Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 6S
Use – Trust – Stay: From Satisfaction to Loyalty Decoding Path for Mobile Banking Apps
Arjun Ganguly, Xavier Business School, St. Xavier’s University, Kolkata
Saugat Ghosh, Xavier Business School, St. Xavier’s University, Kolkata
Citation Information: Ganguly, A., & Ghosh, S. (2025). Use – trust – stay: from satisfaction to loyalty decoding path for mobile banking apps. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(S6), 1-13.
Abstract
Usage of mobile banking apps is a common phenomenon in developed countries while developing countries are still in the process of adopting the practice. This timeframe provides a greater opportunity for financial organizations to increase their business through providing a better experience to their target audience and win them from the market. Although technology is the backbone of this venture, human feeling like satisfaction, trust and loyalty also plays a pivotal role in adoption of a mobile – based banking app of a particular financial organization. but most of the studies conducted in this field only concentrate on the perception of users about the technological aspect of the apps. The present study aims to investigate this interplay of these human feelings with regard to adoption of this service. The study primarily identifies the related variables and dimensions that influence loyalty over mobile – based banking apps. Finally, the interrelationships among these dimensions were also tested with respect to the banking apps. The insight gathered from the research will help the banks design strategies from the human – behaviour perspective to enhance their loyalty among their customers and also to win new markets. Besides this, the methodology used in the present study could be replicated for identification of ways to loyalty for other businesses.
Introduction
The global banking landscape has dramatically transformed with the integration of mobile technology. This has significantly altered behaviour of the consumers and their brand engagement practices. Mobile – based banking applications have emerged as essential tool through providing unprecedented convenience to the users for making financial transactions. Besides this the efficiency of these apps and aligned security made it an easy choice for customers. Thus, all financial – service providing organizations came up with their own version of mobile – based financial apps and also with a lot of offers and tie-in options. The competition in the market intensified as sustainability in the loyalty of the customers became the major concern of the market. The challenge was not to design a user – friendly app, as that is the basic requirement of this market. The challenge lies in creation of a delightful experience for the customers so that loyalty of the customer could be achieved and maintained.
Attitudinal loyalty, which is defined as the psychological commitment toward a brand or service, significantly influences long-term customer relationships and also provide competitive advantage to the organizations. Prior studies on attitudinal loyalty reflected that user satisfaction and trust are pivotal in constructing and shaping attitudinal loyalty. Several researchers have designed theoretical structures on individual relationships between user satisfaction, trust, and loyalty. However, limited studies have comprehensively explored the intricate relationships among these constructs with respect to mobile banking, particularly on mobile – based banking apps.
The aim of the present study is two – fold. The first one is related to providing empirical insights into the identification of constructs of satisfaction, trust and attitudinal loyalty, with respect to mobile – based banking apps. The second one is to test the interrelationships among themand how the satisfaction and trust influence attitudinal loyalty toward mobile – based banking apps. By systematically evaluating these relationships, the research provides strategic insights to banking practitioners to create sustainable loyalty among their customers. The work also enriches theoretical perspectives in digital service marketing literature, emphasizing trust and satisfaction as critical pathways for achieving sustained attitudinal loyalty among consumers.
Literature Review
Mobile Banking: As Viewed by Researchers
The field of study related to mobile – based bank related apps is full of discussions from various perspectives. Some researchers like Kishore et. at., (2016) has provided a suitable definition of the service. According to their understanding, mobile-banking is basically an enhancement and enlargement, an addition in the offerings of banking facility. The nature of this enhancement is technical by nature and the technicality is associated with the mobile phones.Ivatuary and Mas, (2010) identified mobile-banking as a new dimension added to the banking. According to them, the introduction of this form of banking will provide the administration of finance in the hand of the customers.For banks, as stated by the researchers, this mobile-banking will be an element of cost reduction. Dixit and Datta, (2010), claimed that mobile-banking has empowered people by putting a large amount of banking operational activities in the pockets of the users. Similar voice has been raised by Anaysi and Otubu (2009), who stated that this added freedom provided to the customers will result is the development of the economy.
Highlights of Mobile – based Banking Usage
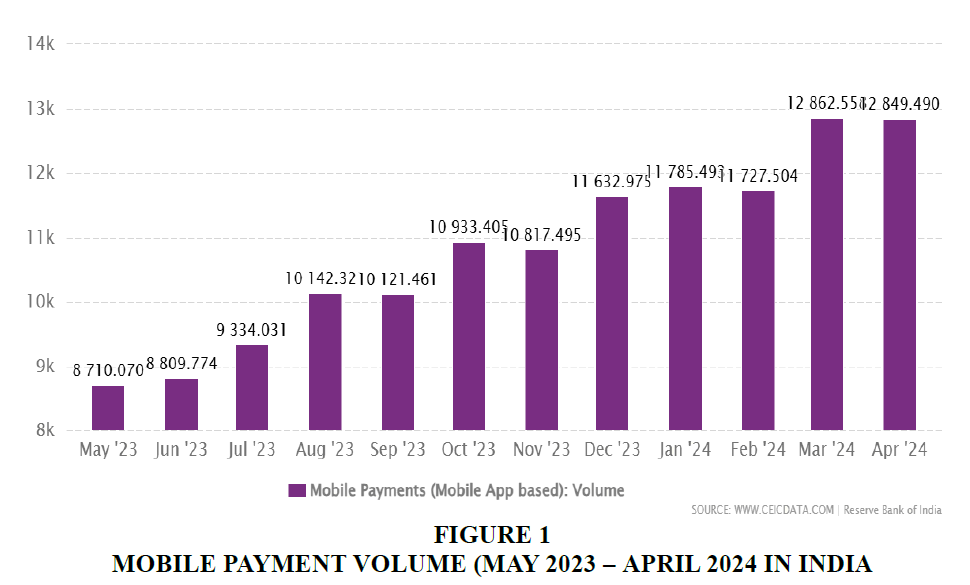
While mobile-banking is defined by several researchers from different perspectives, its use is very much celebrated by the users who are mostly from urban side of the country. The number of users of mobile – based bank related apps have been increasing in our country in a rapid way. Jamaluddin (2013) in his research has given a stunning picture of existing and possible growth in mobile – based bank related activities. According to the findings of his research, in India while more than eight-hundred million people have mobile phones, bank account is there for more than two million only. Thus, the findings show that while 17% of the Indian population have bank accounts, more than 68% of Indian population has mobile phones. This, according to the researcher, shows a huge scope in the increase of mobile phone banking. The data provided by Committee on Electronic Information and Communication (CEIC) shows that volume of India Mobile-banking Transactions was reported at 17117.198 unit million in Mar 2025. The findings actually record a heavy growth from previous month’s number 15003.146 unit million for February 2025. Besides this, India Mobile-banking Transactions related volume data is updated monthly, averaging 245.260-unit million from the month of April 2011 (Median) to March 2025, with 168 number of observations. The data reached an all-time high of 17117.198 unit million in Mar 2025 and a record low of 1.080 Unit million in April 2011 Figures 1-4.
Thus, from the data of received from Committee on Electronic Information and Communication (CEIC) we can get the amount of increase in the usage of mobile-banking app transactions.
Studies on Problems associated with Mobile – based Banking Apps
While the researchers are celebrating the growth of mobile – based bank related activities, several researchers also highlighted the problems associated with it. Although mobile-banking apps have revolutionized the banking system, studies on adoption of mobile – based bank related activities also identified several problems. Jiaqin Yang, Mike Whitefield, Katja Boehme (2016) concentrated their works on the impact of mobile – based bank related activities on small scale rural banks. The finding shows significant problems faced by these banks in comparison with the banks operating in cities and suburbs. Jahangir Nadim, Begum Noorjahan (2007) studied the attitude of the customers, their perception about the benefits from mobile – based bank related activities and also their perspectives related to the security associated with the transactions. According to the findings of the researchers, target audience of the study still have hesitations in accepting this form of banking particularly due to the reasons of security. Although the research work of Dmitri Sokolov (2007) identified the enormous breakthrough in banking transactions of Estonia caused by mobile – based bank related activities, some greater problem avenues have also been identified. The study states that the demand of mobile – based bank related activities also impact the technological growth of the system. This involves high cost in investment avenues which is problematic for banks with lower economic strength.While common retail users are at their highest levels of using mobile – based bank related activity apps, research work of Sedigheh et. al. (2021) identified the problems related to the adaption of mobile – based bank related activities by the merchants in the context of Malaysian market. The researchers identified that although this could be a big issue in the m-banking sector, not much research is conducted in this field. Dr. J. Sundararaj (2022) identified that a potential difference exists between the perception of users and non-users of mobile – based bank related apps. According to the study, it has been identified that the amount of perceived risk is high in case of the non-users. Similarly, there has been a high amount of lack of trust evident in the behaviour of the non-users. The research recommends that banks should identify these problems of non-users and act accordingly.
Studies related to the Perception of Mobile – based bank related facilities from the Perspective of Systems and Service Measures
Several research works have been directed towards gathering the perception of the users and rejectors about mobile – based bank related apps. The perspectives of these researchers are different. Some of them tried to evaluate the perspectives of the users about the quality of the technology while others were interested on the service supports. Some researchers also tried to focus on the qualitative perception of the users about the brands which provide the mobile – based banking facilities. Some prominent studies highlighted the trust, satisfaction and loyalty related aspects associated with the mobile – based banking apps. Researchers like Sharma et. al. (2019) and Baabdullah e. a. (2019) tried to identify the variables which are associated with the quality of the system provided by the mobile – based bank related service providers. Besides this, their researches also have identified crucial variables with regard to the service – related quality provided by these organizations through their apps. The quality related to distribution of relevant information by the service support systems of these organizations were also scanned in their research works. Relevant variables to estimate the perception about the quality of the information has also been identified.
Studies of Perception of Mobile – based bank related services from the Perspective of Values other than Technicality
While some researchers were trying to identify the technical and service – related perceptions of users about the mobile – based bank related apps, a group of researchers were trying to identify the perception of people from the dimensions of values associated with these service apps. One of the USP of mobile – based bank related services is to provide suitability to its users. Perception about the users about the advantages that they receive from the use of this service is studied by Wang et. al. (2008). Their study has identified relevant variables which can be used to identify this perception. The focus of the work conducted by Kim et. al. (2009) was related to the insight of the users about the brand of mobile – based bank related service providers and also related to the items of motivation of the users to use these apps. The research has identified several variables from the study. These variables are associated with the perception of the users about the brand of mobile – based bank related service facility providers. Besides this, their study has also identified significant variables which can trace the motivation of the users to use these facilities.
Studies related to the Perception of Mobile – based bank related service from the Perspective of Satisfaction, Trust and Loyalty
While finance is a matter of deep concern, judgement about the choice of finance – based service providers are also crucial. Perception about the customers about their mobile – based financial service providers are scanned by several researchers from the perspectives of their intention to try the service and also their perception about the level of satisfaction that they have. Gamal and Gebba (2013) studied the perception of trial and adoption of these apps by the users. Their study identified positive intention of the users related to trial of these apps. The study identified suitable and statistically accepted variables in this regard. The study of Sharma et. al. (2019) and Baabdullah e. a. (2019) have identified the relevance of these mobile – based banking apps with regard to the perception of people on the satisfaction derived from the use of these apps. Their findings were showing optimistic insight of the users with regard to satisfaction of the users. Two other important avenues were also the focal point of the researchers. These avenues were related to the trust of the users of these mobile – based bank related service apps and their loyalty to these apps. The research work of Alolwan (2017) was a significant approach to this avenue. Their research identified the level of trust is increasing in these services among the target audience. Besides identifying the increase in the level of trust among the users of these apps, the study also identified several variables to measure the elements of trust among the users and / or target audience. Usage of any product and / or services reaches to its desired platform when it achieves loyalty of the customers. Although several researchers have tried to identify the loyalty – level of customers on their mobile – based banking service providing apps, research work of Baabdullah et. al. (2019) is the most prominent. The research work identified clues of loyalty building up to this relatively new service. Besides this, the study also identified several research questions which can be used further to track the level of loyalty the consumers of these services actually have.
Although the studies conducted so far are of depth, several important areas still require in – depth analysis for better understanding. The following section highlights relevant gaps which require more contemplation.
Research Gaps
RG1: Although much is discussed about the identification of relevant dimensions associated with the satisfaction, trust and attitudinal loyalty of mobile – based banking apps, relevant research work to address this issue could not be identified
RG2: Although the interrelationship among satisfaction, trust and loyalty has been theoretically discussed, relevant research to identify the interrelationship could not be identified
Research Objectives
RO1: To identify relevant dimensions of user satisfaction, trust and loyalty associated with mobile – based banking apps
RO2: To identify the interrelationship between satisfaction, trust and loyalty associated with the mobile – based banking apps
Research Hypothesis
RH1: Significant dimensions of satisfaction, trust and loyalty will be identified for the users of mobile – based banking apps
RH2: Significant interrelationship among satisfaction, trust and loyalty will be identified with respect to mobile – based banking apps
Research Methodology
For identification of the relevant scale items for satisfaction, trust and attitudinal loyaltyresearch works of Sharma et. al. (2019), Baabdulla et. al. (2019), Alalwan et. al (2017) were considered and scale items were gathered from their research works. These items were used to collect the responses from 50 respondents as a pilot survey to check their reliability. Data were collected using a five – level Likert scaling process and the collected data were subjected to the Chronbach’s alpha test. Variables above the Chronbach’s alpha value > 0.7 were considered as the final scale items.
Identification of the Dimensions of Satisfaction, Trust and Loyalty of the Mobile – based bank related Apps
After detection of the reliable scale items related to Satisfaction, Trust and Loyalty associated with the mobile – based bank related apps, they are used for final data collection. Data were planned to be collected from 500 respondents, while 492 respondents’complete response were received.In this case also, a five – level Likert scaling process was used. A Principal Component Analysis has been administered and value of KMO test, Bartlett’s test, values of communality, Total variance table and rotated component matrix with varimax rotation process was checked to identify the relevant dimensions.
Estimation of Indices of the Factors
Indices of perceived satisfaction factors, perceived trust factors and perceived factors of attitudinal loyalty with respect to mobile – based bank related app users, is planned to be estimated. To estimate these indices of dimensions related to satisfaction, trust and loyalty associated with the use of mobile – based bank related apps, factor scores of the dimensions under perceived satisfaction, perceived trust and perceived loyalty were computed. These computed factor scores were then summated and the summated values of all the factors under these dimensions is considered as the index of perceived satisfaction factors, perceived trust factors and perceived loyalty factors. The process is explained below:
Index of Perceived Satisfaction:
Index of Perceived Satisfaction (SatIndx) = Σ Factor Scores associated with Perceived
Satisfaction Components
Index of Perceived Trust:
Index of Perceived Trust (TrstInd) = Σ Factor Scores associated with the Components of Trust
Factors
Perceived Attitudinal Loyalty Index:
Perceived Attitudinal Loyalty Index (LltyInd) = Σ Factor Scores associated with the
Components of Loyalty Factors
Methodology to Estimate Interrelationship Between Perceived Satisfaction and Attitudinal Loyalty of Mobile Banking App Users Mediated by Trust
According to the proposed theoretical construct, interrelationship between the perceived Satisfaction derived from the usage of mobile banking app and attitudinal Loyalty on a particular mobile banking app, is mediated by the factor of Trust. To measure the impact of this mediation, a regression analysis is conducted using PROCESS Macro. The indices estimated in the earlier stage are used in this process of estimation. The dependent variable in this case is Perceived Attitudinal Loyalty Index and the independent variable is the Perceived Satisfaction Index. Perceived Trust index is the mediating variable.
Primarily the direct relationship between the Perceived Satisfaction index and Perceived Trust index has been computed. In this case also, the value of unstandardized coefficient, error and corresponding p-value has been checked. The p-value, in this case has to be ≤ 0.05. This value is the measure of strength of relationship among these two factors. The impact of both independent variables, Perceived Satisfaction Index and Perceived Trust index on the dependent variable, Loyalty Index, has been checked in the second regression. In this case also, the values of unstandardized coefficients and corresponding p-values were checked. Finally, the indirect effect mediated by perceived Trust is also estimated. The indirect effect of Perceived Trust is estimated through measuring the product of both the paths.
Findings and Interpretations
Identification of the scale items for dimensions of Adoption, Satisfaction, Loyalty and Trust
Based on the values of Chronbach’s alpha scale items were chosen for data collection. The list of selected scale items with their sources are as follows tables 1-5:
| Table 1 List of Scale Items, Chronbach’s Alpha and Sources | ||
| List of Scale Items | Chronbach’s Alpha Value | Source of the Scale items |
| I_am_satisfied_with_m-banking_effectiveness | 0.738 | Sharma et. al. (2019) |
| I_’m_satisfied_with_m-bankingefficiency | 0.729 | |
| I_’m_satisfied_with_Mobile_banking_services | 0.810 | Baabdulla et. al. (2019) |
| I_am_satisfied_with_the_way_that_Mobilebanking_has_carriedout_transactions | 0.861 | |
| I_believe_that_mobile_banking_is_trustworthy | 0.740 | Alalwan et. al (2017) |
| I_am_confident_that_my_transaction_through_m-banking_will_always_be_transparent_because_of_the_regulator,_RBI | 0.910 | |
| I_trust_that_mobilemoney-service_providers_will_safeguard_my_money_and_my_personal_information | 0.736 | |
| I’ll_recommend_using_Mobilebanking_to_other_people | 0.818 | |
| I_intend_continue_using_Mobilebanking | 0.749 | |
| I_find_mbanking_is_secure_in_conducting_all_kind_of_transactions | 0.744 | Baabdulla et. al. (2019) |
| I_feel_ _that_legal_and_technological_structures_adequately_protect_me_from_problems_on_Mobile_banking | 0.868 | |
| Table 2 Interrelationship between Satisfaction and Trust of the Mobile Banking Users | ||||||
| OUTCOME VARIABLE: | ||||||
| TrstIndx | ||||||
| ModelSummary | ||||||
| R | R-sq | MSE | F | df1 | df2 | p |
| .6895 | .4754 | .5256 | 444.1025 | 1.0000 | 490.0000 | .0000 |
| Model | ||||||
| coeff | se | t | p | LLCI | ULCI | |
| constant | .0000 | .0327 | .0000 | 1.0000 | . -.0642 | .0642 |
| SatIndx | .6895 | .0327 | 21.0737 | .0000 | .6252 | .7538 |
| Standardized coefficients | ||||||
| coeff | ||||||
| SatIndx | .6895 | |||||
| Table 3 Impact of Satisfaction and Trust on Loyalty of the Mobile Banking Users | ||||||
| OUTCOME VARIABLE: | ||||||
| LltyInd | ||||||
| ModelSummary | ||||||
| R | R-sq | MSE | F | df1 | df2 | p |
| .8910 | .7938 | .2070 | 941.2224 | 2.0000 | 489.0000 | .0000 |
| Model | ||||||
| coeff | se | t | p | LLCI | ULCI | |
| constant | .0000 | .0205 | .0000 | 1.0000 | -.0403 | .0403 |
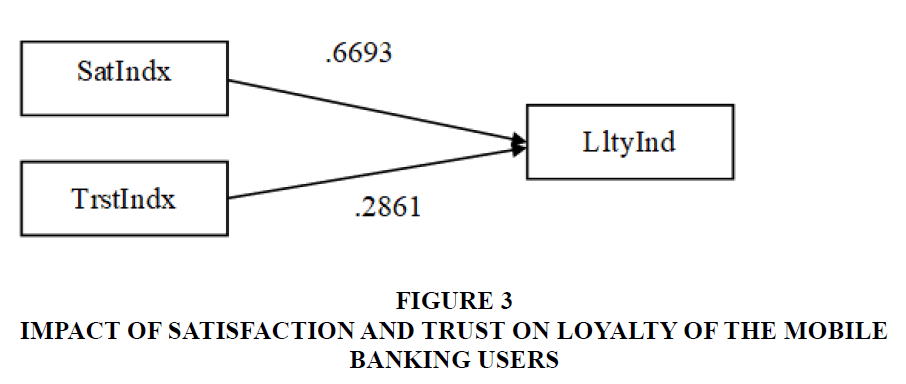
| SatIndx | .6693 | .0284 | 23.6047 | .0000 | .6135 | .7250 |
| TrstIndx | .2861 | .0284 | 10.0906 | .0000 | .2304 | .3418 |
| Standardized coefficients | ||||||
| coeff | ||||||
| SatIndx | .6693 | |||||
| TrstIndx | .2861 | |||||
| Table 4 Indirecteffect(S) of Xony | ||||
| Effect | BootSE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | |
| TrstIndx | .1972 | .0263 | .1483 | .2518 |
| Table 5 Totaleffect Xony | ||||||
| Effect | Se | t | P | LLCI | ULCI | c_cs |
| .8665 | .0225 | 38.4288 | .0000 | .8222 | .9108 | ..8665 |
| Directeffect of XonY | ||||||
| Effect | Se | t | P | LLCI | ULCI | c'_cs |
| .6693 | .0284 | 23.6047 | .0000 | .6135 | .6693 | .6693 |
Identification of the dimensions of Satisfaction, Loyalty and Trust
For identification of the dimensions of Satisfaction, Loyalty and Trust, an EFA has been administered and such are the findings:
Findings of KMO and Bartlett test
The value of K.M.O. is 0.898 which is > 0.6. Thus, K.M.O. findings state that samples are adequate for the study. Bartlett’s test’s p-value is < 0.05 which signifies that matrix which is formed based on the correlation of the identified variables does not follow the pattern of the identity matrix. Therefore, the factor analysis could be carried out.
Findings Related to Communality
All the extraction values are found to be > 0.4. Thus, none of the items are dropped from the study. The highest value of extraction is found to be 0.891, which is associated with “I’mconfident_that_mytransaction_through_mbanking_will_alwaysbe_transparent_because_ofregulatorRBI”. The findings indicate that 89.1% variability of this item is explained by the factor. On the other hand, lowest extraction value, 0.582 is associated with the variable, “I_am_satisfied_with_mbanking_effectiveness”. This shows that 58.2% variability of this item is explained by the factor.
Findings related to Total Variance Explained
The finding identifies three components, 5.132, 2.304, and 1.364 with > 1eigenvalues. Thus, this could be concluded that the test identifies three factors The amounts of variances explained by three factors are 45.560%, 33.174%, and 10.611%. Together, they account for 89.345% of the variance.
Findings Related to Component Matrix
The findings of the Component Matrix table are as follows:
Component 1 – Satisfaction
The elements under component 1 represents consumers’ perception about the satisfaction they receive from using the mobile – based bank related apps and thus, the factor is termed as Satisfaction. The four elements’ factor loadings range between 0.851 to 0.762 and explain 45.560 % of the overall variance.
Component 2 – Trust
The elements under component 3 represents consumers’ perception about their trust on mobile – based bank related apps and thus, the factor is termed as Trust. The five elements’ factor loadings range between 0.886 to 0.753 and explain 33.174% of the overall variance.
Component 3 – Attitudinal Loyalty
The elements under component 3 represents consumers’ attitudinal loyalty on their mobile – based bank related apps and thus, the factor is termed as Attitudinal Loyalty. The two elements’ factor loadings range between 0.611 to 0.550 and explain 10.611% of the overall variance.
Estimation of Interrelationship between Satisfaction, Trust and Loyalty of Mobile Banking Mediated by Trust
As discussed earlier, to measure the interrelationship among satisfaction, trust and loyalty and to measure the impact of mediation effect of trust, a regression analysis is conducted using PROCESS Macro. The indices estimated in the earlier stage are used in this process of estimation. The dependent variable in this case is Loyalty Index and the independent variable is the Perceived Satisfaction Index. Perceived Trust index is the mediating variable.
Results show Satisfaction Index is a significantly predicts Trust (b=.6895, s.e.=.0327, p<.001). The standardized path coefficient is also provided, which is .6895.
The impact of both independent variables, Satisfaction Index and Trust index on the dependent variable, Loyalty Index, has been checked in the second regression. The findings are as follows:
Outcome Variable
We see that in the second regression, both Satisfaction Index (b=.6693, p<.001) and Trust Index (b=.2861, p=.0000) are significant and also positive predictors of Trial. These coefficientsreflect the direct effects of both Satisfaction derived from the use of mobile – based bank related apps and Trust on the mobile – based bank related apps within the path model. The standardized path coefficients for this portion of the model are .6693 and .2861 for Satisfaction derived from the use of mobile – based bank related apps and Trust on the Mobile – based bank related apps, respectively.
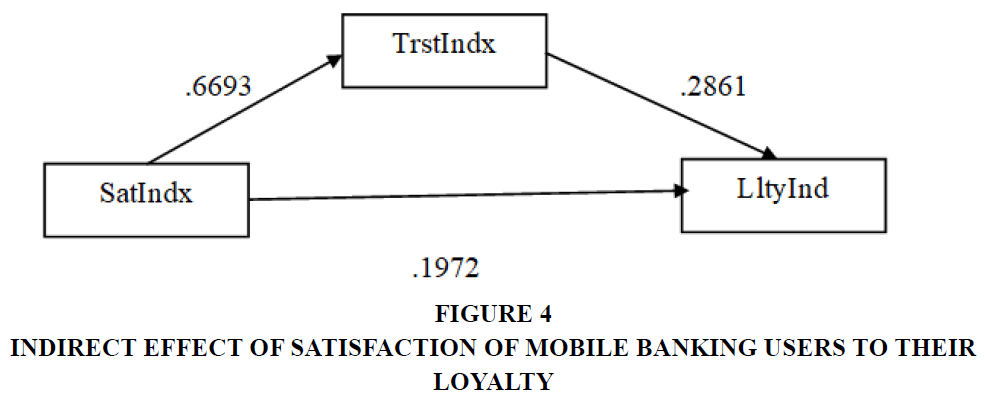
The unstandardized indirect effect of Trust is also estimated. It is estimated through measuring the product of paths (.6895 X .2861). The indirect effect of Satisfaction Index on Loyalty Index is tested using bootstrap standard errors and confidence intervals. The findings are as follows:
The finding shows that zero does not fall between the lower and the upper bound (BootLLCI = .1483 and BootULCI = .2518), and thus, we accept that the indirect effect is positive and statistically significant. In this case the indirect effect is 0.2609.
Finally, the estimation of the total effect of Satisfaction derived from mobile banking apps on Loyalty on the mobile – based bank related apps has been measured and the findings are as follows:
As per the results, the direct impact of Satisfaction derived from mobile – based bank related apps is 0.6693 and the indirect effect is .1972. The total effect is (Direct Impact + Indirect Impact) = (.6693 + .1972) = .8665 and the p value = 0.000 showing statistical significance.
From the findings of the analysis, it could be stated that Satisfaction derived from the usage of mobile – based bank related apps have significant direct and indirect impact on Customer Loyalty of mobile – based bank related apps users. The mediating variable, which is Trust, has significant impact on customer loyalty.
Conclusion
As the world of mobile banking is getting crowded by users and significant competition is rising among the banking service providers to develop loyalty among customers, this research shows a strategic pathway to achieve the desired aim. The research work primarily prepares a theoretical construct where interrelationship among satisfaction, trust and loyalty has been hypothesised. To identify the relevance of the framed theoretical hypothesis, dimensions of satisfaction, trust and loyalty with respect to the mobile – based banking apps were estimated. A unique methodology to estimate the scores of these identified dimensions has been computed. Using these dimensions, the interrelationship among these three dimensions were also estimated. Significant interrelationship among satisfaction, trust and loyalty has been identified with trust playing a mediating impact on loyalty. Findings of this research work could be used for strategic benefits by the banks and other financial organizations. The relevant items constructing satisfaction, trust and loyalty associated with the mobile – based banking app users have been identified by the study. The same can be used by the banks and financial organizations providing similar facilities to measure customers’ satisfaction, trust and loyalty of their own organization. Besides this, with the help of the methodology used in the study estimation of the interrelation among these three constructs could be monitored and relevant measures could be taken.
References
Alalwan, A. A., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Rana, N. P. (2017). Factors influencing adoption of mobile banking by Jordanian bank customers: Extending UTAUT2 with trust. International Journal of Information Management, 37(3), 99–110.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Anayasi, F.I. and Otubu P.A. (2009). Mobile Phone Technology in Banking System: Its Economic Effect. Research Journal of Information Technology, 1(1), 1-5.
Baabdullah, A. M., Alalwan, A. A., Rana, N. P., Kizgin, H., & Patil, P. (2019). Consumer use of mobile banking (M-Banking) in Saudi Arabia: Towards an integrated model. International Journal of Information Management, 44, 38–52.
Dixit,N. and Datta, S.K. (2010). Acceptance of E-banking among Adult Customers: An Empirical Investigation in India. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 15(2), 1-17.
Dmitri Sokotal: (2007) :- E-banking: “ Risk management practices of the Estonian banks” “Institute Of Economics at Tallion University of Technology.
Ivatuary, G. and Mas, I. (2010).The Early Experience with Branchless Banking. Focus note www.ssrnpapers.com accessed on 22-08-2013.
Jahangir Nadim, Begum Noorjahan (2007) :“ Effect of perceived usefulness, ease of use, security & privacy on customer attitude and adaptation in the context of e-banking” “ Journal Of Management Research”, Volume: 7, issue:- 3, ISSN: 0972-5814.
Jamaluddin N. (2013), E-Banking: Challenges and Opportunities in India, Proceedings of 23rd International Business Research Conference 18 - 20 November, 2013, Marriott Hotel, Melbourne, Australia.
Kim, G., Shin, B., & Lee, H. (2009). Understanding dynamics between initial trust and usage intentions of mobile banking. Information Systems Journal, 19(3), 283-311.
Kishore , S. V. Krishna , Sequeira, Aloysius Henry (2016) An Empirical Investigation on Mobile Banking Service Adoption in Rural Karnataka.
Moghavvemi, Txmei SW Phoong (2021) : “Drivers & barriers of mobile payment adoption: Malaysian merchants perspective. Journal Of Retailing & Consumer Services.Vol: 59, March 2021.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mohamed Gamal Aboelmaged, Tarek R. Gebba(2013). Mobile Banking Adoption: An Examination of Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. International Journal of Business Research and Development ISSN 1929‐0977 | Vol. 2 No. 1, pp. 35‐50 (2013).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sharma, S. K., & Sharma, M. (2019). Examining the role of trust and quality dimensions in the actual usage of mobile banking services: An empirical investigation. International Journal of Information Management, 44, 65–75.
Sundararaj (2022): "Opportunities And Challenges On The Adoption of Mobile Banking Services", Journal of Positive School Psychology, , Vol. 6, No. 8, 1951-1958.
Wang, Youwei; Meister, Darren; and Wang, Yinglei, "Relative Advantage and Perceived Usefulness: The Adoption of Competing ICTs" (2008). DIGIT 2008 Proceedings. 6.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yang, M.Whitefield, K.Boehme (2016) :“ New issues & challenges facing e-banking in rural areas: An empirical study “ International Journal Of Electronic Finance.” Vol:1, issues:3, DOI:
Received: 27-Jun-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-16023; Editor assigned: 28-Jun-2025, PreQC No. AMSJ-25-16023(PQ); Reviewed: 10-Jul-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-16023; Revised: 29-Jul-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-16023(R); Published: 06-Aug-2025