Research Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 5
Role of Social Media in University Selection Decision Making Process-An Indian Student Prospective
Rajni Pathak, Sri Balaji University, Pune
Manisha Paliwal, Sri Balaji University, Pune
Yassine Agouzoul, Eaton Mobility Plant, France
Citation Information: Pathak, R., Paliwal, M., & Agouzoul, Y. (2023). Role of social media in university selection decision making process-an indian student prospective. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(5), 1-14.
Abstract
Aim - The purpose of this research is to comprehend the role of social media platform in university selection decision making process of students in Pune City of Maharashtra state in India. Design/Methodology/Approach – Data were collected (qualitative and quantitative both) via an online survey, google form through probabilistic simple random sampling from 222 graduate students analyzed using, factor analysis, regression, Anova test and Amos model. Findings:This study analyses the relevance of different social media platform used by HEI and it influences the potential students during selection process as well help in spreading awareness about college best practices, student’s achievements and information about HEI programs and courses. Results indicated a significant impact of social media on students during university selection decision making process and creating awareness Practitioner/Policy implications- This research is beneficial for students who want to enroll for Higher education studies as well higher education marketers to focus more on social media platform. Findings of this research suggest that higher education marketers and university policy makers should spend more resources in social media platforms so that it becomes the best option for students during their enrollment decision. Research limitation/Implications- The limitation of this research was that due to COVID, researcher was unable to speak personally with respondents as many colleges and universities are conducting admission process through online mode (teams or google meet).Due to the online admission process, students were not available in the campus and completing all admission formalities from their home.
Keywords
Social Media Platform, Higher Education Institutes, Education Marketers, COVID, Online Mode.
Introduction
From last many years, widespread changes happen in higher education sector, in terms of programme, supremacy, organization, and position, which create a significant influence on the higher education institutions’ and its working system. Higher education has become a competitive market with many players but with an imperfect marketing tactics, as it has no competitive and suitable strategy, it needs to be replacing it with some more advanced and student-centric approach keeping in mind the customer-student and other major stakeholder satisfaction (Alexa et al. 2012). Many research studies on the university’s selection decision making process have shown more probability of online and social media advertising and using it as a recruitment tool rather than focusing on traditional mode. Further, social media marketing can fill the gaps in reference of collecting information and understanding the needs of the students. Therefore, using online advertising tools such as social media platform, display ads in Facebook and posting blogs and showing video on you tube channel about college achievement is found to be an essential step to influence prospective students (Jan, 2016). Social media are composed of Web 2.0 and internet based platform that facilitate a both way communication comprising showing and sharing videos, photos certain specific content, and in return receiving feedback, comments and more number of followers. Social media vary ominously from the purported outmoded media. First, they are communicative, which to a large extent promote a dialogue between their consumers with the concurrent flattening-out of the order between them focus by appealing that the advantage of social media is about their capability to expedite the foundation of relationships because they can make communication mutual, communicating, balanced, and conversation-based. With more usage of social media, HEI can learn more about the requirement and demands of their stakeholders, establish a relation between them, focus more on the engagement, advertise and endorse their brands (Mazurek, 2019; Martin, et al. (2017). As HEIs are operational in the progressively competitive environment, the practice of new communiqué platform by HEIs seems to be justified. The social media modes used start from the reputable platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, to currently preferable and newer platforms like Snapchat and Instagram. In this changed world, social media networks have been used for public and private commercial purposes in different ways. The primary and important way is to engross and connect with people in an peripheral milieu with strong stakeholders like students (customers) and other parties, to accomplish this objective, Higher education institutes upkeep with pages and groups of social media on common platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. The next method which is also crucial as the first method, it is internal interaction and rendezvous within the businesses (existing stakeholders, alumni, and employees (Leonardi, et al. 2013, Menzies, et al. (2017). From last many years’ social media platform have grabbed the consideration of universities, and this strategy is helping the HEI to attract and drive prospective students for the admission (Merrill, 2011; Jan, & Ammari, 2016; Hossain, & Sakib, 2016; Nazeer, 2017).
From this context, the aim of this study is to understand how the HEI could device a model of engagement in social media, as an essential component of their student enrollment strategy, in order to acclimatize with the altering business environs. The purpose this study is to understand the importance of social media platform during the university selection decision making process by student in higher education institutes. In order to do this research, the researcher carried out a study through qualitative and quantitative descriptive approach using a probabilistic simple random sample and a self-administered questionnaire on 222 graduates and pursuing post graduate students - from several universities and colleges in Pune. The findings revealed some level of engagement in social media platform by student during their hunt for college or university and course info. Along with that some percentage of students also refer college website, which are not very active on social media. Among social media sources, Facebook, Instagram, Google+ and YouTube showed the highest ranks. Most students have, indeed, contacted a friend or a university staff for university course information using social media sites. The remnants of this paper includes a complete literature review starting with a discussion on the relevance of social media and higher education to how much student rely on social media platform during the selection decision making process for higher education. Further, section covers the research methodology and explains the data collection method. Next, the forth section discusses the findings and results. The last and fifth section discusses the results, limitation and future research.
Literature Review
Social Media & Higher Education
In the era of digital world, various research were there in pursued to understand the relevance of technology in education sector (Brown, 2012; Dermentzi et al., 2016; Hung & Yuen, 2010; Lim et al., 2015). For instance, technologies assisted students in the learning process (Dyson et al., 2015), supporting teachers for teaching purpose (Manca & Ranieri, 2017b), enabling research work for researchers and helping them to connect globally for the same purpose (Gu & Widén-Wulff, 2011),Now, in education sector technology including social media platform are used to enhance staff’s (teaching and non-teaching) professional development and growth (Donelan, 2016). Social media platform is an asset not only for teaching - learning and professional development but also for marketing and branding purpose in higher education institutes (Goldsmith & Foxall, 2003; Manca & Ranieri (2017b). Dorota Buchnowska, Monika Wo?niak (2013) did research to understand how the top level universities advertise themselves by showing ranking on social media esp during admission process as well also engage with international prospective student to get a global reach and showcase themselves as International University. Author also commented that higher education institutes prefer social media not only for global reach but also to strengthen its position against their competitors. One way to strengthen its market position is to conveying it’s all major activities and achievements like placement, number of courses, campus infrastructure etc in social media. In this way, universities and colleges found this platform as best mode of communication with target customer along with that brands themselves as one of the best college. Saleh Ghanayem, (2016) in UK discussed about the factors influencing the student enrollment and university choice. The various driving factors are- word of mouth publicity, friend and family reference, transportation and fees considered as the strongest factor. It was also find that for while selecting university, social media also play a major role. Students and parents before visiting the college and universities, they prefer to see the college presence in social media. Stakeholders could get more information about the college through the posts shared by the existing students as well as academicians. Clark et al. (2016), Calitz & Cullen (2012) conducted a research in USA to explore reasons to be connected with social media, for the benefit to improve the relationship quality between the university and one of its key patron groups, which are students. The author also commented that students follow the university on different sites for the purpose of collecting information. Even though there are many methods in which students can engross with universities through social networking sites such as remarking, sharing photos or videos, content, liking posts, etc as the foremost method of engagement. During this, post created by the university gives them satisfaction, trust and loyalty and a better way to do relationship marketing with students. Rania B. Mustafa did research in Egypt (2015) to understand the regulating influence of students’ willingness for cocreation on the student social media engagement and perceived value relationship. This research is projected to divulge vital acumens for scholars, as well as educationalists and policy creators in higher education institutes in quest of to auxiliary understand the budding student social media engagement notion, and the landscape of the student social media engagement/professed significance connection. Author also commented that for more and better student social media engagement, faculty can also assist them. Omar Salem in Hungary (2020) Redmond, P., Abawi, L.A., Brown, A., Henderson, R. and Heffernan, A. (2018) did research to investigate social media marketing in colleges and universities and define the approaches and stratagems that are used by higher education institutes to advertise their USP’s and how these platforms affects firming up the competitive lead with other higher education institutions. The researcher found that to connect with target group, social media is an important instrument as most of the youngsters are very much connected on these platforms. At the same time, sharing information on college website or conveying details about the achievements and best practices through phone calls by the higher education institutes has become an old and traditional way to do marketing. Galan et al. (2015) did research in one of the Australian University to understand the usage of social media platform in the decision making process of postgraduate students. Through this research, it was found that not only Australian student but also other international students take the help of social media in their educational decision making process. Further in this research, it was found that students not only use Facebook and you tube, but also refer blogs post by alumni and academician for study purpose. As well the prospective students take the help of this platform to understand the student engagement and reading reviews from alumni about that college. Kang (2011), Mazurek, et al. (2019) described the use of a social media platform as a promotion tool by a university in a case study. His findings established a sturdy connection between the number of students who visited and check the university on the social media platform recurrently and their probability of applying to this same university.
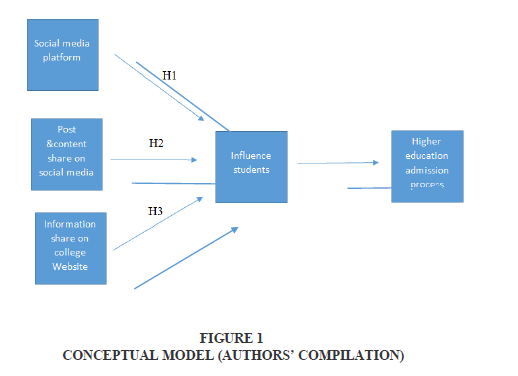
H1: To analyze the impact of social media platform on student’s decision at the time of university selection.
H2: To analyze the impact of posts and content shared on social media platform to drive students during admission process.
Social Media and its Impact in Enrollment in Higher Education
Vrontis, (2018) did research in Lebanese higher education institutes. Author investigated the importance of social media in international student selection in Lebanese higher education institutions (HEIs). Extension of this research, it was found that student use social media as well as traditional platform for their university selection decision making process. In this changing world, HEI find social media platform, a different and advanced way to communicate and engage with the target students. With the help of web 2.0 colleges and universities can build the brand name and brand image as well as create trust in student’s minds. Findings of this research says that local student more prefer traditional mode like reference, visiting college and university website but the international student prefer social media for the university selection decision. Alexa (2012); Martin, et al. (2017) author discussed about the diverse deviations in the worldwide environment had a direct influence over colleges and university and enforced them to reconsider their old and traditional strategy and to adapt some new and advanced method in order to better garb the student-customer info and communication needs. The transformed slant was needed for universities existence in a demand-side market. This makeover inferred that higher education institutes embark on organizational modifications intended to transmute them in more professional service oriented institutions so that communiqué with prospective students became a priority. Social media offers universities numerous marketing instruments intended to accomplish their requirements and to provide correct as well up-to-date information which could help in a proper way of interaction with their target groups, whether they are existing or future customer. Social media ascertains to be an unrestricted reserve of instruments for college and universities to get nearer to their public. This research aims to examine the use of online marketing and social media approaches applied by universities in Romania, both public and private. Constantinides & Stagno (2012); Anderson (2019) author discussed about the Impact of Social Media on Study Selection and University Choice. The significance of the Internet as viable platform is by now universally acknowledged, and businesses progressively adopt online marketing platform rather than traditional ones. Web 2.0 the advanced and improved version of web 1.0 considered as internet world in which Social media, allow interface, one-to-one communication, and work on content part. The inquisitiveness of higher education institutions in social media for branding and promoting its program and courses is increasing, but little is known about the prospective of these platforms in higher education as marketing tool. Even scarcer is identified about the role of social media as influencer for prospective students during selection of university or college. A key subject of research in this field is a Way to do marketing communication, where fissures between the info that target students want and the information delivered by universities in their old forms of communications needs to be changed. This article shows the outcome of a study elaborating the role and importance of social media on the choice of students for a higher education study in college and university as well a comparison with the traditional university marketing channels in the Netherlands. Michael D. Richardson (2015), Mazurek et al. (2019) wanted to study the relevance of social media as marketing tool to drive future or prospective students in higher education institutes as well an advanced platform for educators and students to horn their knowledge level and better learning for the progressive carrier. Facilitators in HEI use social media like you tube channel and other platform to get more expertise in their domain. A t the same time the prospective students find these platform as better way to get better and quick information during admission process. Hartiwi Prabowoa, Ridho Bramulyaa and Yuniartya did research in Jakarta (Indonesia) (2019) to understand the social network marketing on student purchase intension and student engagement as well how student engagement can impact the student purchase intention. Author commented that in this challenging and competitive world it’s very important to be connected with all the social media site like Facebook, you tube, LinkedIn and twitter. It has been found that more engagement on these platforms will bring more trust and loyalty for the existing students as well as for prospective students. Social media have enormous sway on each phase of the consumer’s decision making process, to make mutual belief and approach. Mazurek, et al. (2019) did research to investigate the extent of using social media in Higher education institutes in Poland. Although management still consider these platforms mainly as the way for marketing maneuvers, used to connect with youngsters through ‘youth’ content. Colleges and universities could not use social media platform to promote the achievement and best practices to large extent neither academician use it to promote their research centers. Apart from that the school and university authority were also not able to promote their teaching staff who have lot of expertise and experience in education and teaching sector. Author commented that after the research it was found that Higher education institutes need to work on the optimum use of social media for communicating and influencing the potential and target students as well other stakeholders, Aldahdouh et al. (2020). The higher education institute management should work with other alumni and education expertise to work on how to effectively use social media for driving target and parent during admission process. Alison B. Shields & Adam Peruta conducted a research in one of the college in USA (2019), according to authors, in this web 2.0 world higher education institutes get benefitted if they understand the frequency of using social media by prospective students and accordingly the colleges and universities should be prompt and active in social media. It was found that there are many advantages of web 2.0 like its cost efficient and has flexibility of having control of creating content, post blogs and maintaining a track record of followers and the conversion rate. At the same time it has some challenges like quality of content writing, number of posts, frequency of posts, number of followers in case if social media managers are not active in these activities , target student can assume that the university and its students are not active and not student centric. In last, author concluded that while students may not active on social media sites or may active on social media does not sway their enrolment decision during a survey, the massive number of students stated using social media to acquire more about higher education institutes under consideration. This leads the following hypothesis:
H3: To analyze the role of college website on student decision during higher education admission process.
Research Methodology
Research design -The research model for the present study (Figure 1) was established based on an in-depth process of literature review which helped exemplify the causal relationships between constructs and illustration of hypotheses. The validity of the hypotheses was tested by gathering data from students, and academician of different college and universities of Pune city, India.
The preceding section enclosed a wide literature review regarding social media in general, and social media as used by students during enrollment decision in higher education. The current section discusses first the research methodology used and then discusses findings. This segment specifies why the use of a quantitative approach is more suitable for the study being conducted, as well as the sampling method. Data collection method Survey is the process of collecting information to do statistical analysis to support a group of respondent so that responses can be collected to make a conclusion specify that the self-administered method is useful and is more suitable keeping in mind the cost, time and location of the researcher and the prospective respondents.
Data Collection
Sampling Data collected should be exact, relevant and symbolic of the whole population. Hence accurate sampling is an essential step in any research methodology. In this survey probabilistic simple random sample is used so as to simplify the conclusions and recommend later the appropriate explanations. 222 Students many universities and colleges were surveyed. The survey was filled online and sent as link by email to the respondents. Along with quantitative data, researcher collected qualitative data from director, dy director and staff who are in admission department.
Results and Discussion
Based on Quantitative Data
Of the total of 222 usable responses, male respondents represented 55% or 124, which is slightly greater than the female counterpart with 43.6% or 97. In terms of age, the majority of the respondents (85.2%) were in the age bracket 20–25 years. Further, with regard to the educational background of the respondents, the majorities (79%) were pursuing graduation degree, 10% completed graduation, and 11% students were pursuing their doctorate. The result of the demographic analysis of the respondents’ characteristics, occupation, and education is deemed reasonable as the data were collected from a higher education institution.
Attributes of the Questionnaire
Cronbach’s reliability coefficient is usually calculated in order to ensure the stability and consistency of the research instrument. The value of Cronbach’s alpha closer to 1 specifies better stability and consistency of the scale. Most of the social science research has a cut off value at 0.60 (Tavakol & Dennick, 2011). In the present study, the Cronbach’s alpha based on the standardized items had a value of .894, which confirms high consistencies.
Exploratory Factor Analysis
Exploratory factor analysis (hereafter, EFA) is used in order to explore the variables underlying the data set. First, Bartlett’s test of sphericity and the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test are required with appropriate thresholds to proceed with EFA (Pallant, 2010). In this case, KMO resulted in the
| Table 1 Rotated Component Matrix |
||
|---|---|---|
| Component | ||
| Relevance Of Social Media In Higher Education Institute | Social Media Platforms Creating Brand Value | |
| INFRA STRUCTURE | .859 | |
| ACHIEVEMENT | .823 | |
| GUEST LECTURE | .772 | |
| PLACEMENT | .736 | |
| COURSE OFFERED | .704 | |
| SOCIAL MEDIA INFLUENCE ADMISSION | .690 | |
| BRAND AWARENESS | .557 | |
| GLOBAL EXPOSURE | .672 | |
| TRUST | 0.836 | |
| FASTEST | 0.812 | |
| INFORMATION | 0.754 | |
| ADVANCED METHOD | 0.735 | |
| CREATE AWARENESS | 0.710 | |
| CONNECT WITH ALUMNI | 0.600 | |
| INITIAL EIGENVALUES | 7.7 | 3.02 |
| % OF VARIANCE | 55.5 | 21.5 |
| CUMULATIVE % | 55.5 | 77.1 |
value of 0.928; and Bartlett’s sphericity test was significant (p<0.001) inferring the aptness of the data for conducting EFA Anderson, 2010; Kline, 2011; Pallant, 2010).
The results of EFA indicated two clean factors using eigenvalue greater than 1 as the cut-off value. The extracted factors accounted for 77.123% of the total variance. Factor loadings were all higher than 0.5 on its own factor. Table 1 demonstrates the results of EFA and the variables retained. This study measured reliability using Cronbach’s alpha as suggested by Hair et al. (2010). The result of the present research indicated Cronbach’s coefficient alpha ranging Table 1.
So, from the above table we can say that all the 14 factors were loaded in two component, which is named as Relevance of social media in Higher Education Institute (component 1) & Social media platform creating brand value (component 2).So to conclude it as all values are more than 0.5 we can say that social media platform has positive impact on student decision during university selection (H1).
The hypothesis tests if post shared on social media can connect with alumni, create brand awareness and increase the awareness level of student and so have significant impact to drive students. The dependent variables are student decision, brand awareness and awareness level of student and more connection with alumni where as Independent variable is post shared on social media platform. The dependent variable connection with Alumni, brand awareness and awareness level of student was regressed on predicting variable. Post shared on social media to test the hypothesis H2. Post shared on social media significantly predicted the student decision, brand awareness, more connection with alumni and increase the student awareness level. (F-84.33), P<.001 which indicate the Independent variable can play significant role to drive students. Moreover the R square =0.548 depicts that the model explain 54% of variance in the awareness level, more connection with alumni and so help in driving the students Table 2.
| Table 2 Hypothesis |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Regression Weights | Beta Coefficient | R Square | F | T value | P Value | Hypothesis supported |
| H2 Post shared on social media platform to drive students. |
Post on website-create awareness, connect with alumni, drive students |
0.530 0.323 0.135 |
0.548 | 84.339 | 3.06 8.95 5.64 2.78 |
0.02 0.000 0.000 0.006 |
Yes |
The hypothesis tests if college website has any role in student decision during higher education admission process. The dependent variable is college website help student decision during higher education admission process and independent variable is information shared on college website. The dependent variable student decision was regressed on predicting variable. Information shared on college website to test the hypothesis H3. Information shared on college website significantly predicted and influence the student decision,(F-62.48), P<.001 which indicate the Independent variable play significant role to influence student decision . Moreover the R square =0.474 depicts that the model explain 47% of variance in terms of better knowledge, save time and more knowledge with reference of course offered due to information mentioned on college website Table 3.
| Table 3 Hypothesis Beta Coefficient |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Regression Weights | Beta Coefficient | R Square | F | T value | P Value | Hypothesis supported |
| H3 Information shared on college website drive student during higher education admission process. |
Information shared on website-drive student decision |
0.493 0.057 0.249 |
0.474 | 62.4 | 3.46 1.62 0.831 |
.001 .000 .000 |
Yes |
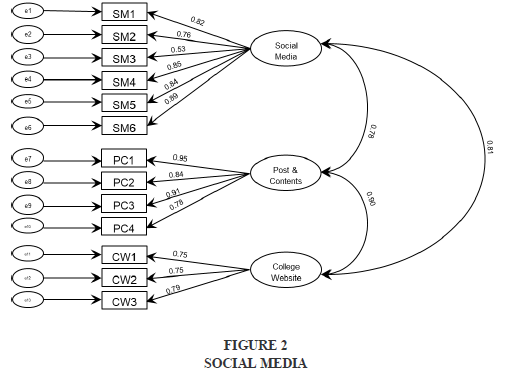
The aim of study was to determine whether students’ prefer social media platform during their university selection decision-making process. (Hypothesis 1) and impact of post and content shared on social media platforms to drive students during the selection process. (Hypothesis 2) the last hypothesis is to analyze the role of information mentioned at college website on student decision during higher education admission process (Hypothesis 3).With respect to Hypothesis 1, results indicate that following the university on a social media platform influence students’ decision of university selection. As prophesied in Hypothesis 2, researcher also found a significant relationship between post and content shared on social media platform esp Facebook, twitter and you tube in driving student decision. Specifically, students get more backing with Facebook post and comments, college you tube channel as well the information cited on college website during university selection decision making process. Along with that social media also help students in creating awareness with reference to the courses, college achievements, cultural, guest lectures and other activities conducted in the college. Overall the research study recommends that students prefer social media during their enrollment process in higher education and has the potential to build a university– student relationship. When asked from students when they start their search and collect information about the college and university courses, 54 % respondent says immediately after graduation, 34 % says during final year and 24 % says after graduation result. Keeping the social media platform, researched asked question from respondent regarding the most preferable social media site, 65.2% students prefer Facebook post and comments given by existing students as well new achievements like global exposure shared by college on college Facebook page drive them during the enrollment decision. Respondent commented that more engagement of existing and alumni on these platform gives the confidence to prospective students as well as help them during the enrollment decision Figure 2.
Conclusion
While taking the opinion from academician and marketing team, on understanding the role of social media in university selection decision process, one of the member of admission department of prestigious MBA College, commented that “In current scenario, students are very active on social media. During the admission process, students as well as parents depend on these platforms to get knowledge about the courses, student activity, placement data, campus infrastructure, cultural events organized in college as well alumni on these platform”. For students who are in different state, take the help of social media for the information purpose on above factors before taking admission. This will not only save student’s time but also help them to take better decision. While interview with one of the Dy. Director of MBA college, commented that Yes, social media make a huge impact and this we understand during the Personal Interview of candidate. She also said, that Social media platform is very helpful now a days not only for students but also for Management College. This platform can spread the information to many viewers in a very short time. College can showcase the cultural events, achievements and latest news on these platforms.
Another Director of MBA college also briefed about the importance of social media during university selection process. Respondent commented that social media creates awareness in students as well as in parents also. As today’s youth is very active on these platforms so information on these platform gives them confidence before they take admission in a particular college. She said in Sri Balaji University, Facebook and you tube channel are the most important platform to spread awareness about the college. In an interview with one of the admission department person said, that social media has relevance in admission process. It helps the student to collect the information about college before they take admission. Social media create trust and bring transparency with college and student. You tube channel and Instagram is very important platform in spreading knowledge. College should keep on updating these platforms so that the prospective students can make decision easily. Another Dy Director of one of management college of Mumbai indicate the impact of social media in university selection decision process. She said, social media has become an important source to collect information as well to showcase the achievement and latest updates about any University or college. It not only helps to improve the brand but also create trust and loyalty in stakeholders. So, social media platform is very helpful during university selection process not only from student point of you but also from management college point of view.
Implications of the Study
Social media is an advanced method to promote and create awareness in both marketing and higher education that is mounting its importance. It can give many profitable results to marketing experts like more exposure, a quick way to spread awareness, a better way to engage the prospective or target student in less market cost and better outcome or, in the case of our study, greater relationship between a university and its prospective students. Collectively, the findings of our study recommend that Higher education institutes should endow more resources in social media platform to attract more students and other stakeholders this will help HEI to get more admission and spread awareness among students. Many institutions of higher education are connected with alumni by sharing their experiences and achievements and this way colleges are making efficient use of website. But nowadays it can be easily done with the help of social media with better outcomes. These platforms have become the best way to reach target customer as youngsters are also very active on these sites. In the university selection decision-making process, LinkedIn and Facebook are the most preferred ways to connect with existing students. LinkedIn is found as a way to connect with professionals for better job prospects. Connecting professionally with passed-out as well as existing students provides opportunities for better exposure and future guidance. Videos shared by existing students, faculties and management staff about their achievement and college success can work as influencer for prospective students during their university selection decision making process.
Limitations and Future Research
The limitation for this research was that due to COVID, researcher was unable to speak personally with respondent as many colleges and university are conducting admission process through online mode (teams or google meet). Due to the online admission process, students were not available in the campus and completing all formalities from their home so researcher was able to target only few colleges and universities.
Future research can be done to understand the role of social media in influencing parent as they are also equally involved in the university selection decision making process of their ward.
References
Aldahdouh, T.Z., Nokelainen, P., & Korhonen, V. (2020). Technology and social media usage in higher education: The influence of individual innovativeness. Sage Open, 10(1), 2158244019899441.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alexa, E. L., Alexa, M., & Stoica, C. M. (2012). The use of online marketing and social media in higher education institutions in Romania. Journal of Marketing Research & Case Studies, 2012, 1.
Anderson T. (2019). Challenges and opportunities for use of social media in higher education. Journal of Learning for Development, 6(1), 6–19.
Brown S. A. (2012). Seeing Web 2.0 in context: A study of academic perceptions. Internet and Higher Education, 15(1), 50–57.
Bruhn M., Schoenmueller, V., & Schafer, D. (2012). Are social media replacing traditional media in terms of brand equity creation? Management Research Review, 35(9), 770- 790.
Buchnowska D., & Wo?niak, M. (2013). The role and use of social media by universities - ranking of universities in social media. Problemy konwergencji mediów, 319-330.
Calitz, A., & Cullen, M. (2012). The Use of Social Media in Business School Marketing. In International Business Conference (IBC).
Clark M., Fine, M., & Scheuer, C. (2016). Relationship quality in higher education marketing: the role of social media engagement. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 27(1), 40-58.
Constantinides E., & Stagno, M. (2012). Higher Education Marketing: A Study on the Impact of Social Media on Study Selection and University Choice. The International Journal of Technology and Education Marketing (IJTEM), 2(1), 41-58.
Donelan H. (2016). Social media for professional development and networking opportunities in academia. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 40(5), 706–729.
Galan M., Lawley, M., & Clements, M. (2015). Social media's use in postgraduate students' decision-making journey: an exploratory study. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 25(2), 287-312.
Hossain S., & Sakib, M.D. (2016). The Impact of Social Media Marketing on University Students' Brand Loyalty. International Journal of Marketing and Business Communication, 5(3), 1-7.
Jan M., & Ammari, D. (2016). Advertising online by educational institutions and students' reaction: a study of Malaysian Universities. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 26(2), 168-180.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kline, R.B. (2011). Principles and practices of structural equation modelling. New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Leonardi P. M., Huysman, M., & Steinfield, C. (2013) Enterprise Social Media: Definition, History, and Prospects for the Study of Social Technologies in Organizations. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 19(1), 1- 19.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Manca S., & Ranieri M. (2017b). Implications of social network sites for teaching and learning: Where we are and where we want to go. Education and Information Technologies, 22(2), 605–622.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Martin, F., Polly, D., Jokiaho, A., & May, B. (2017). Global standards for enhancing quality in online learning. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 18(2), 1-102.
Mazurek G., Korzy?ski, P, & Górska, A. (2019). Social Media in the Marketing of Higher Education Institutions in Poland: Preliminary Empirical Studies. Entrepreneurial Business and Economics Review, 7(1)117- 133.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Menzies R., Petrie, K., & Zarb, M. (2017). A case study of Facebook use: Outlining a multi-layer strategy for higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 22(1), 39–53.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Merrill, N. (2011). Social media for social research: Applications for higher education communications. In Higher education administration with social media (Vol. 2, pp. 25-48). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Nazeer, J. (2017). Impact of Social Media Advertisements on University Students. Arts and Social Sciences Journal, 8(4), 1-6.
Pallant J. (2010). SPSS survival manual: A step-by-step guide to data analysis using SPSS (4th ed.). Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Vrontis, D., Nemar, S., Ouwaida, A., & Shams, S. (2018). The impact of social media on international student recruitment: the case of Lebanon. Journal of International Education in Business, 11(1), 79-103.
Received: 16-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13342; Editor assigned: 20-Mar-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13342(PQ); Reviewed: 26-Apr-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13342; Revised: 28-May-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13342(R); Published: 20-Jul-2023