Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
The Shifts In Millennial Consumer Behaviour Due To Disruption Caused By Digital Wallets In India
Neha Gupta, Somaiya Vidyavihar University
Jennifer Jagose, Somaiya Vidyavihar University
Aditya Mulye, Somaiya Vidyavihar University
Citation Information: Gupta, N. Jagose, J. & Mulye, A. (2022). The Shifts in Millennial Consumer Behaviour Due To Disruption caused by Digital Wallets In India. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(5), 1-7.
Abstract
In a VUCA world, things are extremely unpredictable and the onset of the COVID-19 took every industry by storm. The banking industry is witnessing seismic shifts as traditional net banking banks are being challenged by new-age, digital-only wallets that focus on a hyper-personalized digital-first approach to replace the traditional net banking experience. This research aims to understand the shifts in millennial customer behaviour that have taken place as they progress from net banking to digital wallets for their day-to-day payments. This research is based on primary quantitative data along with an intensive analysis of research papers, articles, and journals. The findings suggest that millennial customers are willing to try out new digital wallet apps and consider them reliable and convenient, indicating high levels of acceptance. Three key factors were majorly responsible for the change in customer behaviour from net banking to digital wallets 1) Performance efficiency 2) social influence 3) Safety. Therefore, digital wallets need to focus on these factors to maximize their digital interactions and embrace innovation to help millennials in their day-to-day banking needs.
Keywords
Digital Wallets, Millennials, Customer Perception, net Banking
Introduction
Katti et al. (2020) For Indian customers, Demonetization has provided a unique platform for the adoption of digital payment as an alternative to cash. It helped India transition into a "Cash-less economy" since it is primarily a cash-driven economy where individuals prefer to carry cash rather than cards. There has been an increased mobile and internet penetration led by a massive surge in digital payments, as well as a revolution in terms of growth, technology content, and market structure in the previous decade, due to government policy reforms. Furthermore, (Digital India Program, 2016) the Digital India is an initiative set in motion by the Indian Government in 2015 to transform Indian society into a digitally empowered society. Attaining a cashless economy is one of the prominent missions of digital India. After the demonetization in 2016, there was a surge observed in the use of digital wallets. (KPMG 2021) India is outpacing several sophisticated non-cash economies in terms of digital payments growth. The digitization of monetary transactions has been driven by technological advances (Hagberg, 2016) which have slowly led to the shift from traditional payment methods an electronic payment system. (KPMG 2021) Due to COVID-19 there was a rise in payments being made online, and as a consequence of convenience of use and a safer way of payment, payments made by digital wallets is anticipated to see a boom in transaction volume and users. A major shift in consumer behaviour and habits has been seen, with consumers preferring to utilise wallets for small ticket purchases that were previously done largely with cash. Varghese (2012) Young Indians are more drawn to new mobile technologies, such as mobile wallets, since they love using them and prefer them for all of their financial and banking requirements. Factors affecting the digital payment system and E-banking sector are least dependent on physical infrastructure and more susceptible to disruption. Thus, the pandemic of Covid-19 positively affected the payment industry, accelerating the usage of digital wallets. Many users face problems while using net banking services, since digital wallets offer a simple user interface and fewer steps to complete a transaction, consumers, specifically millennials, preferred using digital wallets over net banking mobile applications. Katti et al. (2020) The momentum behind these shifts is projected to continue, but at a considerably quicker pace. This shift to digital payment results in increased transaction transparency, which improves the country's economy. This study focuses on the factors that affect consumers' perception of digital wallet systems and net banking payment systems.
Literature Review
(DQ India 2021) Today's biggest issue for BFSI players is moving a branch's degree of trust, flexibility, and security to a digital environment without a hitch. Aditya (2021) Alternative delivery methods for banking, such as net banking and mobile banking are now available along with a smooth onboarding process. The use of digital technology has also become commonplace, with the need to guide customers through the technological changes being the main challenge. Wipro (2020) Online banking has seen a spike due to the pandemic, prompting financial institutions to embrace digitization and a hybrid multi-cloud model to enable a variety of services such as payment gateways, online fund transfers, and transactions, digital wallets, and more, all with the goal of providing a unified customer experience. Vijai (2019) The digital wallet is the equivalent of a physical wallet in which money is carried. The digital wallet allows users to store money, just like a bank account. The key difference between a digital wallet and online bank account transactions are that, digital wallets do not charge a fee for each transaction and relieves the consumer of the effort of inputting card information and pin numbers for each transaction. Wallet businesses have increasingly forged partnerships with service providers and financial institutions in recent years to provide customers with a strong and smooth mobile wallet platform. The digital wallet is becoming more popular in a variety of applications, including money and banking transactions, cell recharge and bill payments, ticket reservations, utility apps, and so on. Ghule (2016) Wallet users now outweigh credit/debit card users in the country, and digital wallets are anticipated to have more users than bank account holders in the near future. The adoption rates amongst wallet players are high enough to indicate that customers are giving agreeing to the limitless experience generated on smartphones. Legters (2022) Due to the epidemic, customers had to adapt what they bought and sold. Because of tokenization, digital and mobile wallets provide a distinct sense of security. Hau et al. (2021) different factors such as performance expectancy, perceived risks and social influence pertaining to digital wallets on consumer behaviours. (Mckinsey & Company, 2020) Finally, behavioral changes are not linear, and their stickiness will depend on the satisfaction of the new experiences. For digital wallets, after the Covid 19 pandemic, it is safe to consider the acceptance and use of digital wallets will continue to grow and expand.
Furthermore, there are various factors leading towards the growing adoption of digital wallets in India-
1. Performance Efficiency – Performance efficiency will be described in the context of recording technologies that are often used in software usability studies Lewis (2011). Efficiency of a digital wallet can be defined by the speed with which it completes a designated task with a stipulated time period. Performance efficiency is a highly important factors for millennials when it comes to using digital wallets. Users may manage their finances more efficiently by integrating their bank accounts, debit cards, credit cards, and mobile bills. Nair et al. (2016)
2. Social Influence - India is a collectivist society where social influence plays a significant role in the intention and behaviour of people. Once millennials see their peers and family using digital wallets they are motivated to do so too, thus driving up the usage of digital wallets. According to Nysveen et al. (2005), social influence is described as "a person's perception that most people who are important to him think he should or should not perform the behavior in question’'.
3. Safety – Yadav (2017) Safety is the extent to which people assume that payments via digital wallets are safe and secure. Privacy and security must be emphasised on, even though it is not one of the primary concerns of millennials as they are more willing to part with their data for additional incentives as compared to other generations, thus positively affecting the growing adoption of digital payment wallets in India.
The purpose of this paper is to examine and highlight the shifts in customer behavior that have taken place from traditional ways of payments to digital payment wallets. It deals with the in-depth study of the factors that led millennials to adopt digital payment wallets as the go-to-option for their day-to-day payments. This paper is also designed to call attention to and discuss contemporary perspectives towards digital banking taken by millennials while exploring the future growth of payment wallets in the years to come.
Research Model
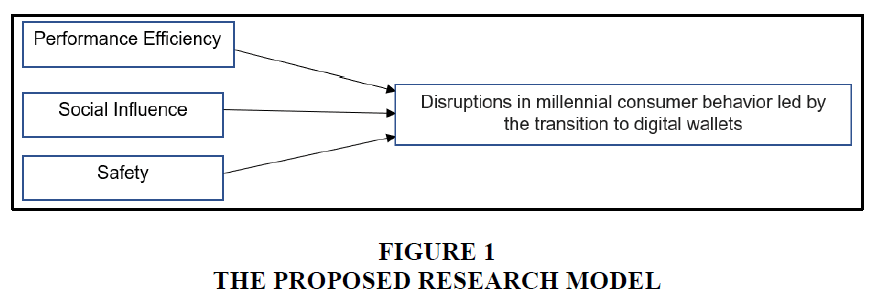
The proposed research model is inspired from Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) proposed by Venkatesh et al in (2003). Furthermore, it is based on the research model used in an empirical study of factors which affect the intention of using digital wallets in Vietnam. The research suggests that UTAUT can explain 70% of the variance in the intention of consumers using digital wallets. To make this research model easier to understand, the UTAUT moderating elements are removed.
The suggested research model comprises of three independent variables, which are -performance efficiency, social influence and safety of the data and one dependent variable is disruption in millennial consumer behavior Figure 1.
Research Methodology
A mixed research methodology of Qualitative & Quantitative data was adopted, and results from primary research via an online survey were analyzed. The questionnaire consisted of 3 parts - the first focusing on demographic information, the second on perception towards net banking and the third section focused on the perception towards digital wallets. The third section of the questionnaire consisted of 15 questions based on the constructs of the study model. The questionnaire for this study is designed using a 5-point Likert scale, which includes 1-strongly disagrees, 2-disagrees, 3-undecided, 4-agree, and 5-strongly agree. The respondents were asked to score their level of agreement on a variety of assertions, which may be positive or negative. The data were analyzed using SPSS software, several statistical tests were performed and data was compiled. A detailed and triangulated secondary data analysis was also used by reviewing fundamental literature in journals, articles, and published papers to identify and analyze the disruption of digital wallets in the banking sector, the factors that affect millennial’s perception towards digital wallets, and the future scope of the same in today’s VUCA world Kohli (2020) Table 1.
| Table 1 Measuring Scales of Factors Impacting the Behavioral Intention of Using Digital Wallets in India | ||
| Constructs | Description | Source |
| Performance Efficiency | Digital wallets would be helpful in my day-to-day activities | Hau et al (2020) |
| Digital wallets would help to speed up my financial transactions | ||
| Digital wallets would help me save time to perform other tasks | ||
| It is easy to access digital wallet apps | ||
| Learning how to use digital wallets is easy for me | ||
| Digital wallets are user-friendly | ||
| Payments via digital wallets are done easily | ||
| Social Influence | I can obtain more incentives from digital wallet services than traditional payment methods | Venkatesh et al (2003) |
| I can quickly sign up for digital wallet services | ||
| My family/relatives/friends think that I should use a digital wallet | ||
| Safety | I don’t feel completely safe while providing personal information for digital wallet services. | Hau et al (2020) |
| I think other people may gain access to my data if I use digital wallets | ||
| I feel concerned about protecting confidential information when it is shared via the digital wallet system | ||
Data Analysis and Findings
A pilot study was conducted with 53 millennial respondents Table 2.
| Table 2 Demographic Profile | |||
| Demographic | Category | No. of Respondents | Percentage |
| AGE | 18-23 | 29 | 54.7 |
| 24-27 | 20 | 37.7 | |
| 27-30 | 4 | 7.6 | |
| GENDER | Male | 24 | 42.9 |
| Female | 29 | 57.1 | |
| EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND | Diploma | 1 | 1.9 |
| Undergraduate | 11 | 19.6 | |
| Graduate | 29 | 51.8 | |
| Post Graduate | 12 | 21.4 | |
| ANNUAL INCOME | 1-5 lakhs | 42 | 79.2 |
| 5-10 lakhs | 8 | 15.1 | |
| 10-15 lakhs | 1 | 1.9 | |
| Above 15 lakhs | 2 | 3.8 | |
The demographic profile of the respondents can be seen from the table above. 54.7% of the respondents fall within the age group of 18-23 years, followed by 37,7% belonging to the age group 24-27 years. There was an ideal balance between male and female respondents with 57.1% being female respondents and 42.9% being male. 51.8% of the respondents are graduates, with there being 21.4% post graduate respondents and 19.6 undergraduate students. The major category of annual income falls between 1-5 lakhs annually and this is mainly made up of millennials who are yet persuing their studies, followed by 15.1% who have an annual income of 5-10 lakhs, thus making up the working millennial population Akhila Pai (2018). Thus, from this demographic profiling both student and working millennials will have an affinity towards using digital wallets Figure 2.
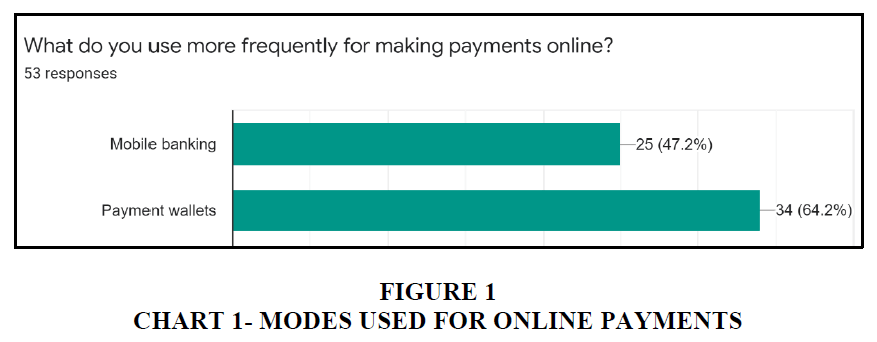
64.2% of millennials use payment wallets like GPay, PayTM, PhonePe and Amazon Pay for making their payments as compared to 47.2% who still continue to use Mobile banking. This shows a wider acceptance of digital wallets and highlights the shifts taking place in the online payment segment Achutamba & Hymavathi (2022) Figure 3.
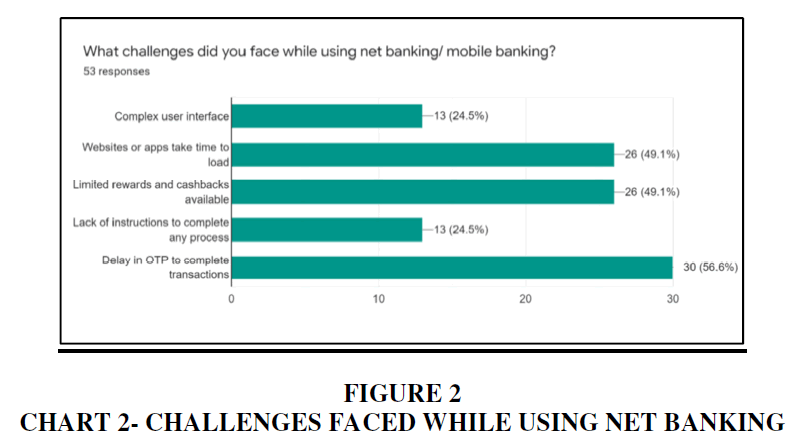
Via the survey, we further saw that the shift from mobile banking to digital banking was pushed due to severe limitations posed by mobile banking- slower websites and unnecessary delays, limited incentives, and poor UI/UX. In today’s ever-evolving and competitive digital world, mobile banking cannot keep up with the growing needs of millennials Vally & Divya (2018).
After performing factor analysis, there are three main factors responsible for the change in customer behaviors from net banking to digital wallets Performance efficiency, safety and social influence Digital India Programme (2016).
Furthermore, since the significance value of performance and social influence is 0.000, we look at standardised coefficient Beta value, thus concluding that performance is the most important variable that plays a primary role in the millennials perception towards digital wallets (highest beta value of 0.555), followed by social influence (0,431) and the least influencing variable being safety (0.174)
From the one sample t-test we can conclude that variables like usefulness, speed of transactions, ease of use along with societal influence, and cashback positively affect the perception of millennials and lead them to make the shift from traditional modes of payment towards digital wallets.
Since p>0.05 the researchers conclude that there is no significance relation between annual income and frequency of use of digital wallets in a month, proving that irrespective of which income bracket millennials come from, they transact frequently using digital wallets.
Thus, the future growth and adoption of digital wallets by millennials will be highly dependent on the ability of digital wallets to quicken the signup process, keeping the transaction process simple and hassle-free and being widely accepted by tying up with more vendors. Inorder to serve this digitally evolved generation of customers, banks and digital wallet apps will need to mine their historical customer data to make sure their offerings add real value to the millennial generation while building a user friendly and efficient system. Banks and Digital wallets service providers should address the pain point of delayed OTPs and build a robust system to minimize these types of hindrances. Finally, along with digitization, this shift demands to revisit the entire value chain, which consists not just any consumer’s journey, but specifically millennials.
Future Scope
The future scope of this research lies in conducting a penetration assesment to dive deeper and find out how the growth of digital wallets can penetrate through different sections of society, while developing an innovation matrix that allows to examine how digital wallets can come up with new technological innovations to address pain points.
Conclusion
Today, mobile wallet startups are quickly reaching out to majority of the population, across all strata of society by taking advantage of disruptions to seize new possibilities. Digitalization of the banking systems and the Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the usage of digital wallets. Millennials are responsible for the rapid shift from traditional net banking to digital wallets. Though Indian banks have grown more customer-friendly, service-oriented, and are considering digitising for most of their functions, they must move faster, overcoming the various customer pain points that exist. Banks must adopt faster to the changes in the payment ecosystem led by digital wallets. Having cutting-edge infrastructure in order to process massive amounts of data, evaluate real-time data, and top-notch security is a must today. The variables of perception and factors leading to the growing adoption of digital wallets were explored in this study. The findings suggest that consumers' perceptions have a favourable influence on their preferences. The most influential criteria in determining the preference level are ease of use, trust, social norms, and security. Our is a unique addition of this study, as there is very little discussion of the factors that influence digital wallet adoption in the literature. Based on the study's findings, it is concluded that factors such as performance efficiency, safety of the data and social influence are extremely important to millennials. Millennials expect end-to-end security of their data, while being able to complete a payment transaction within seconds. There is an upwards trend towards using digital wallets and it will continue to grow in the future.
References
Achutamba, V., & Hymavathi, C.H. (2022). Impact of Covid-19 on Digital Payments in India. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(3), 4394-4400.
Aditya A (2021) 'Impact Of Accentuated Digitalisation On Banking Sector'
Akhila Pai, H. (2018). Study on consumer perception towards digital wallets. International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, 5(3), 385-391.
Digital India Programme (2016) ‘Vision and Vision areas’
Ghule S. (2016). 'How UPI will disrupt the concept of payments in India.'
Hau, H.T., Nhung, D.T.H., & Trang, P.H. (2021). An empirical analysis of factors affecting the intention of using digital wallets in Vietnam. Tạp chí Quản lý Kinh tế Quốc tế (Journal of International Economics and Management), 21(01), 86-107.
Katti S et al (2020) ‘Perception of Indian Consumers towards Digital Wallets a Study’
Kohli S (2020) 'How COVID-19 Is Changing Consumer Behavior -now and Forever'
Legters, B. (2022). Consumer Ownership Of Digital Wallets Is Surging, But Will The Trend Hold?.
Lewis, D. (2011) Performance Efficiency: A Metric and Research Methodology for Task Analysis. 34thannual, 147.
Nair, A., Dahiya, M., & Gupta, N. (2016). Educating consumers about digital wallets. International Journal of Research, 3(13), 743-750.
Nysveen, H., Pedersen, H., Thorbjornsen, H. and Berthon, P. (2005), “Mobilizing the brand”, -Journal of service research.
Vally, K.S., & Divya, K.H. (2018). A study on digital payments in India with perspective of consumer’s adoption. International journal of pure and applied mathematics, 119(15), 1259-1267.
Varghese, T. (2012). Emerging Consumer Demand: Rise of the Small Town Indian. Nielsen, New Delhi.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M.G., Davis, G.B., & Davis, F.D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS quarterly, 425-478.
Vijai, C. (2019). Mobile wallet and its future in India. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research, 6(5), 574-580.
Wipro. (2020) Leveraging Digitization to Drive Customer Experiences in BFSI in the New Normal
Yadav, P. (2017). Active determinants for adoption of mobile wallet. i-manager’s Journal on Management, 12(1), 7-14.
Received: 04-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12188; Editor assigned: 08-Jun-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-12188(PQ); Reviewed: 20-Jun-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-12188; Revised: 20-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-12188(R); Published: 27-Jul-2022