the most prevalent issues and paving the way for prospective research sites. Ultimately, this research paper serves as a valuable resource for policymakers in the formulation of digital currencies and digital finance policies.
Scope for Future Research
The authors propose recommendations for potential avenues of future research and delineate the crucial conceptual framework upon which such research endeavors could be built. Subsequent research endeavors are anticipated to address various epistemological issues surrounding financial competency as a primary focus. The authors are encouraged to delve deeper into the exploration of virtual currencies and their ramifications on various facets such as the economy, banking sector, financial stability and governmental policies, representing one aspect of future research endeavors. Conversely, another avenue for future investigation lies in understanding the adoption of virtual currencies by individuals, nations and global economies, aiming to dissect the underlying reasons or determinants influencing societal adoption intentions. Additionally, an area warranting attention for future studies pertains to the potential impact of virtual currency usage on reducing financial service or transaction costs for individuals, while simultaneously mitigating printing expenses and enhancing governmental savings.
References
References
- Agur, I., Lavayssière, X., Villegas Bauer, G., Deodoro, J., Martinez Peria, S., Sandri, D., & Tourpe, H. (2023). Lessons from crypto assets for the design of energy efficient digital currencies. Ecological Economics, 212, 107888.
- An, L., Wang, Y., Yan, Y., & Ma, C. (2024). The role of emotional factors in the acceptance of digital currency: An extended study of a technology acceptance model. Finance Research Letters, 62, 105090.
- Azzone, M., & Barucci, E. (2023). Evaluation of sight deposits and central bank digital currency. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 88, 101841.
- Ball, R., & Tunger, D. (2007). Science indicators revisited Science Citation Index versus SCOPUS: A bibliometric comparison of both citation databases. Information Services and Use, 26(4), 293-301.
- Baur, D. G., Hong, K., & Lee, A. D. (2018). Bitcoin: Medium of exchange or speculative assets? Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 54, 177-189.
- Bhaskar, R., Hunjra, A. I., Bansal, S., & Pandey, D. K. (2022). Central Bank Digital Currencies: Agendas for future research. Research in International Business and Finance, 62, 101737.
- Chaudhry, A. S., & Al-Ansari, H. (2016). Information behavior of financial professionals in the Arabian Gulf Region. International Information and Library Review, 48(4), 235-248.
- Cheng, P. (2023). Decoding the rise of Central Bank Digital Currency in China: Designs, problems and prospects. Journal of Banking Regulation, 24(2), 156-170.
- Combs, J. G., Ketchen Jr, D. J., Crook, T. R., & Roth, P. L. (2011). Assessing cumulative evidence within ‘macro’ research: why meta-analysis should be preferred over vote counting. Journal of Management Studies, 48(1), 178-197.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, D. F., Carvalho, F. D. M., & Moreira, B. C. D. M. (2019). Behavioral economics and behavioral finance: A bibliometric analysis of the scientific fields. Journal of Economic Surveys, 33(1), 3-24.
- Dahlberg, T., Guo, J., & Ondrus, J. (2015). A critical review of mobile payment research. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 14(5), 265-284.
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296.
- Dunbar, K. (2023). CBDC uncertainty: Financial market implications. International Review of Financial Analysis, 87, 102607.
- Farooq, R. (2024). A review of knowledge management research in the past three decades: A bibliometric analysis. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, 54(2), 339-378.
- Horváth, D. (2023). Money in the digital age: Exploring the potential of central bank digital currency with a focus on social adaptation and education. Sustainable Futures, 6, 100136.
- Ingale, K. K., & Paluri, R. A. (2022). Financial literacy and financial behaviour: A bibliometric analysis. Review of Behavioral Finance, 14(1), 130-154.
- Le, T. D., Tran, S. H., Nguyen, D. T., & Ngo, T. (2023). The degrees of central bank digital currency adoption across countries: A preliminary analysis. Economics and Business Letters, 12(2), 97-104.
- Li, X., & Wang, C. A. (2017). The technology and economic determinants of cryptocurrency exchange rates: The case of Bitcoin. Decision Support Systems, 95, 49-60.
- Liébana-Cabanillas, F., Marinkovic, V., Ramos De Luna, I., & Kalinic, Z. (2018). Predicting the determinants of mobile payment acceptance: A hybrid SEM-neural network approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 129, 117-130.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y., Yang, S., Chau, P. Y. K., & Cao, Y. (2011). Dynamics between the trust transfer process and intention to use mobile payment services: A cross-environment perspective. Information & Management, 48(8), 393-403.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luu, H. N., Nguyen, C. P., & Nasir, M. A. (2023). Implications of central bank digital currency for financial stability: Evidence from the global banking sector. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 89, 101864.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moro, A., & Nispi Landi, V. (2024). The external financial spillovers of CBDCs. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 159, 104801.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S., Samarasinghe, G., Haddaway, N. R., Westgate, M. J., O’Dea, R. E., Noble, D. W. A., & Lagisz, M. (2019). Research weaving: Visualizing the future of research synthesis. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34(3), 224-238.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nobanee, H., & Ellili, N. O. D. (2023). Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): A bibliometric and systematic review, current streams, developments, and directions for future research. International Review of Economics & Finance, 84, 460-473.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, O., Kocaman, R., & Kanbach, D. K. (2024). How to design bibliometric research: An overview and a framework proposal. Review of Managerial Science.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parlina, A., Ramli, K., & Murfi, H. (2020). Theme mapping and bibliometrics analysis of one decade of big data research in the scopus database. Information, 11(2), 69.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, D., Hassan, M. K., Dsouza, A., Tiwari, A., & Devji, S. (2023). Ex-post facto analysis of cryptocurrency literature over a decade using bibliometric technique. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 189, 122339.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romanelli, J. P., Gonçalves, M. C. P., de Abreu Pestana, L. F., Soares, J. A. H., Boschi, R. S., & Andrade, D. F. (2021). Four challenges when conducting bibliometric reviews and how to deal with them. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(43), 60448-60458.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schierz, P. G., Schilke, O., & Wirtz, B. W. (2010). Understanding consumer acceptance of mobile payment services: An empirical analysis. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 9(3), 209-216.
Received: 20-Jan-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-14916; Editor assigned: 23-Jan-2025, Pre QC No. AMSJ-25-14916 (PQ); Reviewed: 06-Feb-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-14916; Revised: 14-June-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-14916 (R); Published: 15-July-2025